C++红黑树模拟实现map和set
C++红黑树模拟实现map和set
- 零、前言
- 一、红黑树及其节点的设计
-
- 1、树节点的设计
- 2、红黑树的设计
- 3、取值仿函数的使用
- 二、红黑树的迭代器
-
- 1、begin()与end()
- 2、operator++()与operator--()
- 3、正反迭代器的实现
- 三、map和set的实现
-
- 1、红黑树的实现
- 2、map的封装
- 3、set的封装
零、前言
本章是继红黑树的介绍和实现后,讲解使用红黑树来封装实现map和set
一、红黑树及其节点的设计
对于底层都是红黑树的map和set来说,他们之间存在的最大的区别就是:对于set是K模型的容器,而map是KV模型的容器。为了更好的灵活兼容实现map和set,就需要在红黑树以及树节点上进行特别的设计
1、树节点的设计
对于红黑树的节点我们需要节点对于set来说储存key,对于map来说储存key-value键值对,所以这里我们就直接让节点类型的阈值类型为T,用来控制储存类型
- 实现代码:
template<class T>struct RBTreeNode{RBTreeNode<T>* _left;RBTreeNode<T>* _right;RBTreeNode<T>* _parent;T _data;//T可以是key也可以是pairColour _col;RBTreeNode(const T& data):_left(nullptr), _right(nullptr), _parent(nullptr), _data(data), _col(RED){}};- 解释:
对于set实现我们传入key,对于map实现我们传入pair,由此满足set和map各自的需求
2、红黑树的设计
想要兼容map和set,我们依旧需要红黑树的模板有两个类型来控制和满足上层对下层的需求
- 实现代码:
template<class K, class T>class RBTree{ typedef RBTreeNode<T> Node;public://.......private:Node* _root;};注:这里的Node我们不想让外部直接获取使用,我们typedef在private域中
- 解释:
为了兼容set和map,对于第一个参数我们是用来比较的key类型,第二个参数是用来储存数据的类型
这里我们对红黑树第二个模板参数进行灵活传参,可能是键值key,也可能是pair
对于set传入底层红黑树的模板参数就是key和key;对于map传入底层红黑树的模板参数就是key和pair
注:对于set来说第二个参数有点多余,但是对于map来说,因为map的接口当中有些是只要求给出键值key用来比较的(如find()和erase()),如果只有一个参数传入pair类型,但是只能得到第一个key类型的值,无法获得key的类型(不能实现模板函数)
3、取值仿函数的使用
我们在设计树节点之后达到了对于不同容器存入不同类型的效果,但是真实在实现时在插入或者删除时,我们需要要拿出节点中储存类型的数据进行比较
- 分析:
对于set的T本身就是键值key,直接用T进行比较即可,但是对于map的储存类型是pair我们需要取出pair的first(key值)进行比较
这两种的都是取值比较,但是需要的行为是不一样的,由此我们还需要一个仿函数用来灵活取值比较
对于不同容器我们需要不同的仿函数类型,由此在红黑树的模板列表中还需要一个模板类型参数,灵活控制传入的仿函数类型
注:仿函数,就是使一个类的使用看上去像一个函数,其实现就是类中实现一个operator(),这个类就有了类似函数的行为,就是一个仿函数类了
- 红黑树框架:
template<class K, class T, class KeyOfT>class RBTree{ typedef RBTreeNode<T> Node;public://...private:Node* _root;};- map实现框架:
namespace cole{template<class K, class V>class map{struct MapOfKey{const K& operator()(const pair<K, V>& kv){return kv.first;}};public://...private:RBTree<K, pair<const K, V>, MapOfKey> _t;};}- set实现框架:
namespace cole{template<class K>class set{struct SetOfKey{const K& operator()(const K& key){return key;}};public://...private:RBTree<K, K, SetOfKey> _t;};}- 仿函数使用示例:
Node* Find(const K& key){ KeyOfT kot; Node* cur = _root; while (cur) { if (kot(cur->_kv.first) > key) { cur = cur->_left; } else if (kot(cur->_kv.first) < key) { cur = cur->_right; } else { return cur; } } return nullptr;}二、红黑树的迭代器
迭代器本质上是指针的一个封装的类,其底层就是指针;好处是可以方便遍历,是数据结构的底层实现与用户透明
对于string,vector,list等容器,其本身的结构上是比较简单的,迭代器的实现也很简单;但是对于二叉树结构的红黑树来说需要考虑很多的问题
1、begin()与end()
STL明确规定:begin()与end()代表的是一段前闭后开的区间
对红黑树进行中序遍历后,可以得到一个有序的序列,因此begin()可以放在红黑树中最小节点(即最左侧节点)的位置,end()放在最大节点(最右侧节点)的下一个位置即nullptr
- 示图:
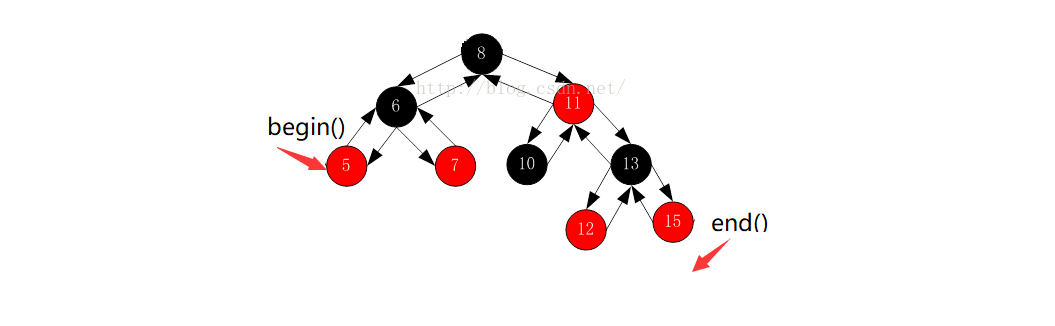
2、operator++()与operator–()
找到begin()和end()之后,要遍历红黑树最主要的还是能找到要遍历的下一个节点
红黑树的中序遍历是有序的,也就是说:当一个结点的正向迭代器进行++操作后,应该根据红黑树中序遍历的序列找到当前结点的下一个结点
- 实现++逻辑:
对于中遍历到当前节点来说,该节点的左子树应该是已经被遍历过了,所以只需要考虑右子树
如果当前结点的右子树不为空,则++操作后应该找到其右子树当中的最左结点
如果当前结点的右子树为空,则该子树已经被遍历完了,则++操作后应该在该结点的祖先结点中找到孩子不在父亲右的祖先
- 说明:
如果是孩子节点在父亲的左,说明父亲的右节点没有遍历
如果孩子在父亲的右,说明以父亲节点为根的子树已经遍历完了,还需要继续向上找
如果一直向上遍历到nullptr说明整颗树已经遍历完了(end()返回的就是nullptr)
注:怎么看该节点的右节点遍历过没有,这里需要一个指针记录上一次经过的节点地址,进行比较地址就行了
- 实现++代码:
Self& operator++(){ if (_node->_right)//右子节点存在 { //找到右子树中最左节点 Node* cur = _node->_right; while (cur->_left) { cur = cur->_left; } _node = cur; } else//右子节点不存在,向上找 { Node* cur = _node;//记录走过的节点 Node* parent = _node->_parent; while (parent && parent->_right == cur) { cur = parent; parent = parent->_parent; } _node = parent; } return *this;}注:对于–来说可以参考++的实现,逻辑是完全相反的
- 实现–代码:
Self& operator--(){ if (_node->_left)//左子节点存在 { //找左子树中的最右节点 Node* cur = _node->_left; while (cur->_right) { cur = cur->_right; } _node = cur; } else//左子节点不存在 { Node* cur = _node; Node* parent = _node->_parent; while (parent && parent->_left == cur) { cur = parent; parent = parent->_parent; } _node = parent; } return *this;}3、正反迭代器的实现
对于正向迭代器与反向迭代器的区别就是:begin()指向的位置不一样;迭代器的++和–的实现相反,但本质上还是差不多的
所以实现正向迭代器后,我们可以直接使用适配器,在正向迭代器的基础上,对其接口进行封装达到反向迭代器的效果
- 正向迭代器实现代码:
template<class T, class Ref, class Ptr>struct _TreeIterator{ //声明类型,便于反向迭代器对类型的提取typedef Ref reference;typedef Ptr pointer;typedef RBTreeNode<T> Node;typedef _TreeIterator<T, Ref, Ptr> Self;Node* _node;_TreeIterator(Node* node):_node(node){}Ref operator*(){return _node->_data;}Ptr operator->(){return &_node->_data;}bool operator==(const Self& it)const{return _node == it._node;}bool operator!= (const Self& it)const{return _node != it._node;}Self& operator++(){if (_node->_right){Node* cur = _node->_right;while (cur->_left){cur = cur->_left;}_node = cur;}else{Node* cur = _node;Node* parent = _node->_parent;while (parent && parent->_right == cur){cur = parent;parent = parent->_parent;}_node = parent;}return *this;}Self& operator--(){if (_node->_left){Node* cur = _node->_left;while (cur->_right){cur = cur->_right;}_node = cur;}else{Node* cur = _node;Node* parent = _node->_parent;while (parent && parent->_left == cur){cur = parent;parent = parent->_parent;}_node = parent;}return *this;}};- 反向迭代器实现代码:
//适配器构造反向迭代器template<class Iterator>struct ReverseIterator{//类型未实例化,无法取出里面的类型,此时需要使用typename:告诉编译器等实例化后再到类里面找对应的类型typedef typename Iterator::reference Ref;typedef typename Iterator::pointer Ptr;typedef ReverseIterator<Iterator> Self;Iterator _it;ReverseIterator(Iterator it):_it(it){} //在正向迭代器接口上进行封装复用 Ref operator*(){return *_it;}Ptr operator->(){return _it.operator->();}bool operator==(const Self& it)const{return it._it==_it;}bool operator!= (const Self& it)const//两个const{return _it != it._it;}Self& operator++(){--_it;return *this;}Self& operator--(){++_it;return *this;}};三、map和set的实现
1、红黑树的实现
- 具体实现代码:
//颜色enum Colour{RED,BLACK,};template<class T>struct RBTreeNode{RBTreeNode<T>* _left;RBTreeNode<T>* _right;RBTreeNode<T>* _parent;T _data;//T可以是key也可以是pairColour _col;RBTreeNode(const T& data):_left(nullptr), _right(nullptr), _parent(nullptr), _data(data), _col(RED){}};template<class K, class T, class KeyOfT>class RBTree{typedef RBTreeNode<T> Node;public:typedef _TreeIterator<T, T&, T*> iterator;typedef _TreeIterator<T,const T&, const T*> const_iterator;typedef ReverseIterator<iterator> reverse_iterator;typedef ReverseIterator<const_iterator> reverse_const_iterator;RBTree():_root(nullptr){}~RBTree(){_Destory(_root);}iterator begin(){Node* cur = _root;while (cur&&cur->_left){cur = cur->_left;}return iterator(cur);}reverse_iterator rbegin(){Node* cur = _root;while (cur&&cur->_right){cur = cur->_right;}return reverse_iterator(iterator(cur));}reverse_iterator rend(){return reverse_iterator(iterator(nullptr));}iterator end(){return iterator(nullptr);}Node* Find(const K& key){KeyOfT kot;Node* cur = _root;while (cur){if (kot(cur->_kv.first) > key){cur = cur->_left;}else if (kot(cur->_kv.first) < key){cur = cur->_right;}else{return cur;}}return nullptr;}pair<iterator, bool> Insert(const T& data){//空树的情况if (_root == nullptr){_root = new Node(data);_root->_col = BLACK;return make_pair(iterator(_root), true);}KeyOfT kot;//查找位置插入节点Node* cur = _root, * parent = _root;while (cur){if (kot(cur->_data) > kot(data)){parent = cur;cur = cur->_left;}else if (kot(cur->_data) < kot(data)){parent = cur;cur = cur->_right;}else{return make_pair(iterator(cur), false);}}//创建链接节点cur = new Node(data);Node* newnode = cur;if (kot(parent->_data) > kot(data)){parent->_left = cur;}else{parent->_right = cur;}cur->_parent = parent;//父节点存在且为红,则需要调整(不能存在连续的红色节点)while (parent && parent->_col == RED){//此时当前节点一定有祖父节点Node* granparent = parent->_parent;//具体调整情况主要看叔叔节点//分左右讨论if (parent == granparent->_left){Node* uncle = granparent->_right;//情况1:叔叔节点存在且为红if (uncle && uncle->_col == RED){//修改颜色,继续向上检查granparent->_col = RED;parent->_col = uncle->_col = BLACK;cur = granparent;parent = cur->_parent;}else//情况2和3:叔叔节点不存在 或者存在且为黑{//单旋(三代节点为斜线)+变色if (cur == parent->_left){RotateR(granparent);granparent->_col = RED;parent->_col = BLACK;}else//双旋(三代节点为折线)+变色{RotateL(parent);RotateR(granparent);cur->_col = BLACK;granparent->_col = RED;}//旋转后不需再向上调整了break;}}else//parent=grandparent->right{Node* uncle = granparent->_left;if (uncle && uncle->_col == RED){parent->_col = uncle->_col = BLACK;granparent->_col = RED;cur = granparent;parent = cur->_parent;}else{if (cur == parent->_right){RotateL(granparent);parent->_col = BLACK;granparent->_col = RED;}else{RotateR(parent);RotateL(granparent);cur->_col = BLACK;granparent->_col = RED;}break;}}}//确保根节点为黑_root->_col = BLACK;return make_pair(iterator(newnode), true);}bool IsRBTree(){if (_root == nullptr){return true;}if (_root->_col == RED){cout << "根节点为红色" << endl;return false;}int Blacknum = 0;Node* cur = _root;while (cur){if (cur->_col == BLACK)Blacknum++;cur = cur->_left;}int i = 0;return _IsRBTree(_root, Blacknum, i);}private: void _Destory(Node*& root){if (root == nullptr)return;_Destory(root->_left);_Destory(root->_right);delete root;root = nullptr;} bool _IsRBTree(Node* root, int blacknum, int count){if (root == nullptr){if (blacknum == count)return true;cout << "各路径上黑色节点个数不同" << endl;return false;}if (root->_col == RED && root->_parent->_col == RED){cout << "存在连续红色节点" << endl;return false;}if (root->_col == BLACK)count++;return _IsRBTree(root->_left, blacknum, count) && _IsRBTree(root->_right, blacknum, count);}void RotateL(Node* parent){Node* subR = parent->_right;Node* subRL = subR->_left;Node* parentP = parent->_parent;parent->_right = subRL;if (subRL){subRL->_parent = parent;}subR->_left = parent;parent->_parent = subR;if (parent == _root){_root = subR;subR->_parent = nullptr;}else{subR->_parent = parentP;if (parentP->_left == parent){parentP->_left = subR;}else{parentP->_right = subR;}}}void RotateR(Node* parent){Node* subL = parent->_left;Node* subLR = subL->_right;Node* parentP = parent->_parent;parent->_left = subLR;if (subLR){subLR->_parent = parent;}subL->_right = parent;parent->_parent = subL;if (parent == _root){_root = subL;subL->_parent = nullptr;}else{subL->_parent = parentP;if (parentP->_left == parent){parentP->_left = subL;}else{parentP->_right = subL;}}}private:Node* _root;};2、map的封装
- 具体实现代码:
namespace cole{template<class K, class V>class map{struct MapOfKey{const K& operator()(const pair<K, V>& kv){return kv.first;}};public:typedef typename RBTree<K, pair<const K, V>, MapOfKey>::iterator iterator;typedef typename RBTree<K, pair<const K, V>, MapOfKey>::reverse_iterator reverse_iterator;iterator begin(){return _t.begin();}iterator end(){return _t.end();}reverse_iterator rbegin(){return _t.rbegin();}reverse_iterator rend(){return _t.rend();}pair<iterator, bool> insert(const pair<const K, V>& kv){return _t.Insert(kv);}V& operator[](const K& key){pair<iterator, bool> ret = insert(make_pair(key, V()));return ret.first->second;}iterator find(const K& key){return _t.Find(key);}private:RBTree<K, pair<const K, V>, MapOfKey> _t;};}3、set的封装
- 具体实现代码:
namespace cole{template<class K>class set{struct SetOfKey{const K& operator()(const K& key){return key;}};public:typedef typename RBTree<K,K, SetOfKey>::iterator iterator;typedef typename RBTree<K,K, SetOfKey>::reverse_iterator reverse_iterator;iterator begin(){return _t.begin();}iterator end(){return _t.end();}reverse_iterator rbegin(){return _t.rbegin();}reverse_iterator rend(){return _t.rend();}pair<iterator, bool> insert(const K& key){return _t.Insert(key);}iterator find(const K& key){return _t.Find(key);}private:RBTree<K, K, SetOfKey> _t;};}

