linux内核源码分析之slab(三)
目录
创建对象obj
释放对象
销毁缓存
创建对象obj
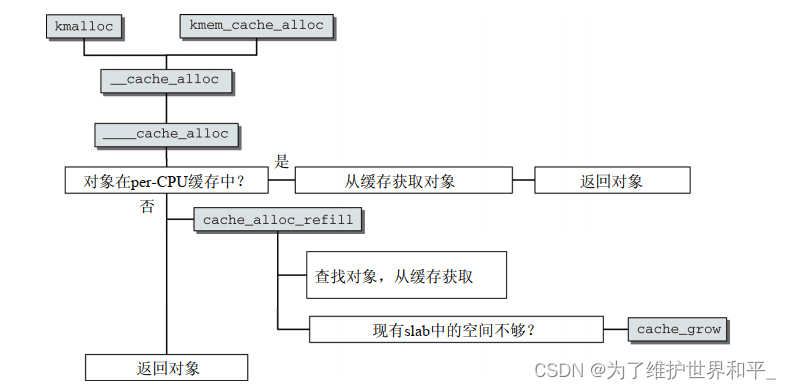
static inline void *____cache_alloc(struct kmem_cache *cachep, gfp_t flags){void *objp;struct array_cache *ac;check_irq_off();//从per-CPU缓存中获取数据ac = cpu_cache_get(cachep);if (likely(ac->avail)) {ac->touched = 1;objp = ac->entry[--ac->avail];STATS_INC_ALLOCHIT(cachep);goto out;}//重新分配STATS_INC_ALLOCMISS(cachep);objp = cache_alloc_refill(cachep, flags);ac = cpu_cache_get(cachep);out:if (objp)kmemleak_erase(&ac->entry[ac->avail]);return objp;}如果在per-CPU缓存中有对象获得,当前活动CPU相关的array_cache实例
在per-CPU缓存中没有对象时,重新填充操作由cache_alloc_refill实现
static struct page *get_first_slab(struct kmem_cache_node *n, bool pfmemalloc){struct page *page;assert_spin_locked(&n->list_lock);//先从kmem_cache_node结构体中slabs_partial 链表上查看有没有pagepage = list_first_entry_or_null(&n->slabs_partial, struct page,slab_list);if (!page) {//如果没有n->free_touched = 1;//从slabs_free 链表上查看有没有pagepage = list_first_entry_or_null(&n->slabs_free, struct page,slab_list);if (page)n->free_slabs--;//空闲数-1}if (sk_memalloc_socks())page = get_valid_first_slab(n, page, pfmemalloc);//返回pagereturn page;}static void *cache_alloc_refill(struct kmem_cache *cachep, gfp_t flags){int batchcount;struct kmem_cache_node *n;struct array_cache *ac, *shared;int node;void *list = NULL;struct page *page;check_irq_off();//获取内存节点node = numa_mem_id();ac = cpu_cache_get(cachep);batchcount = ac->batchcount;if (!ac->touched && batchcount > BATCHREFILL_LIMIT) {batchcount = BATCHREFILL_LIMIT;}//获取cachep所属的kmem_cache_noden = get_node(cachep, node);BUG_ON(ac->avail > 0 || !n);shared = READ_ONCE(n->shared);if (!n->free_objects && (!shared || !shared->avail))goto direct_grow;spin_lock(&n->list_lock);shared = READ_ONCE(n->shared);if (shared && transfer_objects(ac, shared, batchcount)) {shared->touched = 1;goto alloc_done;}while (batchcount > 0) {//获取kmem_cache_node结构体中的kmem_cache,返回pagepage = get_first_slab(n, false);if (!page)goto must_grow;check_spinlock_acquired(cachep);batchcount = alloc_block(cachep, ac, page, batchcount);fixup_slab_list(cachep, n, page, &list);}must_grow:n->free_objects -= ac->avail;alloc_done:spin_unlock(&n->list_lock);fixup_objfreelist_debug(cachep, &list);direct_grow:if (unlikely(!ac->avail)) {if (sk_memalloc_socks()) {void *obj = cache_alloc_pfmemalloc(cachep, n, flags);if (obj)return obj;}//分配新的kmem_cache 并初始化page = cache_grow_begin(cachep, gfp_exact_node(flags), node);ac = cpu_cache_get(cachep);if (!ac->avail && page)alloc_block(cachep, ac, page, batchcount);//让page挂载到kmem_cache_node结构体的slabs_list上cache_grow_end(cachep, page);if (!ac->avail)return NULL;}ac->touched = 1;//重新分配return ac->entry[--ac->avail];}- 获取 cachep 所属的 kmem_cache_node
- 调用 get_first_slab,获取 kmem_cache_node 结构还有没有包含空闲对象的 kmem_cache
- kmem_cache_node 结构没有包含空闲对象的 kmem_cache 了,调用cache_grow_begin 函数
- cache_grow_end 函数,把分配的 page 挂载到 kmem_cache_node 结构的slabs_list 链表上
static struct page *cache_grow_begin(struct kmem_cache *cachep,gfp_t flags, int nodeid){void *freelist;size_t offset;gfp_t local_flags;int page_node;struct kmem_cache_node *n;struct page *page;if (unlikely(flags & GFP_SLAB_BUG_MASK)) {gfp_t invalid_mask = flags & GFP_SLAB_BUG_MASK;flags &= ~GFP_SLAB_BUG_MASK;pr_warn("Unexpected gfp: %#x (%pGg). Fixing up to gfp: %#x (%pGg). Fix your code!\n",invalid_mask, &invalid_mask, flags, &flags);dump_stack();}WARN_ON_ONCE(cachep->ctor && (flags & __GFP_ZERO));local_flags = flags & (GFP_CONSTRAINT_MASK|GFP_RECLAIM_MASK);check_irq_off();if (gfpflags_allow_blocking(local_flags))local_irq_enable();//获取页面page = kmem_getpages(cachep, local_flags, nodeid);if (!page)goto failed;//获取页面所在的内存节点号page_node = page_to_nid(page);//根据内存节点获取对应kmem_cache_node结构n = get_node(cachep, page_node);/* Get colour for the slab, and cal the next value. */n->colour_next++;if (n->colour_next >= cachep->colour)n->colour_next = 0;offset = n->colour_next;if (offset >= cachep->colour)offset = 0;offset *= cachep->colour_off;kasan_poison_slab(page);/* Get slab management. *///分配管理空闲对象的数据结构freelist = alloc_slabmgmt(cachep, page, offset,local_flags & ~GFP_CONSTRAINT_MASK, page_node);if (OFF_SLAB(cachep) && !freelist)goto opps1;//让页面中相关的字段指向kmem_cache和空闲对象slab_map_pages(cachep, page, freelist);//初始化空闲对象管理数据cache_init_objs(cachep, page);if (gfpflags_allow_blocking(local_flags))local_irq_disable();return page;opps1:kmem_freepages(cachep, page);failed:if (gfpflags_allow_blocking(local_flags))local_irq_disable();return NULL;}static void cache_grow_end(struct kmem_cache *cachep, struct page *page){struct kmem_cache_node *n;void *list = NULL;check_irq_off();if (!page)return;//初始化page结构的slab_list链表INIT_LIST_HEAD(&page->slab_list);//根据内存节点获取对应kmem_cache_node结构n = get_node(cachep, page_to_nid(page));spin_lock(&n->list_lock);//slab数增加n->total_slabs++;if (!page->active) {//把这个page结构加入到kmem_cache_node结构的空闲链表中list_add_tail(&page->slab_list, &n->slabs_free);n->free_slabs++;} elsefixup_slab_list(cachep, n, page, &list);STATS_INC_GROWN(cachep);n->free_objects += cachep->num - page->active;spin_unlock(&n->list_lock);fixup_objfreelist_debug(cachep, &list);}释放对象
使用kmem_cache_free返回给slab分配器。
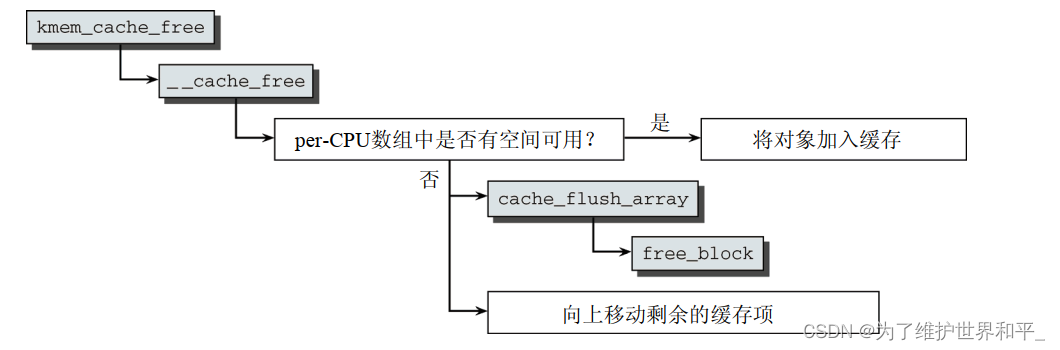
1)如果per-CPU缓存中的对象数目低于允许的限制,则在其中存储一个指向缓存中对象的指针
2)必须将一些对象(准确的数目由array_cache->batchcount给出)从缓存移回slab,从编号最低的数组元素开始。
void ___cache_free(struct kmem_cache *cachep, void *objp,unsigned long caller){struct array_cache *ac = cpu_cache_get(cachep); //小于极限值if (ac->avail limit) {STATS_INC_FREEHIT(cachep);} else {STATS_INC_FREEMISS(cachep);cache_flusharray(cachep, ac);}if (sk_memalloc_socks()) {struct page *page = virt_to_head_page(objp);if (unlikely(PageSlabPfmemalloc(page))) {cache_free_pfmemalloc(cachep, page, objp);return;}}ac->entry[ac->avail++] = objp;}//归还给slabstatic void cache_flusharray(struct kmem_cache *cachep, struct array_cache *ac){ ... //释放free_block(cachep, ac->entry, batchcount, node, &list);free_done:spin_unlock(&n->list_lock);slabs_destroy(cachep, &list);ac->avail -= batchcount;memmove(ac->entry, &(ac->entry[batchcount]), sizeof(void *)*ac->avail);}free_block将对象从缓存移动到原来的slab,并将剩余的对象向数组起始处移动。
static void free_block(struct kmem_cache *cachep, void objpp,int nr_objects, int node, struct list_head *list){int i;struct kmem_cache_node *n = get_node(cachep, node);struct page *page;n->free_objects += nr_objects;for (i = 0; i slab_list);check_spinlock_acquired_node(cachep, node);slab_put_obj(cachep, page, objp);STATS_DEC_ACTIVE(cachep);/* fixup slab chains */if (page->active == 0) {list_add(&page->slab_list, &n->slabs_free);n->free_slabs++;} else {//添加到partial缓存列表中list_add_tail(&page->slab_list, &n->slabs_partial);}}//移动剩余的对象while (n->free_objects > n->free_limit && !list_empty(&n->slabs_free)) {n->free_objects -= cachep->num;page = list_last_entry(&n->slabs_free, struct page, slab_list);list_move(&page->slab_list, list);n->free_slabs--;n->total_slabs--;}}销毁缓存
kmem_cache_destroy函数。该函数主要在删除模块时调用,此时需要将分配的内存都释放。
参考
《深入Linux内核架构》
https://course.0voice.com/v1/course/intro?courseId=2&agentId=0
 创作打卡挑战赛
创作打卡挑战赛 ![]() 赢取流量/现金/CSDN周边激励大奖
赢取流量/现金/CSDN周边激励大奖


