基于CanMV K230视觉检测模块开发的井字棋AI视觉检测项目(2024年电赛E题参考)_k230井字棋决策
实物检测效果
实物检测并下棋视频
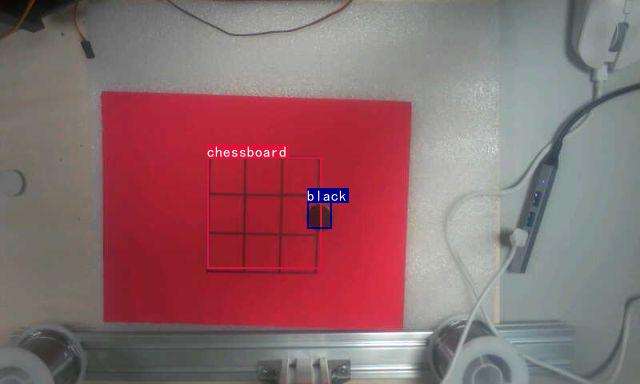
三子棋检测
图片检测效果

硬件准备
01科技的CanMV K230开发板

软件部分详细教程
关于K230的基础操作(如固件安装、程序下载等),01科技官网提供了详细教程,此处不再重复说明。
如何制作自己的AI视觉检测项目?
1.准备自己的数据集
建议使用K230运行摄像程序采集图像数据,这样能有效提升识别精度。数据集规模需根据目标复杂度灵活调整——例如针对棋盘和棋子这类识别任务,我通过拍摄170余张样本照片构建了数据集。
摄像程序代码如下
\'\'\'实验名称:按键拍照保存实验平台:01Studio CanMV K230说明:实现摄像头图像拍照保存到SD卡,使用v1.2.2以上版本micropython固件。\'\'\'import time, os, sysfrom machine import FPIOA,Pinfrom media.sensor import * #导入sensor模块,使用摄像头相关接口from media.display import * #导入display模块,使用display相关接口from media.media import * #导入media模块,使用meida相关接口sensor = Sensor() #构建摄像头对象sensor.reset() #复位和初始化摄像头sensor.set_framesize(Sensor.FHD) #设置帧大小FHD(1920x1080),默认通道0sensor.set_pixformat(Sensor.RGB565) #设置输出图像格式,默认通道0#使用IDE缓冲区输出图像,显示尺寸和sensor配置一致。Display.init(Display.VIRT, sensor.width(), sensor.height())MediaManager.init() #初始化media资源管理器sensor.run() #启动sensortime.sleep_ms(200) #等待摄像头稳定clock = time.clock()#将GPIO21配置为普通GPIO模式fpioa = FPIOA()fpioa.set_function(21,FPIOA.GPIO21)KEY=Pin(21,Pin.IN,Pin.PULL_UP) #构建KEY对象state=0 #LED引脚状态num = 0while True: clock.tick() img = sensor.snapshot() #拍摄一张图 Display.show_image(img) #显示图片 if KEY.value()==0: #按键被按下 time.sleep_ms(10) #消除抖动 if KEY.value()==0: #确认按键被按下 state=not state #使用not语句而非~语句 print(\'KEY\') while not KEY.value(): #检测按键是否松开 pass #将当前img图片保存 img1 = img.crop(roi=(0,0,1920,1080)) #保存图片分辨率可以自行修改,比初始化摄像分辨率小即可 img1.save(\'/data/img/\' + str(num) + \'.jpg\') num=num+1 #图片名称用 print(clock.fps()) #打印FPS程序运行后,按下K230板载的KEY按键即可拍摄照片,再次按压可实现连续拍摄功能,所有拍摄的图像将自动保存在data文件夹中。
2.制作目标检测AI模型
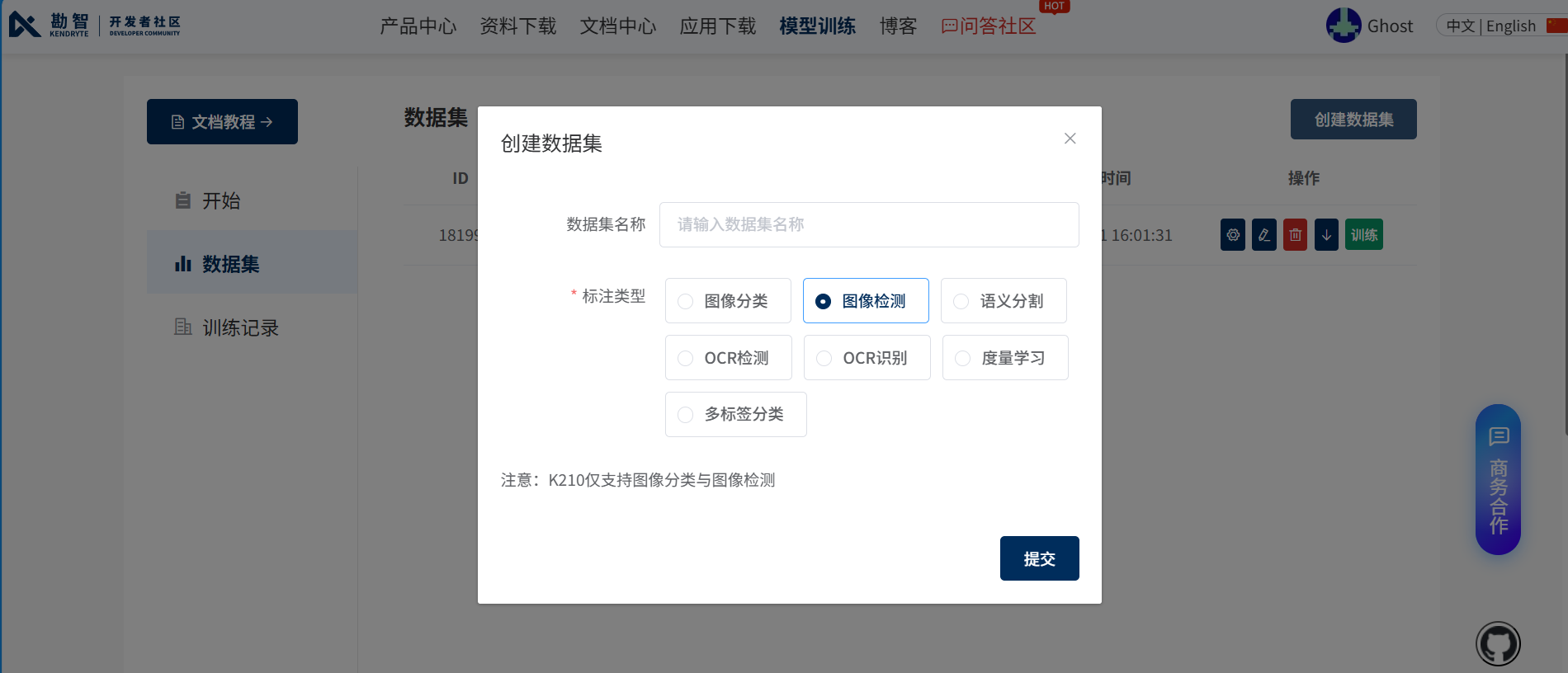
进入嘉楠模型训练网站,注册好账号。链接如下:https://www.kendryte.com/zh/training/dataset
选择创建数据集
选择上传图片/数据集
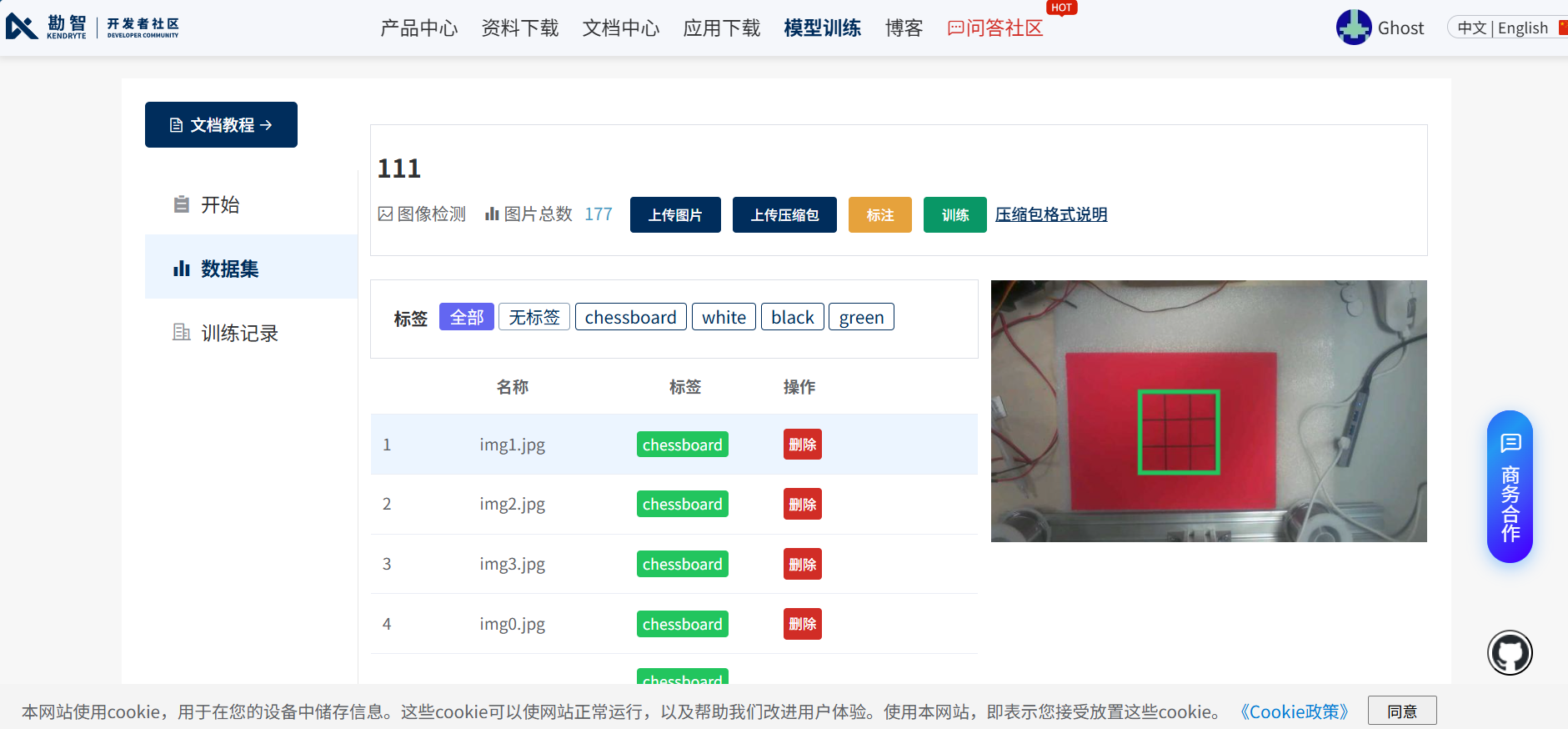
标注图片,将想要检测的物体画进检测框
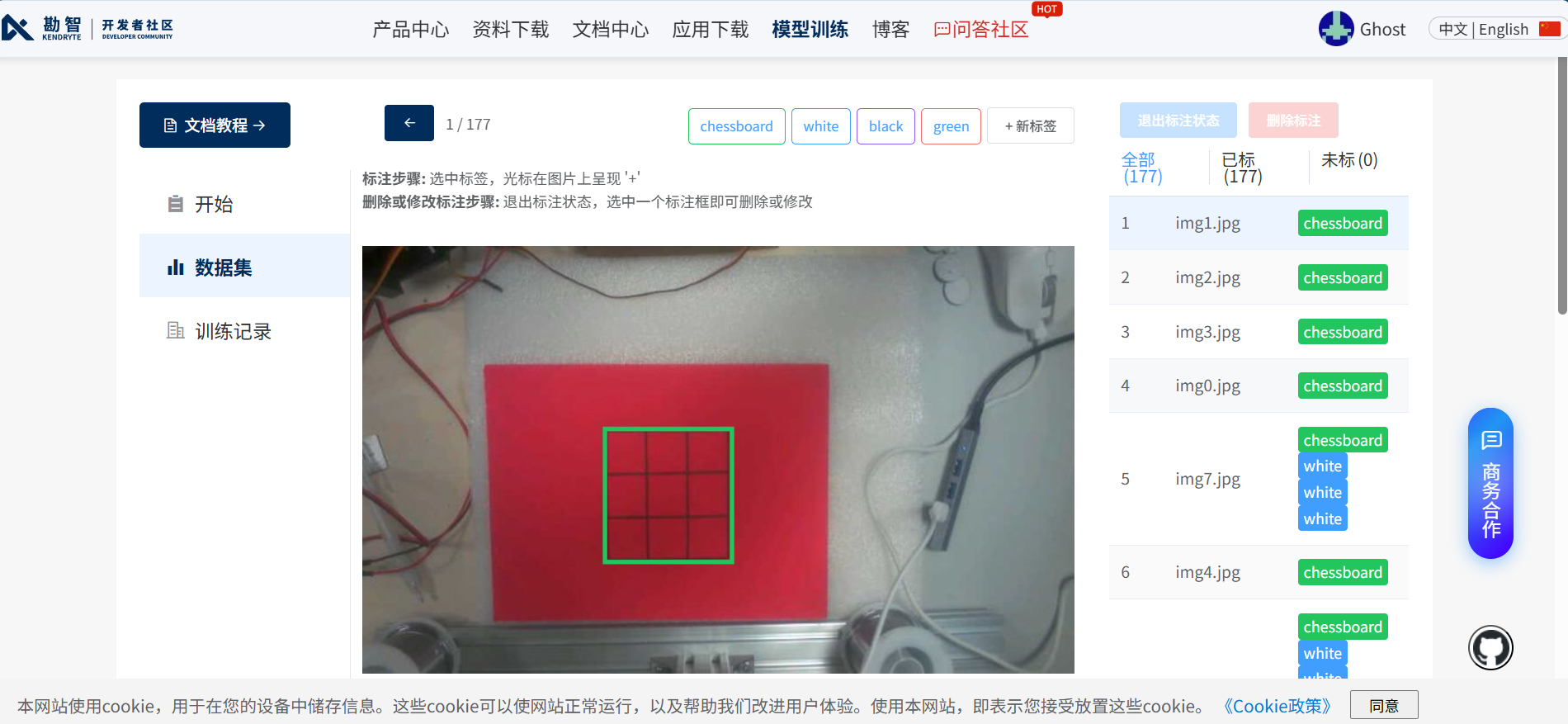
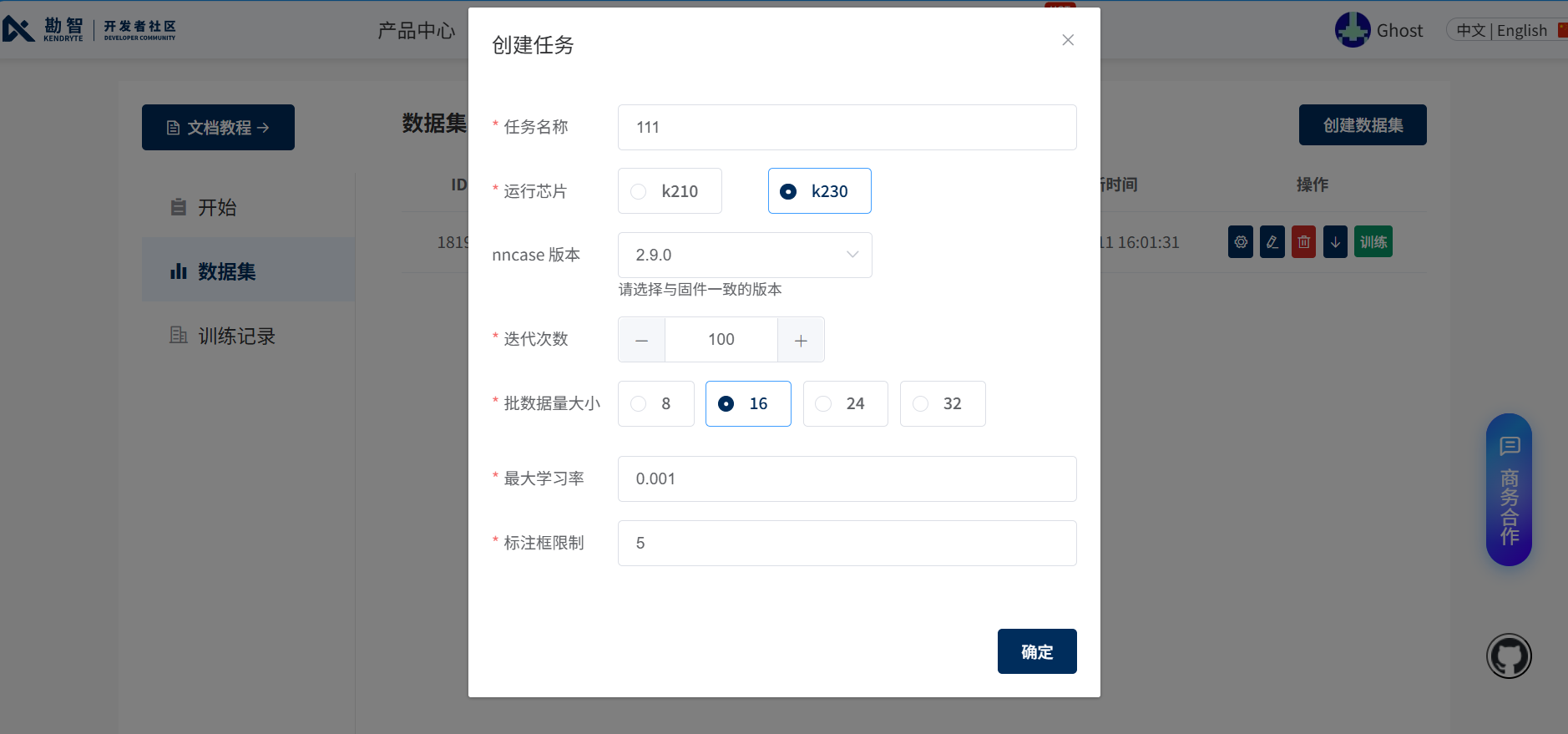
确认所有图片标注无误后进行训练,参数按需求选择
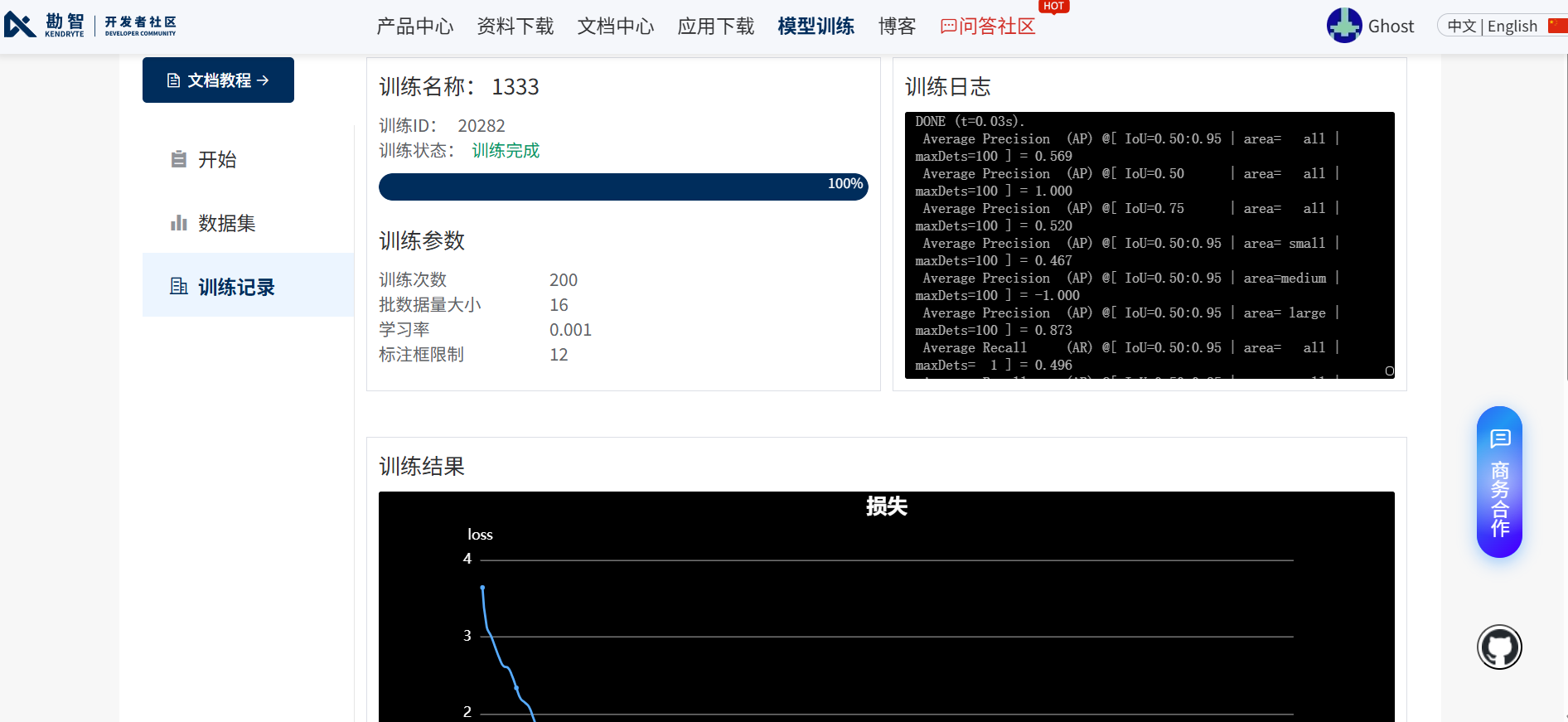
模型自动在云端开始训练,训练完成后会发至注册的邮箱
3.开始识别
下载发送的压缩包
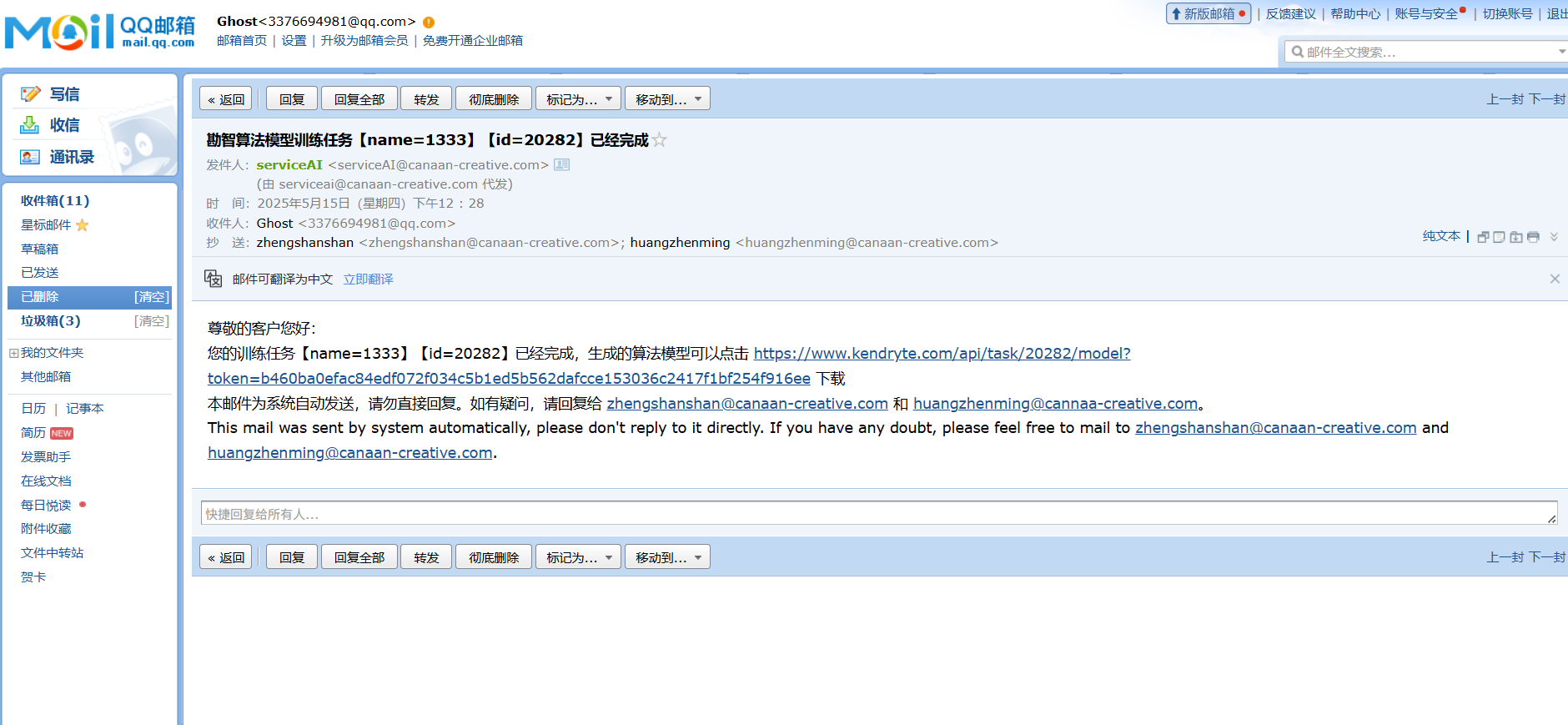
只需要将压缩包中的这个文件夹放入K230的SD卡,其他文件无需处理。
这里提供四个文件:
- AI模型文件
- 配置文件
- 包含目标标注检测功能的Python脚本
- 实时识别代码(运行即可查看效果)
若识别效果不理想,建议:
- 调整拍摄数量和光线条件
- 根据需要修改代码,例如增加图像处理功能来优化识别效果
检测代码(识别棋子棋盘专供)
代码由两大核心模块构成:识别模块与通信模块。
识别模块负责:
- 实时识别棋盘上的棋子状态
- 将识别的坐标数据进行处理
- 将处理后的数据存入数组
通信模块实现:
- 通过串口将数组数据发送至单片机
- 单片机解析接收的数据
import osimport ujsonimport aicubefrom libs.PipeLine import ScopedTimingfrom libs.Utils import *from media.sensor import *from media.display import *from media.media import *import nncase_runtime as nnimport ulab.numpy as npimport imageimport gcfrom machine import UART, FPIOA, TOUCHimport time# -----------------------# UART & Display Setup# -----------------------fpioa = FPIOA()fpioa.set_function(3, FPIOA.UART1_TXD)fpioa.set_function(4, FPIOA.UART1_RXD)uart = UART(UART.UART1, 115200)# 使用 hdmi 模式display_mode = \"hdmi\"if display_mode == \"lcd\": DISPLAY_WIDTH = ALIGN_UP(800, 16) DISPLAY_HEIGHT = 480else: DISPLAY_WIDTH = ALIGN_UP(1920, 16) DISPLAY_HEIGHT = 1080OUT_RGB888P_WIDTH = ALIGN_UP(1280, 16)OUT_RGB888P_HEIGHT = 720# -----------------------# File Paths# -----------------------root_path = \"/sdcard/mp_deployment_source/\"config_path = root_path + \"deploy_config.json\"# -----------------------# 全局变量:保存上一帧检测到的棋盘区域# -----------------------prev_chessboard = None # 格式:(x, y, w, h)# -----------------------# 辅助函数:计算图像填充参数# -----------------------def two_side_pad_param(input_size, output_size): ratio_w = output_size[0] / input_size[0] ratio_h = output_size[1] / input_size[1] ratio = min(ratio_w, ratio_h) new_w = int(ratio * input_size[0]) new_h = int(ratio * input_size[1]) dw = (output_size[0] - new_w) / 2 dh = (output_size[1] - new_h) / 2 top = int(round(dh - 0.1)) bottom = int(round(dh + 0.1)) left = int(round(dw - 0.1)) right = int(round(dw + 0.1)) return top, bottom, left, right, ratio# -----------------------# 辅助函数:读取配置文件# -----------------------def read_deploy_config(path): try: with open(path, \'r\') as f: return ujson.load(f) except Exception as e: print(\"JSON解析错误:\", e) return None# -----------------------# 新数据包构造函数:只发送10个数据# -----------------------def make_packet(chessboard_box, pieces): \"\"\" chessboard_box: (x, y, w, h) (显示坐标);如果当前未检测到,则用上一帧值 pieces: list of (cx, cy, color) ;其中color: 黑棋→1,白棋→2 Data Packet (10 numbers): Data[0] = 0xE8 (校验位) Data[1:10]: 对应棋盘九宫格中每个格子的状态, 如果该格子中心附近(距离<=50像素)检测到棋子,则发送该棋子的颜色(1或2),否则发送0。 \"\"\" packet = [] packet.append(0xE8) if chessboard_box is None: # 没有棋盘则后面9个全部为0 packet.extend([0]*9) return bytearray(packet) x, y, w, h = chessboard_box # 计算棋盘九宫格中心(行优先) cell_centers = [] cell_w = w / 3.0 cell_h = h / 3.0 for row in range(3): for col in range(3): cx = int(x + col * cell_w + cell_w/2) cy = int(y + row * cell_h + cell_h/2) cell_centers.append((cx, cy)) # 对每个 cell 查找最近的棋子 cell_state = [0] * 9 for i, cell in enumerate(cell_centers): best_dist = 1e9 best_color = 0 for p in pieces: dist = ((p[0]-cell[0])**2 + (p[1]-cell[1])**2)**0.5 if dist < 50 and dist < best_dist: best_dist = dist best_color = p[2] if best_dist 1, white -> 2 rgb_img = sensor.snapshot(chn=CAM_CHN_ID_2) try: if rgb_img.format() != image.RGBP888: continue except Exception as e: print(\"获取图像异常:\", e) continue # 使用原始图像进行预处理 ai2d_input = rgb_img.to_numpy_ref() ai2d_input_tensor = nn.from_numpy(ai2d_input) ai2d_builder.run(ai2d_input_tensor, ai2d_output_tensor) kpu.set_input_tensor(0, ai2d_output_tensor) kpu.run() results = [] for i in range(kpu.outputs_size()): out_data = kpu.get_output_tensor(i) res_arr = out_data.to_numpy().reshape(-1) del out_data results.append(res_arr) det_boxes = aicube.anchorbasedet_post_process( results[0], results[1], results[2], kmodel_frame_size, frame_size, strides, num_classes, confidence_threshold, nms_threshold, anchors, nms_option ) # 如果返回为平铺数组,则按每6个数字分组 if det_boxes: if not isinstance(det_boxes[0], (list, tuple)): new_boxes = [] for i in range(0, len(det_boxes), 6): box = det_boxes[i:i+6] if len(box) == 6: new_boxes.append(box) det_boxes = new_boxes osd_img.clear() if det_boxes: for box in det_boxes: label = labels[box[0]].lower() x1 = box[2] y1 = box[3] x2 = box[4] y2 = box[5] x_disp = int(x1 * DISPLAY_WIDTH // OUT_RGB888P_WIDTH) y_disp = int(y1 * DISPLAY_HEIGHT // OUT_RGB888P_HEIGHT) w_disp = int((x2 - x1) * DISPLAY_WIDTH // OUT_RGB888P_WIDTH) h_disp = int((y2 - y1) * DISPLAY_HEIGHT // OUT_RGB888P_HEIGHT) osd_img.draw_rectangle(x_disp, y_disp, w_disp, h_disp, color=(255,0,0)) if label == \"chessboard\": if chessboard_box is None or (w_disp * h_disp) > (chessboard_box[2] * chessboard_box[3]): chessboard_box = (x_disp, y_disp, w_disp, h_disp) elif label in [\"black\", \"white\"]: center = (x_disp + w_disp//2, y_disp + h_disp//2) color_val = 1 if label == \"black\" else 2 pieces.append((center[0], center[1], color_val)) osd_img.draw_string_advanced(x_disp, y_disp-40, 32, labels[box[0]], color=(255,255,255)) # 如果本帧未检测到棋盘,则采用上一帧棋盘坐标 if chessboard_box is None and prev_chessboard is not None: chessboard_box = prev_chessboard elif chessboard_box is not None: prev_chessboard = chessboard_box # 根据棋盘计算九宫格中心,并判断每个格子是否有棋子 cell_values = [0]*9 if chessboard_box is not None: x, y, w, h = chessboard_box cell_centers = [] cell_w = w / 3.0 cell_h = h / 3.0 for row in range(3): for col in range(3): cx = int(x + col * cell_w + cell_w/2) cy = int(y + row * cell_h + cell_h/2) cell_centers.append((cx, cy)) for i, cell in enumerate(cell_centers): best_dist = 1e9 best_color = 0 for p in pieces: dist = ((p[0]-cell[0])**2 + (p[1]-cell[1])**2)**0.5 if dist < 50 and dist < best_dist: best_dist = dist best_color = p[2] if best_dist < 50: cell_values[i] = best_color else: cell_values[i] = 0 # 构造数据包(10个数:第一个为0xE8,其余9个为格子值) packet = make_packet(chessboard_box, pieces) # 新的make_packet根据上述逻辑构造 uart.write(packet) print(packet) # 显示结果图像 Display.show_image(osd_img, 0, 0, Display.LAYER_OSD3) gc.collect() time.sleep(0.1) rgb_img = None sensor.stop() Display.deinit() MediaManager.deinit() gc.collect() time.sleep(0.1) nn.shrink_memory_pool() print(\"det_infer end\") return 0if __name__ == \"__main__\": detection()软件部分开发完毕,效果如视频所示。
另附下棋算法供单片机使用(c语言版)
#include #include #define SIZE 3 // 棋盘尺寸 3x3// 初始化棋盘,将所有单元格置为空格 \' \'void initBoard(char board[SIZE][SIZE]) { int i, j; for (i = 0; i < SIZE; i++) { for (j = 0; j < SIZE; j++) { board[i][j] = \' \'; } }}// 打印棋盘,用于调试或显示当前棋局状态void printBoard(char board[SIZE][SIZE]) { int i, j; printf(\"\\n\"); for (i = 0; i < SIZE; i++) { for (j = 0; j < SIZE; j++) { printf(\" %c \", board[i][j]); if (j < SIZE - 1) printf(\"|\"); } printf(\"\\n\"); if (i < SIZE - 1) printf(\"---+---+---\\n\"); } printf(\"\\n\");}// 尝试在指定位置落子,若该位置为空则放置棋子并返回 1,否则返回 0int makeMove(char board[SIZE][SIZE], int row, int col, char piece) { if (row = SIZE || col = SIZE) { return 0; } if (board[row][col] == \' \') { board[row][col] = piece; return 1; } return 0;}// 判断棋盘中是否还存在空位,若存在返回 1,否则返回 0(棋盘已满)int isMovesLeft(char board[SIZE][SIZE]) { int i, j; for (i = 0; i < SIZE; i++) { for (j = 0; j < SIZE; j++) { if (board[i][j] == \' \') return 1; } } return 0;}// 评估当前棋盘状态// 若 ai(电脑)赢则返回 +10,若 human 赢则返回 -10,否则返回 0int evaluate(char board[SIZE][SIZE], char ai, char human) { int i; // 检查行 for (i = 0; i < SIZE; i++) { if (board[i][0] == board[i][1] && board[i][1] == board[i][2]) { if (board[i][0] == ai) return 10; else if (board[i][0] == human) return -10; } } // 检查列 for (i = 0; i < SIZE; i++) { if (board[0][i] == board[1][i] && board[1][i] == board[2][i]) { if (board[0][i] == ai) return 10; else if (board[0][i] == human) return -10; } } // 检查两条对角线 if (board[0][0] == board[1][1] && board[1][1] == board[2][2]) { if (board[0][0] == ai) return 10; else if (board[0][0] == human) return -10; } if (board[0][2] == board[1][1] && board[1][1] == board[2][0]) { if (board[0][2] == ai) return 10; else if (board[0][2] == human) return -10; } return 0;}// 使用 Minimax 算法计算最佳分数// 参数 depth 用以减少获胜步数的影响(提倡快赢或慢输)// 参数 isMax 指示当前搜索层次属于最大化还是最小化int minimax(char board[SIZE][SIZE], int depth, int isMax, char ai, char human) { int score = evaluate(board, ai, human); // 若终局则返回分数,减去 depth 可使得越快获胜得分更高 if (score == 10) return score - depth; if (score == -10) return score + depth; // 若棋盘无空位,则为平局 if (!isMovesLeft(board)) return 0; int best; int i, j; if (isMax) { best = -1000; // 遍历所有空位,模拟 ai 落子 for (i = 0; i < SIZE; i++) { for (j = 0; j best) best = value; board[i][j] = \' \'; // 撤销落子 } } } } else { best = 1000; // 遍历所有空位,模拟 human 落子 for (i = 0; i < SIZE; i++) { for (j = 0; j < SIZE; j++) { if (board[i][j] == \' \') { board[i][j] = human; int value = minimax(board, depth + 1, 1, ai, human); if (value < best) best = value; board[i][j] = \' \'; // 撤销落子 } } } } return best;}// 根据 Minimax 算法寻找最佳落子位置,并通过 bestRow 与 bestCol 返回该位置void bestMove(char board[SIZE][SIZE], int *bestRow, int *bestCol, char ai, char human) { int bestVal = -1000; *bestRow = -1; *bestCol = -1; int i, j; for (i = 0; i < SIZE; i++) { for (j = 0; j bestVal) { *bestRow = i; *bestCol = j; bestVal = moveVal; } } } }}// 电脑根据当前棋盘状态进行下棋(AI 落子)// 参数 ai 表示电脑(设备)的棋子字符,human 表示人的棋子字符void aiMove(char board[SIZE][SIZE], char ai, char human) { int row = -1, col = -1; // 当棋盘空时,可直接将电脑第一步放到中间位置,实现 “第一步可设置” int isEmpty = 1; int i, j; for (i = 0; i < SIZE; i++) { for (j = 0; j < SIZE; j++) { if (board[i][j] != \' \') { isEmpty = 0; break; } } if (!isEmpty) break; } if (isEmpty) { row = 1; col = 1; } else { bestMove(board, &row, &col, ai, human); } if (row != -1 && col != -1) { makeMove(board, row, col, ai); }}// 辅助函数:检查棋盘胜者,若存在则返回获胜棋子的字符,否则返回空格 \' \'// 注意:平局时此函数返回 \' \',游戏结束判断需要结合 isMovesLeft() 实现char getWinner(char board[SIZE][SIZE]) { int i; // 检查行 for (i = 0; i < SIZE; i++) { if (board[i][0] != \' \' && board[i][0] == board[i][1] && board[i][1] == board[i][2]) return board[i][0]; } // 检查列 for (i = 0; i < SIZE; i++) { if (board[0][i] != \' \' && board[0][i] == board[1][i] && board[1][i] == board[2][i]) return board[0][i]; } // 检查对角线 if (board[0][0] != \' \' && board[0][0] == board[1][1] && board[1][1] == board[2][2]) return board[0][0]; if (board[0][2] != \' \' && board[0][2] == board[1][1] && board[1][1] == board[2][0]) return board[0][2]; return \' \';}

