Windows电脑能装鸿蒙吗_Windows电脑体验鸿蒙电脑操作系统教程_虚拟机安装鸿蒙系统
鸿蒙电脑版操作系统来了,很多小伙伴想体验鸿蒙电脑版操作系统,可惜,鸿蒙系统并不支持你正在使用的传统的电脑来安装。不过可以通过可以使用华为官方提供的虚拟机,来体验大家心心念念的鸿蒙系统啦!注意:虚拟机里面没有应用商店,不能安装别的应用,如果你不会开发软件的话,真的就只能体验系统。

华为鸿蒙电脑操作系统介绍:
华为鸿蒙电脑操作系统,基于鸿蒙OS 5构建,从内核开始重构操作系统,采用微内核设计,支持多设备分布式调度。鸿蒙内核是高性能内核,更匹配全场景体验,支持资源精准供给、内存混合动态大页、精细化低功耗。华为鸿蒙PC操作系统凭借其独特的系统架构、友好的用户界面、强大的性能、丰富的生态兼容性以及诸多特色功能,为用户带来了全新的使用体验,有望在PC操作系统领域开辟新的局面,推动国产操作系统的发展。
华为鸿蒙电脑操作系统体验准备工作及要求说明:
1、 X86架构的windows操作系统(win10以上操作系统)
2、Windows 10 企业版、专业版或教育版及以上,且操作系统版本不低于10.0.18363。
3、具有二级地址转换 (SLAT) 的 64 位处理器。CPU支持AES指令集。CPU 支持 VM 监视器模式扩展(Intel CPU 的 VT-c 技术)。
4、系统内存最少8G,推荐16GB及以上。
5、不支持在虚拟机系统中运行模拟器。
6、系统OpenGL版本4.1及以上。
7、屏幕分辨率1280*800像素以上。
8、华为鸿蒙pc操作系统模拟器下载:https://pan.quark.cn/s/afea2bfd9ef0
华为鸿蒙电脑操作系统体验方法操作步骤:
1、下载后解压,像安装普通软件一样,运行devecostudio-windows-5.0.13.200.exe程序,如下图所示;

2、选择要安装的路径,我们一般默认情况可以不用更改,如下图所示;

3、安装完成后,首次打开,会问你是否导入配置,选择不导入,如下图所示;

4、遇到弹出下图类似的各种协议,都点Agree,接着选择打开虚拟机管理器,如下图所示;

5、此时,你的虚拟机还是一个空壳,没有安装操作系统。需要在华为提供的众多镜像中,选择你需要的。你可以选择手机、平板、二合一等系统镜像。如果要体验电脑版鸿蒙系统,滚动到最后,选Huawei_2in1,点它后面的下载按钮,如下图所示;


6、接着就是设置鸿蒙pc操作系统虚拟硬件配置,如果你的硬件够好,就给这个虚拟机多分配一点内存和存储空间,我就使用的默认8+6,越大越流畅,但你电脑其他东西会更卡,如下图所示;

7、设置好后,我们点击开始按钮就可以运行鸿蒙pc操作系统了,如下图所示;

8、开始加载鸿蒙PC操作系统,如下图所示;

9、鸿蒙PC操作系统加载成功,如下图所示;

华为鸿蒙电脑操作系统安装方法常见问答:
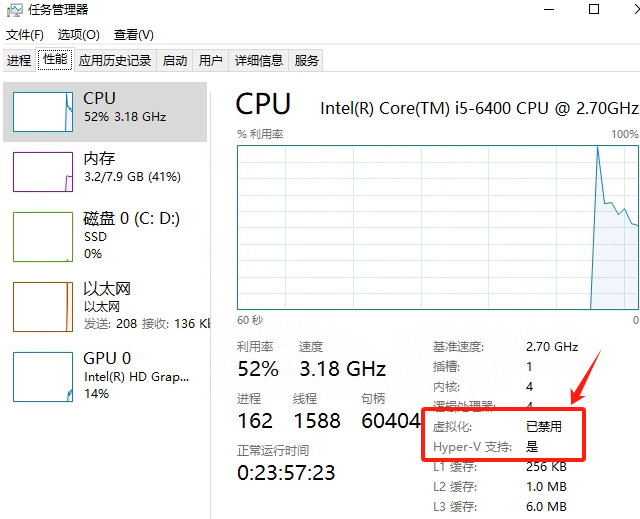
问:启动模拟器时,如果未开启Hyper-V,会弹窗提示“Hyper-V not enabled”,出现这种情况怎么处理?

答:1、请确保模拟器的运行环境符合要求。
2、如果CPU支持虚拟化,打开控制面板 > 程序 > 程序与功能 > 启动或关闭Windows功能(对于Windows 11系统,需打开系统 > 可选功能,在相关设置中点击更多Windows功能),找到并勾选“Hyper-V”、“Windows虚拟机监控程序平台”和“虚拟机平台”,点击确定并重启电脑。若勾选后启动模拟器仍提示错误,需以管理员权限打开命令行窗口,执行 `bcdedit /set hypervisorlaunchtype auto`,然后重启电脑。

3、若勾选后启动模拟器仍然提示该错误,需要以管理员权限打开命令行窗口执行以下命令,并重启电脑。
bcdedit /set hypervisorlaunchtype auto
4、如果上述步骤无法解决问题,打开任务管理器,切换到“性能”选项卡。如果显示虚拟化已禁用或未开启,说明 BIOS 中虚拟化功能未开启。请根据计算机主板型号,进入 BIOS 设置界面,开启虚拟化功能。(具体可参考bios中开启vt虚拟化教程)