【数据结构】——顺序表的基本实现
文章目录
一、顺序表的的结构及概念
二、顺序表接口的实现
- 顺序表初始化
- 检查容量空间并扩容
- 顺序表的尾插和尾删
- 顺序表的头插和头删
- 任意位置的插入和删除
- 顺序表的查找和修改
- 顺序表的销毁
- 头文件
三、顺序表完整代码
一、顺序表的结构及概念
概念:顺序表是用一段物理地址连续的存储单元依次存储数据元素的线性结构,一般情况下采用数组存储。在数组上完成数据的增删查改。
顺序表可以分为两种结构:
1.静态顺序表:使用定长数组存储元素

2.动态顺序表 :使用动态开辟的数组存储
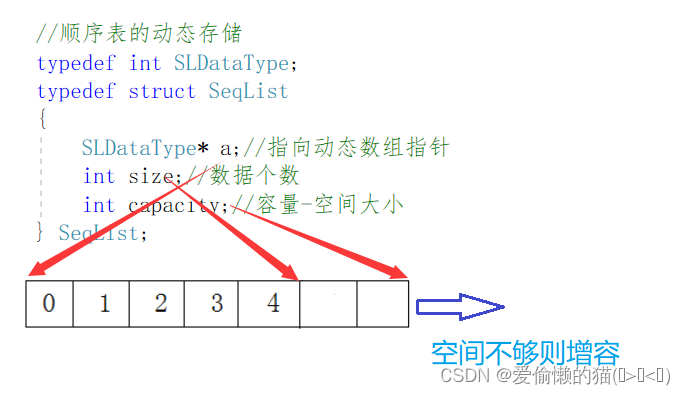
静态顺序表只适用于确定知道需要存多少数据的场景。静态顺序表的定长数组导致N定大了,空
间开多了浪费,而开少了又不够用。所以现实中基本都是使用动态顺序表,根据需要动态的分配空间大小,所以下面我们实现的是动态顺序表。
二、顺序表接口的实现
typedef int SLDataType;typedef struct SeqList{SLDataType* a;//指向动态数组指针int size;//数据个数int capacity;//容量-空间大小}SL;//顺序表实现增删查改void SeqListInit(SL* ps);//顺序表初始化void SLPrint(SL* ps);//打印数据void SLCheckCapacity(SL* ps);//检查容量//时间复杂度O(1)void SLPushBack(SL* ps, SLDataType x);//尾插void SLPopBack(SL* ps);//尾删//时间复杂度O(n)void SLPushFront(SL* ps, SLDataType x);//头插void SLPopFront(SL* ps);//头删void SLInsert(SL* ps, int pos, SLDataType x);//任意位置插void SLErase(SL* ps, int pos);//任意位置删int SLFind(SL* ps, SLDataType x);//查找void SLModify(SL* ps, int pos, SLDataType x);//修改void SLDestory(SL* ps);//销毁这里建议写每个接口时,可以写一个就测试一个,这样更不会出错。
2.1 顺序表初始化
这种方法初始化是最简单的,当然你也可以一上来就malloc10个空间也是可以的。
void SeqListInit(SL* ps){ps->a = NULL;ps->capacity = ps->size = 0;}注:这里传参的时候一定要传址,形参的改变不会影响实参的变化, 这里a,size,capacity都发生了变化,所以要传址。
2.2 检查容量空间并扩容
这个容量检查是关键,否则后面头插、尾插都弄不成了。
void SLCheckCapacity(SL* ps){//检查容量空间,满了就扩容if (ps->size == ps->capacity){int newCapacity = ps->capacity == 0 ? 4 : ps->capacity * 2;SLDataType* tmp = (SLDataType*)realloc(ps->a, newCapacity * sizeof(SLDataType));if (tmp == NULL){printf("realloc fail\n");exit(-1);//结束程序}ps->a = tmp;ps->capacity = newCapacity;}}2.3 顺序表的尾插和尾删
尾插: 这里要注意尾插的时候要先检查容量够不够,再进行尾插。
这里的size是作为下一个数据的下标的。
void SLPushBack(SL* ps, SLDataType x){SLCheckCapacity(ps);ps->a[ps->size] = x;ps->size++;}尾删:尾删的时候要有一个检查顺序表为不为空,有数据就删,没数据就不用删,我这里提供了两种检查方式,一个是比较温柔的检查,另一个是暴力的检查。
void SLPopBack(SL* ps){assert(ps); 温柔检查if (ps->size == 0){printf("SepList is empty\n");return;}// 暴力检查assert(ps->size>0);ps->size--;}2.4 打印数据
这个很简单就不多讲了
void SLPrint(SL* ps){for (int i = 0; i size; i++){printf("%d ", ps->a[i]);}printf("\n");}我们可以将上面的尾插和尾删打印出来看看效果

2.5 顺序表的头插和头删
头插: 这里挪动数据要从后往前挪,你从前往后挪的话会造成数据被覆盖了,就出错了。
不要忘了检查容量哦!!!
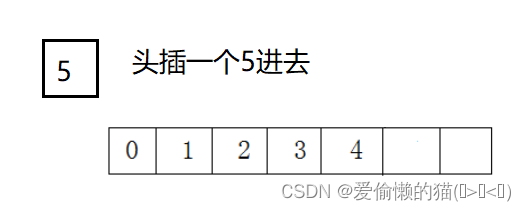

void SLPushFront(SL* ps, SLDataType x){SLCheckCapacity(ps);//挪动数据int end=ps->size-1;while (end >= 0){ps->a[end + 1] = ps->a[end];--end;}ps->a[0] = x;ps->size++;}头删:和头插刚好相反,这里是从前往后挪将数据覆盖,并且也要进行检查,有数据就删,没数据了就不要删。

void SLPopFront(SL* ps){assert(ps);assert(ps->size > 0);int begin = 1;while (begin size){ps->a[begin - 1] = ps->a[begin];begin++;}ps->size--;}2.6 任意位置的插入和删除
任意位置插:这里的pos要进行断言,原因是你插入的数据必须是紧挨着的,要在当前数据范围内插入。
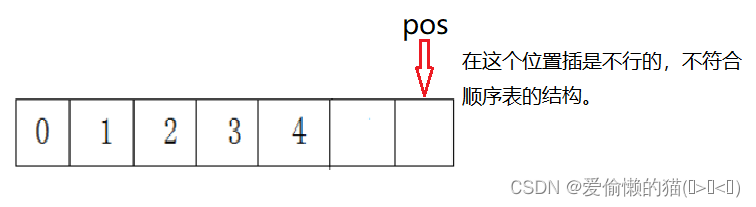
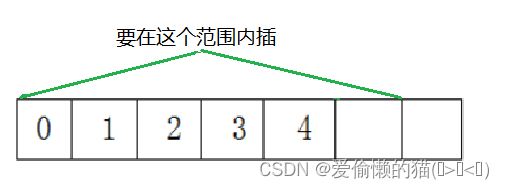
检查容量大小也是必不可少的。插入数据还是从后往前挪。
void SLInsert(SL* ps, int pos, SLDataType x){assert(ps);assert(pos >= 0 && pos size);SLCheckCapacity(ps);int end = ps->size - 1;while (end >= pos){ps->a[end + 1] = ps->a[end];end--;}ps->a[pos] = x;ps->size++;}实现了这个函数,那前面的头插和尾插直接就可以调用这个函数就行了。
尾插:
void SLPushBack(SL* ps, SLDataType x){SLInsert(ps, ps->size, x);}头插:
void SLPushFront(SL* ps, SLDataType x){SLInsert(ps, 0, x);}任意位置删:这里就不用再写对顺序表为空的检查了,因为检查pos的时候顺便检查了为空的情况。挪动数据的时候也是从前往后挪,我这里写了两种写法。挪动数据时要注意越界的问题。
void SLErase(SL* ps, int pos)//任意位置删{ assert(ps); assert(pos >= 0 && pos size);//不用等于size //1. /*int begin = pos; while (begin size - 1) { ps->a[begin] = ps->a[begin + 1]; begin++; } ps->size--;*/ //2. int begin = pos + 1; while (begin size) { ps->a[begin - 1] = ps->a[begin]; begin++; } ps->size--;}当然头删和尾删也可以直接调用这个函数
头删:
void SLPopFront(SL* ps){SLErase(ps, 0);}尾删:
void SLPopBack(SL* ps){SLErase(ps, ps->size - 1);}总结:写好这两个函数头插、尾插、头删、尾删直接调用就可以了,是不是简单很多。
2.7 顺序表的查找和修改
查找和修改是配合起来一起使用的。
查找:
int SLFind(SL* ps, SLDataType x)//查找{assert(ps);int i = 0;for (i = 0; i size; i++){if (ps->a[i] == x){return i;//返回下标}}return -1;}修改:
void SLModify(SL* ps, int pos, SLDataType x)//修改{assert(ps);assert(pos > 0 && pos size);ps->a[pos] = x;}2.8 顺序表的销毁
void SLDestory(SL* ps)//销毁{assert(ps);if (ps->a){free(ps->a);ps->a = NULL;ps->capacity = ps->size = 0;}}2.9 头文件
#include #include #include 三、顺序表完整代码
SeqList.h
#pragma once#include #include #include typedef int SLDataType;typedef struct SeqList{SLDataType* a;//指向动态数组指针int size;//数据个数int capacity;//容量-空间大小}SL;//顺序表实现增删查改void SeqListInit(SL* ps);//顺序表初始化void SLPrint(SL* ps);//打印数据void SLCheckCapacity(SL* ps);//检查容量//时间复杂度O(1)void SLPushBack(SL* ps, SLDataType x);//尾插void SLPopBack(SL* ps);//尾删//时间复杂度O(n)void SLPushFront(SL* ps, SLDataType x);//头插void SLPopFront(SL* ps);//头删void SLInsert(SL* ps, int pos, SLDataType x);//任意位置插void SLErase(SL* ps, int pos);//任意位置删int SLFind(SL* ps, SLDataType x);//查找void SLModify(SL* ps, int pos, SLDataType x);//修改void SLDestory(SL* ps);//销毁SeqList.c
#include "SeqList.h"void SeqListInit(SL* ps){ps->a = NULL;ps->capacity = ps->size = 0;}void SLPrint(SL* ps){for (int i = 0; i size; i++){printf("%d ", ps->a[i]);}printf("\n");}void SLCheckCapacity(SL* ps){//检查容量空间,满了就扩容if (ps->size == ps->capacity){int newCapacity = ps->capacity == 0 ? 4 : ps->capacity * 2;SLDataType* tmp = (SLDataType*)realloc(ps->a, newCapacity * sizeof(SLDataType));if (tmp == NULL){printf("realloc fail\n");exit(-1);//结束程序}ps->a = tmp;ps->capacity = newCapacity;//printf("扩容成功!\n");}}void SLErase(SL* ps, int pos)//任意位置删{assert(ps);assert(pos >= 0 && pos size);//不用等于size/*int begin = pos;while (begin size - 1){ps->a[begin] = ps->a[begin + 1];begin++;}ps->size--;*/int begin = pos + 1;while (begin size){ps->a[begin - 1] = ps->a[begin];begin++;}ps->size--;}void SLInsert(SL* ps, int pos, SLDataType x)//任意位置插{assert(ps);assert(pos >= 0 && pos size);SLCheckCapacity(ps);int end = ps->size - 1;while (end >= pos){ps->a[end + 1] = ps->a[end];end--;}ps->a[pos] = x;ps->size++;}//尾插void SLPushBack(SL* ps, SLDataType x){//1/*SLCheckCapacity(ps);ps->a[ps->size] = x;ps->size++;*///2//直接调用SLInsert(ps, ps->size, x);}//尾删void SLPopBack(SL* ps){//assert(ps);//ps->a[ps->size - 1] = 0;// 温柔检查//if (ps->size == 0)//{//printf("SepList is empty\n");////exit(-1);//return;//}// 暴力检查/*assert(ps->size>0);ps->size--;*/SLErase(ps, ps->size - 1);}//头插void SLPushFront(SL* ps, SLDataType x){//SLCheckCapacity(ps);挪动数据//int end=ps->size-1;//while (end >= 0)//{//ps->a[end + 1] = ps->a[end];//--end;//}//ps->a[0] = x;//ps->size++;SLInsert(ps, 0, x);}//头删void SLPopFront(SL* ps){/*assert(ps);assert(ps->size > 0);int begin = 1;while (begin size){ps->a[begin - 1] = ps->a[begin];begin++;}ps->size--;*/SLErase(ps, 0);}int SLFind(SL* ps, SLDataType x)//查找{assert(ps);int i = 0;for (i = 0; i size; i++){if (ps->a[i] == x){return i;//返回下标}}return -1;}void SLModify(SL* ps, int pos, SLDataType x)//修改{assert(ps);assert(pos > 0 && pos size);ps->a[pos] = x;}void SLDestory(SL* ps)//销毁{assert(ps);if (ps->a){free(ps->a);ps->a = NULL;ps->capacity = ps->size = 0;}}test.c
#include "SeqList.h"void menu(){printf("\n");printf("* 1.尾插 2.头插 *\n");printf("* 3.尾删 4.头删 *\n");printf("* 5.删除 6.插入 *\n");printf("* 7.修改 8.查找 *\n");printf("* 9.打印 0.退出 *\n");printf("\n");}int main(){SL sl;SeqListInit(&sl);SLPushFront(&sl, 1);SLPushFront(&sl, 2);SLPushFront(&sl, 3);SLPushFront(&sl, 2);SLPushFront(&sl, 2);SLPushFront(&sl, 4);SLPushFront(&sl, 5);int option = 0;do{menu();scanf("%d", &option);int x, y, z;int val, pos;switch (option){case 1:printf("请连续输入你要尾插的数据,以-1结束:>");scanf("%d", &val);while (val != -1){SLPushBack(&sl, val);scanf("%d", &val);}break;case 2:printf("请输入要头插的数据:>");scanf("%d", &val);SLPushFront(&sl, val);break;case 3:SLPopBack(&sl);printf("尾删成功\n");break;case 4:SLPopFront(&sl);printf("头删成功\n");break;case 5:printf("请输入你要删除的值:");scanf("%d", &x);int pos = SLFind(&sl, x);while (pos != -1){SLErase(&sl, pos);pos = SLFind(&sl, x);}printf("删除成功\n");break;case 6:printf("请连续输入你要插入的数据和位置:>");scanf("%d%d", &val,&pos);SLInsert(&sl, pos, val);SLPrint(&sl);break;case 7:printf("请输入你要修改的值和修改后的值:");scanf("%d%d", &y, &z);pos = SLFind(&sl, y);if (pos != -1){SLModify(&sl, pos, z);}else{printf("没找到:%d\n", y);}break;case 8:printf("请输入你要查找的值:");scanf("%d", &y);pos = SLFind(&sl, y);if (pos == -1){printf("找不到\n");}else{printf("%d\n", pos);}break;case 9:SLPrint(&sl);break;default:printf("输入错误,请重新输入\n");break;}} while (option != 0);SLDestory(&sl);return 0;}这个菜单你写不写其实无所谓,我这里写的菜单并不唯一,你们可以自由发挥。
总结:学习数据结构要学会用编译器的调试,不然光看代码很难发现问题, 而且还要学会来画图分析,图画的好,代码也好写。
今天就分享到这
觉得内容对你有用的话就个三连吧!!!



