浅入浅出redisson分布式锁_redissonclient.getlock
redisson分布式锁可重入原理
通过redissonClient.getLock获取到redisson分布式锁,其中有一个tryLock方法用于尝试获取锁
可以设置三个参数,包括尝试获取锁的等待时间,锁的过期时间,如果不设置过期时间则默认传一个-1
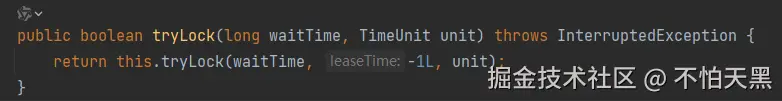
只要传了参数,最终都是调用以下的tryLock方法
![]()
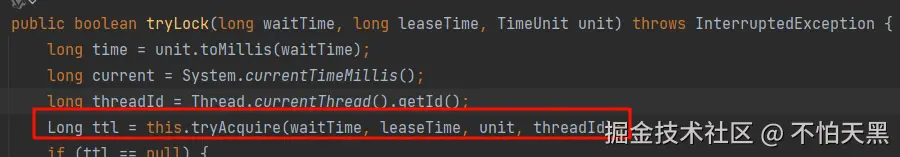
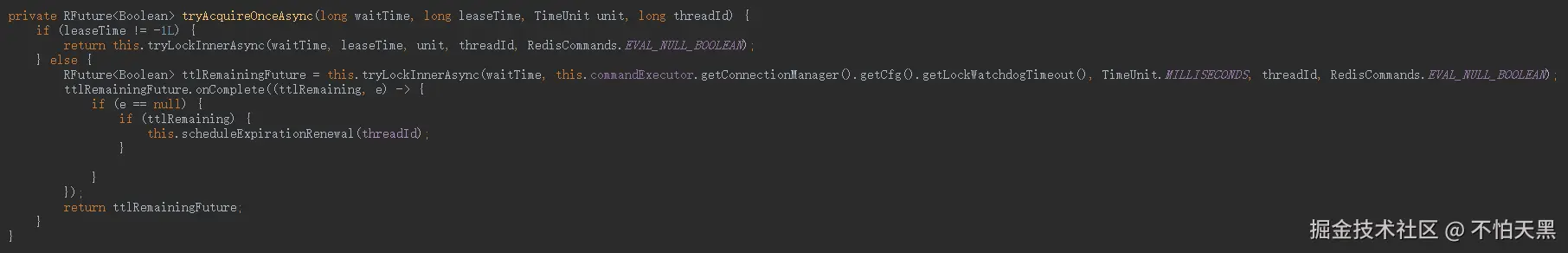
可以看到在方法中,如果自定义了锁的过期时间,则不走看门狗机制,即不进行锁的自动续期
如果没有设置锁的过期时间,则会进入else的执行逻辑,获取看门狗的默认过期时间(30秒),并设置相应的回调函数
在tryLockInnerAsync函数里面会执行lua脚本来是实现锁重入的逻辑
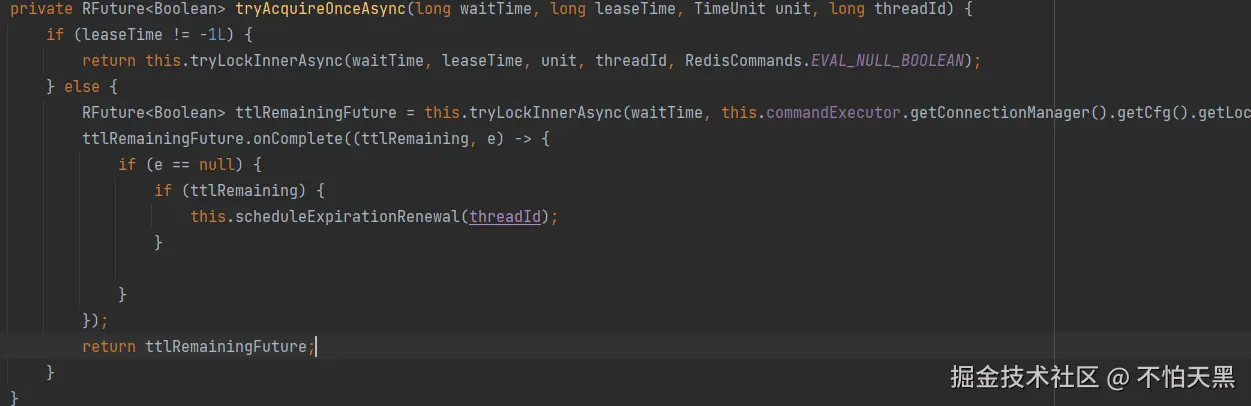
进入该方法后,尝试获取锁,并在里面使用lua脚本实现了一个可重入锁
具体来说,在redis中使用hash来存储锁的信息,包括锁名称,当前持有锁的标识(由线程id组成)以及锁的重入次数

lua脚本如下

整个执行逻辑为,首先通过大key判断当前需要获取的锁是否存在,如果不存在则将锁的标识设置为当前线程,同时将重入次数设置为1,最后设置锁的超时时间,pexpire表示以毫秒为单位设置过期时间
如果锁存在,进一步判断当前持有锁的线程标识是不是自己的,如果是自己的则将锁的重入次数加1,同时重置有效期
如果当前持有锁的线程不是自己,则返回锁的过期时间(以毫秒为单位)
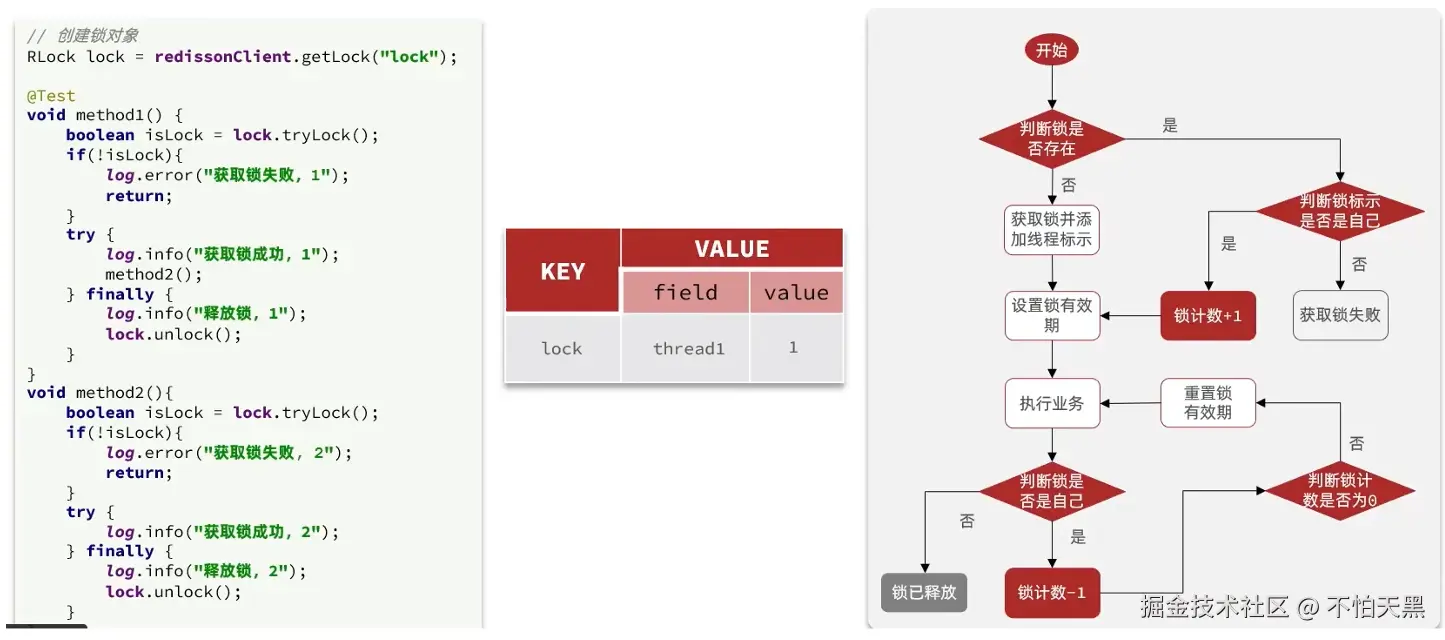
释放锁的逻辑
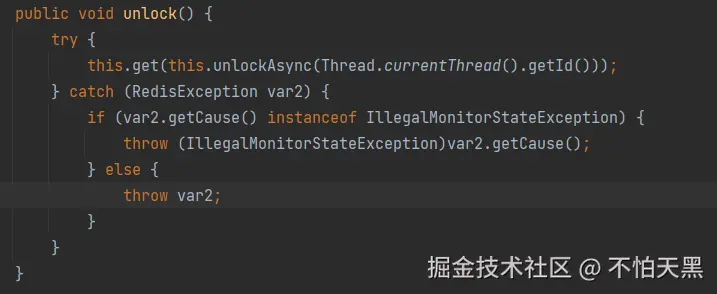
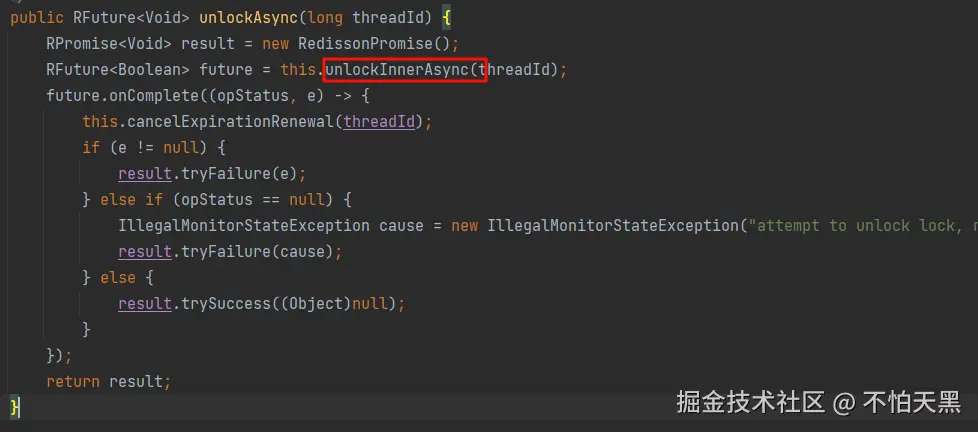
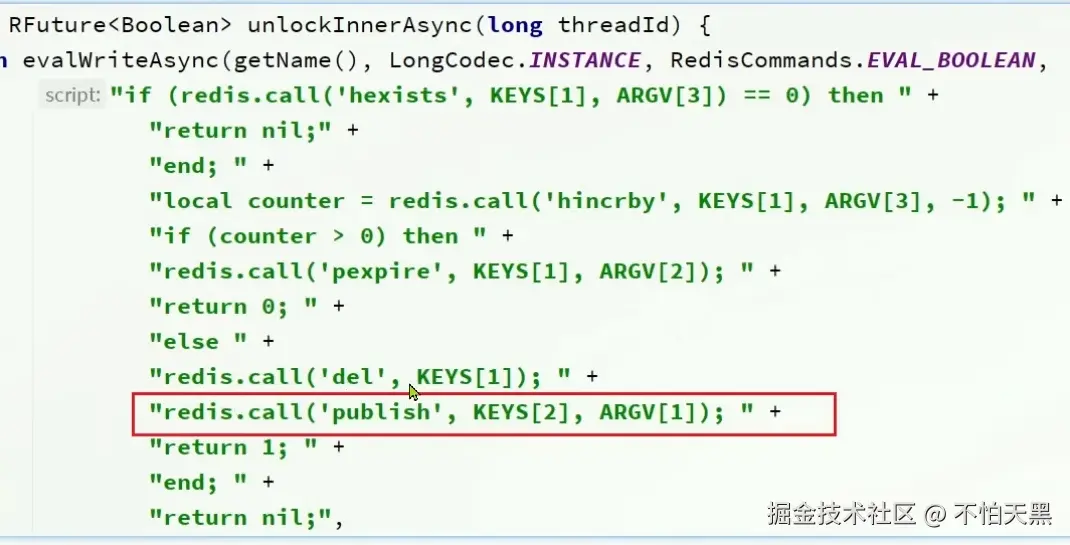
在unlockInnerAsync中调用lua脚本进行锁的释放操作
执行逻辑为,先判断锁是不是自己的,如果不是则直接返回
如果是自己的,将锁的重入次数减1,然后判断剩余的锁重入次数,如果大于0则重置有效期,否则需要将锁释放,即删除key;并使用发布订阅机制将锁释放的消息通知
这里的参数如下:
- key:
key有两个参数,分别是锁的名称以及发布订阅消息的频道
- argv:
argv有三个参数,分别是发布的消息、锁的超时释放时间以及锁的重入次数
![]()
redisson锁重试和watchdog机制
从上面的lua脚本可以得知,如果成功获取到了锁或者进行了锁重入的操作,则会返回null,否则会返回锁的剩余有效期
锁的重试使用到了发布订阅和 信号量机制
ini
代码解读
复制代码
public boolean tryLock(long waitTime, long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException { //将获取锁的超时等待时间转化为毫秒形式 long time = unit.toMillis(waitTime); //获取当前时间 long current = System.currentTimeMillis(); //获取尝试获取锁的线程id long threadId = Thread.currentThread().getId(); //尝试获取锁,使用lua脚本实现锁重入,并设置看门狗机制进行锁的自动续期 //如果获取锁失败,则返回的值为锁的剩余有效期 Long ttl = this.tryAcquire(waitTime, leaseTime, unit, threadId); if (ttl == null) { //获取锁成功,直接返回true return true; } else { //进行锁重试,同时超时时间减去上次获取锁的时间得到剩余的锁超时时间 time -= System.currentTimeMillis() - current; if (time <= 0L) { //剩余的锁超时时间不够了,返回获取失败 this.acquireFailed(waitTime, unit, threadId); return false; } else { //计算当前时间 current = System.currentTimeMillis(); //订阅锁的释放通知,锁释放的时候能够及时接收到消息 //这里锁获取失败后并不是立刻重现竞争获取锁,而是等待通知,避免无谓的cpu消耗 RFuture subscribeFuture = this.subscribe(threadId); //在剩余的超时等待时间等待通知,如果等到了相应的消息则返回true否则返回false if (!subscribeFuture.await(time, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS)) { //取消订阅锁释放通知并返回false if (!subscribeFuture.cancel(false)) { subscribeFuture.onComplete((res, e) -> { if (e == null) { this.unsubscribe(subscribeFuture, threadId); } }); } this.acquireFailed(waitTime, unit, threadId); return false; } else { //成功等到了锁释放的通知 try { //再次获取到现在的剩余的锁等待时间 time -= System.currentTimeMillis() - current; if (time <= 0L) { this.acquireFailed(waitTime, unit, threadId); boolean var20 = false; return var20; } else { boolean var16; do { long currentTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); ttl = this.tryAcquire(waitTime, leaseTime, unit, threadId); if (ttl == null) { var16 = true; return var16; } time -= System.currentTimeMillis() - currentTime; if (time = 0L && ttl 0L); this.acquireFailed(waitTime, unit, threadId); var16 = false; return var16; } } finally { this.unsubscribe(subscribeFuture, threadId); } } } }
接下来看tryAcquire查看具体的看门狗机制实现原理
kotlin
代码解读
复制代码
private RFuture tryAcquireOnceAsync(long waitTime, long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit, long threadId) { if (leaseTime != -1L) { return this.tryLockInnerAsync(waitTime, leaseTime, unit, threadId, RedisCommands.EVAL_NULL_BOOLEAN); } else { RFuture ttlRemainingFuture = this.tryLockInnerAsync(waitTime, this.commandExecutor.getConnectionManager().getCfg().getLockWatchdogTimeout(), TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS, threadId, RedisCommands.EVAL_NULL_BOOLEAN); //这里成功获取锁之后,会执行以下的回调函数 //这两个参数分别是执行结果即剩余有效期以及异常 ttlRemainingFuture.onComplete((ttlRemaining, e) -> { if (e == null) { if (ttlRemaining) { //获取锁成功后,进行过期时间的续约 this.scheduleExpirationRenewal(threadId); } } }); return ttlRemainingFuture; } }
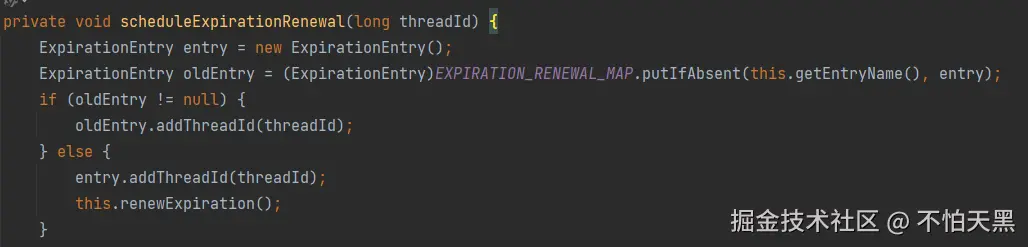
接下来看scheduleExpirationRenewal具体代码
这个putIfAbsent可以保证不管锁重入了多少次,每次拿到的ExpirationEntry拿到的都是同一个值
这个ExpirationEntry保存了每个线程的线程id以及锁的重入次数的对应关系,同时保存了每个锁的延时任务(主要是用来进行锁的续约,接下来会讲)
![]()
java
代码解读
复制代码
public static class ExpirationEntry { private final Map threadIds = new LinkedHashMap(); private volatile Timeout timeout; public ExpirationEntry() { } public synchronized void addThreadId(long threadId) { Integer counter = (Integer)this.threadIds.get(threadId); if (counter == null) { counter = 1; } else { counter = counter + 1; } this.threadIds.put(threadId, counter); } public synchronized boolean hasNoThreads() { return this.threadIds.isEmpty(); } public synchronized Long getFirstThreadId() { return this.threadIds.isEmpty() ? null : (Long)this.threadIds.keySet().iterator().next(); } public synchronized void removeThreadId(long threadId) { Integer counter = (Integer)this.threadIds.get(threadId); if (counter != null) { counter = counter - 1; if (counter == 0) { this.threadIds.remove(threadId); } else { this.threadIds.put(threadId, counter); } } } public void setTimeout(Timeout timeout) { this.timeout = timeout; } public Timeout getTimeout() { return this.timeout; } }
接下来看真正的续约函数
kotlin
代码解读
复制代码
private void renewExpiration() { ExpirationEntry ee = (ExpirationEntry)EXPIRATION_RENEWAL_MAP.get(this.getEntryName()); if (ee != null) { //设置一个延时任务,该任务有两个主要参数,超时任务本身以及延时时间 Timeout task = this.commandExecutor.getConnectionManager().newTimeout(new TimerTask() { public void run(Timeout timeout) throws Exception { ExpirationEntry ent = (ExpirationEntry)RedissonLock.EXPIRATION_RENEWAL_MAP.get(RedissonLock.this.getEntryName()); if (ent != null) { Long threadId = ent.getFirstThreadId(); if (threadId != null) { //重置有效期 RFuture future = RedissonLock.this.renewExpirationAsync(threadId); //重置有效期后再次调用当前函数,相当于实现了一个递归的逻辑 future.onComplete((res, e) -> { if (e != null) { RedissonLock.log.error(\"Can\'t update lock \" + RedissonLock.this.getName() + \" expiration\", e); } else { if (res) { RedissonLock.this.renewExpiration(); } } }); } } } }, this.internalLockLeaseTime / 3L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS); ee.setTimeout(task); } }
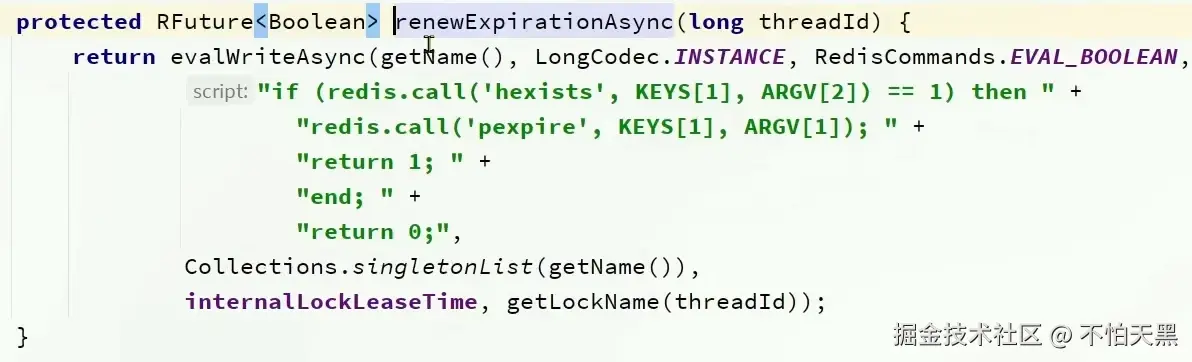
renewExpirationAsync刷新有效期,执行了一个lua脚本
判断如果锁是自己的则进行有效期的重置
锁释放时取消续约
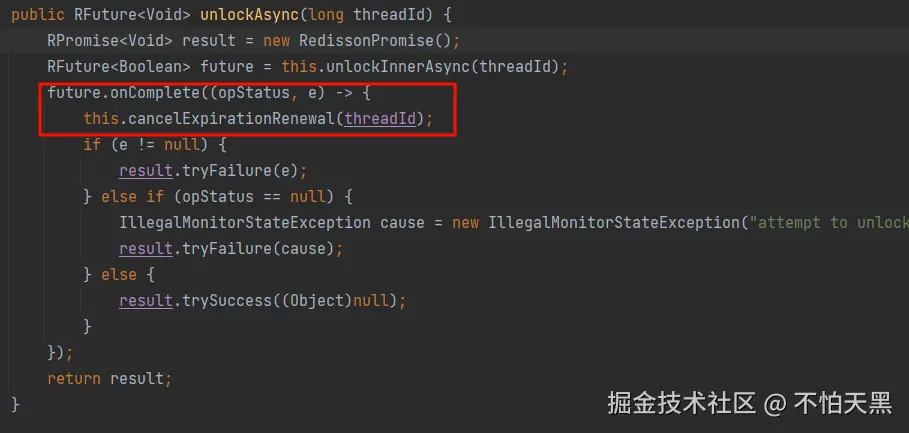
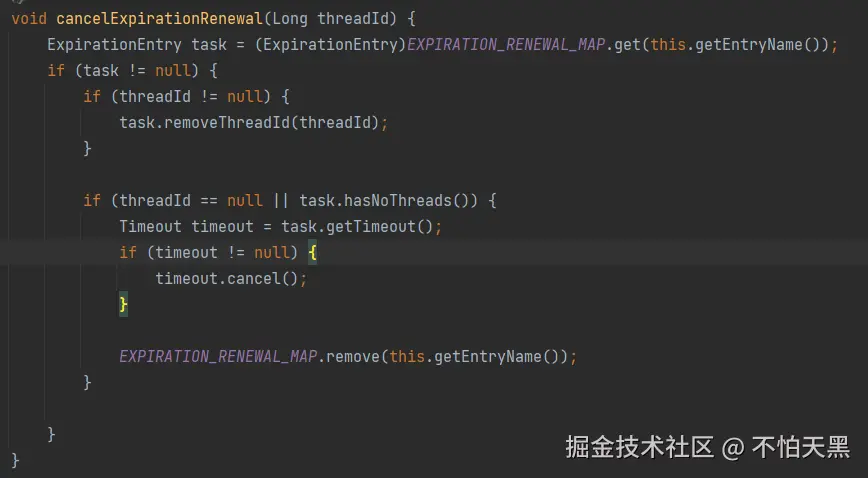
因为ExpirationEntry存储了线程id以及对应的锁重入次数,同时存储了该锁对应的一个用于续约的延时任务
所以取消续约,就是获取根据线程id重新设置ExpirationEntry中的锁重入次数,然后将这个锁对应的延时任务进行取消
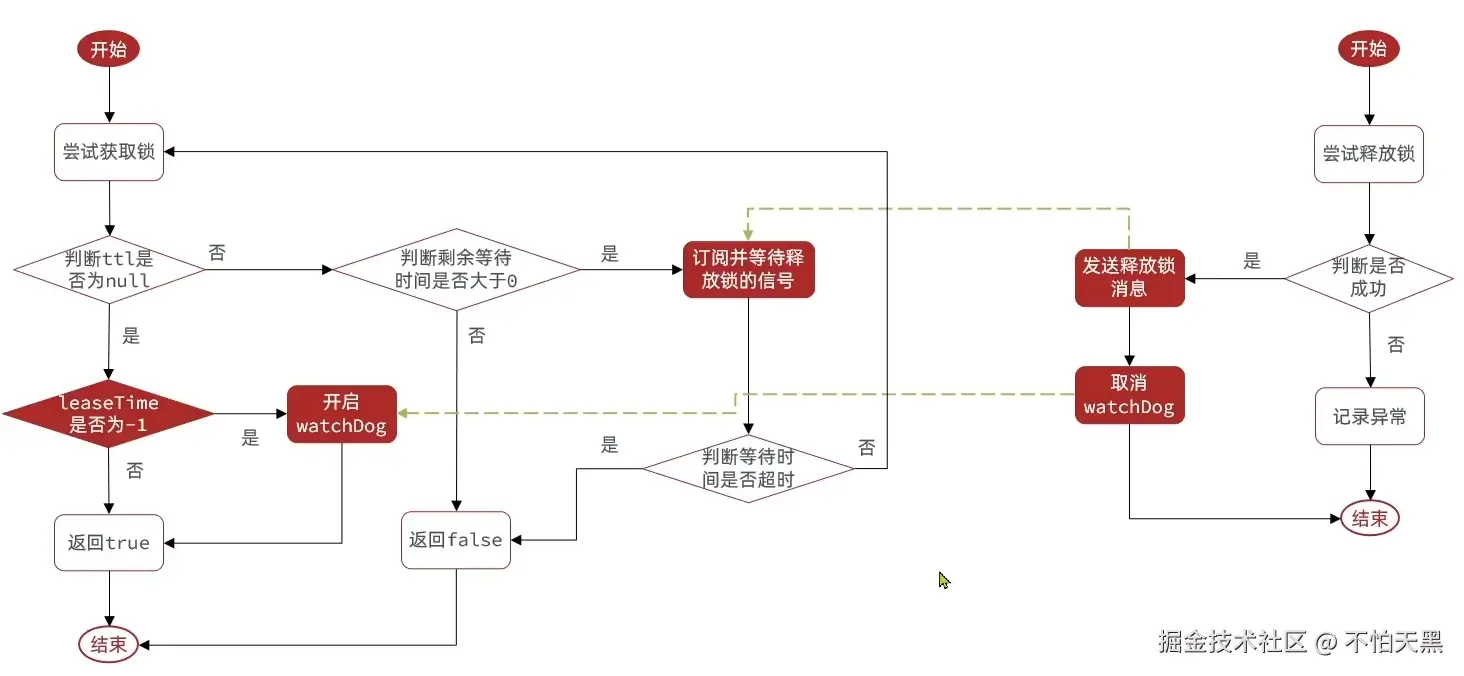

redisson解决主从一致性问题
redis主从模式下,由于主从节点的数据同步有一定延迟,导致主节点成功设置了锁,但是还没有将锁的信息同步到从节点,这时候如果有其它线程在从节点上发现没有锁的相关信息,则也会获取到锁
这时候就出现了线程安全问题,即同时有多个线程同时获取到了锁,进入临界区对共享资源进行操作

或者说在主从模式下,主节点成功设置了锁,但是没有同步到从节点,这时候主节点宕机了,哨兵会从从节点中重新选取新的主节点,但是新的主节点中并没有刚刚的设置的锁的相关信息导致多个线程同时获取到了锁
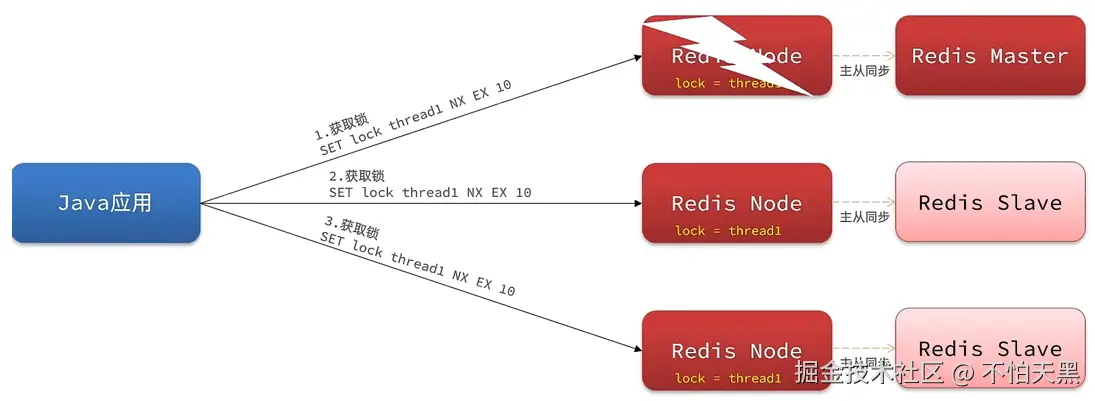
为了解决这个问题,redission提出来了MutiLock锁,使用这把锁咱们就不使用主从了,每个节点的地位 都是一样的, 这把锁加锁的逻辑需要写入到每一个主丛节点上,只有所有的服务器都写入成功,此时才 是加锁成功,假设现在某个节点挂了,那么他去获得锁的时候,只要有一个节点拿不到,都不能算是加 锁成功,就保证了加锁的可靠性。
连锁的获取
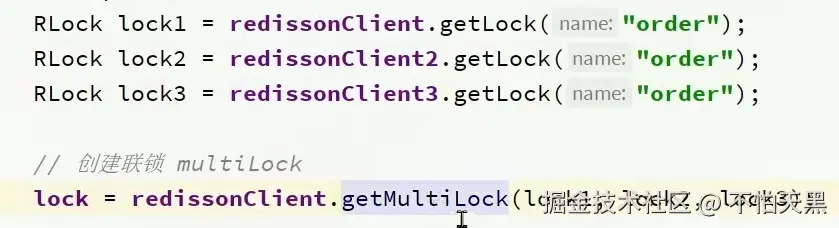
连锁实际上是用一个集合保存了所有的锁
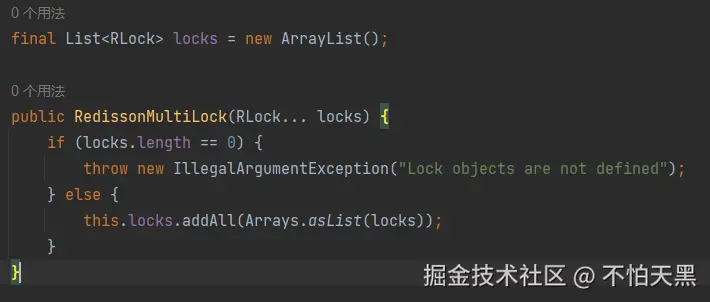
ini
代码解读
复制代码
public boolean tryLock(long waitTime, long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException { long newLeaseTime = -1L; if (leaseTime != -1L) { //如果设置了释放时间,则将超时等待时间进行重置 //至少保证锁重试期间锁不会超时 if (waitTime == -1L) { newLeaseTime = unit.toMillis(leaseTime); } else { newLeaseTime = unit.toMillis(waitTime) * 2L; } } long time = System.currentTimeMillis(); long remainTime = -1L; if (waitTime != -1L) { remainTime = unit.toMillis(waitTime); } long lockWaitTime = this.calcLockWaitTime(remainTime); int failedLocksLimit = this.failedLocksLimit(); List acquiredLocks = new ArrayList(this.locks.size()); ListIterator iterator = this.locks.listIterator(); while(iterator.hasNext()) { RLock lock = (RLock)iterator.next(); boolean lockAcquired; try { if (waitTime == -1L && leaseTime == -1L) { lockAcquired = lock.tryLock(); } else { long awaitTime = Math.min(lockWaitTime, remainTime); lockAcquired = lock.tryLock(awaitTime, newLeaseTime, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS); } } catch (RedisResponseTimeoutException var21) { this.unlockInner(Arrays.asList(lock)); lockAcquired = false; } catch (Exception var22) { lockAcquired = false; } if (lockAcquired) { acquiredLocks.add(lock); } else { if (this.locks.size() - acquiredLocks.size() == this.failedLocksLimit()) { break; } if (failedLocksLimit == 0) { this.unlockInner(acquiredLocks); if (waitTime == -1L) { return false; } failedLocksLimit = this.failedLocksLimit(); acquiredLocks.clear(); while(iterator.hasPrevious()) { iterator.previous(); } } else { --failedLocksLimit; } } if (remainTime != -1L) { remainTime -= System.currentTimeMillis() - time; time = System.currentTimeMillis(); if (remainTime <= 0L) { this.unlockInner(acquiredLocks); return false; } } } if (leaseTime != -1L) { List<RFuture> futures = new ArrayList(acquiredLocks.size()); Iterator var24 = acquiredLocks.iterator(); while(var24.hasNext()) { RLock rLock = (RLock)var24.next(); RFuture future = ((RedissonLock)rLock).expireAsync(unit.toMillis(leaseTime), TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS); futures.add(future); } var24 = futures.iterator(); while(var24.hasNext()) { RFuture rFuture = (RFuture)var24.next(); rFuture.syncUninterruptibly(); } } return true; }


