【Android】四大组件之Service_android service
目录
一、什么是Service
二、启停 Service
三、绑定 Service
四、前台服务
五、远程服务扩展
六、服务保活
七、服务启动方法混用
你可以把Service想象成一个“后台默默打工的工人”。它没有UI界面,默默地在后台干活,比如播放音乐、下载文件、处理网络请求等。即使你退出了App,Service也可以继续运行。
一、什么是Service
Service是Android应用的核心后台组件。
1. 无界面后台任务
- Service 是 Android 系统中无可视化界面、运行于后台的长生命周期组件。
- 核心功能:执行与用户界面无关的持续性任务,如后台播放音乐、文件下载等。
- Service 不依赖用户交互界面,生命周期独立于Activity。
- 典型应用场景:网络请求、传感器数据采集、跨进程通信(AIDL)。
2. 生命周期管理
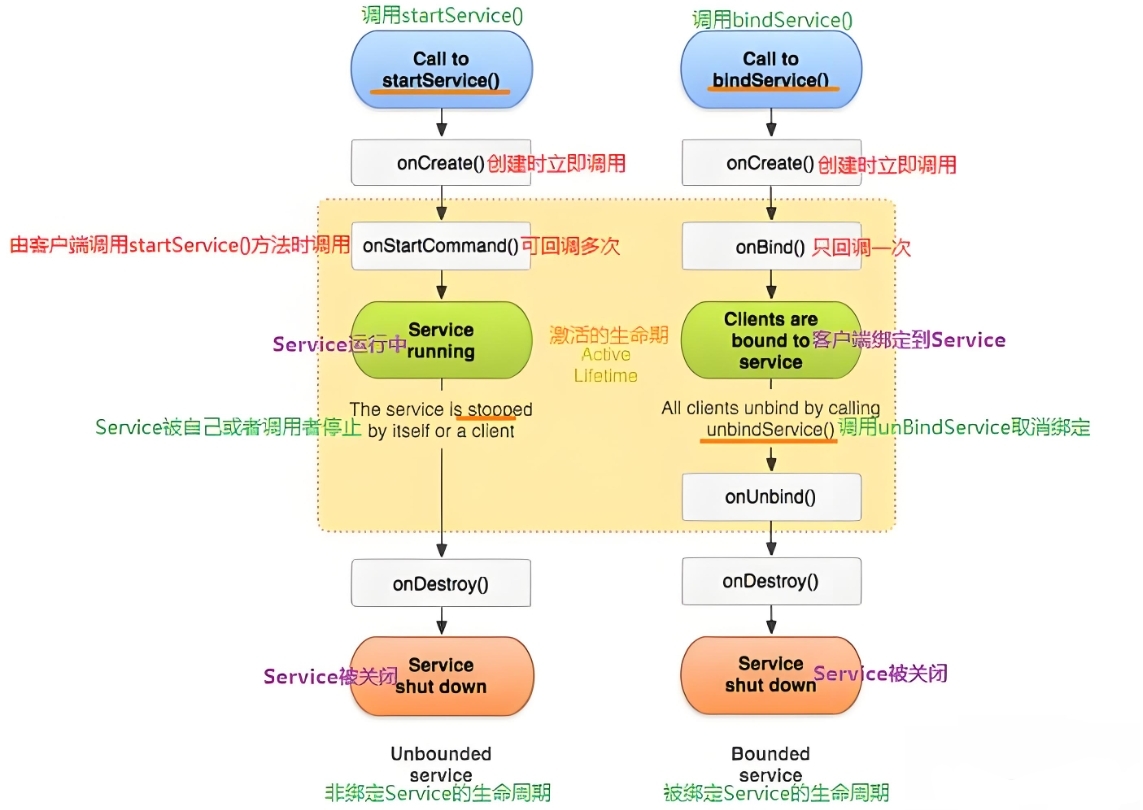
Service有两种主要类型:
startService(Intent) 启动bindService(Intent, ServiceConnection, flags) 启动onCreate() → onStartCommand() → onDestroy()onCreate() → onBind() → onUnbind() → onDestroy()Intent 传递数据Binder 接口直接通信(支持方法调用)stopSelf() 或 stopService()startForeground() 提升为前台服务stopSelf() 和解绑操作才能销毁涉及的生命周期方法:
onCreate()onStartCommand()startService() 启动时调用onBind()bindService() 绑定时调用onUnbind()onDestroy()Service 默认运行在主线程,耗时操作需自行创建子线程或使用
IntentService
二、启停 Service
1. 定义 Service 类
继承 Service 类并实现核心方法:
public class MyService extends Service { private static final String TAG = \"MyService\"; @Override public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) { return null; // 非绑定模式时返回 null } @Override public int onStartCommand(Intent intent, int flags, int startId) { Log.d(TAG, \"Service 启动\"); // 执行后台任务 return START_STICKY; // 服务终止后自动重启 } @Override public void onDestroy() { Log.d(TAG, \"Service 销毁\"); super.onDestroy(); }}2. 注册 Service
在 AndroidManifest.xml 中添加声明:
3. 通过 startService() 启动
在 Activity 或其他组件中调用:
Intent serviceIntent = new Intent(this, MyService.class);startService(serviceIntent); // 启动服务:ml-citation{ref=\"6,8\" data=\"citationList\"}4. 通过 stopService() 或 stopSelf() 停止
stopService(new Intent(this, MyService.class)); // 外部停止// 或在 Service 内部调用 stopSelf();:ml-citation{ref=\"6,8\" data=\"citationList\"}三、绑定 Service
1. 定义 Bound Service
- 通过
LocalBinder返回 Service 实例,实现组件间交互 onBind()返回IBinder对象,供客户端绑定
// MyBoundService.java public class MyBoundService extends Service { private final IBinder binder = new LocalBinder(); private static final String TAG = \"MyBoundService\"; public class LocalBinder extends Binder { MyBoundService getService() { return MyBoundService.this; } } @Override public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) { Log.d(TAG, \"Service 已绑定\"); return binder; } @Override public boolean onUnbind(Intent intent) { Log.d(TAG, \"所有客户端已解绑\"); return super.onUnbind(intent); } // 自定义服务方法(供Activity调用) public void performTask(String data) { Log.d(TAG, \"执行任务:\" + data); } }2. 注册 Service
在 AndroidManifest.xml 中添加声明:
3. Activity 绑定与通信
- 通过
bindService()建立绑定 ServiceConnection处理绑定成功/断开事件- 绑定后通过
myService实例直接调用服务方法 - 必须调用
unbindService()释放资源,避免内存泄漏 - 多个组件可绑定同一服务,全部解绑后服务销毁
// MainActivity.java public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity { private MyBoundService myService; private boolean isBound = false; private ServiceConnection connection = new ServiceConnection() { @Override public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) { MyBoundService.LocalBinder binder = (MyBoundService.LocalBinder) service; myService = binder.getService(); isBound = true; myService.performTask(\"Hello from Activity!\"); // 调用服务方法 } @Override public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName name) { isBound = false; } }; @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); // 绑定服务 Intent intent = new Intent(this, MyBoundService.class); bindService(intent, connection, Context.BIND_AUTO_CREATE); } @Override protected void onDestroy() { super.onDestroy(); if (isBound) { unbindService(connection); // 必须解绑避免泄漏 isBound = false; } } } Activity 创建时: bindService() → Service: onCreate() → onBind()
Activity 销毁时: unbindService() → Service: onUnbind() → onDestroy()
四、前台服务
1. 服务端实现
- Android 8.0+ 必须创建
NotificationChannel,否则通知无法显示 - 通过
IMPORTANCE_LOW设置低优先级(无提示音) startForeground()必须在onCreate()或onStartCommand()中调用,调用后服务优先级提升,避免被系统轻易回收stopForeground(true)确保通知栏通知被移除
// ForegroundService.javapublic class ForegroundService extends Service { private static final int NOTIFICATION_ID = 1001; private static final String CHANNEL_ID = \"foreground_service_channel\"; @Override public void onCreate() { super.onCreate(); createNotificationChannel(); startForegroundWithNotification(\"服务初始化中...\"); } @Override public int onStartCommand(Intent intent, int flags, int startId) { // 获取 Activity 传递的数据(可选) String inputData = intent != null ? intent.getStringExtra(\"input_data\") : null; updateNotification(\"正在运行: \" + inputData); // 模拟耗时任务 new Thread(() -> { for (int i = 0; i = Build.VERSION_CODES.O) { NotificationChannel channel = new NotificationChannel( CHANNEL_ID, \"前台服务示例\", NotificationManager.IMPORTANCE_LOW ); channel.setDescription(\"用于展示前台服务的持续运行状态\"); NotificationManager manager = getSystemService(NotificationManager.class); manager.createNotificationChannel(channel); } } private void startForegroundWithNotification(String text) { Intent notificationIntent = new Intent(this, MainActivity.class); PendingIntent pendingIntent = PendingIntent.getActivity( this, 0, notificationIntent, PendingIntent.FLAG_IMMUTABLE ); Notification notification = new NotificationCompat .Builder(this, CHANNEL_ID) .setContentTitle(\"前台服务示例\") .setContentText(text) .setSmallIcon(R.drawable.ic_notification) .setContentIntent(pendingIntent) .setOnlyAlertOnce(true) // 避免重复提示音 .build(); startForeground(NOTIFICATION_ID, notification); } private void updateNotification(String text) { Notification notification = new NotificationCompat .Builder(this, CHANNEL_ID) .setContentTitle(\"前台服务示例\") .setContentText(text) .setSmallIcon(R.drawable.ic_notification) .setOnlyAlertOnce(true) .build(); NotificationManager manager = getSystemService(NotificationManager.class); manager.notify(NOTIFICATION_ID, notification); } @Override public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) { return null; // 无需绑定功能 } @Override public void onDestroy() { super.onDestroy(); stopForeground(true); // 停止时移除通知 }}2. 配置清单文件注册服务
3. 客户端调用(Activity)
- 通过
stopSelf()或stopService()停止服务
// MainActivity.javapublic class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity { @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); // 启动前台服务按钮 findViewById(R.id.btn_start).setOnClickListener(v -> { Intent serviceIntent = new Intent(this, ForegroundService.class); serviceIntent.putExtra(\"input_data\", \"用户启动任务\"); if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= Build.VERSION_CODES.O) { startForegroundService(serviceIntent); // Android 8.0+ 专用方法 } else { startService(serviceIntent); } }); // 停止服务按钮 findViewById(R.id.btn_stop).setOnClickListener(v -> { Intent serviceIntent = new Intent(this, ForegroundService.class); stopService(serviceIntent); }); }}4. 客户端配置权限
五、远程服务扩展
1. 自定义 Parcelable 对象
// CustomData.java package com.example.model; import android.os.Parcel; import android.os.Parcelable; public class CustomData implements Parcelable { private String content; // 构造函数 public CustomData(String content) { this.content = content; } // Parcelable 反序列化构造函数 protected CustomData(Parcel in) { content = in.readString(); } // Parcelable CREATOR public static final Creator CREATOR = new Creator() { @Override public CustomData createFromParcel(Parcel in) { return new CustomData(in); } @Override public CustomData[] newArray(int size) { return new CustomData[size]; } }; @Override public int describeContents() { return 0; } @Override public void writeToParcel(Parcel dest, int flags) { dest.writeString(content); } // Getter public String getContent() { return content; } } 2. 定义 AIDL 接口
- AIDL 文件定义跨进程通信的接口方法
- 支持基本类型、
String、List、Parcelable等数据类型 - 需在 AIDL 中显式导入
parcelable类型
// IRemoteService.aidl package com.example.service; parcelable CustomData;interface IRemoteService { int add(int a, int b); String getData(String input); void sendData(in CustomData data); void registerCallback(IRemoteCallback callback); void unregisterCallback(IRemoteCallback callback);} // 回调接口(IRemoteCallback.aidl)interface IRemoteCallback { void onResult(int result);}3. 服务端实现 AIDL 接口
- 继承
IRemoteService.Stub实现接口方法 - 通过
onBind()返回IBinder对象 - 直接使用
CustomData对象(已自动反序列化) - 服务端通过
RemoteCallbackList自动清理无效回调,无需手动处理。 RemoteCallbackList.register()会自动去重,多次注册同一回调不会重复触发
public class RemoteService extends Service { private final IBinder binder = new RemoteBinder(); // 使用 RemoteCallbackList 管理跨进程回调(线程安全) private final RemoteCallbackList callbackList = new RemoteCallbackList(); private class RemoteBinder extends IRemoteService.Stub { @Override public int add(int a, int b) { int result = a + b; notifyResult(result); // 触发回调通知 return result; } @Override public String getData(String input) { return \"Processed: \" + input; } @Override public void sendData(CustomData data) throws RemoteException { Log.d(TAG, \"收到数据: \" + data.getContent()); // 处理数据逻辑 } @Override public void registerCallback(IRemoteCallback callback) { if (callback != null) { callbackList.register(callback); } } @Override public void unregisterCallback(IRemoteCallback callback) { if (callback != null) { callbackList.unregister(callback); } } // 通知所有客户端计算结果 private void notifyResult(int result) { int count = callbackList.beginBroadcast(); try { for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) { IRemoteCallback callback = callbackList.getBroadcastItem(i); callback.onResult(result); // 跨进程回调 } } catch (RemoteException e) { e.printStackTrace(); // 客户端已断开,自动从列表中移除 } finally { callbackList.finishBroadcast(); } } } @Override public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) { return binder; } @Override public void onDestroy() { super.onDestroy(); callbackList.kill(); // 清理回调列表 }} 注意:必须使用 Android 提供的
RemoteCallbackList管理跨进程回调(自动处理客户端进程死亡情况),普通集合(如ArrayList)无法正确识别跨进程的IBinder对象。
4. 注册 Service(AndroidManifest.xml)
android:exported=\"true\"允许跨进程访问- 定义唯一
action供客户端绑定 - android:process=\":remote\" 强制指定独立进程,所有跨进程绑定均指向此进程,复用同一实例
<service android:name=\".RemoteService\" android:enabled=\"true\" android:exported=\"true\" android:permission=\"com.example.permission.REMOTE_SERVICE\" android:process=\":remote\"> 5. 客户端绑定与调用远程服务
- 通过隐式 Intent 指定服务端包名和 Action
- 使用
IRemoteService.Stub.asInterface()转换IBinder对象 - 所有跨进程方法调用需处理
RemoteException - 在
onServiceDisconnected()和onBindingDied()中,直接清理本地资源(如置空remoteService),不调用任何远程方法。 - 客户端无需在断开时调用
unregisterCallback(),服务端能正确处理死亡 Binder,其注册的回调会自动从列表中移除。 - 如果客户端维护了本地回调列表(如
localCallbackList),需在断开时直接清理,无需依赖服务端确认。
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity { private IRemoteService remoteService; private boolean isBound = false; private IRemoteCallback callback = new IRemoteCallback.Stub() { @Override public void onResult(int result) { // 注意:此处运行在 Binder 线程,需切到主线程更新 UI new Handler(Looper.getMainLooper()).post(() -> { textView.setText(\"计算结果: \" + result); }); } }; // 绑定服务方法(封装复用) private void bindService() { Intent intent = new Intent(\"com.example.service.IRemoteService\"); intent.setPackage(\"com.example.service\"); // 显式指定包名 // 判断是否 Android 11+ 需要添加 flags if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= Build.VERSION_CODES.R) { bindService(intent, connection, Context.BIND_AUTO_CREATE | Context.BIND_IMPORTANT); } else { bindService(intent, connection, Context.BIND_AUTO_CREATE); } } private ServiceConnection connection = new ServiceConnection() { @Override public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) { remoteService = IRemoteService.Stub.asInterface(service); isBound = true; try { remoteService.registerCallback(callback); // 注册回调 int result = remoteService.add(3, 5); Log.d(\"Client\", \"Result: \" + result); CustomData data = new CustomData(\"Hello from Client\"); remoteService.sendData(data); } catch (RemoteException e) { // 远程调用异常捕获 e.printStackTrace(); Log.e(\"Client\", \"Remote call failed: \" + e.getMessage()); } } @Override public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName name) { isBound = false; remoteService = null; if (reconnectAttempts { reconnectAttempts++; Log.w(TAG, \"尝试第 \" + reconnectAttempts + \" 次重连...\"); bindService(); // 调用绑定方法 }, 3000); // 延迟 3 秒后重试(避免频繁请求) } else { Log.e(TAG, \"已达到最大重连次数,停止尝试\"); } } @Override public void onBindingDied(ComponentName name) { // Android 10+ 新增回调,处理绑定失效场景 onServiceDisconnected(name); } }; @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); bindService(); } @Override protected void onDestroy() { super.onDestroy(); try { if (remoteService != null && callback != null) { remoteService.unRegisterCallback(callback); // 主动注销 remoteService = null; } } catch (RemoteException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } if (isBound) { unbindService(connection); isBound = false; } } } 6. 客户端声明权限
<!-- --> 六、服务保活
1. 前台服务 + 通知 (前面已介绍)
- 使用
startForeground()提升服务优先级至前台级别 - Android 9+ 需动态申请
FOREGROUND_SERVICE权限
public class PersistentService extends Service { @Override public int onStartCommand(Intent intent, int flags, int startId) { // 创建前台通知(Android 8.0+ 需通知渠道) Notification notification = new NotificationCompat .Builder(this, \"channel_id\") .setContentTitle(\"服务运行中\") .setSmallIcon(R.drawable.ic_notification) .build(); startForeground(1, notification); // 必须显示通知 return START_STICKY; // 服务终止后尝试重启: // ml-citation{ref=\"1,6\" data=\"citationList\"} }}2. 粘性服务重启策略
覆盖生命周期方法:
@Overridepublic void onTaskRemoved(Intent rootIntent) { // 任务被移除时(如用户划掉最近任务)触发重启 Intent restartIntent = new Intent(this, PersistentService.class); restartIntent.setPackage(getPackageName()); startService(restartIntent); super.onTaskRemoved(rootIntent);}@Overridepublic void onDestroy() { // 服务被系统杀死时触发重启逻辑 // 发送广播,需要注册一个广播接收器 sendBroadcast(new Intent(\"RESTART_SERVICE_ACTION\")); super.onDestroy();}注册广播接收器,通过广播重新拉起服务 :
频繁调用
startService()可能导致 ANR,建议结合JobScheduler优化
3. 系统广播监听
听高频触发广播,利用网络变化、解锁等事件触发服务重启。
4. 进程守护与JobScheduler
独立进程运行,减少主进程崩溃对服务的影响。
JobScheduler 定时唤醒,定期检查服务状态并拉起。
ComponentName serviceComponent = new ComponentName(this, PersistentService.class);JobInfo jobInfo = new JobInfo.Builder(1, serviceComponent) .setPeriodic(15 * 60 * 1000) // 15分钟间隔 .setPersisted(true) // 设备重启后保持任务 .build();JobScheduler scheduler = (JobScheduler) getSystemService(JOB_SCHEDULER_SERVICE);scheduler.schedule(jobInfo);七、服务启动方法混用
1. startService() 重复调用
- 首次调用:触发
onCreate()→onStartCommand() - 后续调用:仅触发
onStartCommand(),onCreate()不再执行
// 第一次调用startService(intent); // onCreate() -> onStartCommand()// 第二次调用startService(intent); // 仅 onStartCommand()2. bindService() 重复调用
- 首次绑定:触发
onCreate()→onBind() - 后续绑定:若 Service 已存在,直接返回已创建的
IBinder对象,不再触发onBind()
// 第一次绑定// onCreate() -> onBind()bindService(intent, conn, BIND_AUTO_CREATE); // 第二次绑定(同一进程)// 无生命周期方法调用,复用已有 IBinderbindService(intent, conn2, BIND_AUTO_CREATE); 不同进程再次绑定:
- 同一 Service 实例:若
Service已在独立进程运行,后续绑定直接复用已有实例,不再触发onCreate()和onBind(),仅通过ServiceConnection返回IBinder代理对象。- 新 Service 实例:若应用配置多进程且未声明
android:process,不同组件进程可能触发多个Service实例(需避免此设计)
3. 混合调用场景
startService() 后 bindService():
Service 生命周期持续到 unbindService() 和 stopService()/stopSelf() 均被调用
startService(intent); // onCreate() -> onStartCommand()bindService(intent, conn); // onBind(),Service 已存在无需创建同理,先bindService()后startService()
bindService(intent, conn); // 创建 Service 实例,onCreate() → onBind()startService(intent); // onStartCommand(),Service 已存在无需创建混合调用时需同时调用
stopService()和unbindService()才能销毁 Service


