剑指Offer习题整理-链表笔记
链表的习题,其实比较基础,通常画个图来理解会比较好。
🔥 链表
剑指 Offer 06. 从尾到头打印链表
class Solution {public: vector<int> reversePrint(ListNode* head) { vector<int> result; ListNode* cur = head; while(cur !=nullptr){ result.push_back(cur->val); cur = cur->next; } reverse(result.begin(),result.end()); return result; }};不用reverse
/ * Definition for singly-linked list. * struct ListNode { * int val; * ListNode *next; * ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {} * }; */class Solution {public: vector<int> reversePrint(ListNode* head) { vector<int> result; ListNode* cur = head; while(cur !=nullptr){ result.push_back(cur->val); cur = cur->next; } //reverse(result.begin(),result.end()); return vector<int>(result.rbegin(),result.rend()); }};注意:
c.rbegin() 返回一个逆序迭代器,它指向容器c的最后一个元素
剑指 Offer 24. 反转链表
定义一个函数,输入一个链表的头节点,反转该链表并输出反转后链表的头节点。
💀 … 脑子一热
居然就这样做了
执行用时:4 ms, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了91.54%的用户
内存消耗:8.3 MB, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了12.35%的用户
通过测试用例:27 / 27
/ * Definition for singly-linked list. * struct ListNode { * int val; * ListNode *next; * ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {} * }; */class Solution {public: ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) { // 第一反应 用一个容器存储 然后在这个链表上修改 vector<int> result; ListNode* cur = head; // 当链表长度为空 或者为1的时候 直接返回头结点 if(head == nullptr || head->next == nullptr) return head; while(cur!=nullptr){ result.push_back(cur->val); cur = cur->next; } ListNode* newHead = head; for(int i=result.size()-1; i>=0; i--){ newHead->val = result[i]; //cout<val<<endl; newHead = newHead->next; } return head; }};之前做的方法
class Solution {public:ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) {ListNode* new_head = nullptr;while (head){ListNode* next = head->next; //备份 head->next = new_head; // 更新new_head new_head = head;//移动new_head head = next;}return new_head;} };剑指 Offer 35. 复杂链表的复制
class Solution {public: Node* copyRandomList(Node* head) { if(head == NULL) return nullptr; // 用一个哈希表 value 是当前的链表节点 通过Key找到下个节点 unordered_map<Node*, Node*> umap; Node* p=head; // 赋值 while(p){ umap[p] = new Node(p->val); p = p->next; } // 链接 Node* temp_p = head; while(temp_p){ umap[temp_p]->next = umap[temp_p->next]; umap[temp_p]->random = umap[temp_p->random]; temp_p = temp_p->next; } return umap[head]; }};剑指 Offer 18. 删除链表的节点
class Solution {public: ListNode* deleteNode(ListNode* head, int val) { if(head == NULL || head->next ==NULL) return head; if(head->val == val){ head = head->next; return head; } //查找如果当前节点的下一个节点的值 = val 则删除 // temp->next = temp->next->next; ListNode* temp = head; while(temp->next){ if(temp->next->val == val){ temp->next = temp->next->next; return head; } else{ temp = temp->next; } } return head; }};剑指 Offer 22. 链表中倒数第k个节点
class Solution {public: ListNode* getKthFromEnd(ListNode* head, int k) { if(k<=0) return nullptr; if(head == NULL || head->next == NULL) return head; // 遍历得到链表长度 len // len-- == k 则为head = head->next的依据 int len = 0; ListNode* temp = head; while(temp){ temp = temp->next; len++; } while(len-- > k){ head = head->next; } return head; }};剑指 Offer 25. 合并两个排序的链表
创建一个result链表,
ListNode* result = new ListNode(0);
当两个链表均不为空的时候 比较大小 然后插入、移动
当其中一个链表为空的时,将不为空的链表直接插入到其中
class Solution {public: ListNode* mergeTwoLists(ListNode* l1, ListNode* l2) { ListNode *p1=l1; ListNode *p2=l2; ListNode *result=new ListNode(0); ListNode *r=result; while(p1 && p2){ if(p1->val > p2->val){ r->next=p2; r=r->next; p2=p2->next; }else{ r->next=p1; r=r->next; p1=p1->next; } } if(p1){ r->next=p1; }else if(p2){ r->next=p2; } return result->next; }};剑指 Offer 52. 两个链表的第一个公共节点
160. 相交链表
方法一 用set集合完成
https://blog.csdn.net/ETalien_/article/details/89439892
set和map的区别
将链表A 的地址信息存在集合中, 不过存的是地址
在集合中查找链表B的地址
class Solution {public:ListNode *getIntersectionNode(ListNode *headA, ListNode *headB) {std::set<ListNode*> node_set;//将链表A的地址存在集合中while (headA){node_set.insert(headA);headA=headA->next;}//在集合中查找链表B的地址while (headB){//如果找到了headBif (node_set.find(headB) != node_set.end()) {return headB;}headB = headB->next;}return NULL;}};map, set, multimap, and multiset
上述四种容器采用红黑树实现,红黑树是平衡二叉树的一种。不同操作的时间复杂度近似为:
插入: O(logN)
查看:O(logN)
删除:O(logN)
hash_map, hash_set, hash_multimap, and hash_multiset
上述四种容器采用哈希表实现,不同操作的时间复杂度为:
插入:O(1),最坏情况O(N)。
查看:O(1),最坏情况O(N)。
删除:O(1),最坏情况O(N)。
方法二双指针方法
一起走着对方走过的路
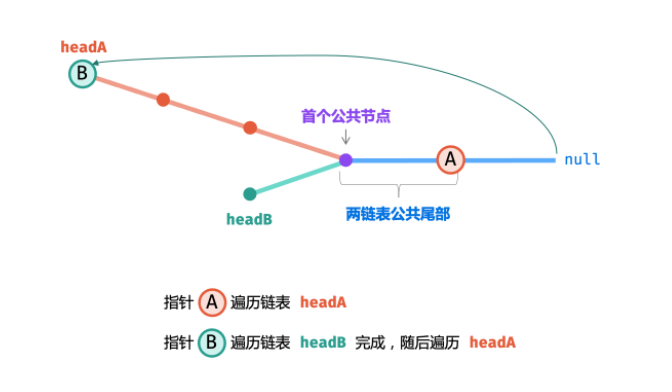
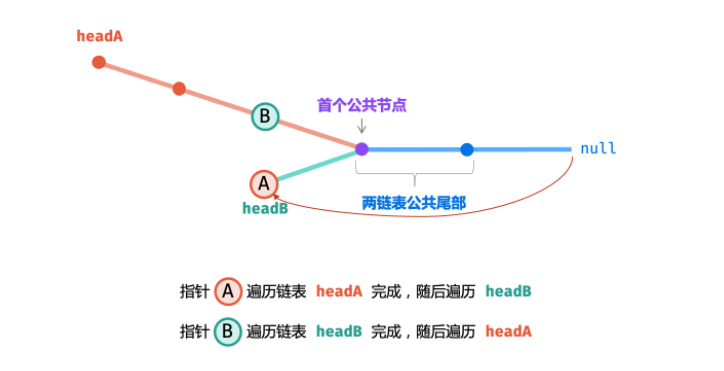
class Solution {public: ListNode *getIntersectionNode(ListNode *headA, ListNode *headB) { // 注意判断链表是否为空 if(headA == nullptr || headB == nullptr) return headA; ListNode* A = headA; ListNode* B = headB; // 注意当A,B个数为1的情况 while(A!=B){ A = A !=nullptr ? A->next : headB; B = B !=nullptr ? B->next : headA; } return A; }};时间复杂度 O(a + b) : 最差情况下(即 |a - b| = 1∣a−b∣=1 , c = 0c=0 ),此时需遍历 a+b 个节点。
空间复杂度 O(1) : 节点指针 A , B 使用常数大小的额外空间。
JZ76 删除链表中重复的结点
在一个排序的链表中删除重复节点
class Solution {public: ListNode* deleteDuplication(ListNode* pHead) { ListNode* dummy = new ListNode(-1); ListNode* tail = dummy; while(pHead !=nullptr){ if(pHead->next == nullptr || pHead->next->val != pHead->val){ tail->next = pHead; tail = pHead; } // 如果 pHead 与下一个有重复 while(pHead->next != nullptr && pHead->val == pHead->next->val) pHead = pHead->next; // 如果有相等也要跳过那个相等的数字 pHead = pHead->next; } tail->next = nullptr; return dummy->next; }};JZ23 链表中环的入口结点
/*struct ListNode { int val; struct ListNode *next; ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) { }};*/class Solution {public: ListNode* EntryNodeOfLoop(ListNode* pHead) { // 快慢指针 ListNode * fast = pHead; ListNode * slow = pHead; while(fast){ slow = slow->next; if(fast->next == nullptr) return nullptr; fast = fast->next->next; // 找到相交节点 if(fast == slow){ fast = pHead;// 快指针重新移动到头 // 直到两指针相遇位置,每次向后走一步 while(fast != slow){ fast = fast->next; slow = slow->next; } return fast; } } return nullptr; }};用哈希集合做
时间复杂度:O(n), n为链表长度,遍历一次链表的时间复杂度为O(n)
空间复杂度:O(n),哈希集合所用的空间
class Solution {public: ListNode* EntryNodeOfLoop(ListNode* pHead) { unordered_set<ListNode*> st; while(pHead){ if(st.count(pHead)) return pHead; st.insert(pHead); pHead = pHead->next; } return nullptr; }};

