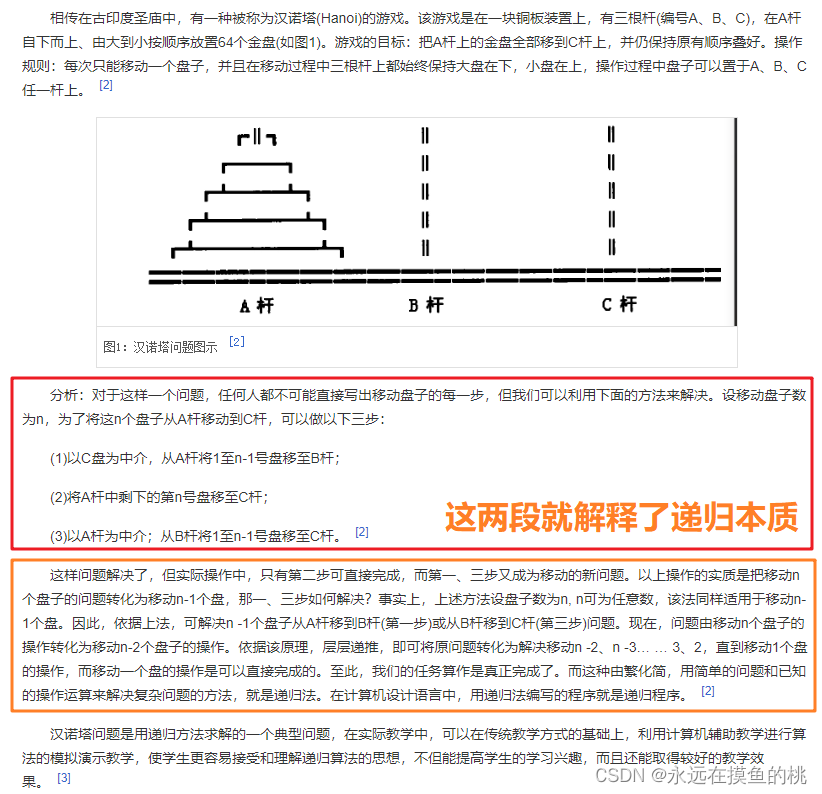
思路

代码实现
package digui;import java.util.Stack;public class Code02_Hanoi { public static void hanoi1(int n) { leftToRight(n); } public static void leftToRight(int n) { if (n == 1) { System.out.println("Move 1 from left to right"); return; } leftToMid(n - 1); System.out.println("Move " + n + " from left to right"); midToRight(n - 1); } public static void leftToMid(int n) { if (n == 1) { System.out.println("Move 1 from left to mid"); return; } leftToRight(n - 1); System.out.println("Move " + n + " from left to mid"); rightToMid(n - 1); } public static void rightToMid(int n) { if (n == 1) { System.out.println("Move 1 from right to mid"); return; } rightToLeft(n - 1); System.out.println("Move " + n + " from right to mid"); leftToMid(n - 1); } public static void midToRight(int n) { if (n == 1) { System.out.println("Move 1 from mid to right"); return; } midToLeft(n - 1); System.out.println("Move " + n + " from mid to right"); leftToRight(n - 1); } public static void midToLeft(int n) { if (n == 1) { System.out.println("Move 1 from mid to left"); return; } midToRight(n - 1); System.out.println("Move " + n + " from mid to left"); rightToLeft(n - 1); } public static void rightToLeft(int n) { if (n == 1) { System.out.println("Move 1 from right to left"); return; } rightToMid(n - 1); System.out.println("Move " + n + " from right to left"); midToLeft(n - 1); } public static void hanoi2(int n) { if (n > 0) { func(n, "left", "right", "mid"); } } public static void func(int N, String from, String to, String other) { if (N == 1) { System.out.println("Move 1 from " + from + " to " + to); } else { func(N-1, from, other, to); System.out.println("Move" + N + " from " + from + " to " + to); func(N-1, other, to, from); } } public static class Record { public boolean finish1; public int base; public String from; public String to; public String other; public Record(boolean f1, int b, String f, String t, String o) { finish1 = false; base = b; from = f; to = t; other = o; } } public static void hanoi3(int N) { if (N < 1) { return; } Stack<Record> stack = new Stack<>(); stack.add(new Record(false, N, "left", "right", "mid")); while (!stack.isEmpty()) { Record cur = stack.pop(); if (cur.base == 1) { System.out.println("Move 1 from " + cur.from + " to " + cur.to); if (!stack.isEmpty()) { stack.peek().finish1 = true; } } else { if (!cur.finish1) { stack.push(cur); stack.push(new Record(false, cur.base - 1, cur.from, cur.other, cur.to)); } else { System.out.println("Move " + cur.base + " from " + cur.from + " to " + cur.to); stack.push(new Record(false, cur.base - 1, cur.other, cur.to, cur.from)); } } } } public static void main(String[] args) { int n = 4; hanoi1(n); System.out.println("============"); hanoi2(n);System.out.println("============");hanoi3(n); }}




