Nginx反向代理与conf原理
推荐一个零声学院免费公开课程,个人觉得老师讲得不错,分享给大家:Linux,Nginx,ZeroMQ,MySQL,Redis,fastdfs,MongoDB,ZK,流媒体,CDN,P2P,K8S,Docker,TCP/IP,协程,DPDK等技术内容,立即学习
Nginx主要功能
Webservice, 反向代理, 负载均衡。
逻辑上,nginx和server的关系是这样的:
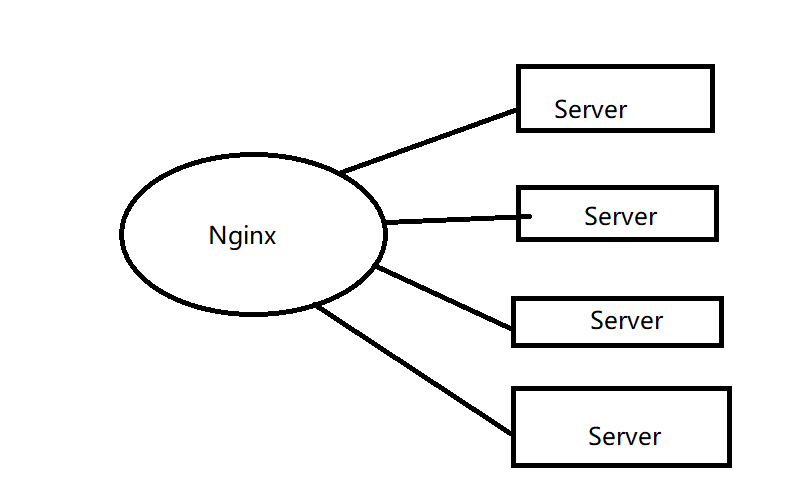
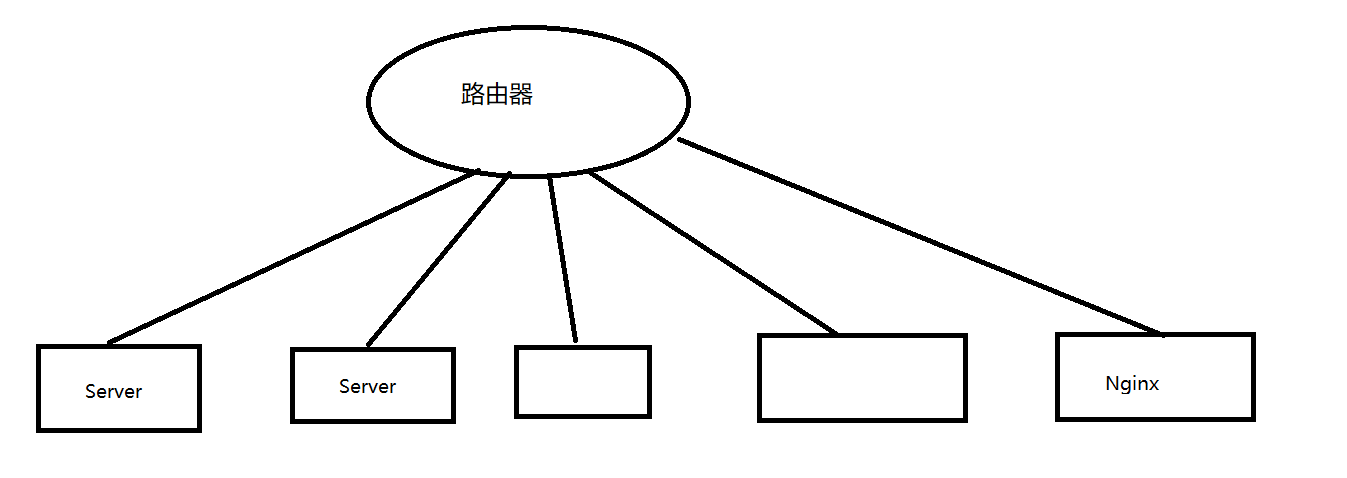
Nginx和路由器/交换机有什么区别?
路由器是物理网关,nginx是应用层网关。
物理上,他们的关系是下图这样的。
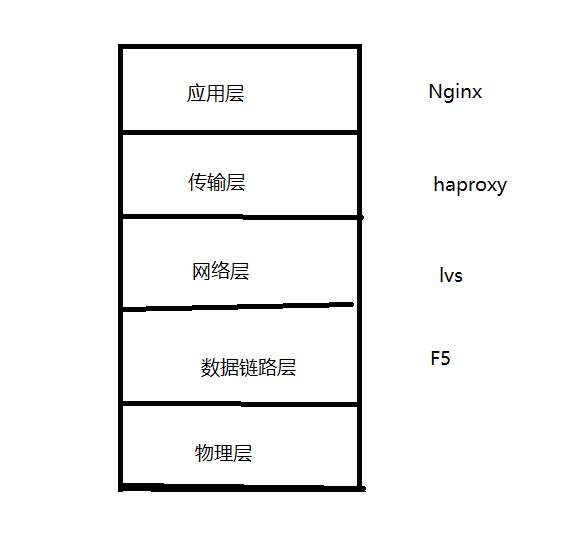
Nginx、haproxy、lvs、F5,都可以做负载均衡,有什么区别?
他们处于tcp/ip协议不同层。
Nginx安装
所需要的安装包nginx、openssl、pcre、zlib

安装命令
./configure --prefix=/usr/local/nginx --with-http_realip_module --with-http_addition_module --with-http_gzip_static_module --with-http_secure_link_module --with-http_stub_status_module --with-stream --with-pcre=/root/nginx/pcre-8.39 --with-zlib=/root/nginx/zlib-1.2.11 --with-openssl=/root/nginx/openssl-1.1.1g
启动nginx
cd /usr/local/nginx
./sbin/nginx -c ./conf/nginx.conf
使用默认配置启动nginx
之后通过浏览器访问nginx。
conf文件使用
最基本的使用如下:
worker_processes 4;events { worker_connections 1024;}http { server { listen 9001; location / { proxy_pass http://172.17.0.2:9004; } } server { listen 9002; } server { listen 9003; } server { listen 9004; location / { root /html; } }}配置worker进程数
worker_processes 4;master进程listen端口,网络io由worker进程处理;对于浏览器发送的请求,会产生两个tcp连接,一个是http请求,一个是keep-alive。
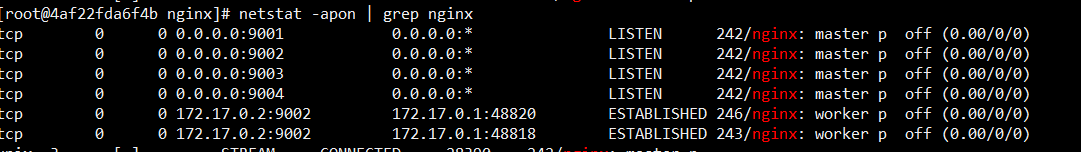
配置服务
nginx支持http,smtp,websocket等多种应用层协议;也可以listen不同的端口;
http { server { listen 9100; }}配置代理
http { server { listen 9001; location / { proxy_pass http://172.17.0.2:9004; } }}重定向
http { server { listen 9001; location / { rewrite ^/(.*) https://github.com/congchp/Linux-server redirect; } }}负载均衡
upstream backend { server 172.17.0.2:9000 weight=2; server 172.17.0.2:9001 weight=1; } location / { proxy_pass http://backend; }提供静态服务内容
图片
location /images/ { root /share/; }视频
location /vedio/ { root /share/; }支持CGI
common gateway interface, 通用网关接口。nginx通过stdin、stdout也cgi程序进行通信。
主要用在哪里?在线编译工具。
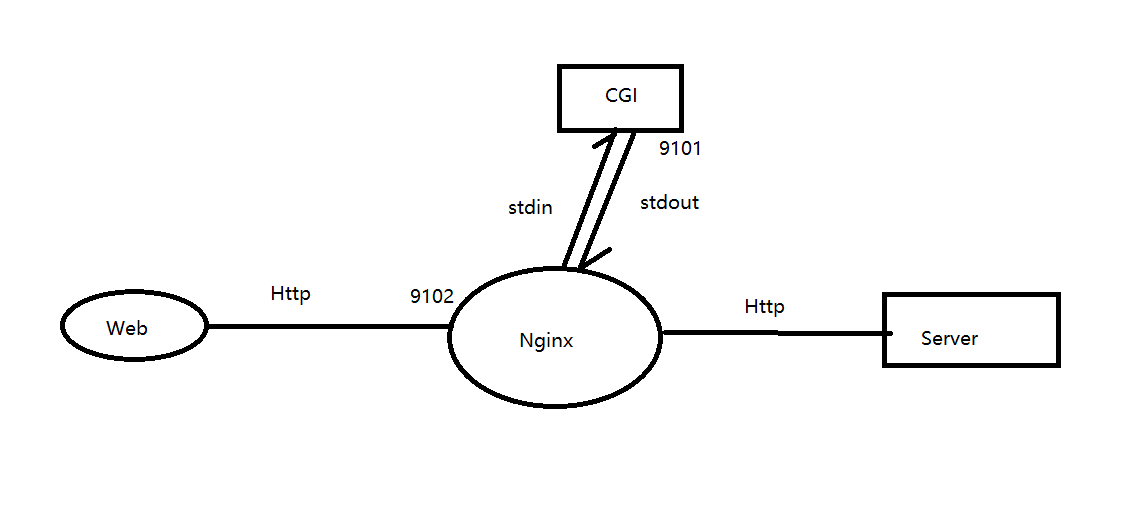
编写一个cgi程序
// gcc -o hello_cgi hello_cgi.h -lfcgi#include #include int main() { while (FCGI_Accept() >= 0) { printf(" Content-type: text/html\r\n"); printf("\r\n"); printf("Fast CGI Hello! "); printf("Congchp cgi
"); printf("Thank you cgi\n"); }}nginx使用cgi,需要安装fastcgi和spawn-fcgi。cgi是一请求一进程;fastcgi是一个进程池,通过进行管理器对cgi进行管理。spawn-fcgi是fastcgi进行管理器,管理cgi。

spawn-fcgi编译
./configuremake#将编译后的spawn-fcgi程序copy到/usr/local/nginx目录下cp ./src/spwan-fcgi /usr/local/nginxfastcgi编译安装
./configuremakemake install通过spawn-fcgi启动cgi程序。
./spawn-fcgi -a 127.0.0.1 -p 9101 -f /share/hello_cginginx配置
server { listen 9102; location / { fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9101; fastcgi_index index.cgi; fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME cgi$fastcgi_script_name; include ../conf/fastcgi_params; } }
什么是惊群?
惊群分为3种:
- accept
- epoll_wait
- pthead_cond_wait
accept惊群和pthead_cond_wait的惊群,内核已经解决了。
nginx是存在epoll_wait惊群的,为什么呢?
所有workder进程都是从master进程fork出来的,都对同一个端口进行listen,如果在所有worker进程中使用epoll对listenfd进行检测,必然会出现epoll_wait的惊群。
惊群并不会导致业务问题,只会造成很多无效的唤醒,高性能的服务器是不能接受这一点的。
nginx是如何解决epoll_wait惊群的?
通过加accept锁,通过shmem共享内存实现进程锁。
为保证只有一个worker进程对新连接进行处理,所有worker进程在向epoll注册listenfd读事件前抢accept_mutex, 抢到互斥锁的那个进程注册listenfd读事件,在读事件里面调用accept接受该连接。当一个worker进程在accept这个连接之后,就开始读取请求,解析请求,处理请求,产生response后,再返回给客户端,最后才断开连接。一个请求,完全由一个worker进程来处理,而且只在一个worker进程中处理。
其他没有抢到accept锁的worker进程,可以处理其他event。
while (1) { ret = try_lock(lock); if (ret == 0) epll_ctl(epfd, EPOLL_ADD, listenfd, EPOLL_IN); epoll_wait(); if (events[i].data.fd == listenfd) unlock(lock);}

