手写分布式雪花(SnowFlake)算法生成ID
SnowFlake算法
SnowFlake是twitter公司内部分布式项目采用的ID生成算法,开源后广受国内大厂的好评。由这种算法生成的ID,我们就叫做SnowFlakeID。
SnowFlake算法生成id的结果是一个64bit大小的整数,它的结构如下图:

分为四段:
第一段: 1位为未使用,永远固定为0。
(因为二进制中最高位是符号位,1表示负数,0表示正数。生成的id一般都是用正整数,所以最高位固定为0 )第二段: 41位为毫秒级时间(41位的长度可以使用69年)
第三段: 10位为workerId(10位的长度最多支持部署1024个节点)
(这里的10位又分为两部分,第一部分5位表示数据中心ID(0-31)第二部分5位表示机器ID(0-31))第四段: 12位为毫秒内的计数(12位的计数顺序号支持每个节点每毫秒产生4096个ID序号)
代码实现:
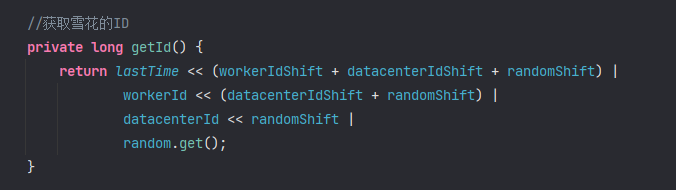
import java.util.HashSet;import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicLong;public class SnowFlake { //时间 41位 private static long lastTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); //数据中心ID 5位(默认0-31) private long datacenterId = 0; private long datacenterIdShift = 5; //机房机器ID 5位(默认0-31) private long workerId = 0; private long workerIdShift = 5; //随机数 12位(默认0~4095) private AtomicLong random = new AtomicLong(); private long randomShift = 12; //随机数的最大值 private long maxRandom = (long) Math.pow(2, randomShift); public SnowFlake() { } public SnowFlake(long workerIdShift, long datacenterIdShift){ if (workerIdShift < 0 || datacenterIdShift < 0 || workerIdShift + datacenterIdShift > 22) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("参数不匹配"); } this.workerIdShift = workerIdShift; this.datacenterIdShift = datacenterIdShift; this.randomShift = 22 - datacenterIdShift - workerIdShift; this.maxRandom = (long) Math.pow(2, randomShift); } //获取雪花的ID private long getId() { return lastTime << (workerIdShift + datacenterIdShift + randomShift) | workerId << (datacenterIdShift + randomShift) | datacenterId << randomShift | random.get(); } //生成一个新的ID public synchronized long nextId() { long now = System.currentTimeMillis(); //如果当前时间和上一次时间不在同一毫秒内,直接返回 if (now > lastTime) { lastTime = now; random.set(0); return getId(); }//将最后的随机数,进行+1操作 if (random.incrementAndGet() < maxRandom) { return getId(); } //自选等待下一毫秒 while (now <= lastTime) { now = System.currentTimeMillis(); } lastTime = now; random.set(0); return getId(); } //测试 public static void main(String[] args) { SnowFlake snowFlake = new SnowFlake(); HashSet<Long> set = new HashSet<>(); for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) { set.add(snowFlake.nextId()); } System.out.println(set.size()); }}代码中获取id的方法利用位运算实现
1 | 41 | 5 | 5 | 12 0|0001100 10100010 10111110 10001001 01011100 00|00000|0 0000|0000 00000000 //41位的时间 0|0000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 00|10001|0 0000|0000 00000000 //5位的数据中心ID 0|0000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 00|00000|1 1001|0000 00000000 //5为的机器IDor 0|0000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 00|00000|0 0000|0000 00000000 //12位的sequence------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ 0|0001100 10100010 10111110 10001001 01011100 00|10001|1 1001|0000 00000000 //结果:910499571847892992SnowFlake优点:
- 所有生成的id按时间趋势递增
- 整个分布式系统内不会产生重复id(因为有datacenterId和workerId来做区分)
SnowFlake不足:
由于SnowFlake强依赖时间戳,所以时间的变动会造成SnowFlake的算法产生错误。



