JavaEE——Spring的注入
目录
1.Spring注入内部Bean
我们将定义在 元素的 或 元素内部的 Bean,称为“内部 Bean”。
1.1setter 方式注入内部 Bean
我们可以通过 setter 方式注入内部 Bean。此时,我们只需要在 标签下的 元素中,再次使用 元素对内部 Bean 进行定义,格式如下。
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beanshttp://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd"> <bean id="outerBean" class="……"> <property name="……" > <bean class="……"> <property name="……" value="……" ></property> …… </bean> </property> </bean> </beans>注意:内部 Bean 都是匿名的,不需要指定 id 和 name 的。即使制定了,IoC 容器也不会将它作为区分 Bean 的标识符,反而会无视 Bean 的 Scope 标签。因此内部 Bean 几乎总是匿名的,且总会随着外部的 Bean 创建。内部 Bean 是无法被注入到它所在的 Bean 以外的任何其他 Bean 的。
public class MainApp { private static final Log LOGGER = LogFactory.getLog(MainApp.class); public static void main(String[] args) { //获取 ApplicationContext 容器 ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("Beans.xml"); //获取名为 employee 的 Bean Employee employee = context.getBean("employee", Employee.class); //通过日志打印员工信息 LOGGER.info(employee.toString()); }}1.2构造函数方式注入内部 Bean
我们可以通过构造方法注入内部 Bean。此时,我们只需要在 标签下的 元素中,再次使用 元素对内部 Bean 进行定义,格式如下。
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beanshttp://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd"> <bean id="……" class="……"> <constructor-arg name="……"> <bean class="……"> <constructor-arg name="……" value="……"></constructor-arg> …… </bean> </constructor-arg> </bean> </beans>public class MainApp { private static final Log LOGGER = LogFactory.getLog(MainApp.class); public static void main(String[] args) { //获取 ApplicationContext 容器 ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("Beans.xml"); //获取名为 employee 的 Bean Employee employee = context.getBean("employee", Employee.class); //通过日志打印员工信息 LOGGER.info(employee.toString()); }}2.Spring注入集合
我们还可以在 Bean 标签下的 元素中,使用以下元素配置 Java 集合类型的属性和参数,例如 List、Set、Map 以及 Properties 等。

在集合中设置普通类型的值
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beanshttp://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd"> <bean id="javaCollection" class="net.biancheng.c.JavaCollection"> <property name="courses"> <array> <value>Java</value> <value>PHP</value> <value>C 语言</value> </array> </property> <property name="list"> <list> <value>张三</value> <value>李四</value> <value>王五</value> <value>赵六</value> </list> </property> <property name="maps"> <map> <entry key="JAVA" value="java"></entry> <entry key="PHP" value="php"></entry> </map> </property> <property name="sets"> <set> <value>MySQL</value> <value>Redis</value> </set> </property> </bean> </beans>在集合中设置对象类型的值
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beanshttp://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd"> <bean id="course" class="net.biancheng.c.Course"> <property name="courseId" value="1"></property> <property name="courseName" value="Java课程"></property> </bean> <bean id="course2" class="net.biancheng.c.Course"> <property name="courseId" value="2"></property> <property name="courseName" value="PHP课程"></property> </bean> <bean id="course3" class="net.biancheng.c.Course"> <property name="courseId" value="3"></property> <property name="courseName" value="C语言课程"></property> </bean> <bean id="javaCollection" class="net.biancheng.c.JavaCollection"> <property name="courses"> <array> <ref bean="course"></ref> <ref bean="course2"></ref> <ref bean="course3"></ref> </array> </property> <property name="list"> <list> <value>张三</value> <value>李四</value> <value>王五</value> <value>赵六</value> </list> </property> <property name="maps"> <map> <entry key="JAVA" value="java"></entry> <entry key="PHP" value="php"></entry> </map> </property> <property name="sets"> <set> <value>MySQL</value> <value>Redis</value> </set> </property> </bean> </beans>3.Spring注入其他类型的属性
除了普通属性、对象属性(Bean)、集合等属性外,Spring 也能够将其他类型的属性注入到 Bean 中,例如 Null 值、字面量、复合物属性等。
注入 Null 值
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beanshttp://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd"> <bean id="exampleBean" class="net.biancheng.c.ExampleBean"> <property name="propertyNull"> <null/> </property> </bean> </beans>注入空字符串
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beanshttp://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd"> <bean id="exampleBean" class="net.biancheng.c.ExampleBean"> <property name="propertyNull"> <null/> </property> <property name="propertyEmpty" value=""></property> </bean> </beans>注入字面量
我们知道,在 XML 配置中“”、“&”等特殊字符是不能直接保存的,否则 XML 语法检查时就会报错。此时,我们可以通过以下两种方式将包含特殊符号的属性注入 Bean 中。
转义
在 XML 中,特殊符号必须进行转义才能保存进 XML 配置中,例如“& lt;”、“& gt;”、“& amp;”等。
在 XML 中,需要转义的字符如下表所示。
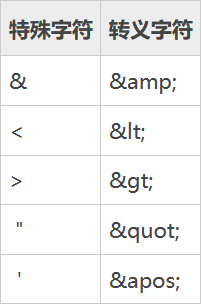
在转义过程中,需要注意以下几点:
- 转义序列字符之间不能有空格;
- 转义序列必须以“;”结束;
- 单独出现的“&”不会被认为是转义的开始;
- 区分大小写。
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beanshttp://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd"> <bean id="exampleBean" class="net.biancheng.c.ExampleBean"> <property name="propertyNull"> <null/> </property> <property name="propertyEmpty" value=""></property> <property name="propertyLiteral" value="<span class="token entity named-entity" title="<C语言中文网">>"></property> </bean> </beans>级联属性赋值
我们可以在 的 子元素中,为它所依赖的 Bean 的属性进行赋值,这就是所谓的“级联属性赋值”。
使用级联属性赋值时,需要注意以下 3点:
- Java 类中必须有 setter 方法;
- Java 类中必须有无参构造器(默认存在);
- 依赖其他 Bean 的类中,必须提供一个它依赖的 Bean 的 getXxx() 方法。
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beanshttp://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd"> <bean id="exampleBean" class="net.biancheng.c.ExampleBean"> <property name="propertyNull"> <null/> </property> <property name="propertyEmpty" value=""></property> <!--使用 将包含特殊符号的字面量注入--> <property name="propertyLiteral"> <value><![CDATA[]]></value> </property> <property name="dependBean" ref="dependBean"></property> <property name="dependBean.dependProperty" value="级联属性赋值"></property> </bean> <bean id="dependBean" class="net.biancheng.c.DependBean"> <property name="dependProperty" value="依赖 Bean 内部赋值"></property> </bean> </beans>

