面试必问-ThreadLocal实现原理-源码分析-面试分析
先看案例
结构分层
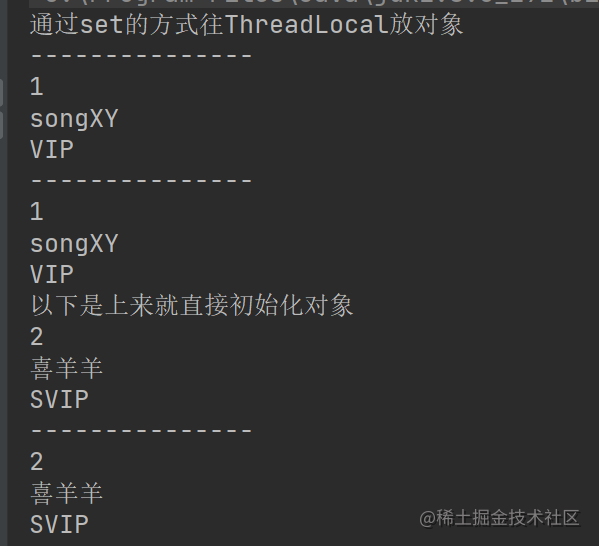
上代码
/ * 功能描述:ThreadLocal案例 * * @author Songxianyang * @date 2022-05-29 12:50 */public class MyThreadLocal { public static void main(String[] args) { UserEntity userEntity = new UserEntity(); userEntity.setId(1); userEntity.setName("songXY"); userEntity.setType("VIP"); new Service1().M(userEntity); System.out.println("以下是上来就直接初始化对象"); new InitialValueService4().M(); }}class Service1 { public void M(UserEntity entity) { ThreadLocalUser.userEntityThreadLocal.set(entity); System.out.println("通过set的方式往ThreadLocal放对象"); System.out.println("---------------"); new Service2().M(); System.out.println("---------------"); new Service3().M(); }}class Service2 { public void M() { UserEntity userEntity = ThreadLocalUser.userEntityThreadLocal.get(); System.out.println(userEntity.getId()); System.out.println(userEntity.getName()); System.out.println(userEntity.getType()); }}class Service3 { public void M() { UserEntity userEntity = ThreadLocalUser.userEntityThreadLocal.get(); System.out.println(userEntity.getId()); System.out.println(userEntity.getName()); System.out.println(userEntity.getType()); // 用完之后记得 remove 掉防止OOM ThreadLocalUser.userEntityThreadLocal.remove(); }}class ThreadLocalUser { public static ThreadLocal<UserEntity> userEntityThreadLocal = new ThreadLocal<>();}class InitialValue { public static ThreadLocal<UserEntity> userEntityThreadLocal = ThreadLocal.withInitial(()->{ UserEntity userEntity = new UserEntity(); userEntity.setId(2); userEntity.setName("喜羊羊"); userEntity.setType("SVIP"); return userEntity; });}class InitialValueService4 { public void M() { UserEntity userEntity = InitialValue.userEntityThreadLocal.get(); System.out.println(userEntity.getId()); System.out.println(userEntity.getName()); System.out.println(userEntity.getType()); System.out.println("---------------"); new InitialValueService5().M(); }}class InitialValueService5 { public void M() { UserEntity userEntity = InitialValue.userEntityThreadLocal.get(); System.out.println(userEntity.getId()); System.out.println(userEntity.getName()); System.out.println(userEntity.getType()); }}运行结果
什么是 ThreadLocal
- ThreadLocal 用的比较多的就是用来维护一个对象。让他在多线程访问下处于线程安全。来保证数据访问的正确性。多线程下不去共享同一个变量。一个线程只维护一个实例。线程若被销毁随着该线程所持有的对象也会被销毁。(销毁可以理解成回收) e.value = null;
我们来分析源码
首先:三个对象来来说明问题
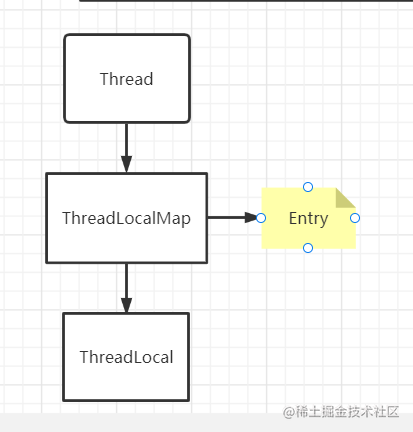
ThreadLocalMap
这个类属于Thread的成员变量且ThreadLocalMap 内部维护了一个 Entry (也就相当于一个map)Entry 与Map的区别
map在hash冲突的时候数组转链表转红黑树Entry 在hash冲突时,在数组中找到空闲位置直接放在空闲问题。也就相当与用数组形式来维护ThreadLocalMapThreadLocalMap 和 Thread 内部关系
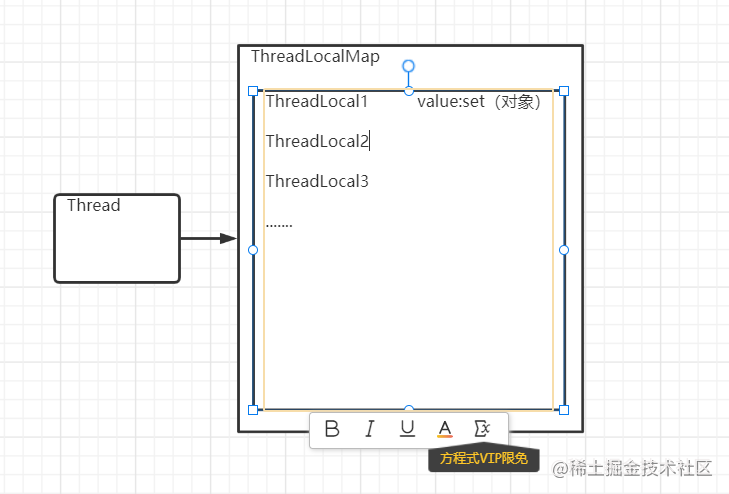
一个线程对一个ThreadLocalMap,map是个集合容器,可以存多个数据
ThreadLocalMap 和ThreadLocal 内部关系
- 在 您 get(),set(),remove()的时候都不然去找 当前线程的ThreadLocalMap,等到下面看源码的时候,就知道了
分析get()源码 非常之简单
public T get() { // 找到当前线程 Thread t = Thread.currentThread(); // 从当前线程中找到 ThreadLocalMap ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t); // map 不等null if (map != null) { // ThreadLocalMap 和 Thread 内部关系 图 // 再看 map.getEntry(this) 中的this 也就是当前的:ThreadLocal ,去找对应的Value值 ThreadLocalMap.Entry e = map.getEntry(this); if (e != null) { @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") // 获取Value的值 T result = (T)e.value; return result; } } return setInitialValue();}private T setInitialValue() {// 获取初始值 T value = initialValue(); Thread t = Thread.currentThread(); ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t); if (map != null) // this 当前的ThreadLocal value:初始值 map.set(this, value); else createMap(t, value); return value;}分析set()源码 非常之简单
public void set(T value) {// 获取当前线程 Thread t = Thread.currentThread(); // 从当前线程中找到 ThreadLocalMap ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t); if (map != null) // this 当前的ThreadLocal value:你传过来的value map.set(this, value); else createMap(t, value);}分析remove源码
public void remove() {// 从当前线程中找到 ThreadLocalMap ThreadLocalMap m = getMap(Thread.currentThread()); if (m != null) //移除对应的key m.remove(this);}内存泄露的源码分析
Entry 构造方法
static class Entry extends WeakReference<ThreadLocal> { / The value associated with this ThreadLocal. */ Object value; // 首先K,WeakReference他来修饰的,弱引用 // V:强应用 。也就是一个对象。 Entry(ThreadLocal k, Object v) { super(k); value = v; }}强引用 弱引用 区别
new 出来的对象都是 强引用对象用完之后立即回收 弱引用ThreadLocal把强引用设置为null 实现被GC回收细节
private int expungeStaleEntry(int staleSlot) { Entry[] tab = table; int len = tab.length; // expunge entry at staleSlot tab[staleSlot].value = null; tab[staleSlot] = null; size--; // Rehash until we encounter null Entry e; int i; for (i = nextIndex(staleSlot, len); (e = tab[i]) != null; i = nextIndex(i, len)) { ThreadLocal<?> k = e.get(); // 如果key 被回收后,key等于null if (k == null) { // 把value 也设置为null 让他被回收 e.value = null; tab[i] = null; size--; } else { int h = k.threadLocalHashCode & (len - 1); if (h != i) { tab[i] = null; // Unlike Knuth 6.4 Algorithm R, we must scan until // null because multiple entries could have been stale. while (tab[h] != null) h = nextIndex(h, len); tab[h] = e; } } } return i;}如何防止内存泄露
- ThreadLocal 用完之后,调用remove方法
ThreadLocal 在使用时 空指针异常如何解决
类型使用基本类型 报空指针包装类型就不会报空指针,如果为null,后台则打印“null",从而不会报异常 开发者涨薪指南
开发者涨薪指南 ![]() 48位大咖的思考法则、工作方式、逻辑体系
48位大咖的思考法则、工作方式、逻辑体系


