【优选算法】BFS解决最短路问题(单源)

目录
- 最短路问题简介
- 一、[迷宫中离入口最近的出口](https://leetcode.cn/problems/nearest-exit-from-entrance-in-maze/description/)
- 二、[最小基因变化](https://leetcode.cn/problems/minimum-genetic-mutation/description/)
- 三、[单词接龙](https://leetcode.cn/problems/word-ladder/description/)
- 四、[为高尔夫比赛砍树](https://leetcode.cn/problems/cut-off-trees-for-golf-event/description/)
- 结尾
最短路问题简介
单源最短路问题指:从图中一个特定的起点(称为 “源点”)出发,求解到图中所有其他顶点的最短路径。
边权为 1 的单源最短路
当图中所有边的权重均为 1 时,图可视为 “等权图”(每条边的 “代价” 相同)。此时,求解单源最短路的核心思路是利用 BFS 的层次遍历特性。
一、迷宫中离入口最近的出口
题目描述:

思路讲解:
本道题需要我们找到从迷宫入口到最近出口的最短路径。以下是具体思路:
- 创建一个队列;创建一个与原二维数组同等规模的二维数组,用于标记该点是否被访问,并将这个二维数组初始化为false,表示未被访问;创建一个变量记录当前步数
- 将入口位置加入队列,并标记为 true ,表示已访问(避免重复处理)。
- BFS遍历过程:
- 从队列中取出当前位置,遍历四个方向的相邻位置,若合法(在范围内、非墙、未访问),检查是否为出口(不能是入口),若为出口,立即返回当前步数
- 若合法并且不是出口,则标记位 true ,表示已访问并加入队列。
- 没有找到出口,返回 - 1。
编写代码:
class Solution { int dx[4] = {0,0,-1,1}; int dy[4] = {1,-1,0,0}; int rows , cols;public: int _bfs(vector<vector<char>>& maze,vector<vector<bool>>& vis,int row,int col) { queue<pair<int,int>> qu; vis[row][col] = true; qu.push({row,col}); int ret = 0; while(!qu.empty()) { int cnt = qu.size(); ret++; while(cnt--) { int qu_x = qu.front().first , qu_y = qu.front().second; qu.pop(); for(int k = 0 ; k < 4 ; k++) { int x = qu_x + dx[k] , y = qu_y + dy[k]; if(x >= 0 && x < rows && y >= 0 && y < cols && maze[x][y] == \'.\' && vis[x][y] == false) { if(x == 0 || x == rows - 1 || y == 0 || y == cols - 1) return ret; vis[x][y] = true; qu.push({x,y}); } } } } return -1; } int nearestExit(vector<vector<char>>& maze, vector<int>& entrance) { rows = maze.size() , cols = maze[0].size(); vector<vector<bool>> vis(rows,vector<bool>(cols,false)); int ans = _bfs(maze,vis,entrance[0],entrance[1]); return ans; }};二、最小基因变化
题目描述:

思路讲解:
本道题需要我们找到从起始基因序列 start 到目标基因序列 end 的最小变化次数,每次变化必须生成基因库 bank 中的有效序列。下面是具体思路:
- 将基因库bank存入哈希集合(unordered_set),方便快速判断某个基因序列是否有效(存在于基因库中)。若end不在基因库中,直接返回-1(无法完成变化)
- 队列存储 “当前基因序列” ,起始时将start加入队列。用另一个哈希集合us_have 记录已访问的基因序列,避免重复处理(防止循环)
- 定义一个变量记录当前步数
- BFS逐层扩展搜索
- 记录当前队列中元素的个数为 cnt,并将步数 +1
- 将以下步骤循环执行 cnt 次
- 从队列中取出当前基因序列,遍历序列的每个位置
- 对每个位置,尝试替换为A、C、G、T中与当前字符不同的字符,生成新基因序列
- 若新序列是end,直接返回当前步数
- 若新序列在基因库中且未被访问,将其加入队列,再添加到 us_have 表示已访问
- 没有找到,返回-1。
编写代码:
class Solution { char d_char[4] = {\'A\',\'C\',\'G\',\'T\'};public: int minMutation(string startGene, string endGene, vector<string>& bank) { unordered_set<string> us_have; // 已经遍历过的 unordered_set<string> us_bank(bank.begin(),bank.end()); // 基因库 queue<string> qu; qu.push(startGene); us_bank.insert(startGene); int ans = 0; while(!qu.empty()) { ans++; int cnt = qu.size(); while(cnt--) { string q_s = qu.front(); qu.pop(); for(int i = 0 ; i < 8 ; i++) { for(int j = 0 ; j < 4 ; j++) { string tmp = q_s; tmp[i] = d_char[j]; if(us_bank.find(tmp) != us_bank.end() && us_have.find(tmp) == us_have.end()) { if(tmp == endGene) return ans; us_have.insert(tmp); qu.push(tmp); } } } } } return -1; }};三、单词接龙
题目描述:

思路讲解:
本道题需要我们找到从起始单词 beginWord 到目标单词 endWord 的最短转换序列,每次转换只能改变一个字母,且转换后的单词必须存在于字典中。本道题与上一道题的思路基本一致,以下是具体思路:
- 将字典 wordList 转换为哈希集合(unordered_set),以便快速检查某个单词是否在字典中存在。若 endWord 不在字典中,直接返回 0。
- 将起始单词 beginWord 加入队列。使用哈希集合 us_have 记录已访问的单词,避免重复处理。
- 定义一个变量记录当前步数(beginWord也算1步)
- BFS逐层扩展搜索:
- 记录当前队列中元素的个数为 cnt,并将步数 +1
- 将以下步骤循环执行 cnt 次
- 从队列中取出当前单词
- 遍历当前单词的每个位置,尝试将该位置的字符替换为 a 到 z 中的任意一个
- 若新单词等于 endWord,直接返回当前步数。
- 若生成的新单词有效(在字典中)且未被访问过,将其加入队列,再添加到 us_have 表示已访问
- 没有找到目标,返回 0。
编写代码:
class Solution {public: int ladderLength(string beginWord, string endWord, vector<string>& wordList) { if (find(wordList.begin(), wordList.end(), endWord) == wordList.end()) return 0; unordered_set<string> us_have; // 已经遍历过的字符串 unordered_set<string> us_words(wordList.begin(), wordList.end()); // 字典 queue<string> qu; qu.push(beginWord); us_have.insert(beginWord); int len = beginWord.size(); // 单词的长度 int ans = 1; while (!qu.empty()) { ans++; int cnt = qu.size(); while (cnt--) { string q_s = qu.front(); qu.pop(); for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < 26; j++) { string tmp = q_s; tmp[i] = \'a\' + j; if (us_words.find(tmp) != us_words.end() && us_have.find(tmp) == us_have.end()) { if (tmp == endWord) return ans; qu.push(tmp); us_have.insert(tmp); } } } } } return 0; }};四、为高尔夫比赛砍树
题目描述:
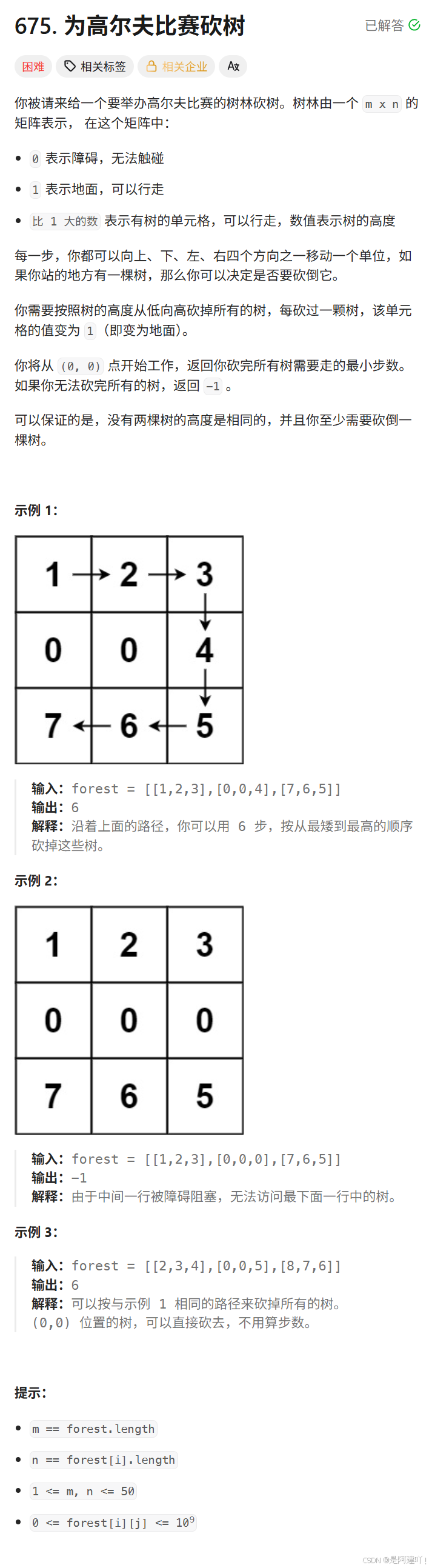
思路讲解:
本道题需要我们按照树的高度从低到高砍树,并计算最小步数。可以使用多次BFS解决,以下是具体思路:
- 遍历矩阵,将所有树的位置和高度存入数组,并按高度排序。
- 遍历数组,依次通过BFS计算从当前位置到下一棵树的最短路径,累加步数。
- 若任意两棵树之间无法到达,返回 - 1。
编写代码:
class Solution { typedef pair<int,int> PII; int dx[4] = {0,0,-1,1}; int dy[4] = {1,-1,0,0}; int rows , cols;public: int bfs(vector<vector<int>>& forest , int row , int col , int erow , int ecol) { if(row == erow && col == ecol) return 0; vector<vector<bool>> vis(rows,vector<bool>(cols,false)); queue<PII> qu; qu.push({row,col}); vis[row][col] = true; int ret = 0; while(!qu.empty()) { ret++; int cnt = qu.size(); while(cnt--) { int qu_x = qu.front().first , qu_y = qu.front().second; qu.pop(); for(int i = 0 ; i < 4 ; i++) { int x = qu_x + dx[i] , y = qu_y + dy[i]; if(x >= 0 && x < rows && y >= 0 && y < cols && forest[x][y] > 0 && vis[x][y] == false) { if(x == erow && y == ecol) return ret; qu.push({x,y}); vis[x][y] = true; } } } } return -1; } int cutOffTree(vector<vector<int>>& forest) { vector<PII> vpos; int ans = 0; rows = forest.size() , cols = forest[0].size(); if(forest[0][0] == 0) return -1; for(int i = 0 ; i < rows ; i++) { for(int j = 0 ; j < cols ; j++) { if(forest[i][j] > 1) { vpos.push_back({i,j}); } } } sort(vpos.begin(),vpos.end(),[&](PII& p1 , PII& p2){ return forest[p1.first][p1.second] < forest[p2.first][p2.second]; }); int size = vpos.size(); int row = 0 , col = 0; for(int i = 0 ; i < size ; i++) { int a = vpos[i].first , b = vpos[i].second; int n = bfs(forest,row,col,a,b); if(n == -1) return -1; else ans += n; row = a , col = b; } return ans; }};结尾
如果有什么建议和疑问,或是有什么错误,大家可以在评论区中提出。
希望大家以后也能和我一起进步!!🌹🌹
如果这篇文章对你有用的话,希望大家给一个三连支持一下!!🌹🌹