鸿蒙Harmony-自定义List组件,解决List组件手势滑动点击卡住问题
一,背景
在OpenHarmony 4.0系统中,可能会存在这样的问题,带滑动的系统组件包括List,Grid,Scrool,Tabs等等,在长时间滑动或多指同时剧烈滑动时,有概率出现该组件所有的触控失效的问题,表现为该组件卡死,但是点击其他组件仍可以正常显示。
二,问题分析
以List组件为例分析,问题发生时,List组件的滑动和点击全部都失效了,但是重写List的onTouch方法时,发现onTouch方法中仍然有日志打印,且在onTouch方法中设置滑动不生效,可见List组件的滑动并不是走的onTouch方法,而是走的手势gesture。
为了复现此问题,又用Scrool,Tabs,Grid等组件尝试复现,发现都存在此问题。
三,解决方案
当我们禁用List的手势时,代码如下:
@Entry@Componentstruct TestPage { @State list:Array =new Array aboutToAppear(){ this.list = [\"111\",\"222\",\"333\",\"444\",\"555\" ,\"666\",\"777\",\"888\",\"999\",\"1010\",\"1111\", \"1212\",\"1313\",\"1414\",\"1515\",\"1616\", \"1717\",\"1818\",\"1919\",\"2020\"] } build() { List() { ForEach(this.list, (item: string) => { ListItem() { Text(item) .width(\'100%\') .height(50) .onClick(() => { console.info(\"yz----点击了\"+item) }) } }) } .enableScrollInteraction(false)//关闭滚动手势 .width(\'100%\') .height(\'100%\') }}用多指复现未复现到卡死问题。因此,可以通过禁用手势滑动,重写onTouch方法,自定义滑动事件,来避免此问题。
四,重写滑动事件
首先我们先重写onTouch事件,代码如下:
@Entry@Componentstruct TestPage { @State list:Array =new Array aboutToAppear(){ this.list = [\"111\",\"222\",\"333\",\"444\",\"555\" ,\"666\",\"777\",\"888\",\"999\",\"1010\",\"1111\", \"1212\",\"1313\",\"1414\",\"1515\",\"1616\", \"1717\",\"1818\",\"1919\",\"2020\"] } build() { List() { ForEach(this.list, (item: string) => { ListItem() { Text(item) .width(\'100%\') .height(50) .onClick(() => { console.info(\"yz----点击了\"+item) }) } }) } .enableScrollInteraction(false)//关闭滚动手势 .width(\'100%\') .height(\'100%\') .onTouch((event: TouchEvent) => { switch (event.type) { case TouchType.Down: //按下 break case TouchType.Move: //移动 break case TouchType.Up: //抬起 break } }) }}我们先重写一跟手指的滑动事件,屏蔽掉多个手指的滑动,写完一个手指的再写多个手指的。
因此要在按下的时候记录此次触摸的手指个数,并且在按下移动和抬起的时候根据此次按下的手指的个数,屏蔽掉多个手指的触摸:
@Entry@Componentstruct TestPage { @State list:Array =new Array //当前按下的手指数量 @State currentFingers: number = 0 aboutToAppear(){ this.list = [\"111\",\"222\",\"333\",\"444\",\"555\" ,\"666\",\"777\",\"888\",\"999\",\"1010\",\"1111\", \"1212\",\"1313\",\"1414\",\"1515\",\"1616\", \"1717\",\"1818\",\"1919\",\"2020\"] } build() { List() { ForEach(this.list, (item: string) => { ListItem() { Text(item) .width(\'100%\') .height(50) .onClick(() => { console.info(\"yz----点击了\"+item) }) } }) } .enableScrollInteraction(false)//关闭滚动手势 .width(\'100%\') .height(\'100%\') .onTouch((event: TouchEvent) => { switch (event.type) { case TouchType.Down: //按下 this.currentFingers = event.touches.length if(this.currentFingers > 1){ console.debug(\"yz-----有多个手指按下,忽略此事件\") return } break case TouchType.Move: //移动 if(this.currentFingers > 1){ console.debug(\"yz-----有多个手指移动,忽略此事件\") return } break case TouchType.Up: //抬起 if(this.currentFingers > 1){ console.debug(\"yz-----有多个手指移动,忽略此事件\") return } break } }) }}然后定义两个变量startX,startY,记录按下时的起始位置:
@Entry@Componentstruct TestPage { @State list:Array =new Array //当前按下的手指数量 @State currentFingers: number = 0 //手指触摸X起始位置 @State startX: number = 0 //手指触摸Y起始位置 @State startY: number = 0 aboutToAppear(){ this.list = [\"111\",\"222\",\"333\",\"444\",\"555\" ,\"666\",\"777\",\"888\",\"999\",\"1010\",\"1111\", \"1212\",\"1313\",\"1414\",\"1515\",\"1616\", \"1717\",\"1818\",\"1919\",\"2020\"] } build() { List() { ForEach(this.list, (item: string) => { ListItem() { Text(item) .width(\'100%\') .height(50) .onClick(() => { console.info(\"yz----点击了\"+item) }) } }) } .enableScrollInteraction(false)//关闭滚动手势 .width(\'100%\') .height(\'100%\') .onTouch((event: TouchEvent) => { switch (event.type) { case TouchType.Down: //按下 this.currentFingers = event.touches.length if(this.currentFingers > 1){ console.info(\"yz-----有多个手指按下,忽略此事件\") return } // 记录起始位置 this.startX = event.touches[0].windowX this.startY = event.touches[0].windowY break case TouchType.Move: //移动 if(this.currentFingers > 1){ console.info(\"yz-----有多个手指移动,忽略此事件\") return } break case TouchType.Up: //抬起 if(this.currentFingers > 1){ console.info(\"yz-----有多个手指移动,忽略此事件\") return } break } }) }}因为要涉及到移动,所以我们需要新建一个Scroller去绑定List组件,来控制滑动,获取偏移距离等:
scroller: Scroller = new Scroller()....List({ scroller: this.scroller}) { ...}这里我们先控制垂直方向的滑动,所以我们在按下的时候要先记录一下Y轴当前的偏移量,什么是偏移量,下面我画个图解释一下:
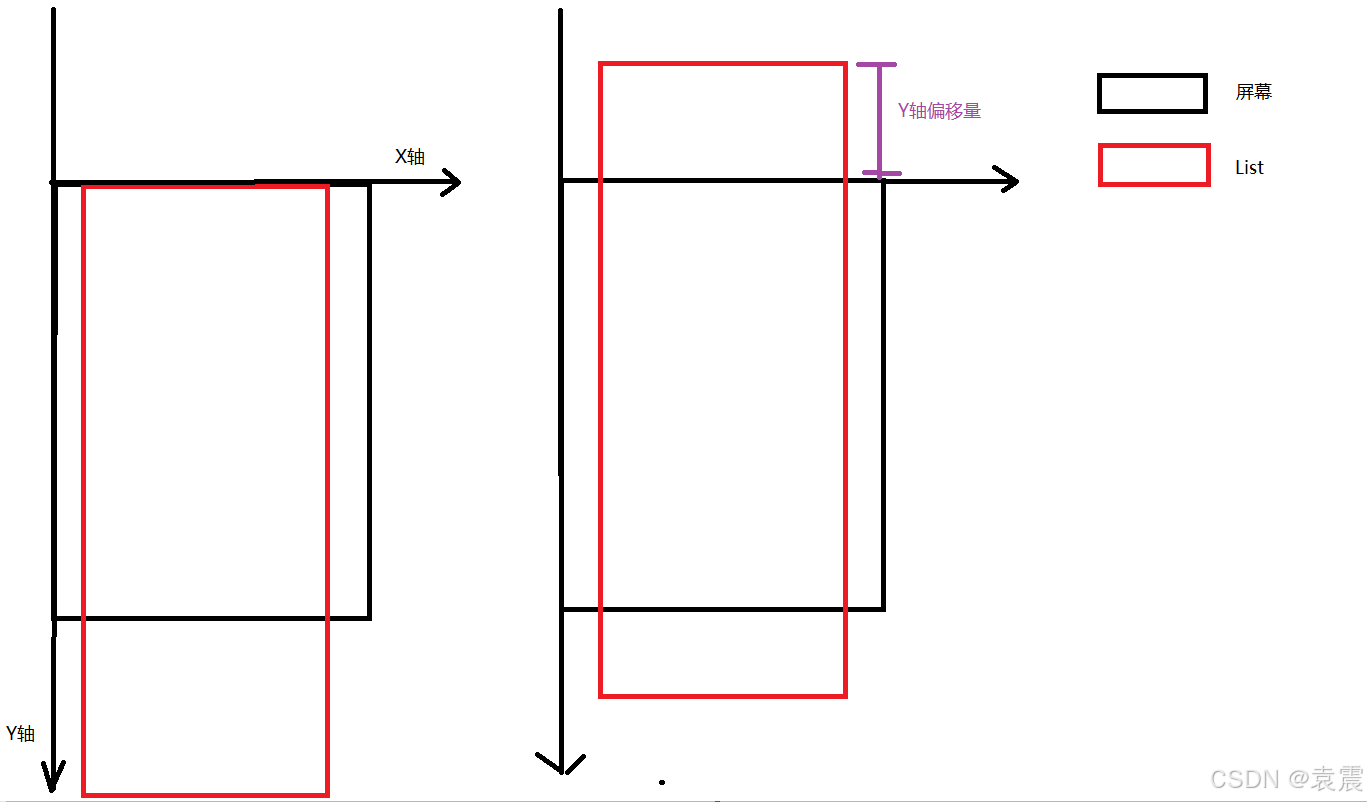
通过上面的图片我们可以看出,当我们向上滑动List组件的时候,向上超出List组件Y轴起始坐标的部分就是Y轴的偏移量。
我们用scrollY来表示目前List组件的Y轴的偏移量,当手指按下的时候,记录一下当前的偏移量。
//上次偏移量@State scrollY: number = 0......onTouch((event: TouchEvent) => { switch (event.type) { case TouchType.Down: //按下 this.currentFingers = event.touches.length if(this.currentFingers > 1){ console.info(\"yz-----有多个手指按下,忽略此事件\") return } // 记录起始位置 this.startX = event.touches[0].windowX this.startY = event.touches[0].windowY // 记录当前偏移量 this.scrollY =this.scroller.currentOffset().yOffset break我们还要记录一下手指最后一次触摸屏幕时,Y轴的位置,方便来计算移动距离,当手指抬起时,清空距离。
//上次触摸Y位置@State lastY: number = 0....onTouch((event: TouchEvent) => { .... case TouchType.Move: //移动 ... this.lastY =event.touches[0].windowY break case TouchType.Up: //抬起 ... this.lastY =0 break 下面我们还要再定义几个变量:
//移动的距离@State moveY: number = 0//阈值THRESHOLD: number = 10;//动画时间@State animationTime: number = 50moveY其实就是实际我们要设置给scrooller的目标偏移量
THRESHOLD就是一个阈值,控制滑动多大才算我们的滑动生效
animationTime是给scrooller设置的滑动的动画时间,也是为了后面滑动看起来更自然有惯性做准备,现在我们只是给他设置一个10的默认值即可
下面就是核心的移动的代码了:
...case TouchType.Move: //移动 if(this.currentFingers > 1){ console.info(\"yz-----有多个手指移动,忽略此事件\") return } let currentY = event.touches[0].windowY; //计算移动距离 const deltaX = event.touches[0].windowX - this.startX const deltaY = currentY - this.startY const absX = Math.abs(deltaX) const absY = Math.abs(deltaY) const changeY =currentY -this.lastY const absChangeY = Math.abs(changeY) if(absY >= absX && absY > this.THRESHOLD){ //计算滑动距离 this.moveY =this.scrollY-deltaY+absChangeY console.debug(\"yh------滑动距离:\"+this.moveY) //滑动 this.scroller.scrollTo({ xOffset: 0, yOffset:this.moveY, animation:{duration:this.animationTime,curve:Curve.Smooth} }) //更新最后一次移动的Y轴坐标 方便计算下一次移动进来的距离计算 this.lastY =event.touches[0].windowY } break....首先计算出x,y轴相比于按下的点滑动的距离deltaX和deltaY,并记录一下移动的绝对值absX和absY
然后计算一下这次移动的Y轴坐标相比于上一次移动的Y轴坐标的距离changeY
然后纵向移动的条件就是absY >= absX && absY > this.THRESHOLD
符合条件的情况下,计算需要移动到的目标偏移量:this.moveY =this.scrollY-deltaY+absChangeY
加上absChangeY是为了让滑动距离更大一点。
调用
this.scroller.scrollTo({ xOffset: 0, yOffset:this.moveY, animation:{duration:this.animationTime,curve:Curve.Smooth} })进行滑动。
到这里一个简单的一指上下滑动就完事了。
下面贴出这部分的完整代码:
@Entry@Componentstruct TestPage { @State list:Array =new Array //当前按下的手指数量 @State currentFingers: number = 0 //手指触摸X起始位置 @State startX: number = 0 //手指触摸Y起始位置 @State startY: number = 0 scroller: Scroller = new Scroller() //上次偏移量 @State scrollY: number = 0 //上次触摸Y位置 @State lastY: number = 0 //移动的距离 @State moveY: number = 0 //阈值 THRESHOLD: number = 10; //动画时间 @State animationTime: number = 50 aboutToAppear(){ this.list = [\"111\",\"222\",\"333\",\"444\",\"555\" ,\"666\",\"777\",\"888\",\"999\",\"1010\",\"1111\", \"1212\",\"1313\",\"1414\",\"1515\",\"1616\", \"1717\",\"1818\",\"1919\",\"2020\"] } build() { List({ scroller: this.scroller}) { ForEach(this.list, (item: string) => { ListItem() { Text(item) .width(\'100%\') .height(50) .onClick(() => { console.info(\"yz----点击了\"+item) }) } }) } .enableScrollInteraction(false)//关闭滚动手势 .width(\'100%\') .height(\'100%\') .onTouch((event: TouchEvent) => { switch (event.type) { case TouchType.Down: //按下 this.currentFingers = event.touches.length if(this.currentFingers > 1){ console.info(\"yz-----有多个手指按下,忽略此事件\") return } // 记录起始位置 this.startX = event.touches[0].windowX this.startY = event.touches[0].windowY // 记录当前偏移量 this.scrollY =this.scroller.currentOffset().yOffset break case TouchType.Move: //移动 if(this.currentFingers > 1){ console.info(\"yz-----有多个手指移动,忽略此事件\") return } let currentY = event.touches[0].windowY; //计算移动距离 const deltaX = event.touches[0].windowX - this.startX const deltaY = currentY - this.startY const absX = Math.abs(deltaX) const absY = Math.abs(deltaY) const changeY =currentY -this.lastY const absChangeY = Math.abs(changeY) if(absY >= absX && absY > this.THRESHOLD){ //计算滑动距离 this.moveY =this.scrollY-deltaY+absChangeY //滑动 this.scroller.scrollTo({ xOffset: 0, yOffset:this.moveY, animation:{duration:this.animationTime,curve:Curve.Smooth} }) //更新最后一次移动的Y轴坐标 方便计算下一次移动进来的距离计算 this.lastY =event.touches[0].windowY } break case TouchType.Up: //抬起 if(this.currentFingers > 1){ console.info(\"yz-----有多个手指移动,忽略此事件\") return } this.lastY =0 break } }) }}五,增加惯性滑动
上面的代码我们虽然完成了List的滑动,但是用起来却非常的别扭,因为我们缺少了在抬起手指时的惯性滑动,下面我们就来解决一下。
关于抬起时的惯性滑动,我们要分三种情况来分析。
第一种就是从手指按下到抬起的时间很短但是有滑动,这种情况我们就认为是扫动,一般这种情况会连续多次去扫动屏幕,这种情况必须要给个惯性滑动
第二种就是从手指按下到抬起额时间很长,但是抬起时的速度很快,我们就认为是滑动了一段距离,但是抬起那一下猛地向上一滑,这种情况也必须要给个惯性滑动
第三种就是从手指按下到抬起额时间很长,而且抬起时的速度很慢,这种情况就是正常的拖动,不能给惯性
5.1 快速扫动增加惯性
上面提到了,这种情况下的惯性滑动,就是从手指按下到抬起的时间很短但是有滑动,这个时间我通过测量定义为300ms比较合适。
为了计算从按下到抬起的总时间,我们记录一个手指按下的时间戳,并计算时间从按下到抬起的总时间,小于300ms时,就认为是第一种情况:
...//手指按下的时间戳@State startTime: number = 0...case TouchType.Down: //按下 ... // 记录起始时间 this.startTime = new Date().getTime() breakcase TouchType.Up: //抬起 if(this.currentFingers > 1){ console.info(\"yz-----有多个手指移动,忽略此事件\") return } //记录抬起时间戳 const nowTime = new Date().getTime() //计算从按下到抬起的时间间隔 const totalDuration = nowTime - this.startTime; //总时间小于300ms,认为是手指的扫动 if(totalDuration < 300 ){ } this.lastY =0 break这种情况下的移动和手指触摸的移动是差不多,但是因为是惯性,我们要将动画时间设置的长一点,我这里是800ms,也可以根据自己的需求更改。
滑动的距离也要根据滑动方向来分开计算,因为向下滑动时,滑动偏移量的最小值是0,向上滑动时,偏移量的最大值就得是根据具体的item大小来计算了。
下面我们先实现向下滑动的惯性:
...case TouchType.Up: //抬起 ... //计算滑动方向和滑动距离const deltaX = event.touches[0].windowX - this.startXconst deltaY = event.touches[0].windowY - this.startYconst absX = Math.abs(deltaX)const absY = Math.abs(deltaY)const changeY =event.touches[0].windowY -this.startYconst absChangeY = Math.abs(changeY)//惯性滑动时,动画时间设置为800msthis.animationTime =800//移动方向为垂直移动 且移动距离大于阈值 则认为是上下滑动if(absY >= absX && absY > this.THRESHOLD){ //上下滑动 let distince = 0 //根据测量得到的比较合适的滑动距离 if(absChangeY 0) { //向下滑动 边界为0 let result =this.moveY-deltaY+(absChangeY-distince) //边界检查 if(result <0){ result =0 } //滑动 this.scroller.scrollTo({ xOffset: 0, yOffset:result, animation:{duration:this.animationTime,curve:Curve.Ease} }) }else { //向上滑动 }由于向上滑动需要计算出List的总高度以及每个item的高度及List的item之间的间隔等距离,所以这里我们先空一下,等到要封装List组件的时候,再把这块加上。
5.2 缓慢滑动,但是抬手比较快,增加惯性
要判断抬手比较快,就要计算抬手时的速度。
要计算抬手时的速度,就得在移动的时候,根据上一次的时间和移动距离实时计算,因为在抬起时,我们是无法计算的。
所以先定义几个变量:
// 上一次移动事件的垂直距离(相对于上一次移动的位置)@State lastMoveY: number = 0@State lastMoveDeltaY: number = 0@State lastMoveInterval: number = 0然后在移动时计算出与上一次移动的位移差和时间差:
。。。 case TouchType.Move: //移动。。。 // 计算与上一次移动的位移差和时间差,用于计算速度 this.lastMoveDeltaY = currentY - this.lastMoveY; this.lastMoveInterval = currentTime - this.lastMoveTime; this.lastMoveY = currentY; this.lastMoveTime = currentTime;。。。 case TouchType.Up: //抬起 。。。 //计算从按下到抬起的时间间隔 const totalDuration = nowTime - this.startTime; // 计算抬起前的瞬时速度 let flickSpeed = 0; if (this.lastMoveInterval > 0) { flickSpeed = this.lastMoveDeltaY / this.lastMoveInterval; } 。。。 if(totalDuration = 500 && Math.abs(flickSpeed)>0.1){ //缓慢滑动 但是抬手比较快 需要给个惯性 看着舒服点 const currentScrollY :number= this.scroller.currentOffset().yOffset; // 根据速度计算惯性滑动距离(速度越大距离越长) 500为惯性系数 const flickDistance = flickSpeed * 500; // 计算滚动距离 let targetY = 0; const changeY =event.touches[0].windowY -this.startY if(changeY>0){ //向下滑动 边界为0 targetY = currentScrollY - Math.abs(flickDistance); if(targetY <0){ targetY =0 } }else { //向上滑动 } //惯性滑动 将动画时间设置为800ms this.animationTime = 800; //滑动 this.scroller.scrollTo({ xOffset: 0, yOffset: targetY, animation: { duration: this.animationTime, curve: Curve.Ease } });} ... 还是先省略向上滑动
六,增加两指操作
要进行两指操作,首先要放开两指:
。。。case TouchType.Down: //按下 this.currentFingers = event.touches.length if(this.currentFingers > 2){ console.info(\"yz-----有多个手指按下,忽略此事件\") return }。。。。case TouchType.Move: //移动 if(this.currentFingers > 2){ console.info(\"yz-----有多个手指移动,忽略此事件\") return }。。。。if(this.currentFingers > 2){ console.info(\"yz-----有多个手指移动,忽略此事件\") return }。。。。这样写完了之后运行会发现,这样会有一个问题,就是当我们两个手指并不是同时落下时,就会有跳动。
为什么会出现这样的情况呢?
比如说我食指先触摸的屏幕,然后中指又触摸的屏幕,食指和中指之间是有一段距离的,离开时我如果是食指先离开的屏幕,中指还在屏幕上,此时我们获取到的点的坐标就是中指的坐标,因为他们两之间有一段距离,所以就会出现跳动的情况。
要解决这种情况,我们就要知道只剩一个手指的时候,在移动的时候就要把两指之间的距离差补齐,这样就不会出现跳动了。
首先我们要知道什么时候只剩一个手指了,所以定义一个变量:
@State isOneFingerLeave: boolean = false在按下时将他初始化为false,在抬起只剩一个手指时,将他置为true
。。。case TouchType.Down: //按下 。。。 this.isOneFingerLeave = false 。。。case TouchType.Up: //抬起 。。。 if(event.touches.length == 2){ this.isOneFingerLeave = true console.debug(\"yz-----抬起一个手指,还剩一个手指,忽略此事件\") return } 。。。。然后定义两个变量,来分别表示两个手指之间的距离和上个手指触摸的坐标
@State twoFingerDistance: number = 0@State lastCurrentY: number = 0按下时将twoFingerDistance置为0,在移动时通过是否还剩一跟手指触摸来计算距离:
...case TouchType.Move: if(this.currentFingers > 2){ console.debug(\"yz-----有多个手指移动,忽略此事件\") return } let currentY = event.touches[0].windowY; if(this.isOneFingerLeave){ console.debug(\"yz----两个手指只剩一个手指了,currentY:\"+currentY+\" lastCurrentY:\"+this.lastCurrentY) if(Math.abs(currentY - this.lastCurrentY) < 5){ console.debug(\"yz----两个手指只剩一个手指了,但是该手指是先触摸屏幕的手指,忽略此事件\") }else { if(this.twoFingerDistance ==0){ this.twoFingerDistance =this.lastCurrentY -currentY } currentY = event.touches[0].windowY+this.twoFingerDistance } }else { this.lastCurrentY = currentY }...这样就解决了跳动的问题。
但是还有一个问题,就是如果两个手指不是同时落下的,Down事件就会走两次,这样初始化操作也会走两次,所以我们要屏蔽掉后面的down事件:
//是否按下了 @State isDownStart: boolean = false。。。case TouchType.Down: //按下 this.currentFingers = event.touches.length if(this.currentFingers > 2){ console.info(\"yz-----有多个手指按下,忽略此事件\") return } if(this.isDownStart){ console.debug(\"yh-----已经按下,忽略此事件\") return } this.isDownStart = true。。。case TouchType.Up:。。。 this.isDownStart = false。。。这样就解决了两个手指按下的问题。
但是经过测试发现还有一个问题,就是当我们第一次滑动的时候,他会先滑动到之前的一个位置,然后再在下次滑动的时候跳转到手指的位置继续滑动,要解决这个问题,就要在第一次滑动的时候首先滑动到当前偏移量的位置,这样就不会出现重复滑动的问题了。
我们定义一个变量来判断是否是第一次滑动:
//是否正在移动中 @State isMoving: boolean = false然后在移动中增加判断:
case TouchType.Move: //移动 ... if(absY >= absX && absY > this.THRESHOLD){ if(this.lastY ==0 && !this.isMoving ){ //第一次移动时,滑动到当前偏移量位置,防止重复滑动 console.debug(\"yh-----第一次进来:scrollY:\"+ this.scrollY) this.scroller.scrollTo({ xOffset: 0, yOffset:this.scrollY }) this.lastY =event.touches[0].windowY return } //记录正在滑动中的状态,判断是否需要进入第一次移动 this.isMoving =true //计算滑动距离 this.moveY =this.scrollY-deltaY+absChangeY //滑动 this.scroller.scrollTo({ xOffset: 0, yOffset:this.moveY, animation:{duration:this.animationTime,curve:Curve.Smooth} }) //更新最后一次移动的Y轴坐标 方便计算下一次移动进来的距离计算 this.lastY =event.touches[0].windowY } breakcase TouchType.Up: //抬起 ... this.isMoving =false break至此,两指操作就完成了。
七,List组件的封装
我们虽然完成了对于List组件的滑动事件的重写,但是总不能任何使用的地方都要写这几百行代码吧,所以我们需要把这些代码封装成一个组件,外部只需要几行代码即可调用。
首先我们要自定义一个组件,YZListView:
@Componentexport default struct YZListView { build(){ } }然后将我们重新的内容移到YZListView里面:
@Componentexport default struct YZListView { @State list:Array =new Array //当前按下的手指数量 @State currentFingers: number = 0 //手指触摸X起始位置 @State startX: number = 0 //手指触摸Y起始位置 @State startY: number = 0 scroller: Scroller = new Scroller() //上次偏移量 @State scrollY: number = 0 //上次触摸Y位置 @State lastY: number = 0 //移动的距离 @State moveY: number = 0 //阈值 THRESHOLD: number = 10; //动画时间 @State animationTime: number = 50 //手指按下的时间戳 @State startTime: number = 0 // 上一次移动事件的时间戳 @State lastMoveTime: number = 0 // 上一次移动事件的垂直距离(相对于上一次移动的位置) @State lastMoveY: number = 0 @State lastMoveDeltaY: number = 0 @State lastMoveInterval: number = 0 @State isOneFingerLeave: boolean = false @State twoFingerDistance: number = 0 @State lastCurrentY: number = 0 //是否按下了 @State isDownStart: boolean = false //是否正在移动中 @State isMoving: boolean = false build(){ List({ scroller: this.scroller}) { ForEach(this.list, (item: string) => { ListItem() { Text(item) .width(\'100%\') .height(50) .onClick(() => { console.info(\"yz----点击了\"+item) }) } }) } .enableScrollInteraction(false)//关闭滚动手势 .width(\'100%\') .height(\'100%\') .onTouch((event: TouchEvent) => { switch (event.type) { case TouchType.Down: //按下 this.currentFingers = event.touches.length if(this.currentFingers > 2){ console.info(\"yz-----有多个手指按下,忽略此事件\") return } if(this.isDownStart){ console.debug(\"yh-----已经按下,忽略此事件\") return } this.isDownStart = true // 记录起始位置 this.startX = event.touches[0].windowX this.startY = event.touches[0].windowY // 记录当前偏移量 this.scrollY =this.scroller.currentOffset().yOffset this.isOneFingerLeave = false this.twoFingerDistance = 0 // 记录起始时间 this.startTime = new Date().getTime() break case TouchType.Move: //移动 if(this.currentFingers > 2){ console.info(\"yz-----有多个手指移动,忽略此事件\") return } let currentY = event.touches[0].windowY; if(this.isOneFingerLeave){ console.debug(\"yh----两个手指只剩一个手指了,currentY:\"+currentY+\" lastCurrentY:\"+this.lastCurrentY) if(Math.abs(currentY - this.lastCurrentY) = absX && absY > this.THRESHOLD){ if(this.lastY ==0 && !this.isMoving ){ //第一次移动时,滑动到当前偏移量位置,防止重复滑动 console.debug(\"yh-----第一次进来:scrollY:\"+ this.scrollY) this.scroller.scrollTo({ xOffset: 0, yOffset:this.scrollY }) this.lastY =event.touches[0].windowY return } //记录正在滑动中的状态,判断是否需要进入第一次移动 this.isMoving =true //计算滑动距离 this.moveY =this.scrollY-deltaY+absChangeY //滑动 this.scroller.scrollTo({ xOffset: 0, yOffset:this.moveY, animation:{duration:this.animationTime,curve:Curve.Smooth} }) //更新最后一次移动的Y轴坐标 方便计算下一次移动进来的距离计算 this.lastY =event.touches[0].windowY } break case TouchType.Up: //抬起 if(this.currentFingers > 2){ console.info(\"yz-----有多个手指移动,忽略此事件\") return } if(event.touches.length == 2){ this.isOneFingerLeave = true console.debug(\"yh-----抬起一个手指,还剩一个手指,忽略此事件\") return } //记录抬起时间戳 const nowTime = new Date().getTime() //计算从按下到抬起的时间间隔 const totalDuration = nowTime - this.startTime; // 计算抬起前的瞬时速度 let flickSpeed = 0; if (this.lastMoveInterval > 0) { flickSpeed = this.lastMoveDeltaY / this.lastMoveInterval; } //总时间小于300ms,认为是手指的扫动 if(totalDuration = absX && absY > this.THRESHOLD){ //上下滑动 let distince = 0 //根据测量得到的比较合适的滑动距离 if(absChangeY 0) { //向下滑动 边界为0 let result =this.moveY-deltaY+(absChangeY-distince) //边界检查 if(result = 500 && Math.abs(flickSpeed)>0.1){ //缓慢滑动 但是抬手比较快 需要给个惯性 看着舒服点 const currentScrollY :number= this.scroller.currentOffset().yOffset; // 根据速度计算惯性滑动距离(速度越大距离越长) 500为惯性系数 const flickDistance = flickSpeed * 500; // 计算滚动距离 let targetY = 0; const changeY =event.touches[0].windowY -this.startY if(changeY>0){ //向下滑动 边界为0 targetY = currentScrollY - Math.abs(flickDistance); if(targetY = n) { return Math.ceil(x / n); } else { return Math.floor(x / n) + 1; } }}这里就会遇到几个比较棘手的问题,
1,我们的item怎么传进来?
2,@Component不能使用继承和泛型,数据类型如何传进来?
首先,要解决数据类型问题,我们可以直接把数据类型定义为Object :
@Prop list:Array =new Array然后,这样就可以定义item了:
@BuilderParam itemBuilder: (item: Object,index: number) => void= this.customBuilder@Builder customBuilder() {}List({ scroller: this.scroller}) { ForEach(this.list, (item: Object,index:number) => { ListItem() { this.itemBuilder(item,index) // 使用外部传入的渲染函数 } })}然后我们再来解决上面遗留的问题,向上滑动的时候,无法计算底部的高度。
这里我们先定义几个变量:
//内容总高度 @State contentHeight: number = 0 //容器高度 @State containerHeight: number = 0 //item 高度 @State itemHeight: number = 0然后在ListItem的onAreaChange方法中获取item的高度:
List({ scroller: this.scroller,space: this.space }) { ForEach(this.list, (item: Object, index: number) => { ListItem() { this.itemBuilder(item,index) // 使用外部传入的渲染函数 }.onAreaChange((_, area) => { if(this.itemHeight==0){ this.itemHeight =area.height as number } }) }) }在List的onAreaChange中获取容器总高度:
List({ scroller: this.scroller,space: this.space }) { ForEach(this.list, (item: Object, index: number) => { ListItem() { this.itemBuilder(item,index) // 使用外部传入的渲染函数 }.onAreaChange((_, area) => { if(this.itemHeight==0){ this.itemHeight =area.height as number } }) }) } .onAreaChange((_, area) => { this.containerHeight =area.height as number })然后在向上滑动的时候计算总高度:
case TouchType.Up: 。。。 //总时间小于300ms,认为是手指的扫动 if(totalDuration < 300 ){ 。。。 else { //向上滑动 let result =this.moveY-deltaY+(absChangeY+distince) //底部边界的计算 根据每行6个item来计算的 //总内容的高度 let count =this.ceilDivision(this.list.length,this.lanes) this.contentHeight =count*this.itemHeight+count*this.space let bottomOffSet =this.contentHeight -this.containerHeight if(bottomOffSet bottomOffSet){ result =bottomOffSet } //滑动 this.scroller.scrollTo({ xOffset: 0, yOffset:result, animation:{duration:this.animationTime,curve:Curve.Ease} }) } }else if(totalDuration >= 500 && Math.abs(flickSpeed)>0.1){ ... else { //向上滑动 //y轴最大边界值 targetY = currentScrollY + Math.abs(flickDistance); let count =this.ceilDivision(this.list.length,this.lanes) this.contentHeight =count*this.itemHeight+count*this.space let bottomOffSet =this.contentHeight -this.containerHeight if(bottomOffSet bottomOffSet){ targetY =bottomOffSet } } //惯性滑动 将动画时间设置为800ms this.animationTime = 800; //滑动 this.scroller.scrollTo({ xOffset: 0, yOffset: targetY, animation: { duration: this.animationTime, curve: Curve.Ease } }); }除此之外,我们还要开放一些变量给外部,方便外部布局使用,下面是完整代码:
@Componentexport default struct YZListView { //---------------------------必需--------------------------------- // 列表数据(必需) @Prop list:Array =new Array // 自定义列表项渲染函数(必需) @BuilderParam itemBuilder: (item: Object,index: number) => void= this.customBuilder //---------------------------可选---------------------------------- // item点击事件(可选) onButtonClick ?:(itemBean:Object,index:number)=>void //每个item之间的间距(可选,默认0) @State paddingNumber:number = 0 // 每行显示的列数(可选,默认1列) @Prop lanes: number = 1 //是否显示滚动条(可选,默认显示) @State barShow:BarState =BarState.On //水平轴的对齐方式(可选,默认居中) @State horizontalAlign:ListItemAlign =ListItemAlign.Center //------------------------分割线属性-------------------------------- //每行之间的间距(可选,默认为0) @State space: number = 0 //分割线宽度 (可选 默认为0) @State strokeWidth:number = 0 //分割线距离左侧距离(可选 默认为0) @State startMargin:number = 0 //分割线距离右侧距离(可选 默认为0) @State endMargin:number = 0 //分割线颜色(可选) @State color: string =\'#ffe9f0f0\' //------------------------分割线属性-------------------------------- //-----------------------组件内部变量 不需要传进来--------------------- onItemClick = (itemBean:Object,index:number)=>{ this.onButtonClick && this.onButtonClick(itemBean,index) } @Builder customBuilder() {} scroller: Scroller = new Scroller() //手指触摸X起始位置 @State startX: number = 0 //手指触摸Y起始位置 @State startY: number = 0 //上次触摸Y位置 @State lastY: number = 0 //上次偏移量 @State scrollY: number = 0 //阈值 THRESHOLD: number = 10; //手指按下的时间戳 @State startTime: number = 0 //动画时间 @State animationTime: number = 50 //移动的距离 @State moveY: number = 0 //移动时最后的时间 @State moveTime: number = 0 //是否正在移动中 @State isMoving: boolean = false // 上一次移动事件的时间戳 @State lastMoveTime: number = 0 // 上一次移动事件的垂直距离(相对于上一次移动的位置) @State lastMoveY: number = 0 @State lastMoveDeltaY: number = 0 @State lastMoveInterval: number = 0 //当前按下的手指数量 @State currentFingers: number = 0 //是否按下了 @State isDownStart: boolean = false @State lastCurrentY: number = 0 @State isOneFingerLeave: boolean = false @State twoFingerDistance: number = 0 //内容总高度 @State contentHeight: number = 0 //容器高度 @State containerHeight: number = 0 //item 高度 @State itemHeight: number = 0 aboutToAppear(){ } build(){ List({ scroller: this.scroller,space: this.space }) { ForEach(this.list, (item: Object, index: number) => { ListItem() { this.itemBuilder(item,index) // 使用外部传入的渲染函数 }.onAreaChange((_, area) => { if(this.itemHeight==0){ this.itemHeight =area.height as number } }) }) } .onAreaChange((_, area) => { this.containerHeight =area.height as number }) .id(\'listContainer\') .lanes(this.lanes) .enableScrollInteraction(false) .padding(this.paddingNumber) .scrollBar(this.barShow) .listDirection(Axis.Vertical) .alignListItem(this.horizontalAlign) .divider({ strokeWidth:this.strokeWidth, startMargin:this.startMargin, endMargin:this.endMargin, color: this.color }) .width(\'100%\') .height(\'100%\') .onTouch((event: TouchEvent) => { switch (event.type) { case TouchType.Down: this.currentFingers = event.touches.length if(this.currentFingers > 2){ console.debug(\"yz-----有多个手指按下,忽略此事件\") return } if(this.isDownStart){ console.debug(\"yz-----已经按下,忽略此事件\") return } this.isDownStart = true this.isOneFingerLeave = false this.twoFingerDistance = 0 // 记录起始位置 this.startX = event.touches[0].windowX this.startY = event.touches[0].windowY // 记录起始时间 this.startTime = new Date().getTime() // 记录当前偏移量 this.scrollY =this.scroller.currentOffset().yOffset this.moveY = 0 // 初始化最后一次移动时间 this.lastMoveTime = this.startTime; // 初始化最后一次移动的Y坐标 this.lastMoveY = this.startY; break case TouchType.Move: if(this.currentFingers > 2){ console.debug(\"yz-----有多个手指移动,忽略此事件\") return } let currentY = event.touches[0].windowY; if(this.isOneFingerLeave){ console.debug(\"yz----两个手指只剩一个手指了,currentY:\"+currentY+\" lastCurrentY:\"+this.lastCurrentY) if(Math.abs(currentY - this.lastCurrentY) = absX && absY > this.THRESHOLD){ if(this.lastY ==0 && !this.isMoving ){ //第一次移动时,滑动到当前偏移量位置,防止重复滑动 console.debug(\"yz-----第一次进来:scrollY:\"+ this.scrollY) this.scroller.scrollTo({ xOffset: 0, yOffset:this.scrollY }) this.lastY =event.touches[0].windowY return } //记录正在滑动中的状态,判断是否需要进入第一次移动 this.isMoving =true //计算滑动距离 this.moveY =this.scrollY-deltaY+absChangeY //滑动 this.scroller.scrollTo({ xOffset: 0, yOffset:this.moveY, animation:{duration:this.animationTime,curve:Curve.Smooth} }) //更新最后一次移动的时间 this.moveTime = new Date().getTime() //更新最后一次移动的Y轴坐标 this.lastY =event.touches[0].windowY+this.twoFingerDistance } break case TouchType.Up: if(this.currentFingers > 2){ console.debug(\"yz-----有多个手指抬起,忽略此事件\") return } if(event.touches.length == 2){ this.isOneFingerLeave = true console.debug(\"yz-----抬起一个手指,还剩一个手指,忽略此事件\") return } //记录抬起时间戳 const nowTime = new Date().getTime() //计算从按下到抬起的时间间隔 const totalDuration = nowTime - this.startTime; // 计算抬起前的瞬时速度 let flickSpeed = 0; if (this.lastMoveInterval > 0) { flickSpeed = this.lastMoveDeltaY / this.lastMoveInterval; } //总时间小于300ms,认为是手指的扫动 if(totalDuration = absX && absY > this.THRESHOLD){ //上下滑动 let distince = 0 //根据测量得到的比较合适的滑动距离 if(absChangeY 0) { //向下滑动 边界为0 let result =this.moveY-deltaY+(absChangeY-distince) //边界检查 if(result <0){ result =0 } //滑动 this.scroller.scrollTo({ xOffset: 0, yOffset:result, animation:{duration:this.animationTime,curve:Curve.Ease} }) }else { //向上滑动 let result =this.moveY-deltaY+(absChangeY+distince) //底部边界的计算 根据每行6个item来计算的 //总内容的高度 let count =this.ceilDivision(this.list.length,this.lanes) this.contentHeight =count*this.itemHeight+count*this.space let bottomOffSet =this.contentHeight -this.containerHeight if(bottomOffSet bottomOffSet){ result =bottomOffSet } //滑动 this.scroller.scrollTo({ xOffset: 0, yOffset:result, animation:{duration:this.animationTime,curve:Curve.Ease} }) } } }else if(totalDuration >= 500 && Math.abs(flickSpeed)>0.1){ //缓慢滑动 但是抬手比较快 需要给个惯性 看着舒服点 const currentScrollY :number= this.scroller.currentOffset().yOffset; // 根据速度计算惯性滑动距离(速度越大距离越长) 500为惯性系数 const flickDistance = flickSpeed * 500; // 计算滚动距离 let targetY = 0; const changeY =event.touches[0].windowY -this.startY if(changeY>0){ //向下滑动 边界为0 targetY = currentScrollY - Math.abs(flickDistance); if(targetY <0){ targetY =0 } }else { //向上滑动 //y轴最大边界值 targetY = currentScrollY + Math.abs(flickDistance); let count =this.ceilDivision(this.list.length,this.lanes) this.contentHeight =count*this.itemHeight+count*this.space let bottomOffSet =this.contentHeight -this.containerHeight if(bottomOffSet bottomOffSet){ targetY =bottomOffSet } } //惯性滑动 将动画时间设置为800ms this.animationTime = 800; //滑动 this.scroller.scrollTo({ xOffset: 0, yOffset: targetY, animation: { duration: this.animationTime, curve: Curve.Ease } }); } this.isDownStart = false this.lastY =0 this.isMoving =false break } }) } ceilDivision(x: number, n: number): number { if (x >= n) { return Math.ceil(x / n); } else { return Math.floor(x / n) + 1; } }}如何使用呢?
首先定义 自己的item:
@Componentexport default struct TestItem{ @State item:string =\"\" index: number = 0 onButtonClick ?:(item:string,index:number)=>void build(){ Text(this.item) .width(\"100%\") .height(50) .onClick(()=>{ this.onButtonClick && this.onButtonClick(this.item,this.index) }) }}然后在page中使用:
import TestItem from \'./TestItem\'import YZListView from \'./YZListView\'@Entry@Componentstruct TestPage { @State list:Array =new Array onButtonClick = (name: Object, index: number) => { //点击列表item console.log(\"yz-----点击了列表:\"+name) } @Builder toomListBuilder(item: Object,index: number) { TestItem({ item: item as string, onButtonClick: this.onButtonClick,index:index }) } aboutToAppear(){ this.list = [\"111\",\"222\",\"333\",\"444\",\"555\" ,\"666\",\"777\",\"888\",\"999\",\"1010\",\"1111\", \"1212\",\"1313\",\"1414\",\"1515\",\"1616\", \"1717\",\"1818\",\"1919\",\"2020\"] } build() { Column(){ YZListView({ onButtonClick: this.onButtonClick, list: this.list as Array, lanes: 1, itemBuilder: this.toomListBuilder, space: 20 }).width(\'100%\') } }}这样使用起来是不是就简便了很多,也避免了系统的手势滑动卡住问题。


