Numpy具体用法相关内容(二)
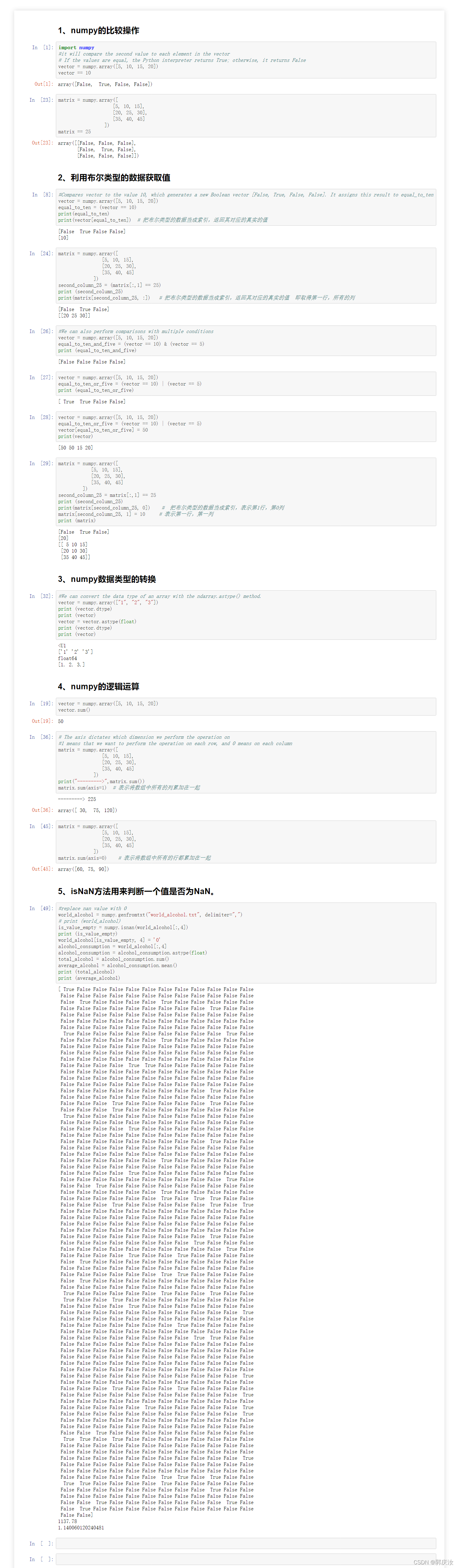
#!/usr/bin/env python# coding: utf-8# ## 1、numpy的比较操作# In[1]:import numpy#it will compare the second value to each element in the vector# If the values are equal, the Python interpreter returns True; otherwise, it returns Falsevector = numpy.array([5, 10, 15, 20])vector == 10# In[23]:matrix = numpy.array([ [5, 10, 15],[20, 25, 30], [35, 40, 45] ])matrix == 25# ## 2、利用布尔类型的数据获取值# In[8]:#Compares vector to the value 10, which generates a new Boolean vector [False, True, False, False]. It assigns this result to equal_to_tenvector = numpy.array([5, 10, 15, 20])equal_to_ten = (vector == 10)print(equal_to_ten)print(vector[equal_to_ten]) # 把布尔类型的数据当成索引,返回其对应的真实的值# In[24]:matrix = numpy.array([ [5, 10, 15], [20, 25, 30], [35, 40, 45] ])second_column_25 = (matrix[:,1] == 25)print (second_column_25)print(matrix[second_column_25, :]) # 把布尔类型的数据当成索引,返回其对应的真实的值 即取得第一行,所有的列# In[26]:#We can also perform comparisons with multiple conditionsvector = numpy.array([5, 10, 15, 20])equal_to_ten_and_five = (vector == 10) & (vector == 5)print (equal_to_ten_and_five)# In[27]:vector = numpy.array([5, 10, 15, 20])equal_to_ten_or_five = (vector == 10) | (vector == 5)print (equal_to_ten_or_five)# In[28]:vector = numpy.array([5, 10, 15, 20])equal_to_ten_or_five = (vector == 10) | (vector == 5)vector[equal_to_ten_or_five] = 50print(vector)# In[29]:matrix = numpy.array([ [5, 10, 15], [20, 25, 30], [35, 40, 45] ])second_column_25 = matrix[:,1] == 25print (second_column_25)print(matrix[second_column_25, 0]) # 把布尔类型的数据当成索引,表示第1行,第0列matrix[second_column_25, 1] = 10 # 表示第一行,第一列print (matrix)# ## 3、numpy数据类型的转换# In[32]:#We can convert the data type of an array with the ndarray.astype() method.vector = numpy.array(["1", "2", "3"])print (vector.dtype)print (vector)vector = vector.astype(float)print (vector.dtype)print (vector)# ## 4、numpy的逻辑运算# In[19]:vector = numpy.array([5, 10, 15, 20])vector.sum()# In[36]:# The axis dictates which dimension we perform the operation on#1 means that we want to perform the operation on each row, and 0 means on each columnmatrix = numpy.array([ [5, 10, 15], [20, 25, 30], [35, 40, 45] ])print("--------->",matrix.sum())matrix.sum(axis=1) # 表示将数组中所有的列累加在一起# In[45]:matrix = numpy.array([ [5, 10, 15], [20, 25, 30], [35, 40, 45] ])matrix.sum(axis=0) # 表示将数组中所有的行都累加在一起# ## 5、isNaN方法用来判断一个值是否为NaN。# In[49]:#replace nan value with 0world_alcohol = numpy.genfromtxt("world_alcohol.txt", delimiter=",")# print (world_alcohol)is_value_empty = numpy.isnan(world_alcohol[:,4])print (is_value_empty)world_alcohol[is_value_empty, 4] = '0'alcohol_consumption = world_alcohol[:,4]alcohol_consumption = alcohol_consumption.astype(float)total_alcohol = alcohol_consumption.sum()average_alcohol = alcohol_consumption.mean()print (total_alcohol)print (average_alcohol)



