OCCT基础类库介绍:Modeling Data - Classes inheriting TopoDS_Shape
Classes inheriting TopoDS_Shape
TopoDS is based on class TopoDS_Shape and the class defining its underlying shape. This has certain advantages, but the major drawback is that these classes are too general. Different shapes they could represent do not type them (Vertex, Edge, etc.) hence it is impossible to introduce checks to avoid incoherences such as inserting a face in an edge.
继承TopoDS_Shape的类
TopoDS基于TopoDS_Shape类及其定义的底层形状类。这有一定优势,但主要缺点是这些类过于通用。它们可表示的不同形状未对其进行类型划分(如顶点、边等),因此无法引入检查来避免不一致性,例如在边中插入面。
TopoDS package offers two sets of classes, one set inheriting the underlying shape with neither orientation nor location and the other inheriting TopoDS_Shape, which represent the standard topological shapes enumerated in TopAbs package.
TopoDS包提供两组类,一组继承无方向和位置的底层形状,另一组继承TopoDS_Shape,后者表示TopAbs包中枚举的标准拓扑形状。
The following classes inherit Shape: TopoDS_Vertex, TopoDS_Edge, TopoDS_Wire, TopoDS_Face, TopoDS_Shell, TopoDS_Solid, TopoDS_CompSolid, and TopoDS_Compound. In spite of the similarity of names with those inheriting from TopoDS_TShape there is a profound difference in the way they are used.
以下类继承Shape:TopoDS_Vertex、TopoDS_Edge、TopoDS_Wire、TopoDS_Face、TopoDS_Shell、TopoDS_Solid、TopoDS_CompSolid和TopoDS_Compound。尽管与继承自TopoDS_TShape的类名称相似,但它们的使用方式存在根本差异。
TopoDS_Shape class and the classes, which inherit from it, are the natural means to manipulate topological objects. TopoDS_TShape classes are hidden. TopoDS_TShape describes a class in its original local coordinate system without orientation. TopoDS_Shape is a reference to TopoDS_TShape with an orientation and a local reference.
TopoDS_Shape类及其继承类是操作拓扑对象的常用方式。TopoDS_TShape类是隐藏的。TopoDS_TShape描述无方向的原始局部坐标系中的类,TopoDS_Shape是带方向和局部引用的TopoDS_TShape引用。
TopoDS_TShape class is deferred; TopoDS_Shape class is not. Using TopoDS_Shape class allows manipulation of topological objects without knowing their type. It is a generic form. Purely topological algorithms often use the TopoDS_Shape class.
TopoDS_TShape类是延迟的,TopoDS_Shape类则不是。使用TopoDS_Shape类可在不知道拓扑对象类型的情况下操作它们,这是一种通用形式。纯拓扑算法常使用TopoDS_Shape类。
TopoDS_TShape class is manipulated by reference; TopoDS_Shape class by value. A TopoDS_Shape is nothing more than a reference enhanced with an orientation and a local coordinate. The sharing of TopoDS_Shapes is meaningless. What is important is the sharing of the underlying TopoDS_TShapes. Assignment or passage in argument does not copy the data structure: this only creates new TopoDS_Shapes which refer to the same TopoDS_TShape.
TopoDS_TShape类通过引用操作,TopoDS_Shape类通过值操作。TopoDS_Shape仅仅是增强了方向和局部坐标的引用,共享TopoDS_Shapes没有意义,重要的是共享底层的TopoDS_TShapes。赋值或参数传递不会复制数据结构,只会创建引用同一TopoDS_TShape的新TopoDS_Shapes。
Although classes inheriting TopoDS_TShape are used for adding extra information, extra fields should not be added in a class inheriting from TopoDS_Shape. Classes inheriting from TopoDS_Shape serve only to specialize a reference in order to benefit from static type control (carried out by the compiler). For example, a routine that receives a TopoDS_Face in argument is more precise for the compiler than the one, which receives a TopoDS_Shape. It is pointless to derive other classes than those found in TopoDS. All references to a topological data structure are made with the Shape class and its inheritors defined in TopoDS.
尽管继承TopoDS_TShape的类用于添加额外信息,但不应在继承TopoDS_Shape的类中添加额外字段。继承TopoDS_Shape的类仅用于专门化引用,以受益于静态类型控制(由编译器执行)。例如,接收TopoDS_Face作为参数的例程对编译器而言比接收TopoDS_Shape的例程更精确。派生TopoDS中没有的其他类是无意义的,所有对拓扑数据结构的引用都使用TopoDS中定义的Shape类及其继承类。
There are no constructors for the classes inheriting from the TopoDS_Shape class, otherwise the type control would disappear through implicit casting (a characteristic of C++). The TopoDS package provides package methods for casting an object of the TopoDS_Shape class in one of these sub-classes, with type verification.
继承TopoDS_Shape类的类没有构造函数,否则类型控制会通过隐式转换消失(C++的特性)。TopoDS包提供包方法,用于将TopoDS_Shape类对象转换为这些子类之一,并进行类型验证。
The following example shows a routine receiving an argument of the TopoDS_Shape type, then putting it into a variable V if it is a vertex or calling the method ProcessEdge if it is an edge.
以下示例显示一个例程,接收TopoDS_Shape类型的参数,如果是顶点则将其放入变量V,如果是边则调用ProcessEdge方法。
#include // 包含顶点类定义#include // 包含边类定义#include // 包含形状基类定义 void ProcessEdge(const TopoDS_Edge&); // 处理边的函数声明 void Process(const TopoDS_Shape& aShape) { // 处理形状的函数 if (aShape.Shapetype() == TopAbs_VERTEX) { // 检查是否为顶点 TopoDS_Vertex V; // 定义顶点变量 V = TopoDS::Vertex(aShape); // 通过类型转换获取顶点,正确方式 TopoDS_Vertex V2 = aShape; // 直接赋值会被编译器拒绝 TopoDS_Vertex V3 = TopoDS::Vertex(aShape); // 正确的类型转换方式 } else if (aShape.ShapeType() == TopAbs_EDGE){ // 检查是否为边 ProcessEdge(aShape); // 直接传递形状会被拒绝 ProcessEdge(TopoDS::Edge(aShape)); // 通过类型转换传递边,正确方式 } else { cout <<\"Neither a vertex nor an edge ?\"; // 输出错误信息 ProcessEdge(TopoDS::Edge(aShape)); // 编译器允许但运行时若类型不匹配会抛出异常 }}Exploration of Topological Data Structures
The TopExp package provides tools for exploring the data structure described with the TopoDS package. Exploring a topological structure means finding all sub-objects of a given type, for example, finding all the faces of a solid.
拓扑数据结构的探索
TopExp 包提供了用于探索 TopoDS 包所描述数据结构的工具。探索拓扑结构意味着查找给定类型的所有子对象,例如查找实体的所有面。
The TopExp package provides the class TopExp_Explorer to find all sub-objects of a given type. An explorer is built with:
- The shape to be explored.
- The type of shapes to be found e.g. VERTEX, EDGE with the exception of SHAPE, which is not allowed.
- The type of Shapes to avoid. e.g. SHELL, EDGE. By default, this type is SHAPE. This default value means that there is no restriction on the exploration.
TopExp 包提供 TopExp_Explorer 类来查找给定类型的所有子对象。创建探索器时需要:
- 要探索的形状。
- 要查找的形状类型(如 VERTEX、EDGE,但不允许 SHAPE)。
- 要排除的形状类型(如 SHELL、EDGE)。默认类型为 SHAPE,意味着探索无限制。
The Explorer visits the whole structure in order to find the shapes of the requested type not contained in the type to avoid. The example below shows how to find all faces in the shape S:
void test() { TopoDS_Shape S; TopExp_Explorer Ex; for (Ex.Init(S,TopAbs_FACE); Ex.More(); Ex.Next()) { ProcessFace(Ex.Current()); } } 探索器遍历整个结构,以查找不属于排除类型的请求类型形状。下面的示例展示了如何查找形状 S 中的所有面:
void test() { TopoDS_Shape S; TopExp_Explorer Ex; // 初始化探索器,查找S中的面,无排除类型 for (Ex.Init(S, TopAbs_FACE); Ex.More(); Ex.Next()) { ProcessFace(Ex.Current()); // 处理当前面 } } Find all the vertices which are not in an edge
for (Ex.Init(S, TopAbs_VERTEX, TopAbs_EDGE); ...) 查找所有不在边中的顶点
for (Ex.Init(S, TopAbs_VERTEX, TopAbs_EDGE); ...) // 初始化探索器,查找S中的顶点,并排除边类型Find all the faces in a SHELL, then all the faces not in a SHELL:
void test() { TopExp_Explorer Ex1, Ex2; TopoDS_Shape S; for (Ex1.Init(S, TopAbs_SHELL); Ex1.More(); Ex1.Next()) { // 遍历所有壳 for (Ex2.Init(Ex1.Current(), TopAbs_FACE); Ex2.More(); Ex2.Next()) { // 遍历当前壳的所有面 ProcessFaceinAshell(Ex2.Current()); ... } } for (Ex1.Init(S, TopAbs_FACE, TopAbs_SHELL); Ex1.More(); Ex1.Next()) { // 遍历所有不在壳中的面 ProcessFace(Ex1.Current()); }}查找壳中的所有面,然后查找不在壳中的所有面:
void test() { TopExp_Explorer Ex1, Ex2; TopoDS_Shape S; // 遍历S中的所有壳 for (Ex1.Init(S, TopAbs_SHELL); Ex1.More(); Ex1.Next()) { // 遍历当前壳中的所有面 for (Ex2.Init(Ex1.Current(), TopAbs_FACE); Ex2.More(); Ex2.Next()) { ProcessFaceinAshell(Ex2.Current()); // 处理壳中的面 ... } } // 遍历S中不属于壳的所有面 for (Ex1.Init(S, TopAbs_FACE, TopAbs_SHELL); Ex1.More(); Ex1.Next()) { ProcessFace(Ex1.Current()); // 处理非壳中的面 }}The Explorer presumes that objects contain only objects of an equal or inferior type. For example, if searching for faces it does not look at wires, edges, or vertices to see if they contain faces.
探索器假定对象仅包含相同或更低类型的对象。例如,搜索面时,不会检查线框、边或顶点是否包含面。
The MapShapes method from TopExp package allows filling a Map. An exploration using the Explorer class can visit an object more than once if it is referenced more than once. For example, an edge of a solid is generally referenced by two faces. To process objects only once, they have to be placed in a Map.
TopExp 包中的 MapShapes 方法允许填充映射。如果对象被多次引用,使用 Explorer 类的探索会多次访问该对象。例如,实体的边通常被两个面引用。要仅处理对象一次,必须将其放入映射中。
Example
void TopExp::MapShapes (const TopoDS_Shape& S, const TopAbs_ShapeEnum T, TopTools_IndexedMapOfShape& M) { TopExp_Explorer Ex(S,T); while (Ex.More()) { M.Add(Ex.Current()); Ex.Next(); }}示例
void TopExp::MapShapes (const TopoDS_Shape& S, const TopAbs_ShapeEnum T, TopTools_IndexedMapOfShape& M) { TopExp_Explorer Ex(S, T); // 初始化探索器 while (Ex.More()) { M.Add(Ex.Current()); // 将当前形状添加到映射 Ex.Next(); // 移动到下一个形状 }}In the following example all faces and all edges of an object are drawn in accordance with the following rules:
- The faces are represented by a network of NbIso iso-parametric lines with FaceIsoColor color.
- The edges are drawn in a color, which indicates the number of faces sharing the edge:
- FreeEdgeColor for edges, which do not belong to a face (i.e. wireframe element).
- BorderEdgeColor for an edge belonging to a single face.
- SharedEdgeColor for an edge belonging to more than one face.
在以下示例中,对象的所有面和边按以下规则绘制:
- 面由 NbIso 条等参数线组成的网络表示,颜色为 FaceIsoColor。
- 边按共享面的数量绘制颜色:
- 不属于面的边(线框元素)为 FreeEdgeColor。
- 属于单个面的边为 BorderEdgeColor。
- 属于多个面的边为 SharedEdgeColor。
The methods DrawEdge and DrawFaceIso are also available to display individual edges and faces.
The following steps are performed:
- Storing the edges in a map and create in parallel an array of integers to count the number of faces sharing the edge. This array is initialized to zero.
- Exploring the faces. Each face is drawn.
- Exploring the edges and for each of them increment the counter of faces in the array.
- From the Map of edges, drawing each edge with the color corresponding to the number of faces.
也可使用 DrawEdge 和 DrawFaceIso 方法显示单个边和面。执行以下步骤:
- 将边存储在映射中,并并行创建整数数组以计算共享边的面数,数组初始化为零。
- 遍历面并绘制每个面。
- 遍历边并递增数组中的面计数器。
- 根据边映射,按面数对应的颜色绘制每条边。
原始代码:
void DrawShape ( const TopoDS_Shape& aShape, const Standard_Integer nbIsos, const Color FaceIsocolor, const Color FreeEdgeColor, const Color BorderEdgeColor, const Color SharedEdgeColor) { // Store the edges in aMap. TopTools_IndexedMapOfShape edgemap; TopExp::MapShapes(aShape, TopAbs_EDGE, edgeMap); // Create an array set to zero. TColStd_Array1OfInteger faceCount(1, edgeMap.Extent()); faceCount.Init (0); // Explore the faces. TopExp_Explorer expFace(aShape, TopAbs_FACE); while (expFace.More()) { // Draw the current face. DrawFaceIsos(TopoDS::Face(expFace.Current()), nbIsos, FaceIsoColor); // Explore the edges of the face. TopExp_Explorer expEdge(expFace.Current(), TopAbs_EDGE); while (expEdge.More()) { // Increment the face count for this edge. faceCount(edgemap.FindIndex(expEdge.Current()))++; expEdge.Next(); } expFace.Next(); } // Draw the edges of theMap Standard_Integer i; for (i = 1; i <= edgemap.Extent(); i++) { switch (faceCount(i)) { case 0 : DrawEdge(TopoDS::Edge(edgemap(i)), FreeEdgeColor); break; case 1 : DrawEdge(TopoDS::Edge(edgemap(i)), BorderEdgeColor); break; default : DrawEdge(TopoDS::Edge(edgemap(i)), SharedEdgeColor); break; } } } 带注释的代码:
void DrawShape (const TopoDS_Shape& aShape, const Standard_Integer nbIsos, const Color FaceIsocolor, const Color FreeEdgeColor, const Color BorderEdgeColor, const Color SharedEdgeColor) { // 将边存储到映射中 TopTools_IndexedMapOfShape edgemap; TopExp::MapShapes(aShape, TopAbs_EDGE, edgeMap); // 创建初始化为0的面计数数组 TColStd_Array1OfInteger faceCount(1, edgeMap.Extent()); faceCount.Init(0); // 遍历所有面 TopExp_Explorer expFace(aShape, TopAbs_FACE); while (expFace.More()) { // 绘制当前面(等参数线) DrawFaceIsos(TopoDS::Face(expFace.Current()), nbIsos, FaceIsoColor); // 遍历当前面的所有边 TopExp_Explorer expEdge(expFace.Current(), TopAbs_EDGE); while (expEdge.More()) { // 递增边的面计数 faceCount(edgemap.FindIndex(expEdge.Current()))++; expEdge.Next(); } expFace.Next(); } // 按面计数绘制边 Standard_Integer i; for (i = 1; i <= edgemap.Extent(); i++) { switch (faceCount(i)) { case 0: // 无边所属面(线框边) DrawEdge(TopoDS::Edge(edgemap(i)), FreeEdgeColor); break; case 1: // 属于单个面 DrawEdge(TopoDS::Edge(edgemap(i)), BorderEdgeColor); break; default: // 属于多个面 DrawEdge(TopoDS::Edge(edgemap(i)), SharedEdgeColor); break; } } } Lists and Maps of Shapes
TopTools package contains tools for exploiting the TopoDS data structure. It is an instantiation of the tools from TCollection package with the Shape classes of TopoDS.
形状的列表和映射
TopTools 包包含用于利用 TopoDS 数据结构的工具,它是 TCollection 包工具与 TopoDS 形状类的实例化。
-
TopTools_Array1OfShape, HArray1OfShape – instantiation of the NCollection_Array1 with TopoDS_Shape.
-
TopTools_SequenceOfShape – instantiation of the NCollection_Sequence with TopoDS_Shape.
-
TopTools_MapOfShape - instantiation of the NCollection_Map. Allows the construction of sets of shapes.
-
TopTools_IndexedMapOfShape - instantiation of the NCollection_IndexedMap. Allows the construction of tables of shapes and other data structures.
-
TopTools_Array1OfShape, HArray1OfShape:NCollection_Array1 与 TopoDS_Shape 的实例化。
-
TopTools_SequenceOfShape:NCollection_Sequence 与 TopoDS_Shape 的实例化。
-
TopTools_MapOfShape:NCollection_Map 的实例化,允许构造形状集合。
-
TopTools_IndexedMapOfShape:NCollection_IndexedMap 的实例化,允许构造形状表和其他数据结构。
With a TopTools_Map, a set of references to Shapes can be kept without duplication. The following example counts the size of a data structure as a number of TShapes.
#include Standard_Integer Size(const TopoDS_Shape& aShape) { // 递归方法:形状大小=1+子形状大小之和 TopoDS_Iterator It; Standard_Integer size = 1; for (It.Initialize(aShape); It.More(); It.Next()) { size += Size(It.Value()); } return size; } 使用 TopTools_Map 可保留形状引用集合而不重复。以下示例将数据结构的大小计为 TShapes 的数量。
#include Standard_Integer Size(const TopoDS_Shape& aShape) { TopoDS_Iterator It; Standard_Integer size = 1; // 当前形状计数 for (It.Initialize(aShape); It.More(); It.Next()) { size += Size(It.Value()); // 递归累加子形状大小 } return size; } This program is incorrect if there is sharing in the data structure.
Thus for a contour of four edges it should count 1 wire + 4 edges + 4 vertices with the result 9, but as the vertices are each shared by two edges this program will return 13. One solution is to put all the Shapes in a Map so as to avoid counting them twice, as in the following example:
如果数据结构中存在共享,此程序会出错。例如,对于四条边的轮廓,应计数 1 线框 + 4 边 + 4 顶点,结果为 9,但由于每个顶点被两条边共享,程序会返回 13。一种解决方案是将所有形状放入映射以避免重复计数,如下例所示:
原始代码:
#include #include void MapShapes(const TopoDS_Shape& aShape, TopTools_MapOfShape& aMap){ // 递归辅助方法:将aShape的所有子形状存储到映射 if (aMap.Add(aShape)) { // Add返回True表示aShape未在映射中 TopoDS_Iterator It; for (It.Initialize(aShape); It.More(); It.Next()) { MapShapes(It.Value(), aMap); } } } Standard_Integer Size(const TopoDS_Shape& aShape) { // 将形状存入映射并返回大小 TopTools_MapOfShape M; MapShapes(aShape, M); return M.Extent();}带注释的代码:
#include #include void MapShapes(const TopoDS_Shape& aShape, TopTools_MapOfShape& aMap){ // 若形状未在映射中,则添加并递归处理子形状 if (aMap.Add(aShape)) { TopoDS_Iterator It; for (It.Initialize(aShape); It.More(); It.Next()) { MapShapes(It.Value(), aMap); // 递归处理子形状 } } } Standard_Integer Size(const TopoDS_Shape& aShape) { TopTools_MapOfShape M; MapShapes(aShape, M); // 存储所有形状到映射 return M.Extent(); // 返回映射大小(去重后)}Note For more details about Maps, refer to the TCollection documentation (Foundation Classes Reference Manual).
注意 有关映射的更多详细信息,请参考 TCollection 文档(基础类参考手册)。
The following example is more ambitious and writes a program which copies a data structure using an IndexedMap. The copy is an identical structure but it shares nothing with the original. The principal algorithm is as follows:
- All Shapes in the structure are put into an IndexedMap.
- A table of Shapes is created in parallel with the map to receive the copies.
- The structure is copied using the auxiliary recursive function, which copies from the map to the array.
以下示例更复杂,编写了一个使用 IndexedMap 复制数据结构的程序。复制结构与原始结构相同,但不共享任何内容。主要算法如下:
- 将结构中的所有形状放入 IndexedMap。
- 与映射并行创建形状表以接收副本。
- 使用辅助递归函数将结构从映射复制到数组。
原始代码:
#include #include #include #include #include TopoDS_Shape Copy(const TopoDS_Shape& aShape, const TopoDS_Builder& aBuilder) { // 使用aBuilder复制aShape的整个结构 // 将所有子形状存储到IndexedMap TopTools_IndexedMapOfShape theMap; TopoDS_Iterator It; Standard_Integer i; TopoDS_Shape S; TopLoc_Location Identity; S = aShape; S.Location(Identity); S.Orientation(TopAbs_FORWARD); theMap.Add(S); for (i = 1; i <= theMap.Extent(); i++) { for (It.Initialize(theMap(i)); It.More(); It.Next()) { S = It.Value(); S.Location(Identity); S.Orientation(TopAbs_FORWARD); theMap.Add(S); } } 带注释的代码:
#include #include #include #include #include TopoDS_Shape Copy(const TopoDS_Shape& aShape, const TopoDS_Builder& aBuilder) { // 初始化映射以存储所有形状 TopTools_IndexedMapOfShape theMap; TopoDS_Iterator It; Standard_Integer i; TopoDS_Shape S; TopLoc_Location Identity; // 单位位置和方向 S = aShape; S.Location(Identity); S.Orientation(TopAbs_FORWARD); theMap.Add(S); // 添加原始形状 // 遍历映射并添加所有子形状 for (i = 1; i <= theMap.Extent(); i++) { for (It.Initialize(theMap(i)); It.More(); It.Next()) { S = It.Value(); S.Location(Identity); // 重置位置和方向 S.Orientation(TopAbs_FORWARD); theMap.Add(S); // 添加子形状到映射 } } 原始代码(续):
// 创建数组存储副本 TopTools_Array1OfShape theCopies(1, theMap.Extent()); // 使用递归函数复制第一个元素 void AuxiliaryCopy (Standard_Integer, const TopTools_IndexedMapOfShape &, TopTools_Array1OfShape &, const TopoDS_Builder&); AuxiliaryCopy(1, theMap, theCopies, aBuilder); // 获取具有正确位置和方向的结果 S = theCopies(1); S.Location(aShape.Location()); S.Orientation(aShape.Orientation()); return S; 带注释的代码(续):
// 创建与映射大小相同的数组 TopTools_Array1OfShape theCopies(1, theMap.Extent()); // 声明辅助复制函数 void AuxiliaryCopy (Standard_Integer, const TopTools_IndexedMapOfShape &, TopTools_Array1OfShape &, const TopoDS_Builder&); AuxiliaryCopy(1, theMap, theCopies, aBuilder); // 从索引1开始复制 // 恢复原始位置和方向 S = theCopies(1); S.Location(aShape.Location()); S.Orientation(aShape.Orientation()); return S; 原始代码(辅助函数):
void AuxiliaryCopy(Standard_Integer index, const TopTools_IndexedMapOfShape& sources, TopTools_Array1OfShape& copies, const TopoDS_Builder& aBuilder) { // 若副本为空,则执行复制 if (copies(index).IsNull()) { copies(index) = sources(index).EmptyCopied(); // 插入子形状的副本 TopoDS_Iterator It; TopoDS_Shape S; TopLoc_Location Identity; for (It.Initialize(sources(index)); It.More(); It.Next()) { S = It.Value(); S.Location(Identity); S.Orientation(TopAbs_FORWARD); AuxiliaryCopy(sources.FindIndex(S), sources, copies, aBuilder); S.Location(It.Value().Location()); S.Orientation(It.Value().Orientation()); aBuilder.Add(copies(index), S); } }}带注释的代码(辅助函数):
void AuxiliaryCopy(Standard_Integer index, const TopTools_IndexedMapOfShape& sources, TopTools_Array1OfShape& copies, const TopoDS_Builder& aBuilder) { // 若当前索引位置未复制,则创建空副本 if (copies(index).IsNull()) { copies(index) = sources(index).EmptyCopied(); // 创建空副本 // 处理当前形状的所有子形状 TopoDS_Iterator It; TopoDS_Shape S; TopLoc_Location Identity; for (It.Initialize(sources(index)); It.More(); It.Next()) { S = It.Value(); S.Location(Identity); // 重置位置方向以便递归 S.Orientation(TopAbs_FORWARD); AuxiliaryCopy(sources.FindIndex(S), sources, copies, aBuilder); // 恢复子形状的原始位置方向并添加到副本 S.Location(It.Value().Location()); S.Orientation(It.Value().Orientation()); aBuilder.Add(copies(index), S); // 将子形状添加到当前副本 } }}Wire Explorer
BRepTools_WireExplorer class can access edges of a wire in their order of connection.
线框探索器
BRepTools_WireExplorer 类可以按连接顺序访问线框的边。
For example, in the wire in the image we want to recuperate the edges in the order {e1, e2, e3, e4, e5} :
例如,对于图中的线框,我们希望按 {e1, e2, e3, e4, e5} 的顺序获取边:
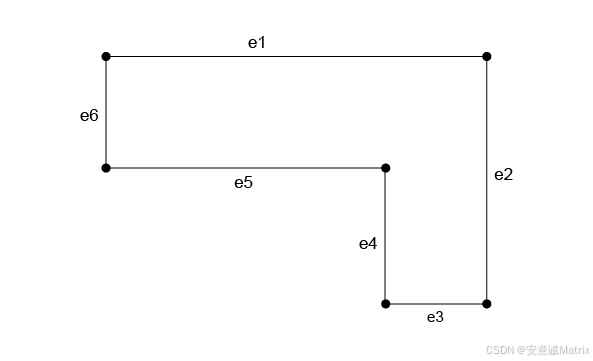
A wire composed of 6 edges.
TopExp_Explorer, however, recuperates the lines in any order.
TopoDS_Wire W = ...; BRepTools_WireExplorer Ex; for (Ex.Init(W); Ex.More(); Ex.Next()) { ProcessTheCurrentEdge(Ex.Current()); ProcessTheVertexConnectingTheCurrentEdgeToThePrevious One(Ex.CurrentVertex()); }由 6 条边组成的线框。然而,TopExp_Explorer 会以任意顺序获取线。
TopoDS_Wire W = ...; BRepTools_WireExplorer Ex; // 按连接顺序初始化线框探索器for (Ex.Init(W); Ex.More(); Ex.Next()) { ProcessTheCurrentEdge(Ex.Current()); // 处理当前边 // 处理当前边与前一条边连接的顶点 ProcessTheVertexConnectingTheCurrentEdgeToThePreviousOne(Ex.CurrentVertex()); }

