FlinkCDC 达梦数据库实时同步_flink cdc 达梦
一、Flink部署
1.1、JAVA环境
vi /etc/profileexport JAVA_HOME=/data/flinkcdc/jdk1.8.0_181export CLASSPATH=$JAVA_HOME/lib/tools.jar:$JAVA_HOME/lib/dt.jarexport PATH=$JAVA_HOME/bin:$PATHsource /etc/profilevi ~/.bash_profileexport FLINK_HOME=/data/flinkcdc/flink-1.17.0export PATH=$PATH:$FLINK_HOME/binsource ~/.bash_profile1.2、配置Flink
vim conf/flink-conf.yaml添加配置:env.java.home=/data/flinkcdc/jdk1.8.0_181①、localhost 修改为IP地址rest.port: 8088rest.address: 192.168.33.231②、关闭防火墙systemctl status firewalldsystemctl stop firewalld1.3、Flink CDC Jar包
CDC jar放到Flink安装包解压之后的lib目录
1.4、启动flink
bin/start-cluster.shFlink Web-UIhttp://192.168.33.231:80881.5、启动 Flink SQL CLI
bin/sql-client.sh二、达梦数据库搭建
2.1、docker dm8
docker run -d \\--name dm8 \\--restart=always \\--privileged=true \\-e LD_LIBRARY_PATH=/opt/dmdbms/bin \\-e PAGE_SIZE=16 \\-e EXTENT_SIZE=32 \\-e LOG_SIZE=1024 \\-e CASE_SENSITIVE=0 \\-e UNICODE_FLAG=1 \\-e INSTANCE_NAME=DM8_CDC \\-e SYSDBA_PWD=SYSDBA001 \\-v /docker/dm8_data_cdc:/opt/dmdbms/data \\-p 5236:5236 \\dm8_flinkcdc:dm8查看容器运行情况
查看数据库容器lsof -i:5236docker logs -f dm8docker exec -it dm8 bash2.2、开启达梦日志归档
##查看当前数据库是否开启归档select arch_mode from v$database;##查询有哪些归档日志SELECT NAME , FIRST_TIME , NEXT_TIME , FIRST_CHANGE# , NEXT_CHANGE# FROM V$ARCHIVED_LOG; SELECT * FROM V$ARCH_FILE##修改数据库实例的 /dmdata/DAMEGN/dm.ini文件中 ARCH_INI 参数值vi /dmdata/DAMENG/dm.ini##将 ARCH_INI 值改为 1,保存后退出ARCH_INI = 1 #开启归档功能RLOG_APPEND_LOGIC = 1##新增文件dmarch.inivi /dmdata/DAMENG/dmarch.ini##新增如下内容[ARCHIVE_LOCAL1]ARCH_TYPE = LOCALARCH_DEST = /dmarchARCH_FILE_SIZE = 2048ARCH_SPACE_LIMIT = 102400##最后重启数据库完成归档配置#DaMeng Database Archive Configuration file#this is comments ARCH_WAIT_APPLY = 0[ARCHIVE_LOCAL1] ARCH_TYPE = LOCAL ARCH_DEST = /opt/dmdbms/data/DAMENG/arch ARCH_FILE_SIZE = 1024 ARCH_SPACE_LIMIT = 51200 ARCH_FLUSH_BUF_SIZE = 0 ARCH_HANG_FLAG = 12.3、重启dm8数据库
docker restart dm8三、实时同步测试
##达梦CREATE TABLE t_source_dm ( id INT, name VARCHAR, insert_date DATE, PRIMARY KEY (id) NOT ENFORCED) WITH ( \'connector\' = \'dm\', \'startupOptions\' = \'Initial\', \'hostname\' = \'192.168.33.231\', \'port\' = \'5236\', \'username\' = \'SYSDBA\', \'password\' = \'SYSDBA001\', \'database\' = \'DM8_CDC\', \'schema\' = \'SYSDBA\', \'table\' = \'dm_flinkcdc\');##MYSQLCREATE TABLE sink_mysql_test ( id int, name STRING, insert_date date, PRIMARY KEY (id) NOT ENFORCED) WITH ( \'connector\' = \'jdbc\', \'url\' = \'jdbc:mysql://192.168.33.231:3306/flinkcdc\', \'driver\' = \'com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver\', \'username\' = \'root\', \'password\' = \'YTP1101102233\', \'table-name\' = \'dm_to_mysql\');insert into sink_mysql_test select * from t_source_dm;四、数据实时同步样本(很多留言说没有用,这里证实一下,不成功重点检查达梦配置)
4.1、代码
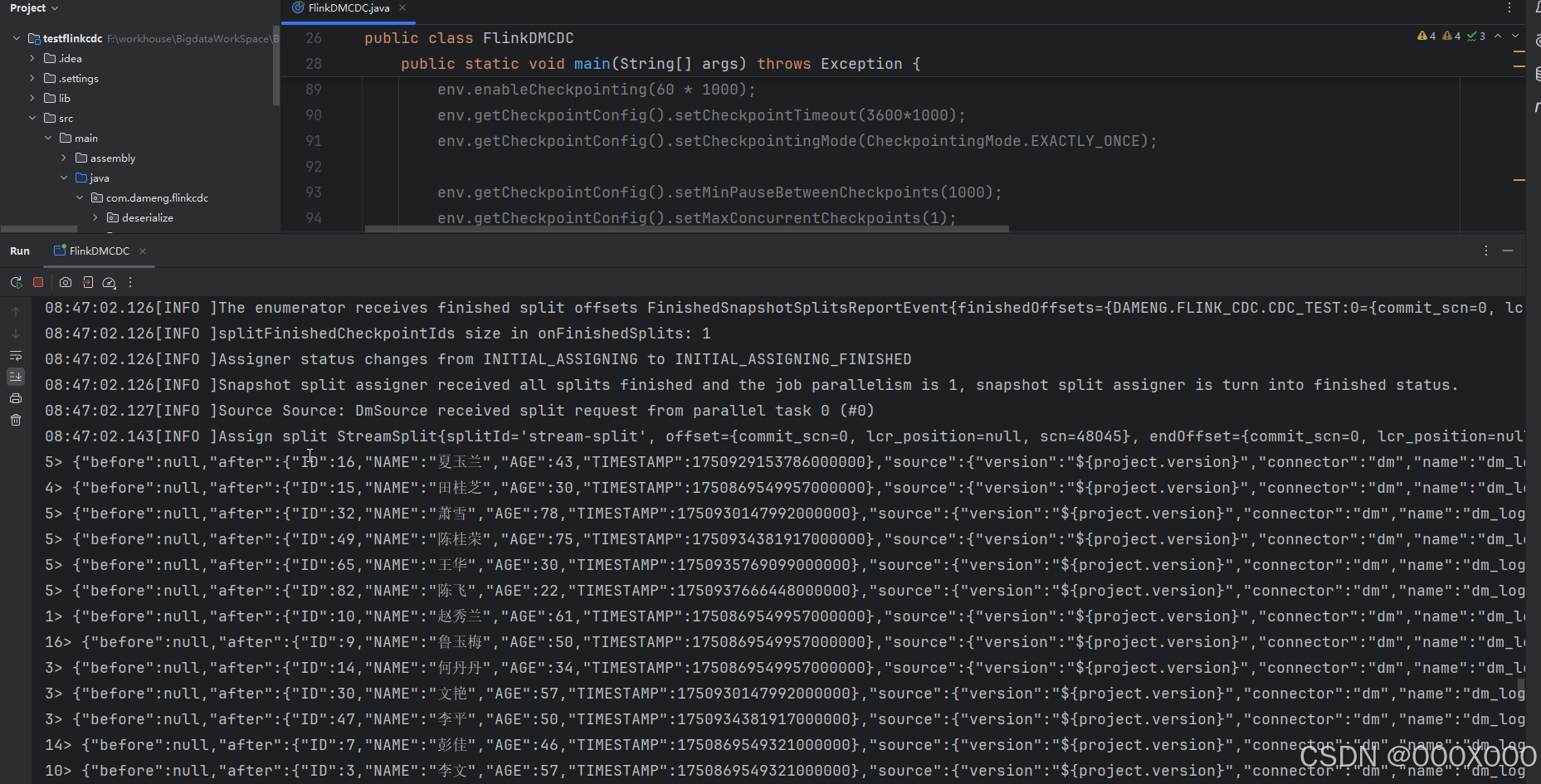
/* * @(#)FlinkDMCDC.java, 2023年8月5日 上午10:33:17 * * Copyright (c) 2000-2020, 达梦数据库有限公司. * All rights reserved. */package com.dameng.flinkcdc.dm;import java.io.File;import java.util.Properties;import org.apache.flink.api.common.eventtime.WatermarkStrategy;import org.apache.flink.cdc.connectors.base.options.StartupOptions;import org.apache.flink.cdc.connectors.base.source.jdbc.JdbcIncrementalSource;import org.apache.flink.cdc.connectors.dm.source.DMSourceBuilder;import org.apache.flink.cdc.debezium.JsonDebeziumDeserializationSchema;import org.apache.flink.configuration.Configuration;import org.apache.flink.core.fs.FileSystem;import org.apache.flink.runtime.state.filesystem.FsStateBackend;import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.environment.StreamExecutionEnvironment;public class FlinkDMCDC{public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {Properties properties = new Properties();properties.setProperty(\"database.tablename.case.insensitive\", \"false\");properties.setProperty(\"log.mining.strategy\", \"offline_catalog\");properties.setProperty(\"log.mining.continuous.mine\", \"true\");//properties.setProperty(\"provide.transaction.metadata\", \"true\");properties.setProperty(\"lob.enabled\", \"true\");JdbcIncrementalSource changeEventSource = new DMSourceBuilder() .hostname(\"localhost\").port(15236).databaseList(\"DAMENG\").tableList(\"FLINK_CDC.CDC_TEST\").schemaList(\"FLINK_CDC\").username(\"SYSDBA\").password(\"SYSDBA112233\").startupOptions(StartupOptions.initial()).dmProperties(properties).includeSchemaChanges(true).deserializer(new JsonDebeziumDeserializationSchema()).sliceSize(20).scanNewlyAddedTableEnabled(true).build();Configuration configuration = new Configuration();//检查点文件StreamExecutionEnvironment env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment(configuration);env.enableCheckpointing(20 * 1000);env.getCheckpointConfig().setMinPauseBetweenCheckpoints(6*1000);env.getCheckpointConfig().setMaxConcurrentCheckpoints(1);env.fromSource(changeEventSource, WatermarkStrategy.noWatermarks(), \"DmSource\").setParallelism(1).print()env.execute();}}4.1.1、从头开始采集数据,运行结果
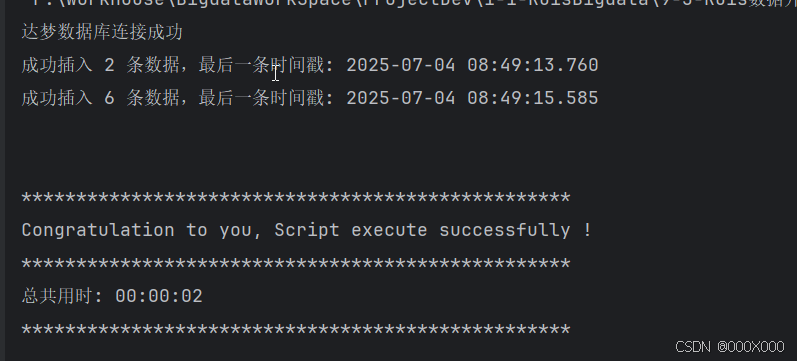
4.1.2、数据插入 结果:
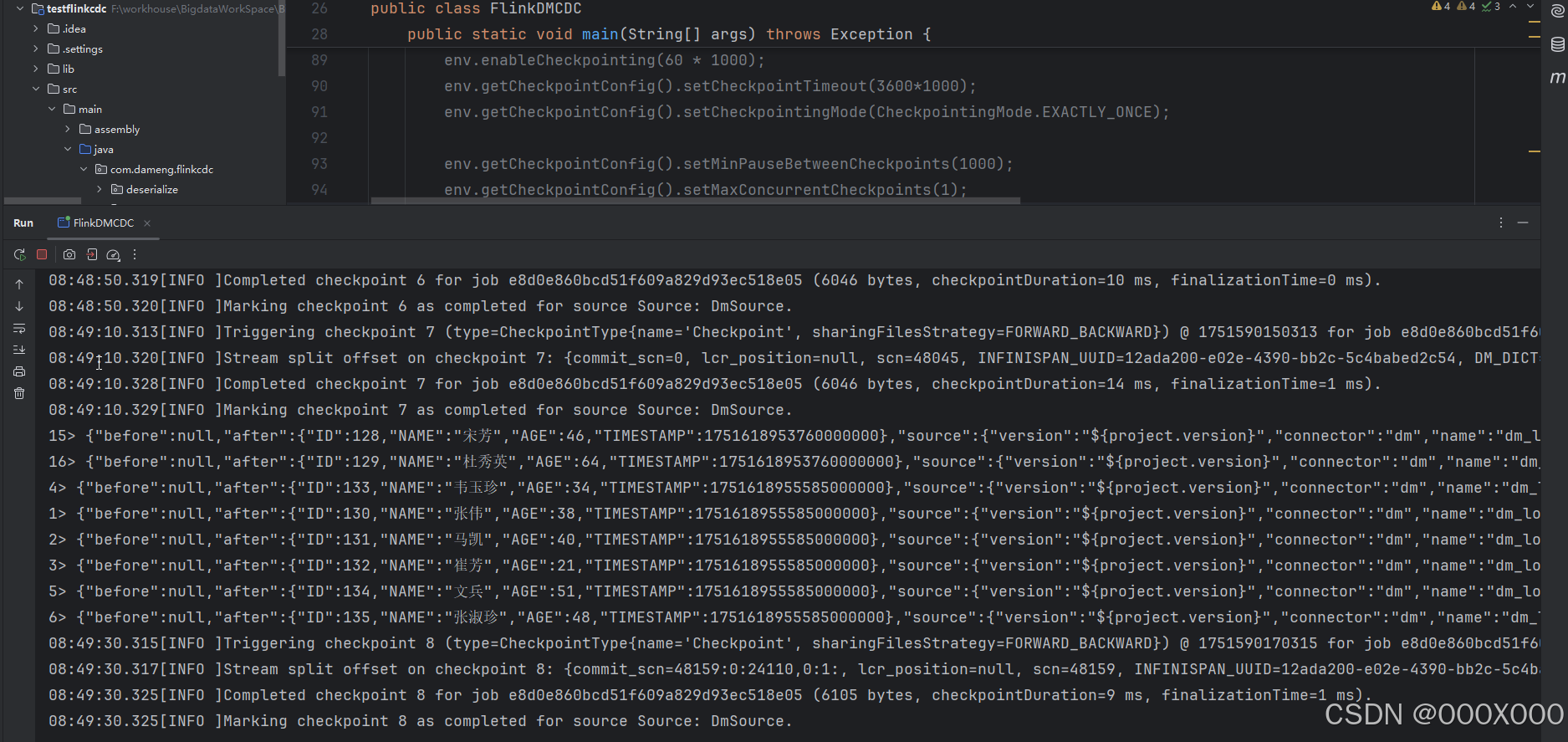
4.1.3、数据更新 结果:
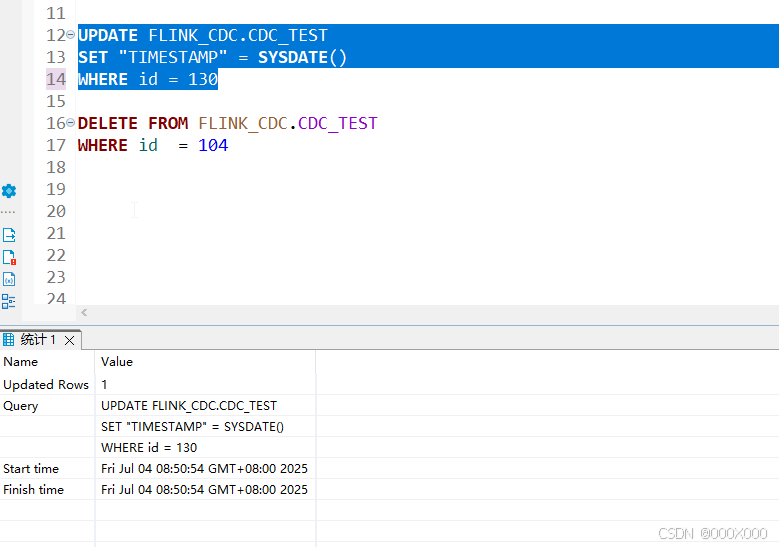
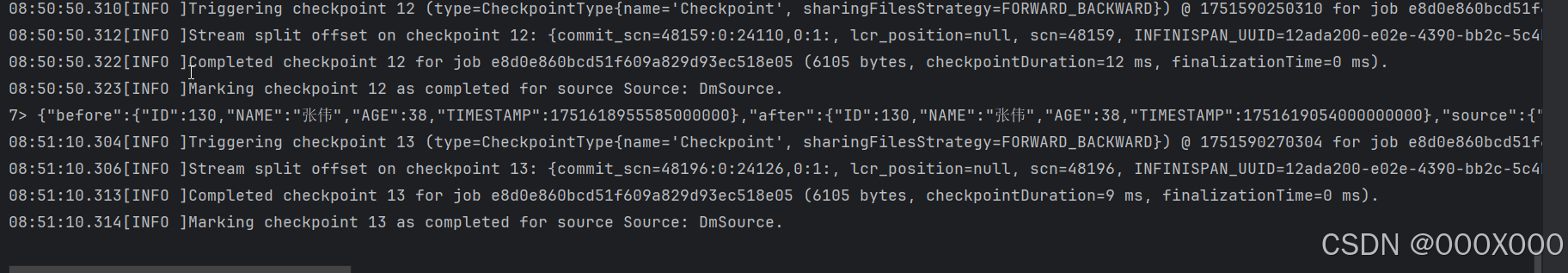
4.1.4、数据删除 结果:
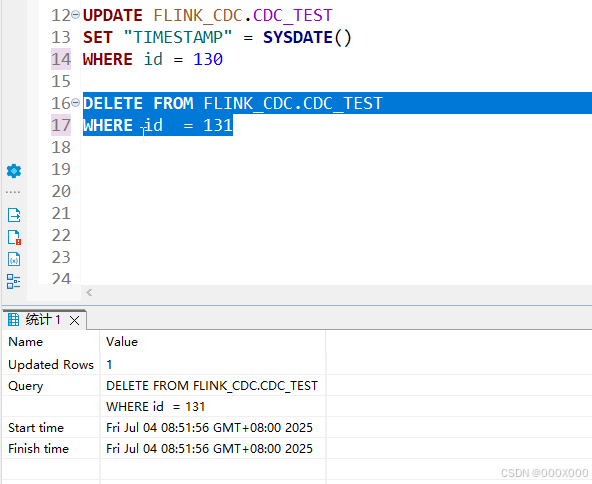
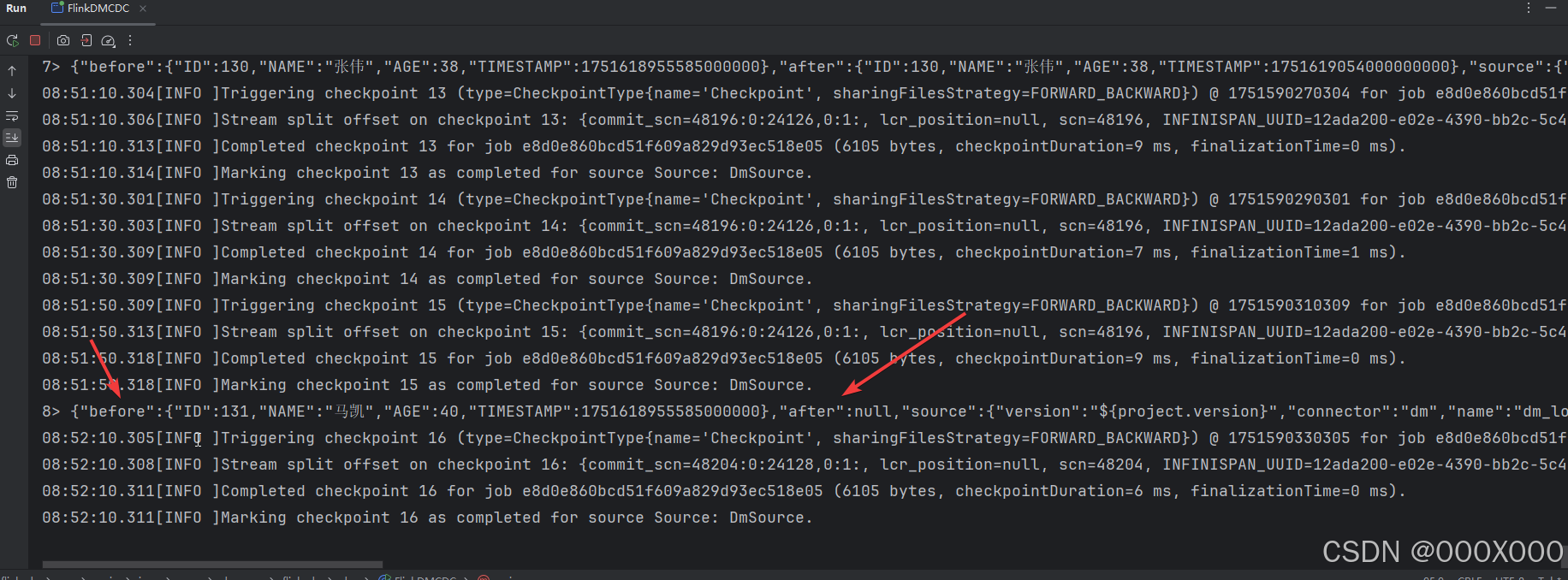
4.2、达梦实时同步CDC 转换为SQL代码(直接拿去用)
/* * @(#)FlinkDMCDC.java, 2023年8月5日 上午10:33:17 * * Copyright (c) 2000-2020, 达梦数据库有限公司. * All rights reserved. */package com.dameng.flinkcdc.dm;import java.io.File;import java.util.Properties;import org.apache.flink.api.common.eventtime.WatermarkStrategy;import org.apache.flink.cdc.connectors.base.options.StartupOptions;import org.apache.flink.cdc.connectors.base.source.jdbc.JdbcIncrementalSource;import org.apache.flink.cdc.connectors.dm.source.DMSourceBuilder;import org.apache.flink.cdc.debezium.JsonDebeziumDeserializationSchema;import org.apache.flink.configuration.Configuration;import org.apache.flink.core.fs.FileSystem;import org.apache.flink.runtime.state.filesystem.FsStateBackend;import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.environment.StreamExecutionEnvironment;import org.apache.flink.api.common.functions.MapFunction;import org.apache.flink.api.java.tuple.Tuple2;import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.environment.StreamExecutionEnvironment;import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.functions.sink.SinkFunction;import org.apache.flink.configuration.Configuration;import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.datastream.DataStream;import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.JsonNode;import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.node.ObjectNode;import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.node.JsonNodeFactory;import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;import java.util.Date;/** * * Created by wuxin on 2023年8月5日 上午10:33:17 */public class FlinkDMCDCSQL{ public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { Properties properties = new Properties(); properties.setProperty(\"database.tablename.case.insensitive\", \"false\"); properties.setProperty(\"log.mining.strategy\", \"offline_catalog\"); properties.setProperty(\"log.mining.continuous.mine\", \"true\"); properties.setProperty(\"lob.enabled\", \"true\"); JdbcIncrementalSource changeEventSource = new DMSourceBuilder() .hostname(\"localhost\") .port(15236) .databaseList(\"DAMENG\") .tableList(\"FLINK_CDC.CDC_TEST\") .schemaList(\"FLINK_CDC\") .username(\"SYSDBA\") .password(\"SYSDBA112233\") .startupOptions(StartupOptions.initial()) .dmProperties(properties) .includeSchemaChanges(true) .deserializer(new JsonDebeziumDeserializationSchema()) .sliceSize(20) .scanNewlyAddedTableEnabled(true) .build(); Configuration configuration = new Configuration(); //检查点文件 StreamExecutionEnvironment env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment(configuration); env.enableCheckpointing(20 * 1000); env.getCheckpointConfig().setMinPauseBetweenCheckpoints(6*1000); env.getCheckpointConfig().setMaxConcurrentCheckpoints(1); env.setStateBackend(new FsStateBackend(\"file:///D:/tmp/ck\")); DataStream sourceStream = env.fromSource( changeEventSource, WatermarkStrategy.noWatermarks(), \"DmSource\" ); // 处理CDC数据并生成JSON格式的SQL语句 DataStream jsonStream = sourceStream.map(new MapFunction() { private transient ObjectMapper objectMapper; private final JsonNodeFactory nodeFactory = JsonNodeFactory.instance; @Override public String map(String value) throws Exception { if (objectMapper == null) { objectMapper = new ObjectMapper(); } JsonNode rootNode = objectMapper.readTree(value); String op = rootNode.path(\"op\").asText(); JsonNode sourceNode = rootNode.path(\"source\"); String schema = sourceNode.path(\"schema\").asText(); String table = sourceNode.path(\"table\").asText(); long tsMs = rootNode.path(\"ts_ms\").asLong(); // 创建JSON结构 ObjectNode json = nodeFactory.objectNode(); // 1. 添加metadata部分 ObjectNode metadata = json.putObject(\"metadata\") .put(\"schema\", schema) .put(\"table\", table) .put(\"source_timestamp\", tsMs); // 处理时间戳字段 JsonNode afterNode = rootNode.path(\"after\"); if (!afterNode.isMissingNode() && afterNode.has(\"TIMESTAMP\")) { long timestampNs = afterNode.path(\"TIMESTAMP\").asLong(); metadata.put(\"event_time\", formatTimestamp(timestampNs)); } else { metadata.put(\"event_time\", formatTimestamp(tsMs * 1000000L)); } // 2. 根据操作类型生成SQL并添加到JSON String sql = \"\"; switch (op) { case \"r\": sql = generateInsertSQL(schema + \".\" + table, afterNode); json.putObject(\"sql\").put(\"insert\", sql); break; case \"c\": sql = generateInsertSQL(schema + \".\" + table, afterNode); json.putObject(\"sql\").put(\"insert\", sql); break; case \"u\": JsonNode beforeNode = rootNode.path(\"before\"); sql = generateUpdateSQL(schema + \".\" + table, beforeNode, afterNode); json.putObject(\"sql\").put(\"update\", sql); break; case \"d\": JsonNode beforeNodeDelete = rootNode.path(\"before\"); sql = generateDeleteSQL(schema + \".\" + table, beforeNodeDelete); json.putObject(\"sql\").put(\"delete\", sql); break; default: json.put(\"error\", \"UNKNOWN OPERATION: \" + op); } return objectMapper.writerWithDefaultPrettyPrinter().writeValueAsString(json); } private String generateInsertSQL(String tableName, JsonNode afterNode) { StringBuilder fields = new StringBuilder(); StringBuilder values = new StringBuilder(); afterNode.fieldNames().forEachRemaining(fieldName -> { if (fields.length() > 0) { fields.append(\", \"); values.append(\", \"); } fields.append(fieldName); JsonNode valueNode = afterNode.get(fieldName); if (valueNode.isNull()) { values.append(\"NULL\"); } else if (valueNode.isTextual()) { values.append(\"\'\").append(escapeSQL(valueNode.asText())).append(\"\'\"); } else { values.append(valueNode.asText()); } }); return String.format(\"INSERT INTO %s (%s) VALUES (%s)\", tableName, fields.toString(), values.toString()); } private String generateUpdateSQL(String tableName, JsonNode beforeNode, JsonNode afterNode) { StringBuilder setClause = new StringBuilder(); StringBuilder whereClause = new StringBuilder(); // 构建SET部分 afterNode.fieldNames().forEachRemaining(fieldName -> { if (!fieldName.equals(\"ID\")) { // 假设ID是主键,不更新 if (setClause.length() > 0) { setClause.append(\", \"); } JsonNode valueNode = afterNode.get(fieldName); if (valueNode.isNull()) { setClause.append(fieldName).append(\" = NULL\"); } else if (valueNode.isTextual()) { setClause.append(fieldName) .append(\" = \'\") .append(escapeSQL(valueNode.asText())) .append(\"\'\"); } else { setClause.append(fieldName) .append(\" = \") .append(valueNode.asText()); } } }); // 构建WHERE部分(使用所有字段作为条件以确保准确性) beforeNode.fieldNames().forEachRemaining(fieldName -> { if (whereClause.length() > 0) { whereClause.append(\" AND \"); } JsonNode valueNode = beforeNode.get(fieldName); if (valueNode.isNull()) { whereClause.append(fieldName).append(\" IS NULL\"); } else if (valueNode.isTextual()) { whereClause.append(fieldName) .append(\" = \'\") .append(escapeSQL(valueNode.asText())) .append(\"\'\"); } else { whereClause.append(fieldName) .append(\" = \") .append(valueNode.asText()); } }); return String.format(\"UPDATE %s SET %s WHERE %s\", tableName, setClause.toString(), whereClause.toString()); } private String generateDeleteSQL(String tableName, JsonNode beforeNode) { StringBuilder whereClause = new StringBuilder(); beforeNode.fieldNames().forEachRemaining(fieldName -> { if (whereClause.length() > 0) { whereClause.append(\" AND \"); } JsonNode valueNode = beforeNode.get(fieldName); if (valueNode.isNull()) { whereClause.append(fieldName).append(\" IS NULL\"); } else if (valueNode.isTextual()) { whereClause.append(fieldName) .append(\" = \'\") .append(escapeSQL(valueNode.asText())) .append(\"\'\"); } else { whereClause.append(fieldName) .append(\" = \") .append(valueNode.asText()); } }); return String.format(\"DELETE FROM %s WHERE %s\", tableName, whereClause.toString()); } private String escapeSQL(String value) { return value.replace(\"\'\", \"\'\'\"); } // 时间戳格式化方法 private String formatTimestamp(long timestampNs) { long timestampMs = timestampNs / 1000000L; SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat(\"yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss\"); return sdf.format(new Date(timestampMs)); } }); // 将SQL语句写入文件 jsonStream.writeAsText(\"D:\\\\tmp\\\\flink-cdc-sql-output.txt\", FileSystem.WriteMode.OVERWRITE) .setParallelism(1); env.execute(); }}4.3、达梦实时同步CDC 推送Kafka,解耦代码(直接拿去用)
/* * @(#)FlinkDMCDC.java, 2023年8月5日 上午10:33:17 * * Copyright (c) 2000-2020, 达梦数据库有限公司. * All rights reserved. */package com.dameng.flinkcdc.dm;import java.io.File;import java.time.Instant;import java.time.ZoneId;import java.time.format.DateTimeFormatter;import java.util.Properties;import org.apache.flink.api.common.eventtime.WatermarkStrategy;import org.apache.flink.api.common.serialization.SimpleStringSchema;import org.apache.flink.cdc.connectors.base.options.StartupOptions;import org.apache.flink.cdc.connectors.base.source.jdbc.JdbcIncrementalSource;import org.apache.flink.cdc.connectors.dm.source.DMSourceBuilder;import org.apache.flink.cdc.debezium.JsonDebeziumDeserializationSchema;import org.apache.flink.configuration.Configuration;import org.apache.flink.connector.base.DeliveryGuarantee;import org.apache.flink.core.fs.FileSystem;import org.apache.flink.runtime.state.filesystem.FsStateBackend;import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.environment.StreamExecutionEnvironment;import org.apache.flink.api.common.functions.MapFunction;import org.apache.flink.api.java.tuple.Tuple2;import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.environment.StreamExecutionEnvironment;import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.functions.sink.SinkFunction;import org.apache.flink.configuration.Configuration;import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.datastream.DataStream;import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.JsonNode;import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.node.ObjectNode;import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.node.JsonNodeFactory;import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;import java.util.Date;import org.apache.flink.connector.kafka.sink.KafkaRecordSerializationSchema;import org.apache.flink.connector.kafka.sink.KafkaSink;/** * * Created by wuxin on 2023年8月5日 上午10:33:17 */public class FlinkDMCDCSQLKafka{ public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { Properties properties = new Properties(); properties.setProperty(\"database.tablename.case.insensitive\", \"false\"); properties.setProperty(\"log.mining.strategy\", \"offline_catalog\"); properties.setProperty(\"log.mining.continuous.mine\", \"true\"); properties.setProperty(\"lob.enabled\", \"true\"); JdbcIncrementalSource changeEventSource = new DMSourceBuilder() .hostname(\"localhost\") .port(15236) .databaseList(\"DAMENG\") .tableList(\"FLINK_CDC.CDC_TEST\") .schemaList(\"FLINK_CDC\") .username(\"SYSDBA\") .password(\"SYSDBA112233\") .startupOptions(StartupOptions.initial()) .dmProperties(properties) .includeSchemaChanges(true) .deserializer(new JsonDebeziumDeserializationSchema()) .sliceSize(20) .scanNewlyAddedTableEnabled(true) .build(); Configuration configuration = new Configuration(); //检查点文件 StreamExecutionEnvironment env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment(configuration); env.enableCheckpointing(20 * 1000); env.getCheckpointConfig().setMinPauseBetweenCheckpoints(6*1000); env.getCheckpointConfig().setMaxConcurrentCheckpoints(1); env.setStateBackend(new FsStateBackend(\"file:///D:/tmp/ck\")); DataStream sourceStream = env.fromSource( changeEventSource, WatermarkStrategy.noWatermarks(), \"DmSource\" ); // 处理CDC数据并生成JSON格式的SQL语句 DataStream jsonStream = sourceStream.map(new MapFunction() { private transient ObjectMapper objectMapper; private final JsonNodeFactory nodeFactory = JsonNodeFactory.instance; @Override public String map(String value) throws Exception { if (objectMapper == null) { objectMapper = new ObjectMapper(); } JsonNode rootNode = objectMapper.readTree(value); String op = rootNode.path(\"op\").asText(); JsonNode sourceNode = rootNode.path(\"source\"); String schema = sourceNode.path(\"schema\").asText(); String table = sourceNode.path(\"table\").asText(); long tsMs = rootNode.path(\"ts_ms\").asLong(); // 创建JSON结构 ObjectNode json = nodeFactory.objectNode(); // 1. 添加metadata部分 ObjectNode metadata = json.putObject(\"metadata\") .put(\"schema\", schema) .put(\"table\", table) .put(\"source_timestamp\", tsMs); // 处理时间戳字段 JsonNode afterNode = rootNode.path(\"after\"); if (!afterNode.isMissingNode() && afterNode.has(\"TIMESTAMP\")) { long timestampNs = afterNode.path(\"TIMESTAMP\").asLong(); metadata.put(\"event_time\", formatTimestamp(timestampNs)); } else { metadata.put(\"event_time\", formatTimestamp(tsMs * 1000000L)); } // 2. 根据操作类型生成SQL并添加到JSON String sql = \"\"; switch (op) { case \"r\": sql = generateInsertSQL(schema + \".\" + table, afterNode); json.putObject(\"sql\").put(\"dml\", sql); break; case \"c\": sql = generateInsertSQL(schema + \".\" + table, afterNode); json.putObject(\"sql\").put(\"dml\", sql); break; case \"u\": JsonNode beforeNode = rootNode.path(\"before\"); sql = generateUpdateSQL(schema + \".\" + table, beforeNode, afterNode); json.putObject(\"sql\").put(\"dml\", sql); break; case \"d\": JsonNode beforeNodeDelete = rootNode.path(\"before\"); sql = generateDeleteSQL(schema + \".\" + table, beforeNodeDelete); json.putObject(\"sql\").put(\"dml\", sql); break; default: json.put(\"error\", \"UNKNOWN OPERATION: \" + op); } // 配置ObjectMapper禁用美化打印(默认即为紧凑格式)// ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper();// String jsonString = mapper.writeValueAsString(json); return objectMapper.writerWithDefaultPrettyPrinter().writeValueAsString(json); } private String generateInsertSQL(String tableName, JsonNode afterNode) { StringBuilder fields = new StringBuilder(); StringBuilder values = new StringBuilder(); afterNode.fieldNames().forEachRemaining(fieldName -> { if (fields.length() > 0) { fields.append(\", \"); values.append(\", \"); } fields.append(fieldName); JsonNode valueNode = afterNode.get(fieldName); if (valueNode.isNull()) { values.append(\"NULL\"); } else if (valueNode.isTextual()) { // 处理文本类型(含转义) values.append(\"\'\").append(escapeSQL(valueNode.asText())).append(\"\'\"); } else if (valueNode.isLong() && isTimestampField(fieldName)) { // 处理时间戳转换(纳秒/毫秒级) values.append(\"\'\").append(formatTimestamp(valueNode.asLong())).append(\"\'\"); } else if (valueNode.isNumber()) { // 处理其他数字类型 values.append(valueNode.asText()); } else { // 默认处理(如布尔值等) values.append(valueNode.asText()); } }); return String.format(\"INSERT INTO %s (%s) VALUES (%s)\", tableName, fields.toString(), values.toString()); } private String generateUpdateSQL(String tableName, JsonNode beforeNode, JsonNode afterNode) { StringBuilder setClause = new StringBuilder(); StringBuilder whereClause = new StringBuilder(); // 构建SET部分 afterNode.fieldNames().forEachRemaining(fieldName -> { if (!fieldName.equals(\"ID\")) { // 假设ID是主键,不更新 if (setClause.length() > 0) { setClause.append(\", \"); } JsonNode valueNode = afterNode.get(fieldName); if (valueNode.isNull()) { setClause.append(fieldName).append(\" = NULL\"); } else if (valueNode.isTextual()) { setClause.append(fieldName) .append(\" = \'\") .append(escapeSQL(valueNode.asText())) .append(\"\'\"); } else if (valueNode.isLong() && isTimestampField(fieldName)) { // 处理时间戳转换(纳秒/毫秒级) setClause.append(fieldName) .append(\" = \'\") .append(formatTimestamp(valueNode.asLong())) .append(\"\'\"); } else { setClause.append(fieldName) .append(\" = \") .append(valueNode.asText()); } } }); // 构建WHERE部分(使用所有字段作为条件以确保准确性) beforeNode.fieldNames().forEachRemaining(fieldName -> { if (whereClause.length() > 0) { whereClause.append(\" AND \"); } JsonNode valueNode = beforeNode.get(fieldName); if (valueNode.isNull()) { whereClause.append(fieldName).append(\" IS NULL\"); } else if (valueNode.isTextual()) { whereClause.append(fieldName) .append(\" = \'\") .append(escapeSQL(valueNode.asText())) .append(\"\'\"); } else if (valueNode.isLong() && isTimestampField(fieldName)) { // 处理时间戳转换(纳秒/毫秒级) whereClause.append(fieldName) .append(\" = \'\") .append(formatTimestamp(valueNode.asLong())) .append(\"\'\"); } else { whereClause.append(fieldName) .append(\" = \") .append(valueNode.asText()); } }); return String.format(\"UPDATE %s SET %s WHERE %s\", tableName, setClause.toString(), whereClause.toString()); } private String generateDeleteSQL(String tableName, JsonNode beforeNode) { StringBuilder whereClause = new StringBuilder(); beforeNode.fieldNames().forEachRemaining(fieldName -> { if (whereClause.length() > 0) { whereClause.append(\" AND \"); } JsonNode valueNode = beforeNode.get(fieldName); if (valueNode.isNull()) { whereClause.append(fieldName).append(\" IS NULL\"); } else if (valueNode.isTextual()) { whereClause.append(fieldName) .append(\" = \'\") .append(escapeSQL(valueNode.asText())) .append(\"\'\"); } else if (valueNode.isLong() && isTimestampField(fieldName)) { // 处理时间戳转换(纳秒/毫秒级) whereClause.append(fieldName) .append(\" = \'\") .append(formatTimestamp(valueNode.asLong())) .append(\"\'\"); } else { whereClause.append(fieldName) .append(\" = \") .append(valueNode.asText()); } }); return String.format(\"DELETE FROM %s WHERE %s\", tableName, whereClause.toString()); } // 判断字段是否为时间戳字段(根据命名约定或业务逻辑) private boolean isTimestampField(String fieldName) { return fieldName.toLowerCase().contains(\"time\") || fieldName.toLowerCase().contains(\"date\") || fieldName.toLowerCase().contains(\"ts\"); } // 格式化时间戳(支持纳秒/毫秒/秒级) private String formatTimestamp(long timestamp) { // 判断时间戳精度(假设大于1e16为纳秒,大于1e12为微秒,其余为毫秒/秒) if (timestamp > 1e16) { timestamp /= 1_000_000; // 纳秒转毫秒 } else if (timestamp > 1e12) { timestamp /= 1_000; // 微秒转毫秒 } else if (timestamp < 1e10) { timestamp *= 1_000; // 秒转毫秒 } // 使用Java 8时间API格式化(线程安全) return Instant.ofEpochMilli(timestamp) .atZone(ZoneId.systemDefault()) .format(DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern(\"yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss\")); } // SQL特殊字符转义(防止注入) private String escapeSQL(String input) { return input.replace(\"\'\", \"\'\'\"); } }); // 创建Kafka Sink KafkaSink kafkaSink = KafkaSink.builder() .setBootstrapServers(\"172.30.139.111:19092,172.30.139.111:29092,172.30.139.111:39092,172.30.139.111:49092\") // Kafka broker地址 .setRecordSerializer(KafkaRecordSerializationSchema.builder() .setTopic(\"dm-cdc-topic\") // Kafka主题名称 .setValueSerializationSchema(new SimpleStringSchema()) // 使用字符串序列化 .build() ) .setDeliverGuarantee(DeliveryGuarantee.EXACTLY_ONCE) // 精确一次交付 .setProperty(\"transaction.timeout.ms\", \"300000\") // 设置为5分钟(需小于Broker的15分钟限制) .setProperty(\"acks\", \"all\") // 确保高可靠性 .build(); // 构建数据处理管道 jsonStream.sinkTo(kafkaSink); // 将数据发送到Kafka env.execute(); }}五、FlinkCDC 达梦数据库 所需文件下载
5.1、所需Jar包

5.2、支持JAVA程序和SQL

5.3、完成程序和说明文档下载地址
版本1:
https://download.csdn.net/download/ytp552200ytp/90103896
版本2(最新版本截止:2025-06-03)
https://download.csdn.net/download/ytp552200ytp/91119461
如果实在没有CSDN积分,后台联系我留下邮箱,我看到后私信发到邮箱,支持共享。
6、情况说明
我看很多说没用,不增量啥的,核心原因是DM数据库没有配置好,按照上面的步骤去配置或查看文档中的说明操作,保证DM数据库归档日志正常,上面的代码直接可以使用拿去测试吧。归档日志查询SQL,查查核验一下!!!
1、通过开启归档日志 SQL查询处理 (SCN 作为标记增量查询)-- 查看所有归档日志文件信息SELECT * FROM SYS.V$ARCHIVED_LOG;-- 或使用以下视图查看归档文件详细信息SELECT * FROM SYS.V$ARCH_FILE;--添加文件DBMS_LOGMNR.ADD_LOGFILE(\'./dmarch/ARCHIVE_LOCAL1_0x1873DFE0_EP0_2025-06-26_11-34-09.log\')-- 或使用默认参数分析所有添加的日志DBMS_LOGMNR.START_LOGMNR(OPTIONS => 2130);--查询 日志明细SELECT *FROM V$LOGMNR_CONTENTSSELECT OPERATION_CODE, SCN, SQL_REDO, TIMESTAMP, SEG_OWNER, TABLE_NAME FROM V$LOGMNR_CONTENTSWHERE TABLE_NAME IS NOT NULL-- 查看特定表的操作SELECT OPERATION_CODE, SCN, SQL_REDO, TIMESTAMP, SEG_OWNER, TABLE_NAME FROM V$LOGMNR_CONTENTSWHERE TABLE_NAME = \'YOUR_TABLE_NAME\';-- 查看DDL操作SELECT SQL_REDO FROM V$LOGMNR_CONTENTS WHERE SQL_REDO LIKE \'%CREATE%\' OR SQL_REDO LIKE \'%ALTER%\' OR SQL_REDO LIKE \'%DROP%\';--结束日志分析DBMS_LOGMNR.END_LOGMNR();

