【图解】ThreadLocal底层实现原理
1、ThreadLocal的底层原理图
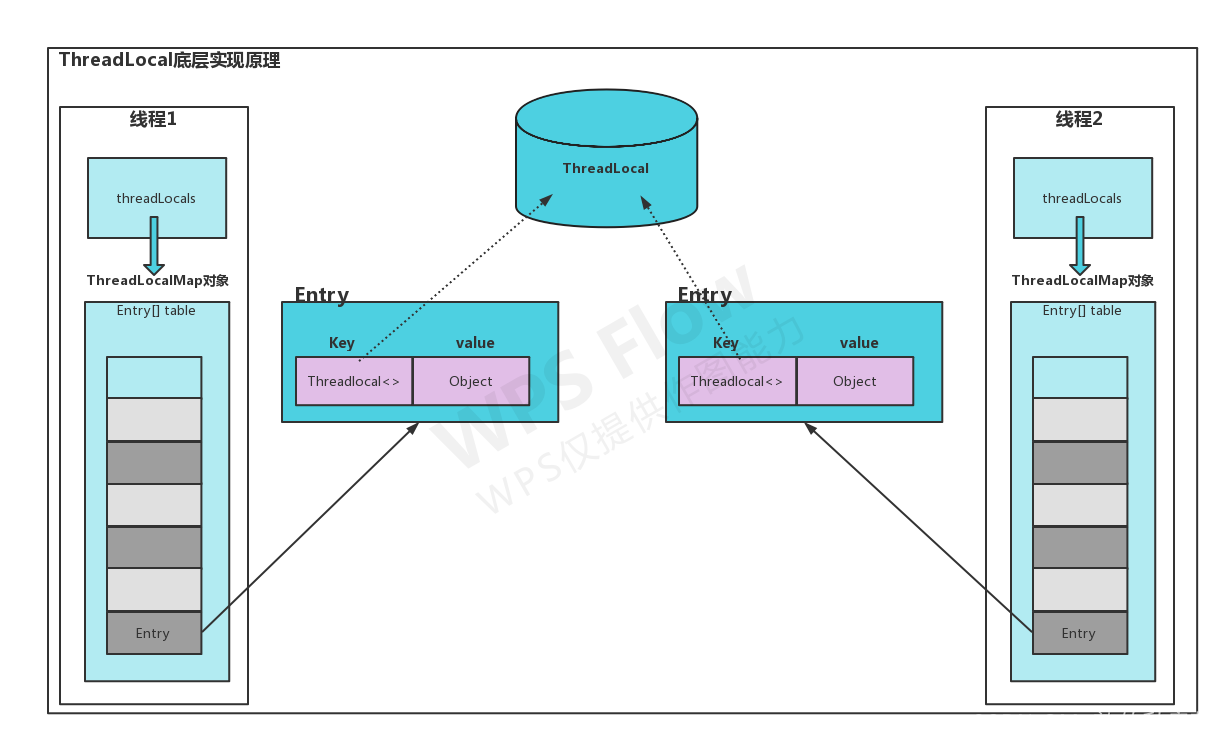
说明:Thread中有threadLocals成员变量,threadLocal会在threadlocal首次set时进行赋值【这会在非main线程中复现,主线程启动即会进行赋值】,ThreadLocalMap是ThreadLocal的静态内部类,在set时,会将我们新建threadLocal引用地址作为key,以此封装成一个Entry<ThreadLocal,Object>对象,可以存在多个不同的threadlocal,如果set的引用地址相同,就会进行覆盖,此处key的类型ThreadLocal继承弱引用也是会造成内存泄露的主要原因,在下面源码中会对此段相关点分别说明。
2.源码解析
package com.adun.test_threadlocal;/ * @author ADun * @date 2022/4/27 11:14 */public class ThreadLocalTest { public static final ThreadLocal<Integer> threadLocal = new ThreadLocal(); public static final ThreadLocal<Integer> threadLocal2 = new ThreadLocal(); public static void main(String[] args) { threadLocal.set(1234); Integer num1 = threadLocal.get(); System.out.println(num1); Integer num2 = threadLocal.get(); System.out.println(num2); threadLocal2.set(111); System.out.println(threadLocal2.get());//最后必须remove,避免内存泄露threadLocal.remove(); threadLocal2.remove(); }}ThreadLocal中的set方法以及涉及到的相关方法
public void set(T value) { Thread t = Thread.currentThread(); //获取当前线程的threadLocals ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t); if (map != null) map.set(this, value); else //如果获取不到当前线程的threadlocals成员变量,则新建并将value放入 createMap(t, value); } / * 获取当前线程的threadlocals * Get the map associated with a ThreadLocal. Overridden in * InheritableThreadLocal. * * @param t the current thread * @return the map */ ThreadLocalMap getMap(Thread t) { return t.threadLocals; }/ * 创建ThreadLocalMap,并对当前线程的threadlocals进行赋值 * Create the map associated with a ThreadLocal. Overridden in * InheritableThreadLocal. * * @param t the current thread * @param firstValue value for the initial entry of the map */ void createMap(Thread t, T firstValue) { t.threadLocals = new ThreadLocalMap(this, firstValue); }ThreadLocal静态内部类ThreadLocalMap
/ * 初始化ThreadLocalMap的构造器 * Construct a new map initially containing (firstKey, firstValue). * ThreadLocalMaps are constructed lazily, so we only create * one when we have at least one entry to put in it. */ ThreadLocalMap(ThreadLocal<?> firstKey, Object firstValue) { table = new Entry[INITIAL_CAPACITY]; int i = firstKey.threadLocalHashCode & (INITIAL_CAPACITY - 1); table[i] = new Entry(firstKey, firstValue); size = 1; setThreshold(INITIAL_CAPACITY); }/ * 玩当前线程的threadlocals对应的threadLocalMap中赋值 * 用户new的threadlocal的引用地址作为key,value作为value进行赋值构建Entry对象,如果已存在,则进行覆盖* Set the value associated with key. @param key the thread local object* @param value the value to be set*/ private void set(ThreadLocal<?> key, Object value) { // We don't use a fast path as with get() because it is at // least as common to use set() to create new entries as // it is to replace existing ones, in which case, a fast // path would fail more often than not. //Entry<ThreadLocal,Object>数组,存放多个threadlocal的数据 Entry[] tab = table; int len = tab.length; int i = key.threadLocalHashCode & (len-1); for (Entry e = tab[i]; e != null; e = tab[i = nextIndex(i, len)]) {ThreadLocal<?> k = e.get();if (k == key) { e.value = value; return;}if (k == null) { replaceStaleEntry(key, value, i); return;} } tab[i] = new Entry(key, value); int sz = ++size; if (!cleanSomeSlots(i, sz) && sz >= threshold)rehash(); }ThreadLocalMap内部类Entry
/ * The entries in this hash map extend WeakReference, using * its main ref field as the key (which is always a * ThreadLocal object). Note that null keys (i.e. entry.get() * == null) mean that the key is no longer referenced, so the * entry can be expunged from table. Such entries are referred to * as "stale entries" in the code that follows. */ static class Entry extends WeakReference<ThreadLocal<?>> { / The value associated with this ThreadLocal. */ Object value;//Entry继承弱引用,弱引用的特点是在jvm进行gc扫描中直接进行回收//这种操作既有可能k的引用被回收,而v的值失去所有到达的引用,造成内存泄露,所以在最后必须remove Entry(ThreadLocal<?> k, Object v) { super(k); value = v; } }

