Java 核心工具类 API 详解(一):从 Math 到 Runtime 的实用指南
文章主页-爱因斯晨
文章专栏-Java专栏

加速更新中!感谢大家支持和陪伴!
祝兄弟们得偿所愿天天开心!文末有投票哦!
文章目录
-
- 文章主页-爱因斯晨
- 文章专栏-Java专栏
- 一、Math
-
- Math类的常用方法
- 二、System
- 三、Runtine
一、Math
不需要背,要学会记一下类名和类的作用,养成查阅API帮助文档的习惯
是一个帮助我们用于进行数学计算的工具类
私有化静态方法,里面的所有的方法全是静态的
Math类的常用方法

package demo01;public class MathDemo01 { public static void main(String[] args) { //abs 获取参数的绝对值 System.out.println(Math.abs(-3.14)); System.out.println(Math.abs(3.14)); //bug解释 //以int型为例,int的取值范围是-2147483648到2147483647 //如果参数是-2147483648,那么取绝对值后就会超出int的取值范围,所以会返回-2147483648 //如果参数是-2147483647,那么取绝对值后就会返回2147483647 //可以索引到源码中的abs方法,发现abs方法的返回值是int类型,所以会返回-2147483648 System.out.println(Math.abs(-2147483648)); //ceil 向上取整 数学中的进一法,往数轴中的正方向取整,即大于等于该数的最小整数 System.out.println(Math.ceil(3.9)); System.out.println(Math.ceil(-3.9)); //floor 向下取整 数学中的去一法,往数轴中的负方向取整,即小于等于该数的最大整数 System.out.println(Math.floor(3.9)); System.out.println(Math.floor(-3.9)); //round 四舍五入 System.out.println(Math.round(3.4)); System.out.println(Math.round(-3.6)); System.out.println(Math.round(-3.5)); //pow 求幂 System.out.println(Math.pow(2,3)); //max 获取最大值 System.out.println(Math.max(3.4,5.6)); //random 获取随机数 System.out.println(Math.random()); }}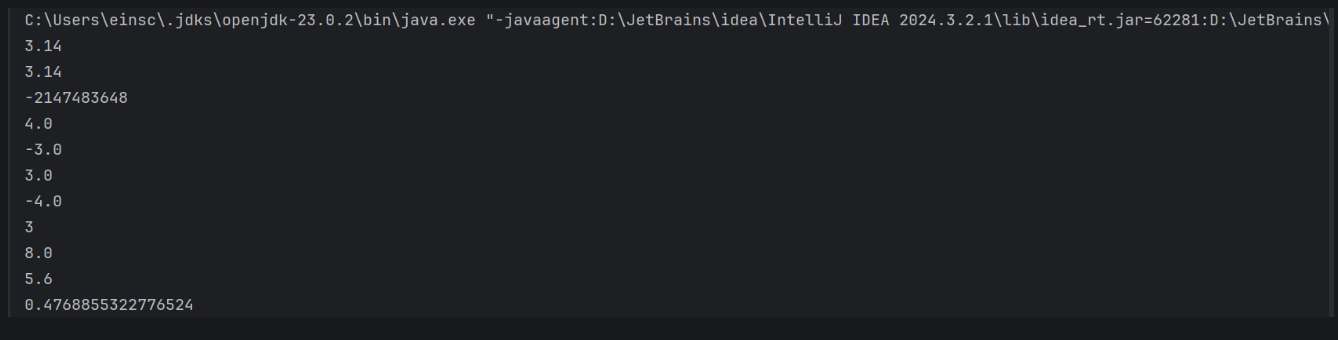
关于abs我们可以回溯源码,可以看到他们做了一个判断
public static long absExact(long a) { if (a == Long.MIN_VALUE) throw new ArithmeticException( \"Overflow to represent absolute value of Long.MIN_VALUE\"); else return abs(a); } /** * Returns the absolute value of a {@code float} value. * If the argument is not negative, the argument is returned. * If the argument is negative, the negation of the argument is returned. * Special cases: * - If the argument is positive zero or negative zero, the * result is positive zero. *
- If the argument is infinite, the result is positive infinity. *
- If the argument is NaN, the result is NaN.
* * @apiNote As implied by the above, one valid implementation of * this method is given by the expression below which computes a * {@code float} with the same exponent and significand as the * argument but with a guaranteed zero sign bit indicating a * positive value:
* {@code Float.intBitsToFloat(0x7fffffff & Float.floatToRawIntBits(a))} * * @param a the argument whose absolute value is to be determined * @return the absolute value of the argument. */ 在max判断中,其实源码中也做了一个三元计算符的判断
@IntrinsicCandidate public static double max(double a, double b) { if (a != a) return a; // a is NaN if ((a == 0.0d) && (b == 0.0d) && (Double.doubleToRawLongBits(a) == negativeZeroDoubleBits)) { // Raw conversion ok since NaN can\'t map to -0.0. return b; } return (a >= b) ? a : b; } /** * Returns the smaller of two {@code int} values. That is, * the result the argument closer to the value of * {@link Integer#MIN_VALUE}. If the arguments have the same * value, the result is that same value. * * @param a an argument. * @param b another argument. * @return the smaller of {@code a} and {@code b}. */ 练习:
判断一个数是否为质数
public static boolean isPrime(int number){ for (int i = 2 ; i < number ; i++){ if (number%i==0){ return false ; } } return true ;}我们发现这样效率太慢了,于是我们发现一个数的因子在平方根的左边,于是我们可以从左边遍历,这样可以节省时间
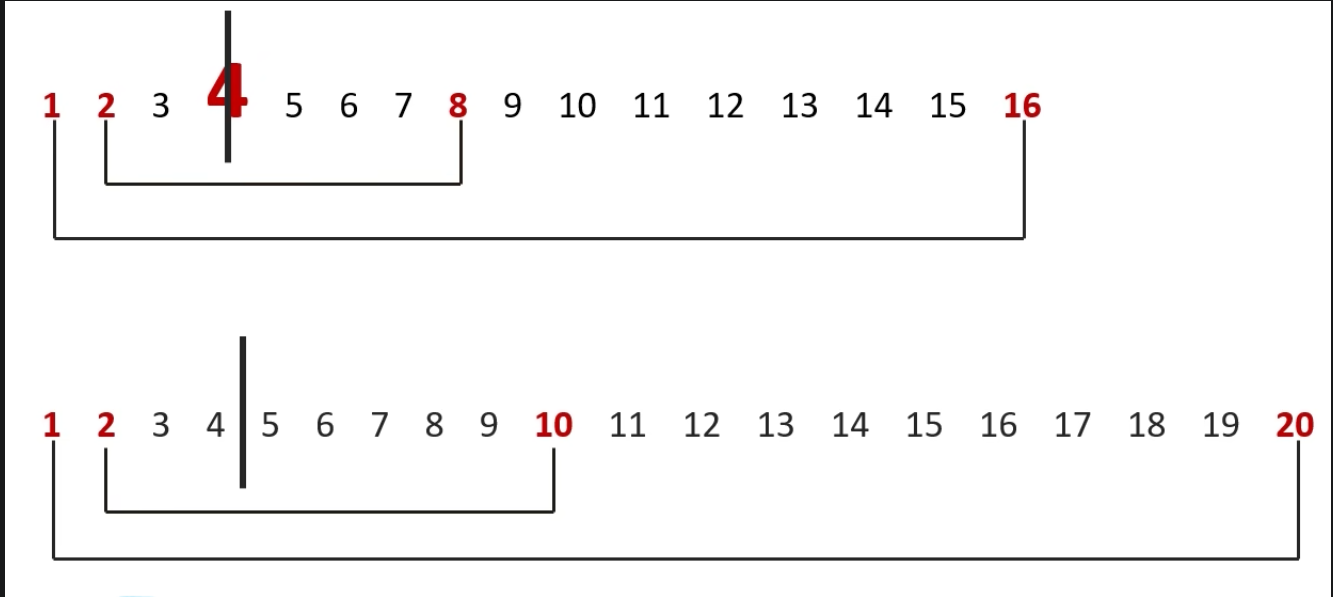
public static boolean isPrime(int number){ for (int i = 2 ; i < Math.sqrt(number) ; i++){ if (number%i==0){ return false ; } } return true ;}练习2:

要求1:统计一共有多少个水仙花数
package demo01;public class MathDemo02 { public static void main(String[] args) { //要求1:统计一共有多少个水仙花数字 //水仙花数:100-999之间的数字 int count = 0; for (int i = 100; i < 1000; i++) { int ge = i % 10; int shi = i / 10 % 10; int bai = i / 100 % 10; //判断是否为水仙花数 double sum =Math.pow(ge,3) + Math.pow(shi,3) + Math.pow(bai,3); if (sum == i) { count++; System.out.println(i); } } System.out.println(count); }}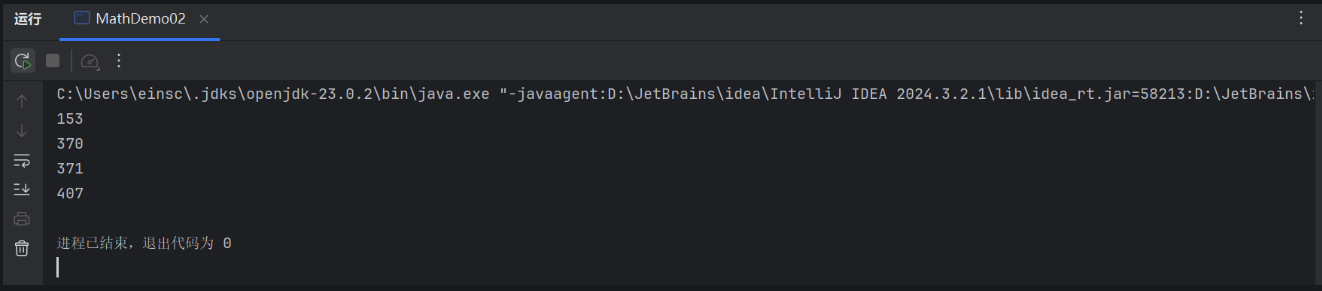
要求2:(课后作业)证明没有两位的自幂数
package demo01;public class MathDemo03 { public static void main(String[] args) { //要求1:统计一共有多少个水仙花数字 //水仙花数:100-999之间的数字 int count = 0; for (int i = 10; i < 99; i++) { int ge = i % 10; int shi = i / 10 % 10; //判断是否为水仙花数 double sum =Math.pow(ge,2) + Math.pow(shi,2); if (sum == i) { count++; System.out.println(i); } } System.out.println(count); }}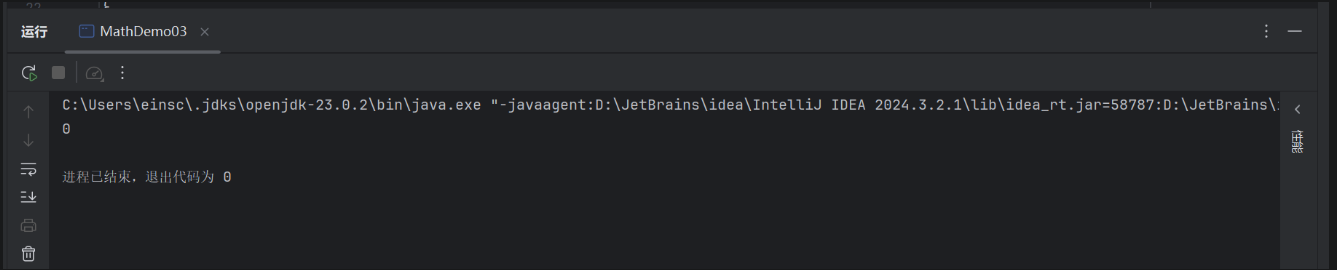
要求3:统计有多少个四叶玫瑰数
package demo01;public class MathDemo04 { public static void main(String[] args) { //要求1:统计一共有多少个水仙花数字 //水仙花数:100-999之间的数字 int count = 0; for (int i = 1000; i < 9999; i++) { int ge = i % 10; int shi = i / 10 % 10; int bai = i / 100 % 10; int qian = i / 1000 % 10; //判断是否为水仙花数 double sum =Math.pow(ge,4) + Math.pow(shi,4) + Math.pow(bai,4)+Math.pow(qian,4); if (sum == i) { count++; System.out.println(i); } } System.out.println(count); }}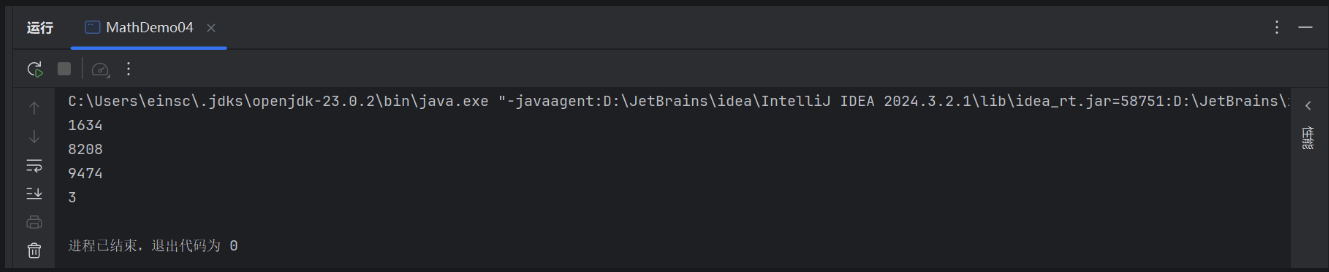
二、System
System也是一个工具类,提供了一个选哪个与系统相关的方法

计算机中的时间原点:1970年1月1日 00:00:00 也就是C语言的生日
我们是东八区所以是 1970年1月1日 08:00:00

package demo02;public class SystemDemo01 { public static void main(String[] args) { //终止当前的虚拟机推出程序// public static void exit(int status) {// System.out.println(\"退出程序\");// } //方法的形参: //状态码: //0:正常退出 //非0:异常退出 System.exit(0); System.out.println(\"看看我执行了吗?\"); }}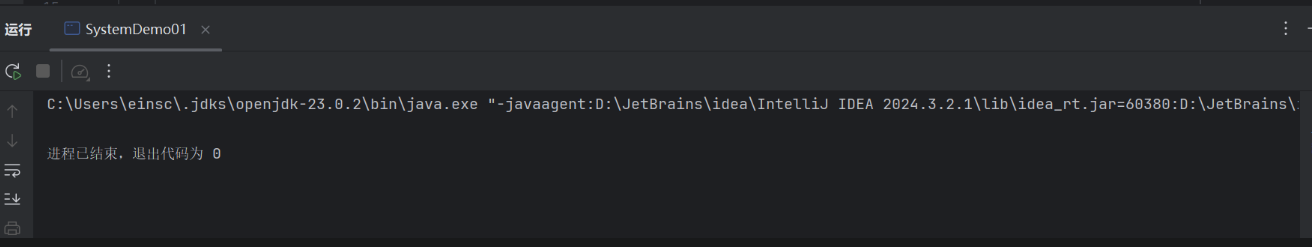
显而易见,程序在输出语句前就退出了执行
package demo02;public class SystemDemo01 { public static void main(String[] args) { //终止当前的虚拟机推出程序// public static void exit(int status) {// System.out.println(\"退出程序\");// } //方法的形参: //状态码: //0:正常退出 //非0:异常退出 //System.exit(0); // System.out.println(\"看看我执行了吗?\"); //获取当前系统的毫秒值 long l = System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println(l); }}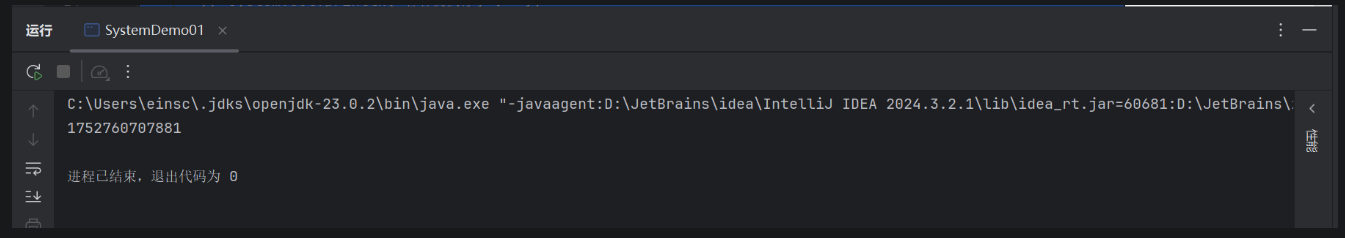
这个类可以获得程序运行的时间
package demo02;public class SystemDemo01 { public static void main(String[] args) { //终止当前的虚拟机推出程序// public static void exit(int status) {// System.out.println(\"退出程序\");// } //方法的形参: //状态码: //0:正常退出 //非0:异常退出 //System.exit(0); // System.out.println(\"看看我执行了吗?\"); //获取当前系统的毫秒值 //long l = System.currentTimeMillis(); //System.out.println(l); //拷贝数组 int [] arr1 = {1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9}; int [] arr2 = new int [9]; //参数1:源数组 //参数2:源数组的起始索引 //参数3:目标数组 //参数4:目标数组的起始索引 //参数5:拷贝的个数 System.arraycopy(arr1, 0, arr2, 0, 9); for (int i = 0; i < arr2.length; i++) { System.out.print(arr2[i]); } }}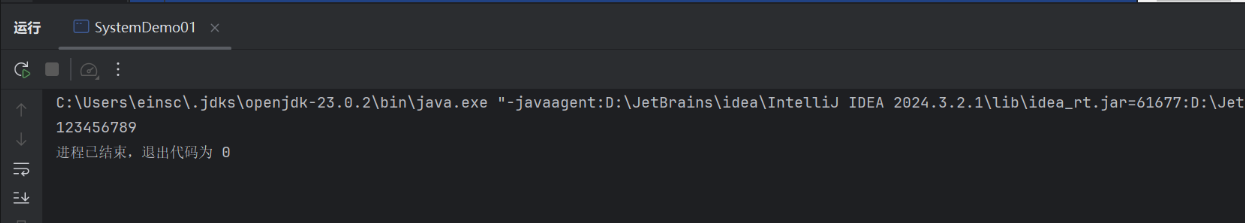
第三个方法细节:
1.如果数据源数组和目的地数组都是基本数据类型,那么两者的类型必须保持一致,否则会报错
2.再拷贝的时候需要考虑数组的长度,如果超出范围也会报错
3.如果数据源数组和目的地数组都是引用数据类型,那么子类类型可以赋值给父类类型
三、Runtine

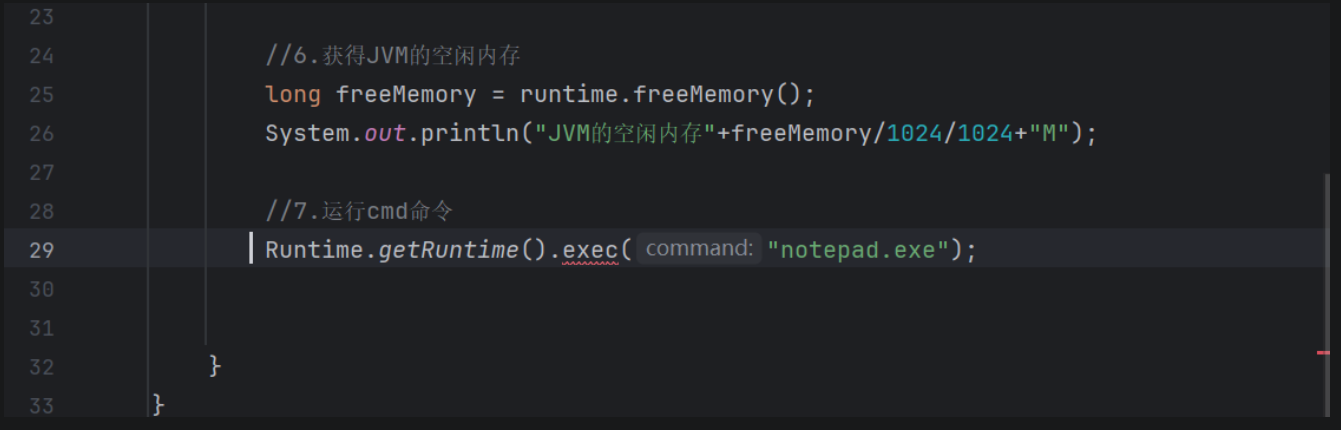
package demo03;public class RoutineDemo01 { public static void main(String[] args) { //1.获取Runtime对象 Runtime runtime = Runtime.getRuntime(); //2.exit停止虚拟机 //runtime.exit(0); //System.out.println(\"看看我执行了吗?\"); //3.获取虚拟机的最大内存 long maxMemory = runtime.maxMemory(); System.out.println(\"虚拟机的最大内存\"+maxMemory); //4.获得CPU的核数 int availableProcessors = runtime.availableProcessors(); System.out.println(\"CPU的核数\"+availableProcessors); //5.获得JVM的总内存 long totalMemory = runtime.totalMemory(); System.out.println(\"JVM的总内存\"+totalMemory/1024/1024+\"M\"); //6.获得JVM的空闲内存 long freeMemory = runtime.freeMemory(); System.out.println(\"JVM的空闲内存\"+freeMemory/1024/1024+\"M\"); //7.运行cmd命令 Runtime.getRuntime().exec(\"notepad.exe\"); }}在第29行代码中会遇到红色波浪线,这就是我们后面要学到的异常
我们可以将鼠标点击红色波浪线然后Alt+回车
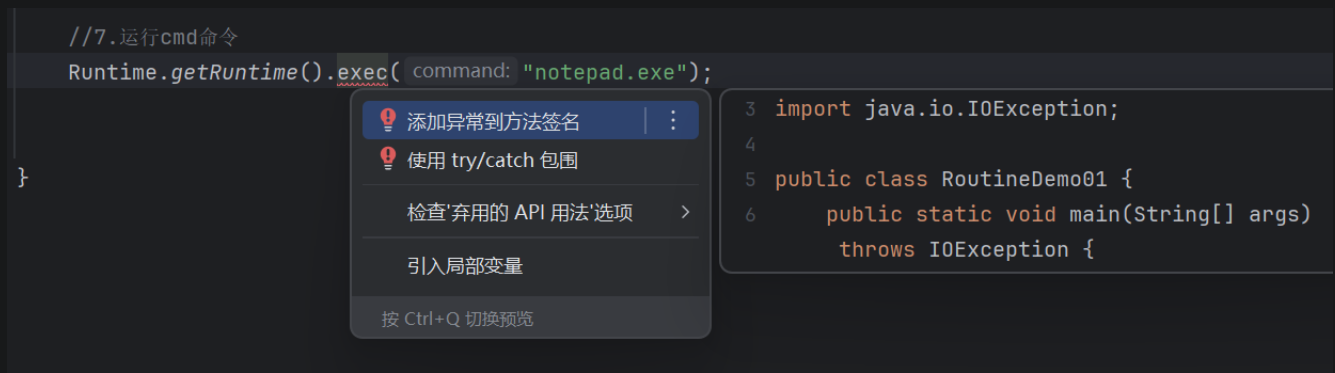
修改后的代码:
package demo03;import java.io.IOException;public class RoutineDemo01 { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { //1.获取Runtime对象 Runtime runtime = Runtime.getRuntime(); //2.exit停止虚拟机 //runtime.exit(0); //System.out.println(\"看看我执行了吗?\"); //3.获取虚拟机的最大内存 long maxMemory = runtime.maxMemory(); System.out.println(\"虚拟机的最大内存\"+maxMemory); //4.获得CPU的核数 int availableProcessors = runtime.availableProcessors(); System.out.println(\"CPU的核数\"+availableProcessors); //5.获得JVM的总内存 long totalMemory = runtime.totalMemory(); System.out.println(\"JVM的总内存\"+totalMemory/1024/1024+\"M\"); //6.获得JVM的空闲内存 long freeMemory = runtime.freeMemory(); System.out.println(\"JVM的空闲内存\"+freeMemory/1024/1024+\"M\"); //7.运行cmd命令 Runtime.getRuntime().exec(\"notepad.exe\"); }}

