【初探篇】反向代理在系统结构中的应用场景
大家知道反向代理在系统设计中扮演着"明星的经纪人"角色吗?它不仅能让你的服务器免于被疯狂粉丝(请求)的围攻,还能帮你在后台搞定负载均衡、内容缓存等工作。想象一下,如果你的网站突然爆红,请求量激增,单靠一台服务器肯定会扛不住,于是就需要反向代理来帮你筹码,它会将请求智慧地分发给多台服务器,保证大家都能分得均匀的工作量。就像电商大促时,系统得提前部署好反向代理,否则服务器崩溃的场面就像春节联欢晚会突然停电,场面十分尴尬。
文章目录
-
- 反向代理在系统结构中的应用场景
-
- Nginx的反向代理配置
- 基于反向代理的负载均衡器
-
- 将101代理到102
- 配置101的负载均衡(轮询模式)
- 配置101的负载均衡(权重模式)
- 其他负载均衡策略(不常用)
反向代理在系统结构中的应用场景
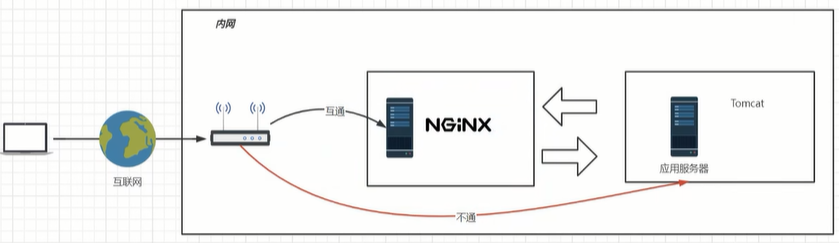
反向代理方式是指以代理服务器来接受Internet上的连接请求,然后将请求转发给内部网络上的服务器;并将从服务器上得到的结果返回给Internet上请求连接的客户端,此时代理服务器对外就表现为一个服务器。
反向代理服务器通常有两种模型,一种是作为内容服务器的替身,另一种作为内容服务器集群的负载均衡器。
- 作内容服务器的替身
如果您的内容服务器具有必须保持安全的敏感信息,如信用卡号数据库,可在防火墙外部设置一个代理服务器作为内容服务器的替身。当外部客户机尝试访问内容服务器时,会将其送到代理服务器。实际内容位于内容服务器上,在防火墙内部受到安全保护。代理服务器位于防火墙外部,在客户机看来就像是内容服务器。
当客户机向站点提出请求时,请求将转到代理服务器。然后,代理服务器通过防火墙中的特定通路,将客户机的请求发送到内容服务器。内容服务器再通过该通道将结果回传给代理服务器。代理服务器将检索到的信息发送给客户机,好像代理服务器就是实际的内容服务器。如果内容服务器返回错误消息,代理服务器会先行截取该消息并更改标头中列出的任何 URL,然后再将消息发送给客户机。如此可防止外部客户机获取内部内容服务器的重定向 URL。
这样,代理服务器就在安全数据库和可能的恶意攻击之间提供了又一道屏障。与有权访问整个数据库的情况相对比,就算是侥幸攻击成功,作恶者充其量也仅限于访问单个事务中所涉及的信息。未经授权的用户无法访问到真正的内容服务器,因为防火墙通路只允许代理服务器有权进行访问。
- 作为内容服务器的负载均衡器
可以在一个组织内使用多个代理服务器来平衡各 Web 服务器间的网络负载。在此模型中,可以利用代理服务器的高速缓存特性,创建一个用于负载平衡的服务器池。此时,代理服务器可以位于防火墙的任意一侧。如果 Web 服务器每天都会接收大量的请求,则可以使用代理服务器分担 Web 服务器的负载并提高网络访问效率。
对于客户机发往真正服务器的请求,代理服务器起着中间调停者的作用。代理服务器会将所请求的文档存入高速缓存。如果有不止一个代理服务器,DNS 可以采用“轮询法”选择其 IP 地址,随机地为请求选择路由。客户机每次都使用同一个 URL,但请求所采取的路由每次都可能经过不同的代理服务器。
可以使用多个代理服务器来处理对一个高用量内容服务器的请求,这样做的好处是内容服务器可以处理更高的负载,并且比其独自工作时更有效率。在初始启动期间,代理服务器首次从内容服务器检索文档,此后,对内容服务器的请求数会大大下降。
Nginx的反向代理配置
配置如下:
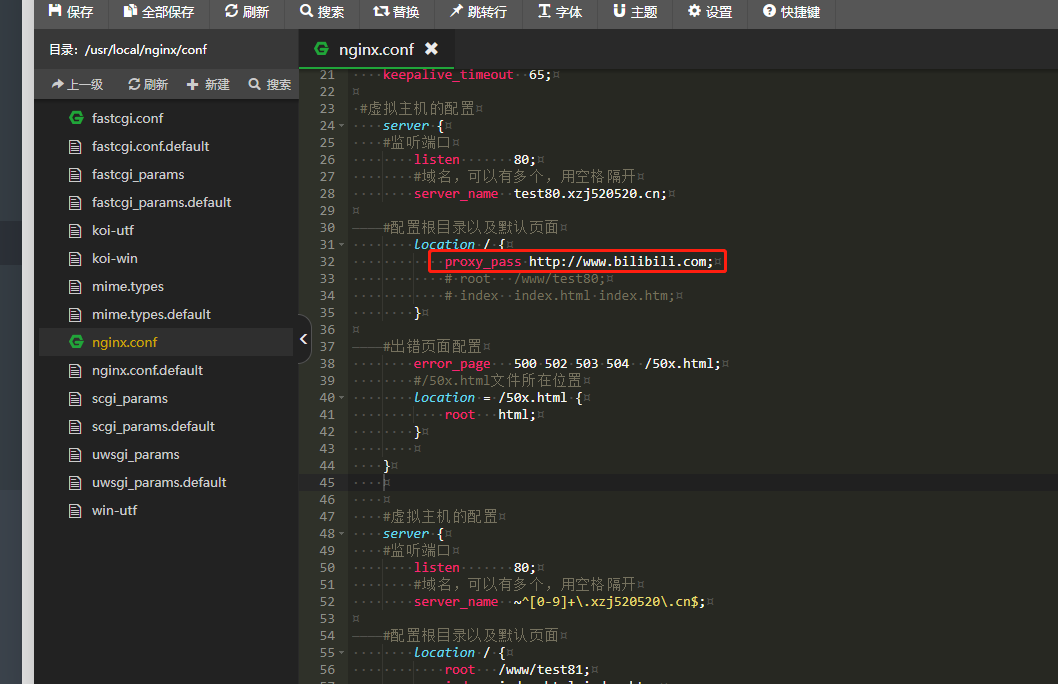
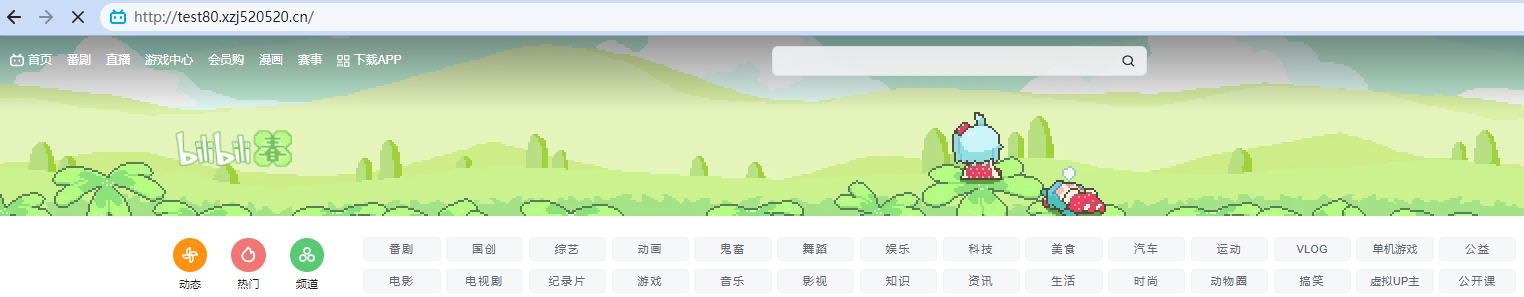
访问http://test80.xzj520520.cn/:
基于反向代理的负载均衡器
克隆两个centos,ip分别设为192.168.8.102,192.168.8.103(网段要用自己的电脑对应)
修改静态ip

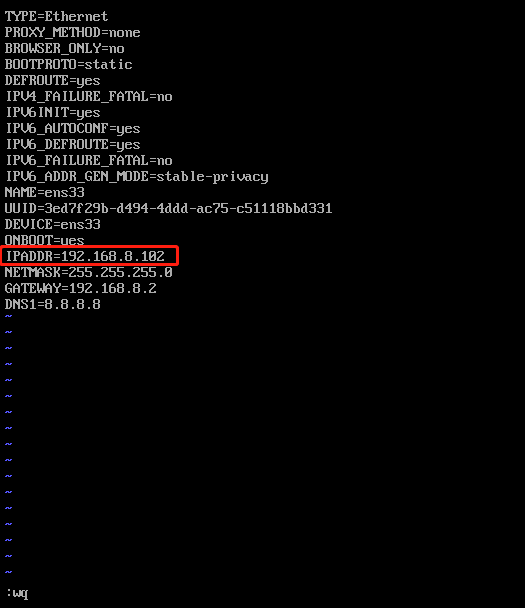
重启网络服务:

另一个虚拟机的配置也是一样。配置好虚拟机之后,配置nginx.cfg
102的nginx.cfg
#user nobody;worker_processes 1;#error_log logs/error.log;#error_log logs/error.log notice;#error_log logs/error.log info;#pid logs/nginx.pid;events { worker_connections 1024;}http { includemime.types; default_type application/octet-stream; #log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" ' # '$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" ' # '"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"'; #access_log logs/access.log main; sendfile on; #tcp_nopush on; #keepalive_timeout 0; keepalive_timeout 65; #gzip on; server { listen80; server_name localhost; #charset koi8-r; #access_log logs/host.access.log main; location / { root html; index index.html index.htm; } #error_page 404/404.html; # redirect server error pages to the static page /50x.html # error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html; location = /50x.html { root html; } # proxy the PHP scripts to Apache listening on 127.0.0.1:80 # #location ~ \.php$ { # proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1; #} # pass the PHP scripts to FastCGI server listening on 127.0.0.1:9000 # #location ~ \.php$ { # root html; # fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000; # fastcgi_index index.php; # fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME /scripts$fastcgi_script_name; # include fastcgi_params; #} # deny access to .htaccess files, if Apache's document root # concurs with nginx's one # #location ~ /\.ht { # deny all; #} } # another virtual host using mix of IP-, name-, and port-based configuration # #server { # listen8000; # listensomename:8080; # server_name somename alias another.alias; # location / { # root html; # index index.html index.htm; # } #} # HTTPS server # #server { # listen443 ssl; # server_name localhost; # ssl_certificate cert.pem; # ssl_certificate_key cert.key;


