CUDA实例系列四:利用GPU加速Sobel边缘检测(含源码)
CUDA实例系列四:利用GPU加速Sobel边缘检测
先简单的介绍一下Sobel边缘检测:
Sobel算子是图像处理中常用的算子之一, 在计算机视觉中常用来做边缘检测. 它是一个比较小并且是整数的filter, 所需要的计算相对较少, 但是对于图像中频率变化较高的地方,他所得的梯度近似值会比较粗糙.

它包含两组 3 x 3的矩阵,分别为横向和纵向与图像做平面卷积. 即:
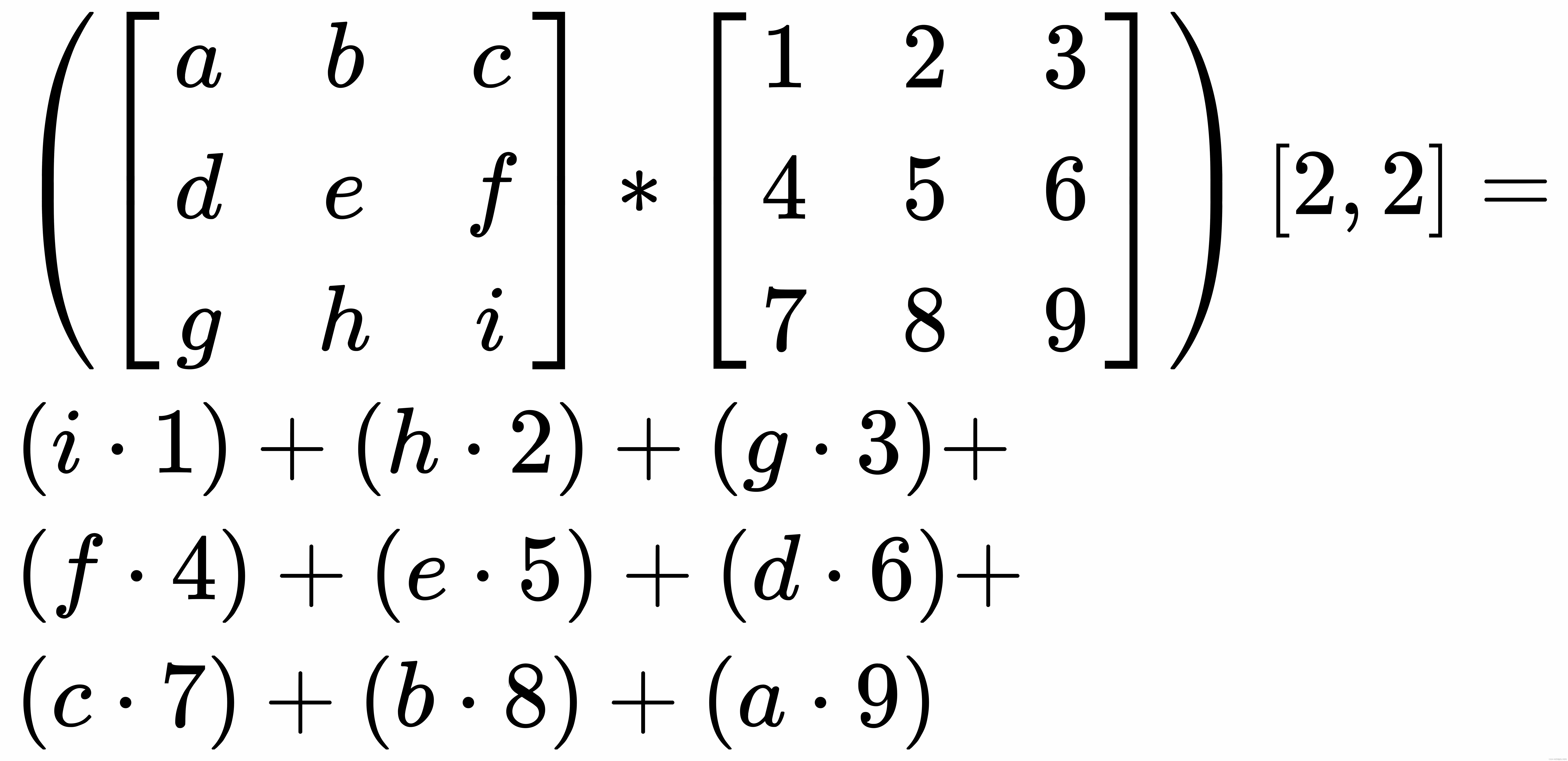
即可分别得出横向及纵向的亮度差分近似值. 如果A代表原始图像, G x G_x Gx和 G y G_y Gy分别代表横向及纵向边缘检测的图像, 公式如下:
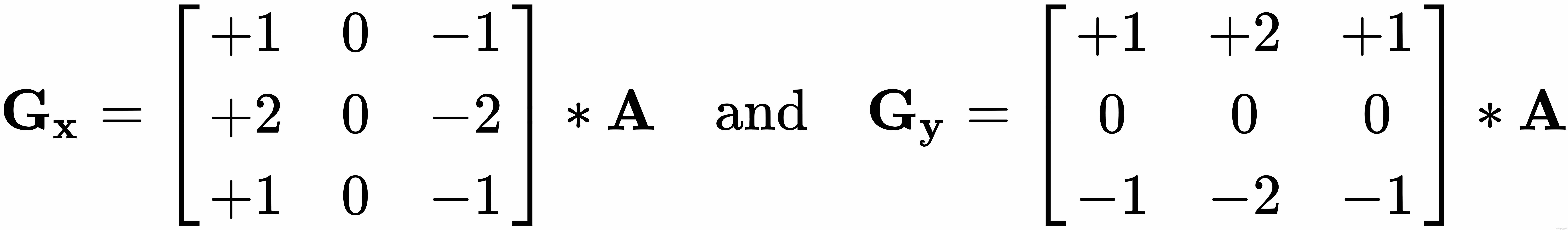
图像的每一个像素的横向及纵向梯度近似值可用以下公式结合, 来计算梯度大小.

简单点说用个动画来表示可能更清晰:

而用CUDA解决这个问题的原理就是, 每个线程处理一个像素.每个线程读取一个像素周围的数值(下面代码注释中的x0~x8), 然后进行计算
代码如下:
#include "cuda_runtime.h"#include #include #include #include #include using namespace std;using namespace cv;//GPU实现Sobel边缘检测// x0 x1 x2 // x3 x4 x5 // x6 x7 x8 __global__ void sobel_gpu(unsigned char* in, unsigned char* out, int imgHeight, int imgWidth){ int x = threadIdx.x + blockDim.x * blockIdx.x; int y = threadIdx.y + blockDim.y * blockIdx.y; int index = y * imgWidth + x; int Gx = 0; int Gy = 0; unsigned char x0, x1, x2, x3, x4, x5, x6, x7, x8; if (x > 0 && x 0 && y < imgHeight-1) { x0 = in[(y - 1) * imgWidth + x - 1]; x1 = in[(y - 1) * imgWidth + x ]; x2 = in[(y - 1) * imgWidth + x + 1]; x3 = in[(y ) * imgWidth + x - 1]; x4 = in[(y ) * imgWidth + x ]; x5 = in[(y ) * imgWidth + x + 1]; x6 = in[(y + 1) * imgWidth + x - 1]; x7 = in[(y + 1) * imgWidth + x ]; x8 = in[(y + 1) * imgWidth + x + 1]; Gx = (x0 + 2 * x3 + x6) - (x2 + 2 * x5 + x8); Gy = (x0 + 2 * x1 + x2) - (x6 + 2 * x7 + x8); out[index] = (abs(Gx) + abs(Gy)) / 2; //printf("out[%d]: %d", index, out[index]); }}//CPU实现Sobel边缘检测void sobel_cpu(Mat srcImg, Mat dstImg, int imgHeight, int imgWidth){ int Gx = 0; int Gy = 0; for (int i = 1; i < imgHeight - 1; i++) { uchar* dataUp = srcImg.ptr(i - 1); uchar* data = srcImg.ptr(i); uchar* dataDown = srcImg.ptr(i + 1); uchar* out = dstImg.ptr(i); for (int j = 1; j < imgWidth - 1; j++) { Gx = (dataUp[j + 1] + 2 * data[j + 1] + dataDown[j + 1]) - (dataUp[j - 1] + 2 * data[j - 1] + dataDown[j - 1]); Gy = (dataUp[j - 1] + 2 * dataUp[j] + dataUp[j + 1]) - (dataDown[j - 1] + 2 * dataDown[j] + dataDown[j + 1]); out[j] = (abs(Gx) + abs(Gy)) / 2; } }}int main(){ //利用opencv的接口读取图片 Mat img = imread("1.jpg",0); int imgWidth = img.cols; int imgHeight = img.rows; //int imgChannel = img.channels();//利用opencv的接口对读入的grayImg进行去噪 Mat gaussImg; GaussianBlur(img, gaussImg, Size(3, 3), 0, 0, BORDER_DEFAULT); //CPU结果为dst_cpu, GPU结果为dst_gpu Mat dst_cpu(imgHeight, imgWidth, CV_8UC1, Scalar(0)); Mat dst_gpu(imgHeight, imgWidth, CV_8UC1, Scalar(0,0,0));//调用sobel_cpu处理图像 sobel_cpu(gaussImg, dst_cpu, imgHeight, imgWidth); //申请指针并将它指向GPU空间 size_t num = imgHeight * imgWidth * sizeof(unsigned char); unsigned char* in_gpu; unsigned char* out_gpu; cudaMalloc((void)&in_gpu, num); cudaMalloc((void)&out_gpu, num); //定义grid和block的维度(形状) dim3 threadsPerBlock(32, 32); dim3 blocksPerGrid((imgWidth + threadsPerBlock.x - 1) / threadsPerBlock.x, (imgHeight + threadsPerBlock.y - 1) / threadsPerBlock.y); //将数据从CPU传输到GPU cudaMemcpy(in_gpu, img.data, num, cudaMemcpyHostToDevice); //调用在GPU上运行的核函数 sobel_gpu <<> > (in_gpu, out_gpu, imgHeight, imgWidth); //将计算结果传回CPU内存 cudaMemcpy(dst_gpu.data, out_gpu, num, cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost); /*for (int i = 0; i < num; i++) { printf("%d ", dst_gpu.data[i]); if (i % imgWidth == 0) printf("\n"); }*/ //显示处理结果 imshow("gpu", dst_gpu); imshow("cpu", img); waitKey(0); //释放GPU内存空间 cudaFree(in_gpu); cudaFree(out_gpu); return 0;}

