数据结构:树基础
- 力扣教程
文章目录
- 一、树
-
- 1.1、什么是树
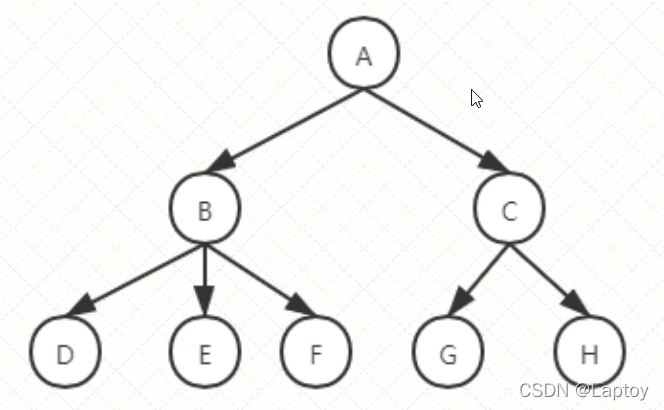
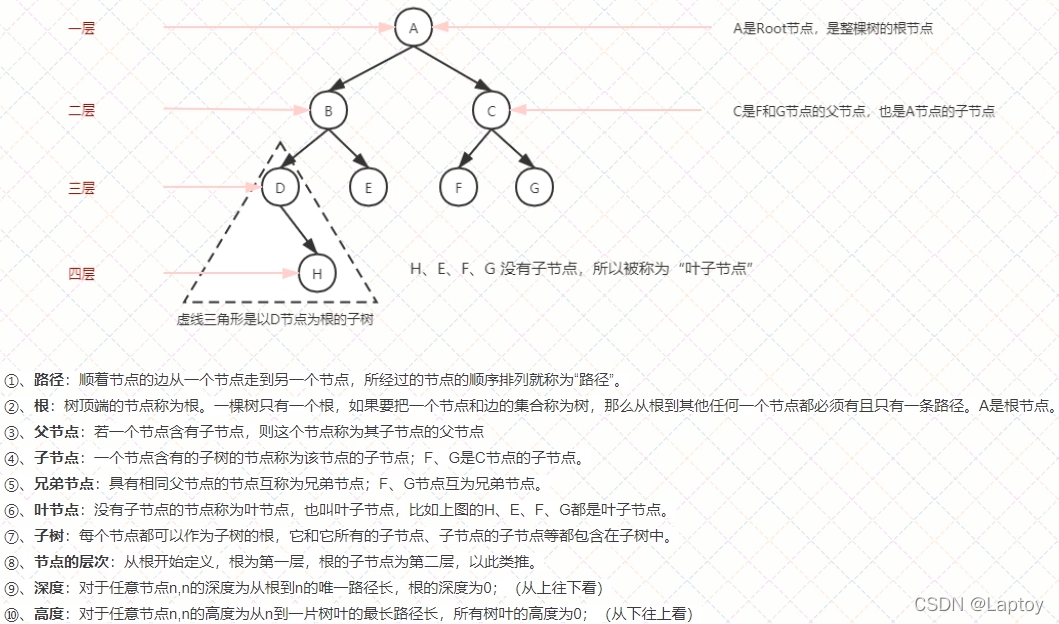
- 1.2、常用术语
- 二、二叉树概念
-
- 2.1、基本二叉树
- 2.2、满二叉树
- 2.3、完全二叉树
- 三、二叉树的遍历
-
- 3.1、遍历方式
- 3.2、递归遍历
- 3.3、迭代遍历代码演示
- 四、二叉树的查找
- 五、二叉树的删除
- 六、顺序存储二叉树
-
- 6.1、基本说明
- 6.2、实现代码
- 七、线索化二叉树
-
- 7.1、基本说明
- 7.2、图解
- 7.3、线索化实现代码
- 7.4、遍历实现代码
一、树
1.1、什么是树
树是一种抽象数据类型(ADT),用来模拟具有树状结构性质的数据集合,他是由n个有限节点通过连接它们的边组成的一个具有层次关系的集合
1.2、常用术语
二、二叉树概念
2.1、基本二叉树
每个节点最多只能有两个子节点的一种形式称为二叉树
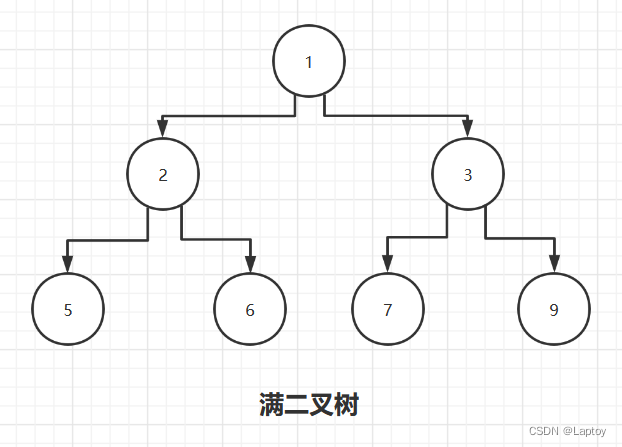
2.2、满二叉树
如果该二叉树的所有叶子节点都在最后一层,并且结点总数 = 2n -1,n为层数,则我们称为满二叉树。
2.3、完全二叉树
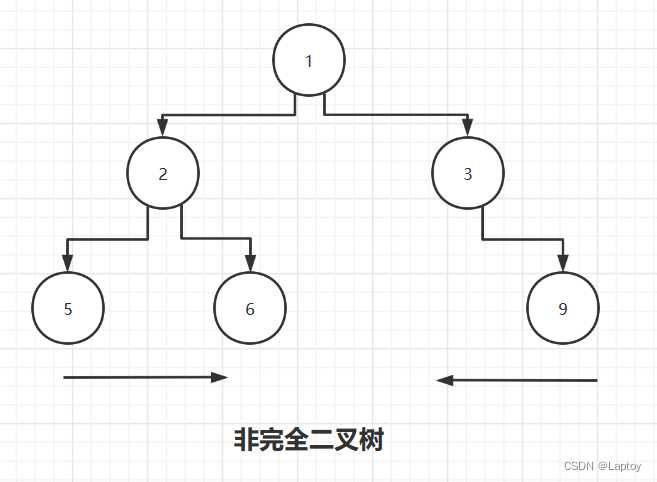
如果该二叉树的所有叶子节点都在最后一层或者倒数第二层,而且最后一层的叶子节点在左边连续,倒数第二层的叶子节点在右边连续,我们称为完全二叉树
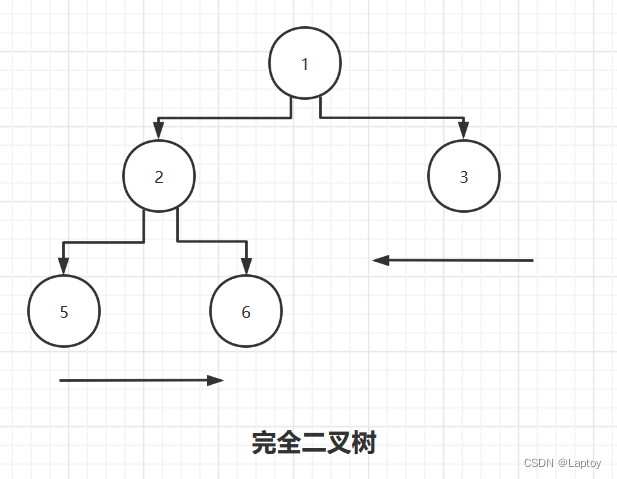

下图为非完全二叉树示例
三、二叉树的遍历
3.1、遍历方式
可以看出按照父节点的遍历时机命名,且先左再右
- 前序遍历:先遍历父节点,再遍历左子节点,最后遍历右子节点
- 中序遍历:先遍历左子节点,再遍历父节点,最后遍历右子节点
- 后序遍历:先遍历左子节点,再遍历右子节点,最后遍历父节点
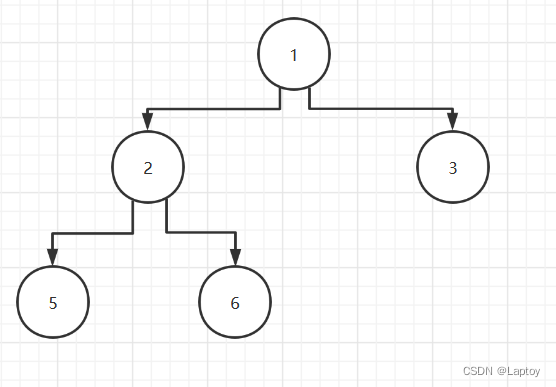
- 前序遍历结果:1、2、5、6、3
- 中序遍历结果:5、2、6、1、3
- 后序遍历结果:5、6、2、3、1
3.2、递归遍历
以该二叉树为案例进行代码演示遍历

1、定义节点类
class Node { private int id; private Node left; private Node right; public Node(int id) { this.id = id; } // 前序遍历-----》 父 左 右 public void preOrder() { // 输出父节点 System.out.println(this); // 递归向左子树前序遍历 if (this.left != null) { this.left.preOrder(); } // 递归向右子树前序遍历 if (this.right != null) { this.right.preOrder(); } } // 中序遍历-----》 左 父 右 public void infixOrder() { // 递归向左子树前序遍历 if (this.left != null) { this.left.infixOrder(); } // 输出父节点 System.out.println(this); // 递归向右子树前序遍历 if (this.right != null) { this.right.infixOrder(); } } // 后序遍历----》 左 右 父 public void suffixOrder() { // 递归向左子树前序遍历 if (this.left != null) { this.left.suffixOrder(); } // 递归向右子树前序遍历 if (this.right != null) { this.right.suffixOrder(); } // 输出父节点 System.out.println(this); } // Getter、Setter @Override public String toString() { return "Node{" + "id=" + id + '}'; }}2、定义树
// 定义树class BinaryTree { private Node root; public void setRoot(Node root) { this.root = root; } // 前序遍历 public void preOrder() { if (this.root != null) { this.root.preOrder(); } else { System.out.println("二叉树为空,无法遍历"); } } // 中序遍历 public void infixOrder() { if (this.root != null) { this.root.infixOrder(); } else { System.out.println("二叉树为空,无法遍历"); } } // 后序遍历 public void suffixOrder() { if (this.root != null) { this.root.suffixOrder(); } else { System.out.println("二叉树为空,无法遍历"); } }}3、测试前序遍历
public class Test01 { public static void main(String[] args) { BinaryTree binaryTree = new BinaryTree(); Node a = new Node(1); Node b = new Node(2); Node c = new Node(3); Node e = new Node(5); Node f = new Node(6); binaryTree.setRoot(a); a.setLeft(b); a.setRight(c); b.setLeft(e); b.setRight(f); binaryTree.preOrder(); }}- 前序遍历结果:1、2、5、6、3
- 中序遍历结果:5、2、6、1、3
- 后序遍历结果:5、6、2、3、1
3.3、迭代遍历代码演示
使用迭代对二叉树进行遍历与递归类似,不过需要自己维护一个栈用于存放节点
public class Test02 { public static void main(String[] args) { TreeNode node1 = new TreeNode(1); TreeNode node2 = new TreeNode(2); TreeNode node3 = new TreeNode(3); node1.left = node2; node1.right = node3; List<Integer> integers = preTraverse(node1); System.out.println("前序遍历结果"); for (Integer integer : integers) { System.out.print(integer); System.out.print(" "); } System.out.println(); List<Integer> integers2 = midTraverse(node1); System.out.println("中遍历结果"); for (Integer integer : integers2) { System.out.print(integer); System.out.print(" "); } System.out.println(); List<Integer> integers3 = lastTraverse(node1); System.out.println("后遍历结果"); for (Integer integer : integers3) { System.out.print(integer); System.out.print(" "); } System.out.println(); } /** * 使用迭代法对二叉树进行前序遍历 * @param root 二叉树根节点 * @return 遍历后的集合 */ public static List<Integer> preTraverse(TreeNode root) { // 用于存放结果的集合 List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>(); if (root == null) { return result; } // 栈,用于存放遍历的节点 Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>(); stack.push(root); // 遍历二叉树 while (!stack.isEmpty()) { // 栈顶元素出栈,并放入集合中 root = stack.pop(); result.add(root.val); // 先遍历右子树,将其压栈 if (root.right != null) { stack.push(root.right); } // 遍历左子树,压栈 if (root.left != null) { stack.push(root.left); } } return result; } /** * 使用迭代法对二叉树进行中序遍历 * @param root 二叉树根节点 * @return 中序遍历结果集合 */ public static List<Integer> midTraverse(TreeNode root) { List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>(); if (root == null) { return result; } Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>(); while (root != null || !stack.isEmpty()) { // 节点压栈,并遍历其左子树 while (root != null) { stack.push(root); root = root.left; } // 栈顶元素出栈,放入结果集合 root = stack.pop(); result.add(root.val); // 遍历该节点的右子树 root = root.right; } return result; } /** * 使用迭代法的后序遍历 * @param root 二叉树根节点 * @return 后序遍历集合 */ public static List<Integer> lastTraverse(TreeNode root) { List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>(); if (root == null) { return result; } Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>(); // 保存放入集合的右子树,避免重复放入 TreeNode pre = null; while (root != null || !stack.isEmpty()) { while (root != null) { stack.push(root); root = root.left; } // 获取栈顶元素 root = stack.pop(); // 如果该元素没有右子树,或者右子树已近被遍历过了,就放入集合 if (root.right == null || root.right == pre) { result.add(root.val); pre = root; root = null; } else { // 否则就继续遍历该节点的右子树 stack.push(root); root = root.right; } } return result; }}四、二叉树的查找

前、中、后序查找的思路与遍历相似,当找到对应的元素时,直接返回即可
// 节点类class Node { private int id; private Node left; private Node right; // 前序遍历查找 public Node preOrderSearch(int id) { // 判断当前节点是否匹配 if (this.id == id) { return this; } Node result = null; // 向左递归查找 if (this.left != null) { result = this.left.preOrderSearch(id); } // 如果找到直接返回 if (result != null) { return result; } // 向右递归查找 if (this.right != null) { result = this.right.preOrderSearch(id); } return result; } // 中序遍历查找 public Node infixOrderSearch(int id) { Node result = null; // 向左递归 if (this.left != null) { result = this.left.infixOrderSearch(id); } // 如果找到直接返回 if (result != null) { return result; } // 判断当前节点是否匹配 if (this.id == id) { return this; } // 向右递归 if (this.right != null) { result = this.right.infixOrderSearch(id); } return result; } // 后序遍历查找 public Node suffixOrderSearch(int id) { Node result = null; // 向左递归 if (this.left != null) { result = this.left.suffixOrderSearch(id); } if (result != null) { return result; } // 向右递归 if (this.right != null) { result = this.right.suffixOrderSearch(id); } if (result != null) { return result; } // 判断当前节点是否匹配 if (this.id == id) { return this; } return result; } // Getter、Getter @Override public String toString() { return "Node{" + "id=" + id + '}'; }} // 定义树class BinaryTree { private Node root; public void setRoot(Node root) { this.root = root; } // 前序遍历查找 public Node preOrderSearch(int id) { if (this.root != null) { return this.root.preOrderSearch(id); } else { return null; } } // 前序遍历查找 public Node infixOrderSearch(int id) { if (this.root != null) { return this.root.infixOrderSearch(id); } else { return null; } } // 前序遍历查找 public Node suffixOrderSearch(int id) { if (this.root != null) { return this.root.suffixOrderSearch(id); } else { return null; } }}public class Test01 { public static void main(String[] args) { BinaryTree binaryTree = new BinaryTree(); Node a = new Node(1); Node b = new Node(2); Node c = new Node(3); Node e = new Node(5); Node f = new Node(6); binaryTree.setRoot(a); a.setLeft(b); a.setRight(c); b.setLeft(e); b.setRight(f); Node node = binaryTree.preOrderSearch(1); System.out.println(node); }}五、二叉树的删除
1、删除要求
- 如果删除的是叶子节点,则直接删除即可
- 如果删除的是非叶子节点,则删除该子树
2、删除思路
- 因为我们的二叉树是单向的,所以我们是判断当前结点的子结点是否需要删除结点,而不能去判断当前这个结点是不是需要删除结点
- 如果当前结点的左子结点不为空,并且左子结点就是要删除结点,就将
this.left = null,并且就返回 (结束递归删除) - 如果当前结点的右子结点不为空,并且右子结点就是要删除结点,就将
this.right= null,并且就返回 (结束递归删除) - 如果第2和第3步没有删除结点,那么我们就需要向左子树进行递归删除
- 如果4步也没有删除结点,则应当向右子树进行递归删除
// 定义树class BinaryTree { private Node root; public void setRoot(Node root) { this.root = root; } // 删除 public void deleteNode(int id) { if (this.root.getId() == id) { this.root = null; System.out.println("根节点被删除"); return; } this.root.deleteNode(id); }} // 节点类class Node { private int id; private Node left; private Node right; // 删除节点 public void deleteNode(int id) { //如果左子树不为空且是要查找的节点,就删除 if (this.left != null && this.left.id == id) { this.left = null; System.out.println("删除成功"); return; } //如果右子树不为空且是要查找的节点,就删除 if (this.right != null && this.right.id == id) { this.right = null; System.out.println("删除成功"); return; } if (this.left != null) { this.left.deleteNode(id); } if (this.right != null) { this.right.deleteNode(id); } } // Getter、Getter @Override public String toString() { return "Node{" + "id=" + id + '}'; }}public class Test01 { public static void main(String[] args) { BinaryTree binaryTree = new BinaryTree(); Node a = new Node(1); Node b = new Node(2); Node c = new Node(3); Node e = new Node(5); Node f = new Node(6); binaryTree.setRoot(a); a.setLeft(b); a.setRight(c); b.setLeft(e); b.setRight(f); binaryTree.deleteNode(6); binaryTree.preOrder(); }}删除成功Node{id=1}Node{id=2}Node{id=5}Node{id=3}六、顺序存储二叉树
6.1、基本说明
从数据存储来看,数组存储方式和树的存储方式可以相互转换,即数组可以转换成树,树也可以转换成数组
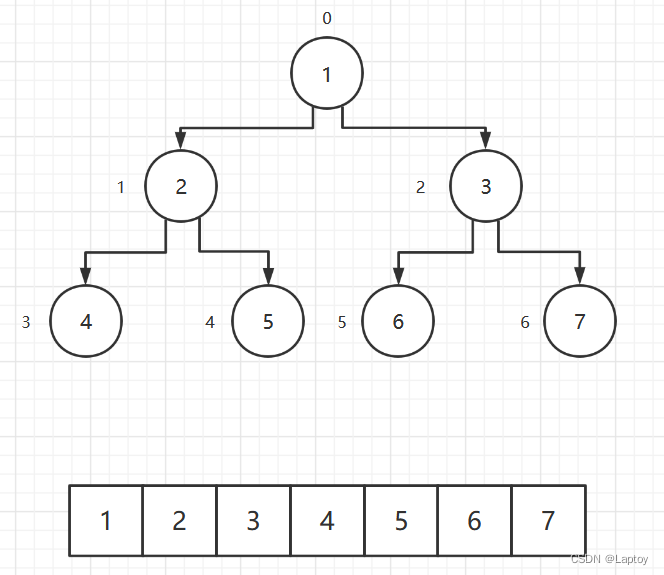
- 顺序二叉树通常只考虑完全二叉树
- 第n个元素的左子节点为
2 × n + 1 - 第n个元素的右子节点为
2 × n + 2 - 第n个元素的父节点为
(n - 1) ÷ 2
6.2、实现代码
public class Test02 { public static void main(String[] args) { int[] arr = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7}; ArrayBinaryTree arrayBinaryTree = new ArrayBinaryTree(arr); arrayBinaryTree.preOrder(); }}class ArrayBinaryTree { private int[] arr; public ArrayBinaryTree(int[] arr) { this.arr = arr; } public void preOrder(){ this.preOrder(0); } // 二叉树前序遍历 public void preOrder(int index) { if (arr == null || arr.length == 0) { System.out.println("数组为空"); return; }// 输出当前节点 System.out.print(arr[index] + " "); // 向左 int leftIndex = 2 * index + 1; if (leftIndex < arr.length) { preOrder(leftIndex); } // 向右 int rightIndex = 2 * index + 2; if (rightIndex < arr.length) { preOrder(rightIndex); } }}数组前序遍历1 2 4 5 3 6 7 七、线索化二叉树
7.1、基本说明
因为一般的二叉树,叶子节点的左右指针都为空,这样就会造成空间的浪费。为了减少浪费,便有了线索化二叉树
- n个结点的二叉链表中含有
n+1【2n-(n-1)=n+1】个空指针域 - 利用二叉链表中的空指针域,存放指向该结点在某种遍历次序下的前驱和后继结点的指针
- 这种加上了线索的二叉链表称为线索链表,相应的二叉树称为线索二叉树
- 根据线索性质的不同,线索二叉树可分为前序线索二叉树、中序线索二叉树和后序线索二叉树三种
- 如果一个节点已经有了左右孩子,那么该节点就不能被线索化了,所以线索化二叉树后,节点的left和right有如下两种情况
- left可能指向的是左孩子,也可能指向的是前驱节点
- right可能指向的是右孩子,也可能指向的是后继节点
7.2、图解
中序线索化前
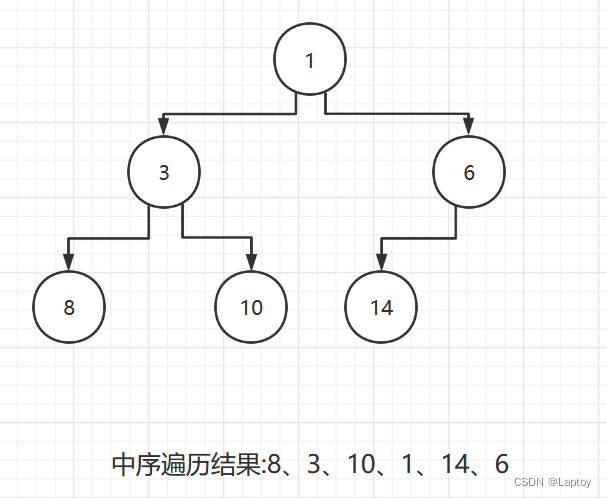
中序线索化后
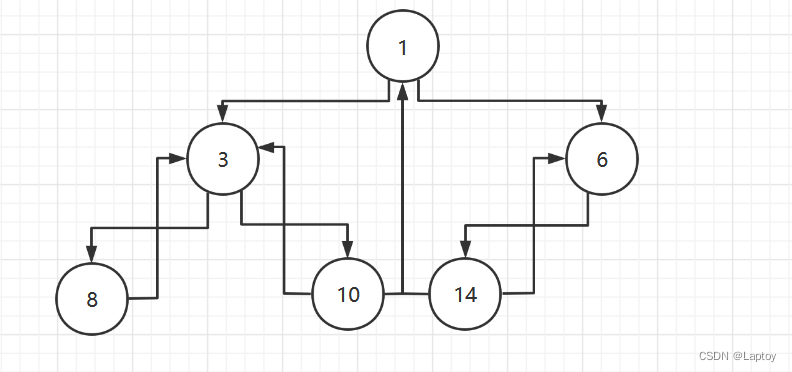
线索化思路
- 每个节点需要用两个变量来表示左右指针的类型(保存左右子树,还是前驱后继)
- 需要用两个变量来表示当前节点和当前节点的前驱节点
- 通过将当前节点的左指针指向前驱节点,来实现前驱节点的绑定
- 通过将前驱节点的右指针指向当前节点,来实现后继节点的绑定
遍历方式
- 各个节点可以通过线性的方式遍历,无需使用递归的方式遍历
- 首先有一个外循环,代替递归操作,循环条件的暂存节点不为空
- 第一个内循环用于找到第一个元素,然后打印
- 第二个循环用于找到节点的后继元素
- 最后将暂存节点令为右孩子
7.3、线索化实现代码
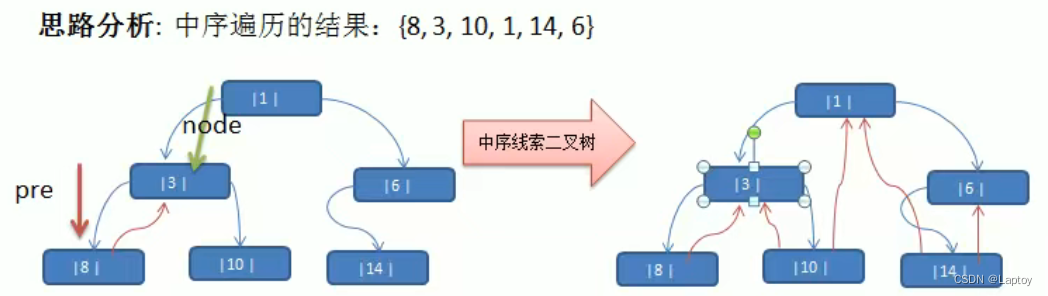
设当前节点为A,下一个处理的节点为B
定义临时节点 pre ,处理A后,让A变为B的前驱节点,以该临时节点在B处理时为A设置后继节点
1、定义方法
class ThreadedBinaryTree { private Student root; /** * 指向当前节点的前一个节点 */ private Student pre; public void setRoot(Student root) { this.root = root; } /** * 中序线索化 * * @param node 当前节点 */ private void midThreaded(Student node) { if (node == null) { return; } // 左线索化 midThreaded(node.getLeft()); // 线索化当前节点 // 如果当前节点的左指针为空,就指向前驱节点,并改变左指针类型 if (node.getLeft() == null) { node.setLeft(pre); node.setLeftType(1); } // 通过前驱节点来将右指针的值令为后继节点 if (pre != null && pre.getRight() == null) { pre.setRight(node); pre.setRightType(1); } // 处理一个节点后,让当前节点变为下一个节点的前驱节点 pre = node; // 右线索化 midThreaded(node.getRight()); } public void midThreaded() { midThreaded(root); }}class Student { private int id; private String name; private Student left; private Student right; /** * 左、右指针的类型,0-->指向的是左右孩子,1-->指向的是前驱、后续节点 */ private int leftType = 0; private int rightType = 0; public Student(int id, String name) { this.id = id; this.name = name; }// Getter、Setter @Override public String toString() { return "Student{" + "id=" + id + ", name='" + name + '\'' + '}'; }}2、测试
public class Test03 { public static void main(String[] args) { //初始化节点 Student student1 = new Student(1, "A"); Student student2 = new Student(3, "B"); Student student3 = new Student(6, "C"); Student student4 = new Student(8, "D"); Student student5 = new Student(10, "E"); Student student6 = new Student(14, "F"); //手动创建二叉树 ThreadedBinaryTree tree = new ThreadedBinaryTree(); tree.setRoot(student1); student1.setLeft(student2); student1.setRight(student3); student2.setLeft(student4); student2.setRight(student5); student3.setLeft(student6); tree.midThreaded(); //得到第五个节点的前驱节点和后继节点 System.out.println("第五个节点的前驱节点和后继节点"); System.out.println(student5.getLeft()); // 3 System.out.println(student5.getRight()); // 1 }}7.4、遍历实现代码
class ThreadedBinaryTree { private Student root; /** * 指向当前节点的前一个节点 */ private Student pre; public void setRoot(Student root) { this.root = root; } /** * 遍历线索化后的二叉树 */ public void midThreadedTraverse() { // 暂存遍历到的节点 Student tempNode = root; // 非递归的方法遍历,如果tempNode不为空就一直循环 while (tempNode != null) { // 一直访问二叉树的左子树,直到某个节点的左子树指向前驱节点 while (tempNode.getLeftType() != 1) { tempNode = tempNode.getLeft(); } // 找到了第一个节点 System.out.println(tempNode); // 再访问该节点的右子树,看是否保存了后继节点 // 如果是,则打印该节点的后继节点信息 while (tempNode.getRightType() == 1) { tempNode = tempNode.getRight(); System.out.println(tempNode); } tempNode = tempNode.getRight(); } }}