redis7.0源码阅读(三):哈希表扩容、缩容以及rehash
redis7.0源码阅读(三):哈希表扩容、缩容以及rehash
- 一、哈希冲突
- 二、哈希表扩容
-
- 1.定位到相应的代码部分
- 2.扩容条件
-
- 写时复制(copy on write):fork持久化
- 3.扩容大小
- 三、哈希表缩容(resize)
-
- 1.缩容的条件 `htNeedsResize`
- 2.如何缩容 `dictResize`
- 3.什么时候需要缩容呢? `databasesCron`
- 四、rehash
-
- 1.为什么需要rehash?
- 2.`dictRehash`
- 3.渐进式rehash
- 4.定时任务触发rehash
- 5.rehash未完成的时候如何去查找数据呢
- 6.rehash结束后要做的事情
- 五、总结:哈希扩容和rehash
参考链接
一、哈希冲突
当哈希值相同的时候会发生哈希冲突,可以通过拉链法,将将他们通过链表连接起来,链式哈希会产生一个问题,随着哈希表数据越来越多,哈希冲突越来越多,单个哈希桶链表上数据越来越多,查找时间复杂度退化到 O(n),查找耗时增加,效率降低
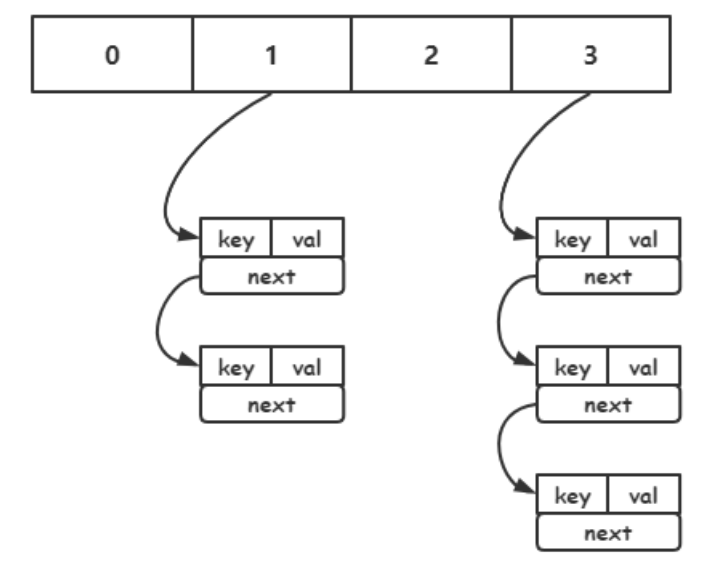
可以通过负载因子(used/size)来表述哈希冲突的激烈程度,负载因子越大,冲突越激烈。
size表示哈希表的大小,也就是哈希桶的个数
used表示有多少个 键值对实体(dictEntry),used越多,哈希冲突的情况越多
因此在必要时对哈希表进行扩容,将新添加的键值对,放入新的哈希桶,从而减少哈希冲突的情况
二、哈希表扩容
1.定位到相应的代码部分
首先要,找到对应代码,在setCommand中主要是设置string,在这里面可以找到。
_dictKeyIndex是为了获取要添加dict的索引位置,会出现扩容的情况
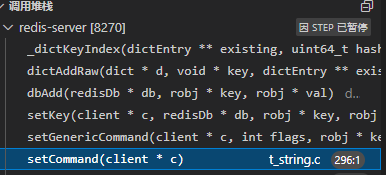
里面有_dictExpandIfNeeded这个函数,进行扩容判断和扩容
2.扩容条件
_dictExpandIfNeeded中判断扩容可分为3个情况
情况1:
在rehash的时候,是不能扩容的
情况2:
如果第一张哈希表的大小是0,就根据初始值DICT_HT_INITIAL_SIZE(默认为4)给它扩容
情况3:
条件1:负载因子大于1(d->ht_used[0] >= DICTHT_SIZE(d->ht_size_exp[0]))
条件2:允许扩容dict_can_resize或者负载因子大于指定阈值dict_force_resize_ratio(默认为5)
当两条件都满足,才会进行扩容
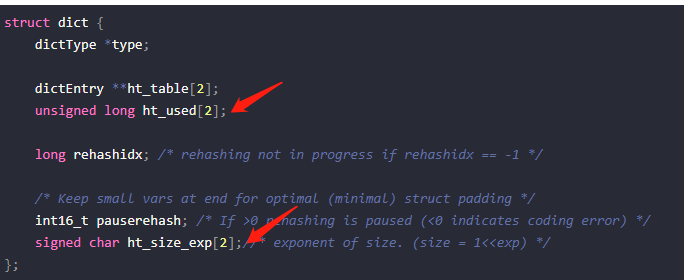
static int _dictExpandIfNeeded(dict *d){ /* Incremental rehashing already in progress. Return. */ if (dictIsRehashing(d)) return DICT_OK; /* If the hash table is empty expand it to the initial size. */ if (DICTHT_SIZE(d->ht_size_exp[0]) == 0) return dictExpand(d, DICT_HT_INITIAL_SIZE); /* If we reached the 1:1 ratio, and we are allowed to resize the hash * table (global setting) or we should avoid it but the ratio between * elements/buckets is over the "safe" threshold, we resize doubling * the number of buckets. */ if (d->ht_used[0] >= DICTHT_SIZE(d->ht_size_exp[0]) && (dict_can_resize || d->ht_used[0]/ DICTHT_SIZE(d->ht_size_exp[0]) > dict_force_resize_ratio) && dictTypeExpandAllowed(d)) { return dictExpand(d, d->ht_used[0] + 1); } return DICT_OK;}上述条件2中可以看到dict_can_resize,那什么时候会修改dict_can_resize呢?
void dictEnableResize(void) { dict_can_resize = 1;}void dictDisableResize(void) { dict_can_resize = 0;}如果有子进程的情况下,dict_can_resize = 0
没有子进程的情况下,dict_can_resize = 1
/* This function is called once a background process of some kind terminates, * as we want to avoid resizing the hash tables when there is a child in order * to play well with copy-on-write (otherwise when a resize happens lots of * memory pages are copied). The goal of this function is to update the ability * for dict.c to resize the hash tables accordingly to the fact we have an * active fork child running. */void updateDictResizePolicy(void) { if (!hasActiveChildProcess()) dictEnableResize(); else dictDisableResize();}为什么会fork子进程?redis有4种持久化方案,其中3种都是通过fork来进行持久化。
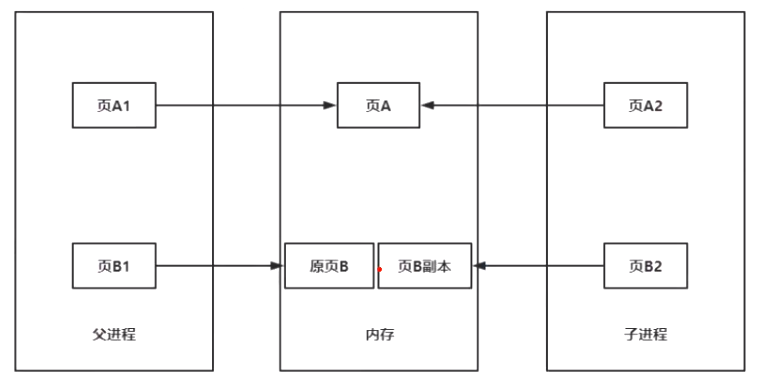
写时复制(copy on write):fork持久化
父进程由于执行命令对页B1进行修改,指向内存中的原页B。子进程会指向页B副本(对原页B进行拷贝),来保证持久化。
3.扩容大小
通过<<左移位运算保证是2的n次幂,扩容到大于dictEntry的数量used为止。
注意下面的size并不是哈希桶的数量,而是d->ht_used[0] + 1,也就是dict的数量
比如:哈希表(数组)长度为4,但是里面有9个哈希键值对(dictEntry),那么应扩容到16(比9大的最小2的n次幂)
static signed char _dictNextExp(unsigned long size){ unsigned char e = DICT_HT_INITIAL_EXP; if (size >= LONG_MAX) return (8*sizeof(long)-1); while(1) { if (((unsigned long)1<<e) >= size) return e; e++; }}三、哈希表缩容(resize)
在tryResizeHashTables中通过htNeedsResize判断受否需要缩容,需要的话就重新调整大小(缩容)dictResize
void tryResizeHashTables(int dbid) { if (htNeedsResize(server.db[dbid].dict)) dictResize(server.db[dbid].dict); if (htNeedsResize(server.db[dbid].expires)) dictResize(server.db[dbid].expires);}1.缩容的条件 htNeedsResize
负载因子(used/size)小于0.1就会进行缩容,默认HASHTABLE_MIN_FILL=10,把100移过来就是0.1
比如哈希表size大小是32,那么实际used数量为3的时候,3/32<0.1那么会进行缩容
int htNeedsResize(dict *dict) { long long size, used; size = dictSlots(dict); used = dictSize(dict); return (size > DICT_HT_INITIAL_SIZE && (used*100/size < HASHTABLE_MIN_FILL));}2.如何缩容 dictResize
int dictResize(dict *d){ unsigned long minimal; if (!dict_can_resize || dictIsRehashing(d)) return DICT_ERR; minimal = d->ht_used[0]; if (minimal < DICT_HT_INITIAL_SIZE) minimal = DICT_HT_INITIAL_SIZE; return dictExpand(d, minimal);}3.什么时候需要缩容呢? databasesCron
Cron表示定时检查的意思
!hasActiveChildProcess()在没有子进程的时候,会尝试缩容(resize)
void databasesCron(void) { /* Expire keys by random sampling. Not required for slaves * as master will synthesize DELs for us. */ if (server.active_expire_enabled) { if (iAmMaster()) { activeExpireCycle(ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_SLOW); } else { expireSlaveKeys(); } } /* Defrag keys gradually. */ activeDefragCycle(); /* Perform hash tables rehashing if needed, but only if there are no * other processes saving the DB on disk. Otherwise rehashing is bad * as will cause a lot of copy-on-write of memory pages. */ if (!hasActiveChildProcess()) {//没有子进程的时候才会进行缩容 /* We use global counters so if we stop the computation at a given * DB we'll be able to start from the successive in the next * cron loop iteration. */ static unsigned int resize_db = 0; static unsigned int rehash_db = 0; int dbs_per_call = CRON_DBS_PER_CALL; int j; /* Don't test more DBs than we have. */ if (dbs_per_call > server.dbnum) dbs_per_call = server.dbnum; /* Resize */ for (j = 0; j < dbs_per_call; j++) { tryResizeHashTables(resize_db % server.dbnum); resize_db++; } /* Rehash */ if (server.activerehashing) { for (j = 0; j < dbs_per_call; j++) { int work_done = incrementallyRehash(rehash_db); if (work_done) { /* If the function did some work, stop here, we'll do* more at the next cron loop. */ break; } else { /* If this db didn't need rehash, we'll try the next one. */ rehash_db++; rehash_db %= server.dbnum; } } } }}四、rehash
1.为什么需要rehash?
链式哈希会产生一个问题,随着哈希表数据越来越多,哈希冲突越来越多,单个哈希桶链表上数据越来越多,查找时间复杂度退化到 O(n)。
因此redis 会对哈希表做 rehash 操作。rehash 也就是增加现有的哈希桶数量,让逐渐增多的 entry 元素能在更多的桶之间分散保存,减少单个桶中的元素数量,从而减少单个桶中的冲突
2.dictRehash
n就是移动的哈希桶是数量(从哈希表1移动到哈希表2),也就是哈希表(数组)移动槽位
int dictRehash(dict *d, int n) { int empty_visits = n*10; /* Max number of empty buckets to visit. */ //最多访问n*10个空桶,否则会阻塞过长时间 if (!dictIsRehashing(d)) return 0; while(n-- && d->ht_used[0] != 0) { dictEntry *de, *nextde; /* Note that rehashidx can't overflow as we are sure there are more * elements because ht[0].used != 0 */ assert(DICTHT_SIZE(d->ht_size_exp[0]) > (unsigned long)d->rehashidx); while(d->ht_table[0][d->rehashidx] == NULL) { d->rehashidx++; if (--empty_visits == 0) return 1; } de = d->ht_table[0][d->rehashidx];//要移动的哈希桶 /* Move all the keys in this bucket from the old to the new hash HT */ while(de) {//遍历ht0中哈希桶中每个k-v对,都进行重新哈希 uint64_t h; nextde = de->next; /* Get the index in the new hash table */ h = dictHashKey(d, de->key) & DICTHT_SIZE_MASK(d->ht_size_exp[1]); de->next = d->ht_table[1][h];//如果一个哈希桶有多个元素就将dict接入哈希桶的头部 d->ht_table[1][h] = de; d->ht_used[0]--; d->ht_used[1]++; de = nextde; } d->ht_table[0][d->rehashidx] = NULL;//删除哈希桶 d->rehashidx++; } /* Check if we already rehashed the whole table... */ if (d->ht_used[0] == 0) { zfree(d->ht_table[0]); /* Copy the new ht onto the old one */ d->ht_table[0] = d->ht_table[1]; d->ht_used[0] = d->ht_used[1]; d->ht_size_exp[0] = d->ht_size_exp[1]; _dictReset(d, 1); d->rehashidx = -1; return 0; } /* More to rehash... */ return 1;}设置了empty_visits,最多访问n*10个空桶,否则会阻塞过长时间
移动过来的dictEntry都是往哈希桶的链表头部插入的
关键部分:
一般情况下, h=hash(key)%size,也就是根据哈希值取余,来确定存放在哪个哈希桶位置上。
由于新的哈希表size都是2的n次幂,因此可以优化成h=hash(key)&(size-1)(位运算速度更快)
rehash的时候,将哈希表1中的一个桶的每个键值对dictEntry都通过这种方式,放到哈希表2指定的哈希桶下面。
h = dictHashKey(d, de->key) & DICTHT_SIZE_MASK(d->ht_size_exp[1]);3.渐进式rehash
如果服务器一口气,将第一个hashtable移动到第二个hashtable上,就会出现等待响应的时间过长,因此可以将一个大的任务拆分成一个个小的任务,一步一步挪,对一个哈希桶(同一个哈希桶中多个元素用一个链表保存)进行挪到第二个哈希table去,也就是每次只挪哈希表中的一个槽位(哈希桶)。
可以看到dictRehash(d,1),参数1就是挪动的哈希桶个数为1
static void _dictRehashStep(dict *d) { if (d->pauserehash == 0) dictRehash(d,1);}什么时候会进行渐进式rehash呢?
当有很多命令的时候,比如增删改查的时候,需要渐进式rehash,这样响应时间就比较段。但是当空闲时间的时候,就可以进行大步大步挪了(hashtable1移动到hashtable2上)。
4.定时任务触发rehash
当定时任务检测到服务器空闲的时候,就可以大步移动hashtable1到hashtable2
dictRehashMilliseconds(dict *d, int ms)就是rehash移动指定毫秒时间,dictRehash(d,100)可以看到,一次挪100个槽位(哈希桶)
因此在指定毫秒时间内,每次挪动100个哈希桶,直到超时了为止。
/* Rehash in ms+"delta" milliseconds. The value of "delta" is larger * than 0, and is smaller than 1 in most cases. The exact upper bound * depends on the running time of dictRehash(d,100).*/int dictRehashMilliseconds(dict *d, int ms) { if (d->pauserehash > 0) return 0; long long start = timeInMilliseconds(); int rehashes = 0; while(dictRehash(d,100)) { rehashes += 100; if (timeInMilliseconds()-start > ms) break; } return rehashes;}5.rehash未完成的时候如何去查找数据呢
首先在第一张哈希表查找,如果没有,然后再去第二章哈希表查找
6.rehash结束后要做的事情
当哈希表1已经搬空了d->ht_used[0] == 0,说明rehash已经结束了
这一步主要是将哈希表1指向哈希表2,然后将哈希表2指向的清空(也就是说把rehash后的结果全部从哈希表2还给哈希表1了)
/* Check if we already rehashed the whole table... */ if (d->ht_used[0] == 0) { zfree(d->ht_table[0]); /* Copy the new ht onto the old one */ d->ht_table[0] = d->ht_table[1]; d->ht_used[0] = d->ht_used[1]; d->ht_size_exp[0] = d->ht_size_exp[1]; _dictReset(d, 1); d->rehashidx = -1; return 0; }五、总结:哈希扩容和rehash
下图是扩容和rehash的结果
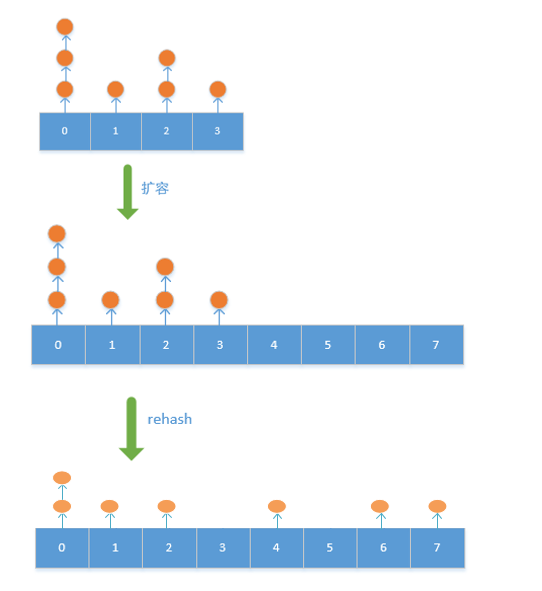
放在哪个哈希桶上,取决于h=hash(key)%size
比如:原先哈希表大小为4,新的为8
原先对应索引为0的,新的只可能对应索引0或者4
原先索引为2的,新的只可能是2或者6


