【MM32F5270开发板试用】依靠SPI_SD,移植FatFs文件系统
【MM32F5270开发板试用】依靠SPI_SD,移植FatFs文件系统
本次所有代码按照以前习惯全部开源:我的Github地址是:https://github.com/kings669/MM32F5
我的初步计划将完成音乐播放器的开发,所有代码均会在仓库中更新。
一、FatFs
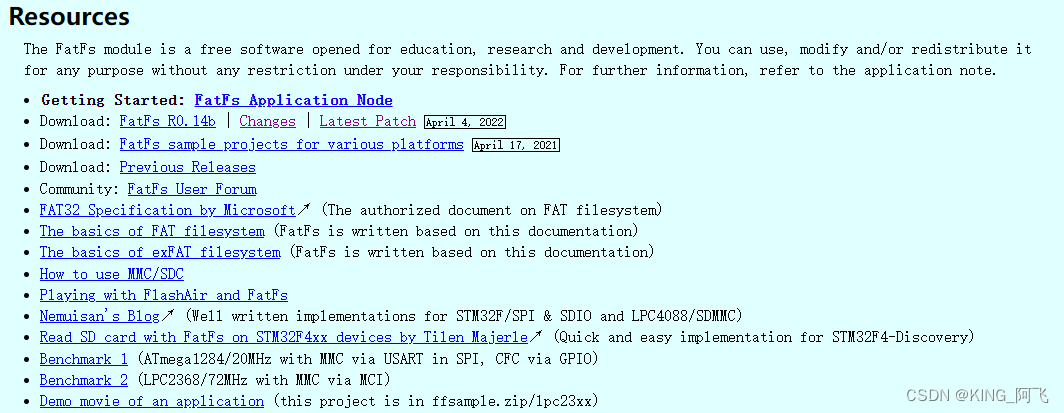
官网:http://elm-chan.org/fsw/ff/00index_e.html
我们先下载源码包,或者在MindSDK中也有。
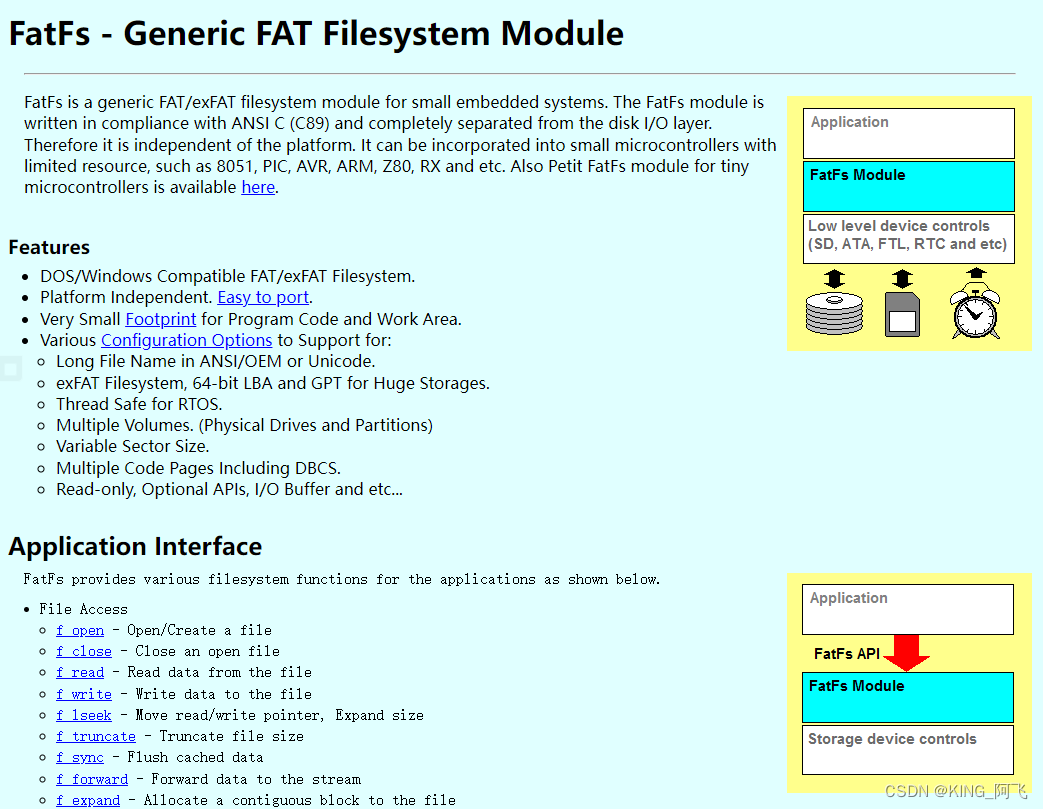
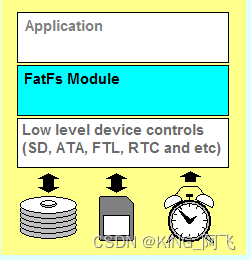
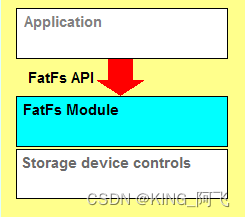
FatFs是用于小型嵌入式系统的通用FAT / exFAT文件系统模块。FatFs模块是按照ANSI
C(C89)编写的,并且与磁盘I/O层完全分开。因此,它独立于平台。它可以并入资源有限的小型微控制器中,例如8051,PIC,AVR,ARM,Z80,RX等。“FatFs模块是为教育,研究和开发开放的免费软件。您可以在个人项目或商业产品中使用,修改和/或重新分发它,而不受您的责任限制。”
特征
- DOS / Windows兼容的FAT / exFAT文件系统。
- 平台无关。易于移植。
- 程序代码和工作区的占用空间非常小。
支持以下各种配置选项: - ANSI / OEM或Unicode中的长文件名。
- exFAT文件系统,64位LBA和GPT可存储大量数据。
- RTOS的线程安全。
- 多个卷(物理驱动器和分区,最多10个卷)。
- 可变扇区大小。 多个代码页,包括DBCS。
- 只读,可选API,I /O缓冲区等…
层级结构
文件夹
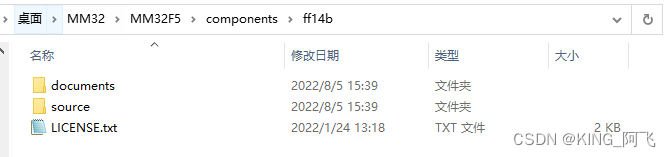
documents文件夹中就是官方的文档文件
source文件中就是我们的源文件
还有证书文件
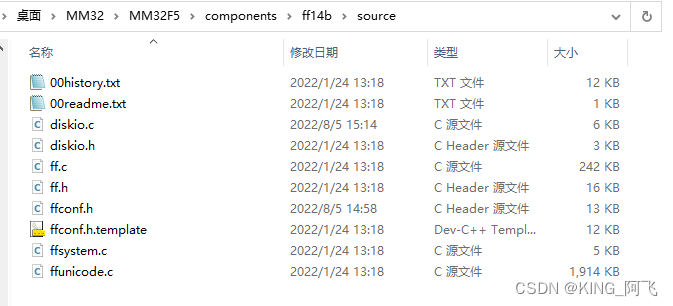
00history.txt 介绍了 FatFs 的版本更新情况。
00readme.txt 说明了当前目录下 diskio.c 、 diskio.h、 ff.c、 ff.h、 integer.h 的功能。
diskio.c 文件是 FatFs 移植最关键的文件,它为文件系统提供了最底层的访问 SPI Flash芯片的方法, FatFs 有且仅有它需要用到与 SPI Flash 芯片相关的函数。
diskio.h 定义了FatFs 用到的宏,以及 diskio.c 文件内与底层硬件接口相关的函数声明。
源码文件功能简介如下:
diskio.c:包含底层存储介质的操作函数,这些函数需要用户自己实现,主要添加底层驱动函数。
ff.c:FatFs 核心文件,文件管理的实现方法。该文件独立于底层介质操作文件的函数,利用这些函数实现文件的读写。
二、MindSDK——SD_SPI
我们打开MindSDK的官网:https://mindsdk.mindmotion.com.cn,没有账户的需要注册一下。
我们构建F5270,系统我的是Win10,编译器是keil,这是我的选择,大家可以根据自己的来选择。
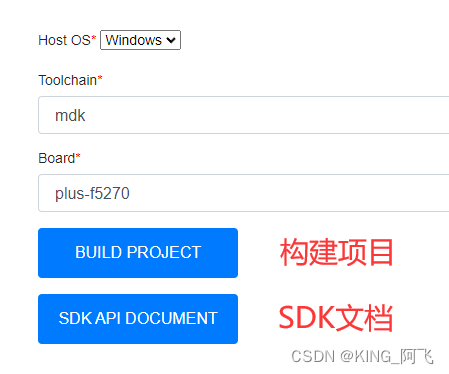
构建完成后,我们来到以下页面,点击进入
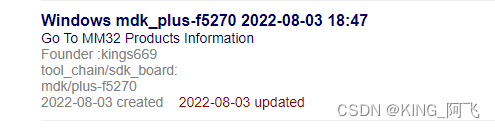
我们选择进入例程文件中
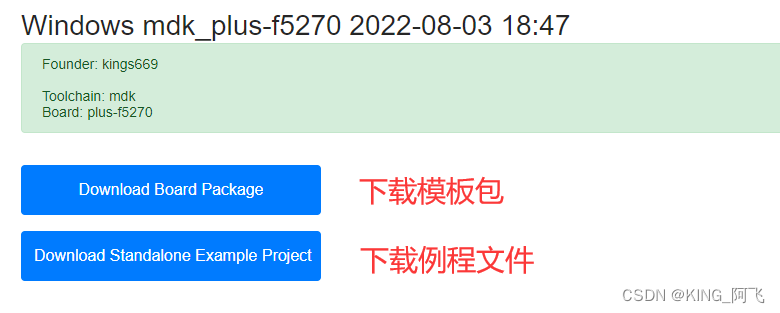
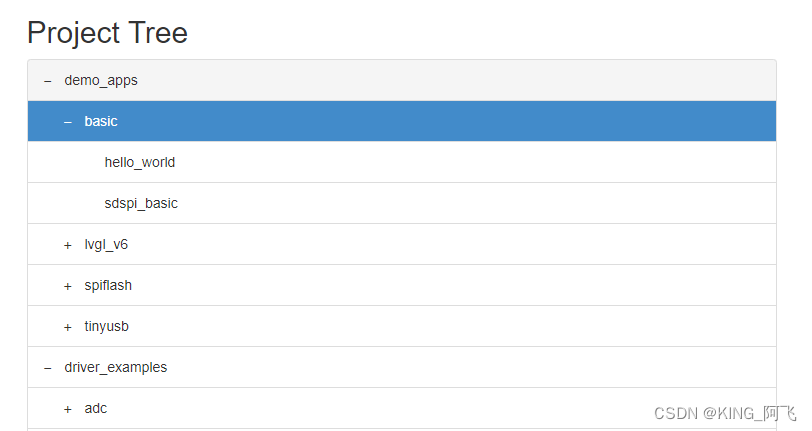
我们选中sdspi_basic,然后点击下载。

我们编译一下,很好没有问题:

三、移植FatFS
我们把FatFS源代码放在components文件夹中。
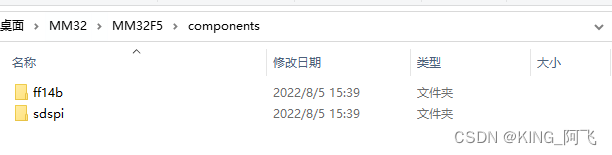
我们需要修改diskio.c文件中的东西。
/*-----------------------------------------------------------------------*//* Low level disk I/O module SKELETON for FatFs (C)ChaN, 2019 *//*-----------------------------------------------------------------------*//* If a working storage control module is available, it should be *//* attached to the FatFs via a glue function rather than modifying it. *//* This is an example of glue functions to attach various exsisting *//* storage control modules to the FatFs module with a defined API.*//*-----------------------------------------------------------------------*/#include "ff.h" /* Obtains integer types */#include "diskio.h" /* Declarations of disk functions */#include "sdspi.h"/* Definitions of physical drive number for each drive */#define DEV_RAM 0 /* Example: Map Ramdisk to physical drive 0 */#define DEV_MMC 1 /* Example: Map MMC/SD card to physical drive 1 */#define DEV_USB 2 /* Example: Map USB MSD to physical drive 2 */SDSPI_ApiRetStatus_Type app_sdspi_ret;SDSPI_CardHandler_Type app_sdspi_card;extern const SDSPI_Interface_Type board_sdspi_if;/*-----------------------------------------------------------------------*//* Get Drive Status *//*-----------------------------------------------------------------------*/DSTATUS disk_status ( BYTE pdrv /* Physical drive nmuber to identify the drive */){ DSTATUS stat; int result; switch (pdrv) { case DEV_RAM : //result = RAM_disk_status(); // translate the reslut code here return stat; case DEV_MMC : //result = MMC_disk_status(); stat = RES_OK; // translate the reslut code here return stat; case DEV_USB : //result = USB_disk_status(); // translate the reslut code here return stat; } return STA_NOINIT;}/*-----------------------------------------------------------------------*//* Inidialize a Drive *//*-----------------------------------------------------------------------*/DSTATUS disk_initialize ( BYTE pdrv /* Physical drive nmuber to identify the drive */){ DSTATUS stat; //int result; switch (pdrv) { case DEV_RAM : //result = RAM_disk_initialize(); // translate the reslut code here return stat; case DEV_MMC : //result = MMC_disk_initialize(); if(!SDSPI_Init(&app_sdspi_card, &board_sdspi_if)){ stat = RES_OK; }else{ stat = STA_NOINIT; } // translate the reslut code here return stat; case DEV_USB : //result = USB_disk_initialize(); // translate the reslut code here return stat; } return STA_NOINIT;}/*-----------------------------------------------------------------------*//* Read Sector(s)*//*-----------------------------------------------------------------------*/DRESULT disk_read ( BYTE pdrv, /* Physical drive nmuber to identify the drive */ BYTE *buff, /* Data buffer to store read data */ LBA_t sector, /* Start sector in LBA */ UINT count /* Number of sectors to read */){ DRESULT res; //int result; switch (pdrv) { case DEV_RAM : // translate the arguments here //result = RAM_disk_read(buff, sector, count); // translate the reslut code here return res; case DEV_MMC : // translate the arguments here //result = MMC_disk_read(buff, sector, count); if(!SDSPI_ReadBlocks(&app_sdspi_card,buff, sector, count)) { res = RES_OK; }else{ res = RES_ERROR; } // translate the reslut code here return res; case DEV_USB : // translate the arguments here //result = USB_disk_read(buff, sector, count); // translate the reslut code here return res; } return RES_PARERR;}/*-----------------------------------------------------------------------*//* Write Sector(s) *//*-----------------------------------------------------------------------*/#if FF_FS_READONLY == 0DRESULT disk_write ( BYTE pdrv, /* Physical drive nmuber to identify the drive */ const BYTE *buff, /* Data to be written */ LBA_t sector, /* Start sector in LBA */ UINT count /* Number of sectors to write */){ DRESULT res; //int result; switch (pdrv) { case DEV_RAM : // translate the arguments here //result = RAM_disk_write(buff, sector, count); // translate the reslut code here return res; case DEV_MMC : // translate the arguments here //result = MMC_disk_write(buff, sector, count); if(!SDSPI_WriteBlocks(&app_sdspi_card,(uint8_t *)buff, sector, count)) { res = RES_OK; }else{ res = RES_ERROR; } // translate the reslut code here return res; case DEV_USB : // translate the arguments here //result = USB_disk_write(buff, sector, count); // translate the reslut code here return res; } return RES_PARERR;}#endif/*-----------------------------------------------------------------------*//* Miscellaneous Functions *//*-----------------------------------------------------------------------*/DRESULT disk_ioctl ( BYTE pdrv, /* Physical drive nmuber (0..) */ BYTE cmd, /* Control code */ void *buff /* Buffer to send/receive control data */){ DRESULT res; int result; switch (pdrv) { case DEV_RAM : // Process of the command for the RAM drive return res; case DEV_MMC : // Process of the command for the MMC/SD card switch(cmd) { case GET_SECTOR_COUNT: *(DWORD *)buff = app_sdspi_card.blockCount; res = RES_OK; break; case GET_BLOCK_SIZE: *(DWORD *)buff = SDSPI_DEFAULT_BLOCK_SIZE; res = RES_OK; break; } return res; case DEV_USB : // Process of the command the USB drive return res; } return RES_PARERR;}mian.c:
/* * Copyright 2021 MindMotion Microelectronics Co., Ltd. * All rights reserved. * * SPDX-License-Identifier: BSD-3-Clause */#include "board_init.h"#include "ffconf.h"#include "ff.h"/* * Macros. *//* * Variables. */FATFS fs;const TCHAR fs_drv[] = "1:/";TCHAR fs_path[256] = "\0";/* * Declerations. */ FRESULT app_fatfs_listfiles(const char * dir_path);/* * Functions. */int main(void){ uint8_t ch; BOARD_Init(); printf("sdspi_basic example.\r\n"); /* f_mount().\r\n */ printf("f_mount(). "); if( !f_mount(&fs, fs_drv ,1) ) { printf("succ.\r\n"); } else { printf("fail.\r\n"); while (1) {} } /* root dir. */ app_fatfs_listfiles(fs_drv); /* dir0. */ fs_path[0] = '\0'; strcat(fs_path, fs_drv); strcat(fs_path, "dir0/"); app_fatfs_listfiles(fs_path); /* dir1. */ fs_path[0] = '\0'; strcat(fs_path, fs_drv); strcat(fs_path, "dir1/"); app_fatfs_listfiles(fs_path); printf("app_fatfs_listfiles() done.\r\n"); while (1) { ch = getchar(); putchar(ch); }}/* list the file items under the indecated path. */FRESULT app_fatfs_listfiles(const char * dir_path){ FRESULT res; FILINFO fno; DIR dir; char *fn; printf("* %s ->\r\n", dir_path); res = f_opendir(&dir, dir_path); if (res != FR_OK) { return res; } for (;;) { /* read iterator. */ res = f_readdir(&dir, &fno); if ( (res != FR_OK) || (fno.fname[0] == 0) ) { break; } /* skip the "self" and "father" dir item. */ if (fno.fname[0] == '.') { continue; } /* collect the dir or file name. */ fn = fno.fname; if (fno.fattrib & AM_DIR) /* dir name. */ { printf("\t%s/\r\n", fn); } else /* file name */ { printf("\t%s: %u B\r\n", fn, (unsigned)fno.fsize); } } /* close the opened dir to reest the iterator. */ res = f_closedir(&dir); return res;}/* EOF. */
四、验证
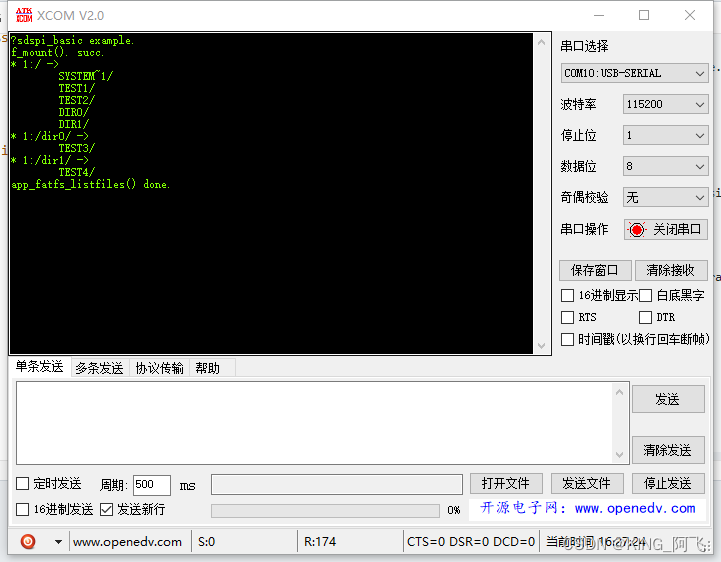
我们插上读卡器:
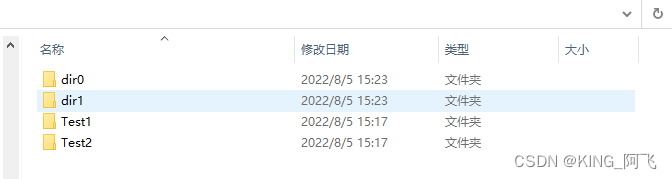
在dir0和dir1中也有两个文件夹,是Test3和Test4.这些文件夹都是我自己创建的,MCU已经能够查看到了。没有问题
五、总结
MindSDK使用体验还行,只能提供例子。最好能够有CubeMX这样的配置,添加包就行,就会方便很多。现在移植好了文件系统,下一步就是要进行软解码了,加油💪💪


