InternVL3:最强开源OCR大模型,轻松应对手写体、模糊PDF和表格识别!
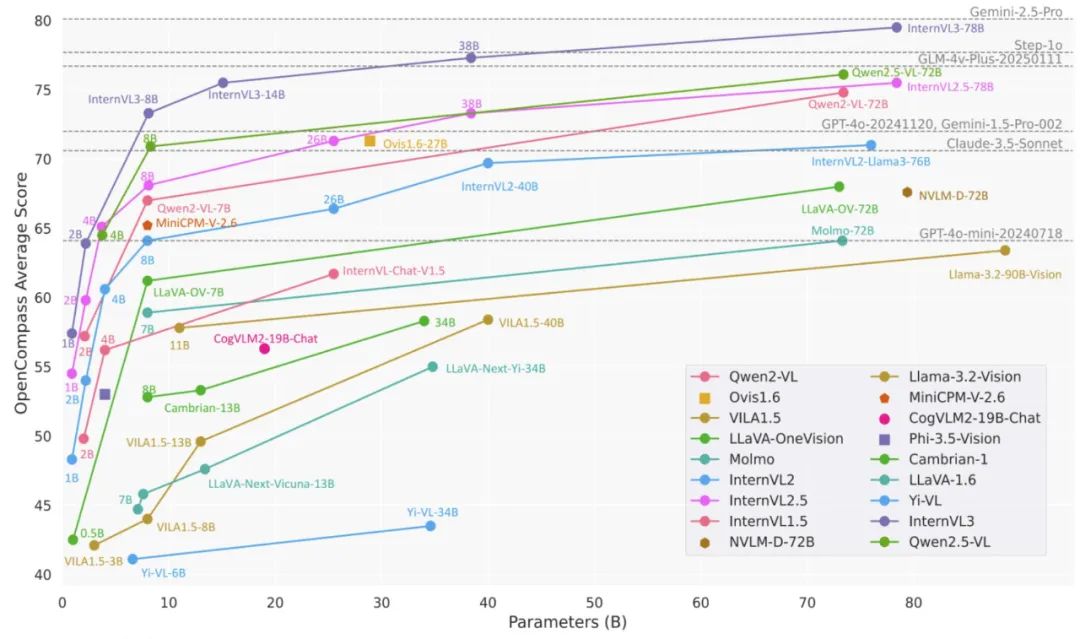
InternVL3,这是一个高级的多模态大型语言模型(MLLM)系列,展示了卓越的整体性能。与 InternVL 2.5 相比,InternVL3 表现出更优越的多模态感知和推理能力,并将多模态能力进一步扩展到工具使用、GUI 代理、工业图像分析、3D 视觉感知等地方。此外, 比较了 InternVL3 与 Qwen2.5 Chat 模型,其对应的预训练基础模型被用作 InternVL3 中语言组件的初始化。得益于原生多模态预训练,InternVL3 系列在整体文本性能上甚至优于 Qwen2.5 系列。
InternVL3 系列概述:
Model Name
Vision Part
Language Part
HF Link
InternVL3-1B
InternViT-300M-448px-V2_5
Qwen2.5-0.5B
link链接
InternVL3-2B
InternViT-300M-448px-V2_5
Qwen2.5-1.5B
link链接
InternVL3-8B
InternViT-300M-448px-V2_5
Qwen2.5-7B
link链接
InternVL3-9B
InternViT-300M-448px-V2_5
internlm3-8b-instruct
link链接
InternVL3-14B
InternViT-300M-448px-V2_5
Qwen2.5-14B
link链接
InternVL3-38B
InternViT-6B-448px-V2_5
Qwen2.5-32B
link链接
InternVL3-78B
InternViT-6B-448px-V2_5
Qwen2.5-72B
link链接
模型架构:
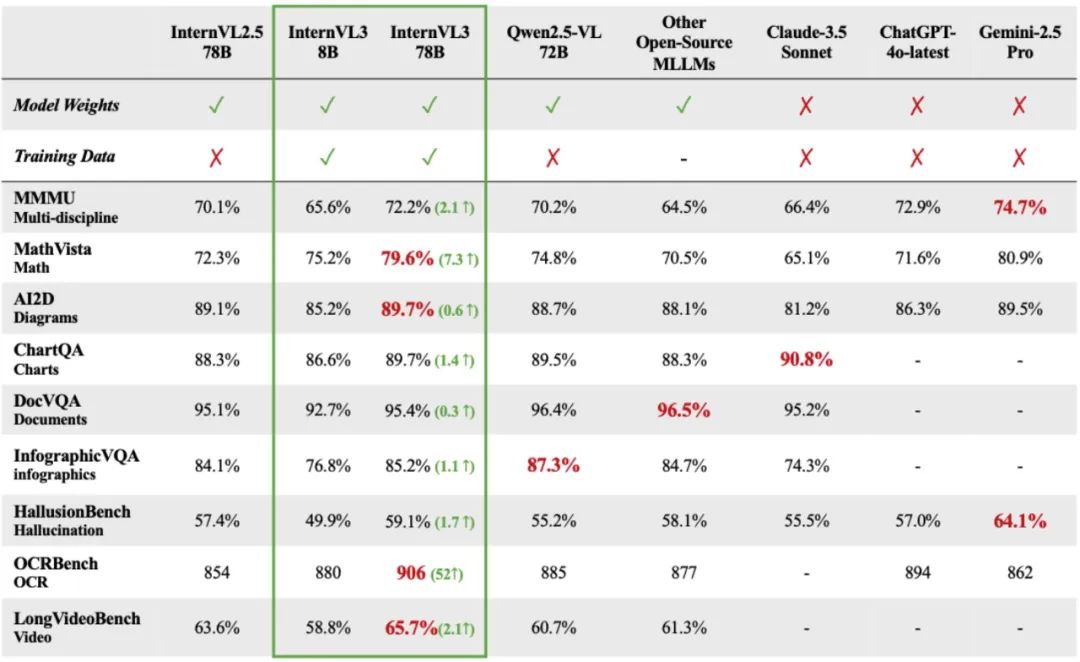
InternVL3 保留了与 InternVL 2.5 及其前辈 InternVL 1.5 和 2.0 相同的模型架构,遵循\"ViT-MLP-LLM\"范式。在新版本中,集成了一种新的增量预训练的 InternViT,并使用随机初始化的 MLP 投影仪整合了各种预训练模型,包括 InternLM 3 和 Qwen 2.5。
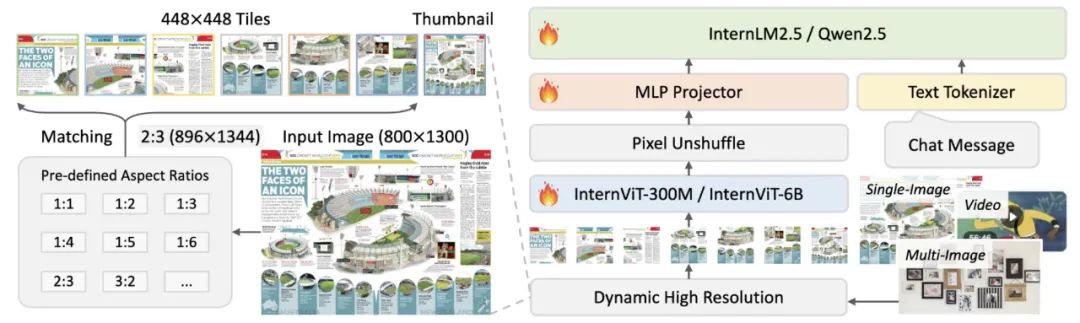
与上一版本类似,应用了像素解乱序操作,将视觉标记的数量减少到原来的四分之一。此外,采用了与 InternVL 1.5 类似的动态分辨率策略,将图像划分为 448×448 像素的瓦片。从 InternVL 2.0 开始的关键区别是,增加了对多图像和视频数据的支持。
显著的是,在 InternVL3 中,集成了可变视觉位置编码(V2PE),它使用更小、更灵活的位置增量来表示视觉标记。得益于 V2PE,InternVL3 相比其前辈展现出更好的长上下文理解能力。
训练策略:
提出了一种原生多模态预训练方法,将语言和视觉学习整合到单个预训练阶段。与先训练语言模型然后再适应处理其他模态的标准范式不同, 将多模态数据(例如,图像-文本、视频-文本或图像-文本交织序列)与大规模文本语料库交织。这种统一的训练方案允许模型同时学习语言和多模态表示,最终增强其处理视觉-语言任务的能力,无需单独的对齐或桥接模块。
监督微调:
在这个阶段,InternVL2.5 中提出的随机 JPEG 压缩、平方损失重新加权和多模态数据打包技术也被应用于 InternVL3 系列。与 InternVL2.5 相比,InternVL3 中 SFT 阶段的主要进步在于使用了更高质量和更多样化的训练数据。具体来说,我们进一步扩展了工具使用、3D 场景理解、GUI 操作、长上下文任务、视频理解、科学图表、创意写作和多模态推理的训练样本。
混合偏好优化:
在预训练和微调过程中,模型被训练为根据之前的真实标记预测下一个标记。然而,在推理过程中,模型根据其自身的先前输出预测每个标记。这种真实标记和模型预测标记之间的差异引入了分布偏移,这可能会损害模型的思维链(CoT)推理能力。为了减轻这个问题,采用 MPO,它从正样本和负样本中引入额外的监督,以使模型响应分布与真实分布对齐,从而提高推理性能。
测试时间缩放:
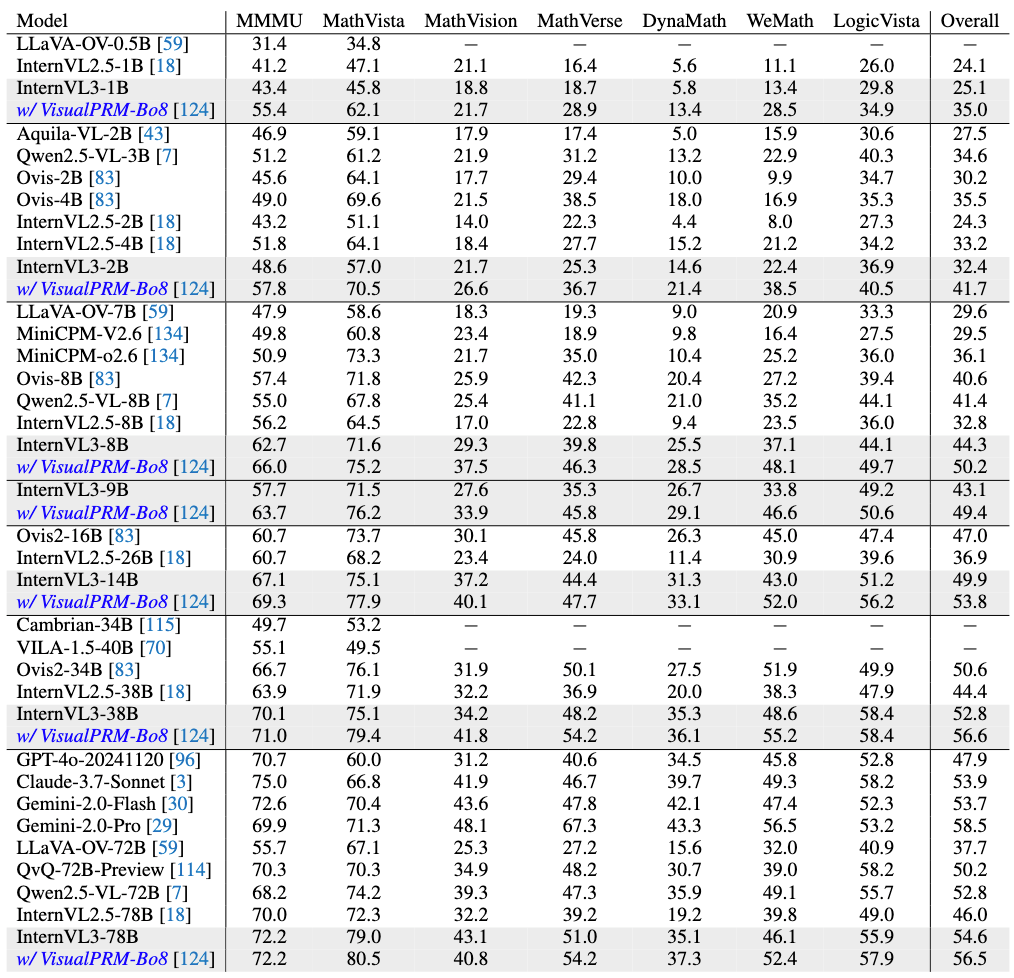
测试时缩放已被证明是增强LLMs和 MLLM 推理能力的一种有效方法。在这项工作中,我们使用 Best-of-N 评估策略,并采用 VisualPRM-8B 作为评判模型来选择最佳推理和数学评估的响应。

多模态能力评估-多模态推理与数学:
光学字符识别、图表和文档理解:
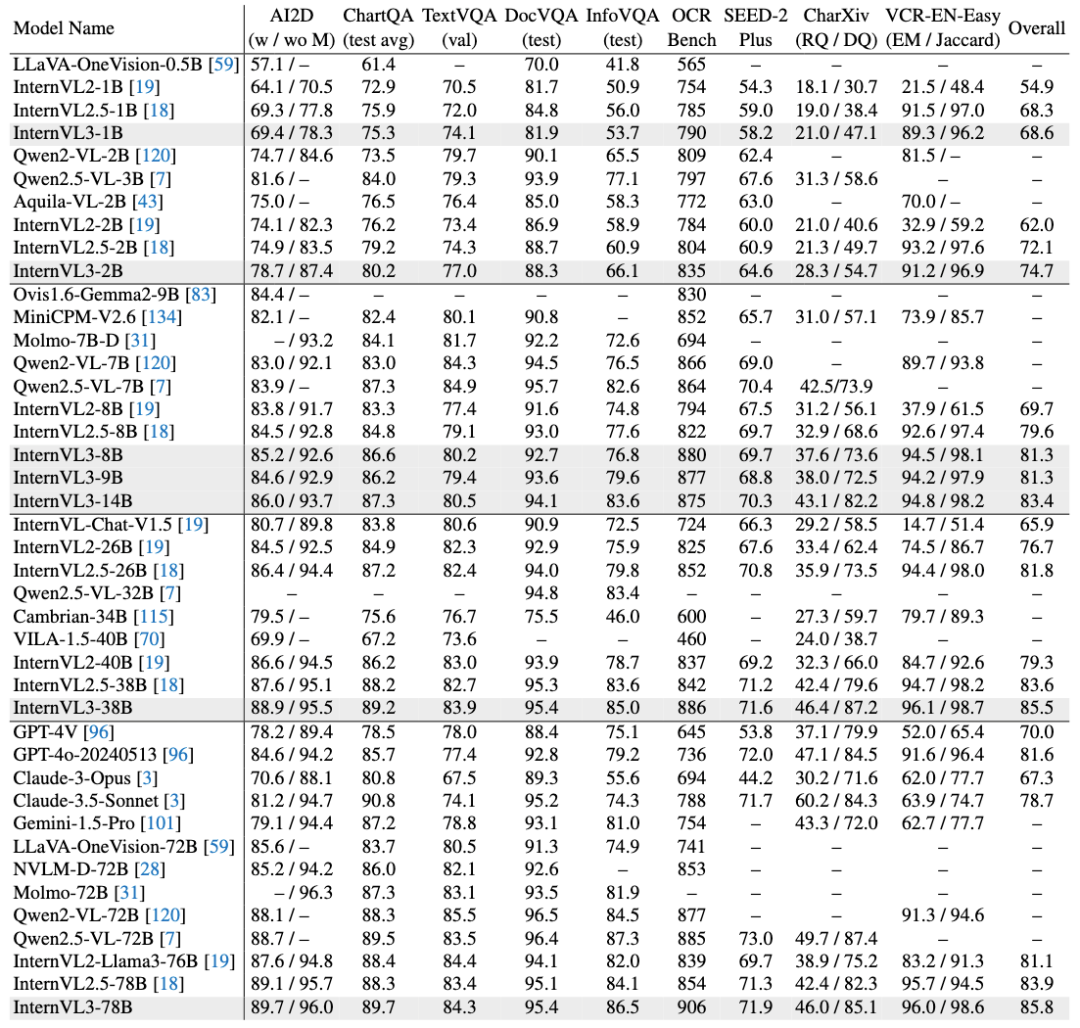
测试用例:
手写体:

票据内容提取:
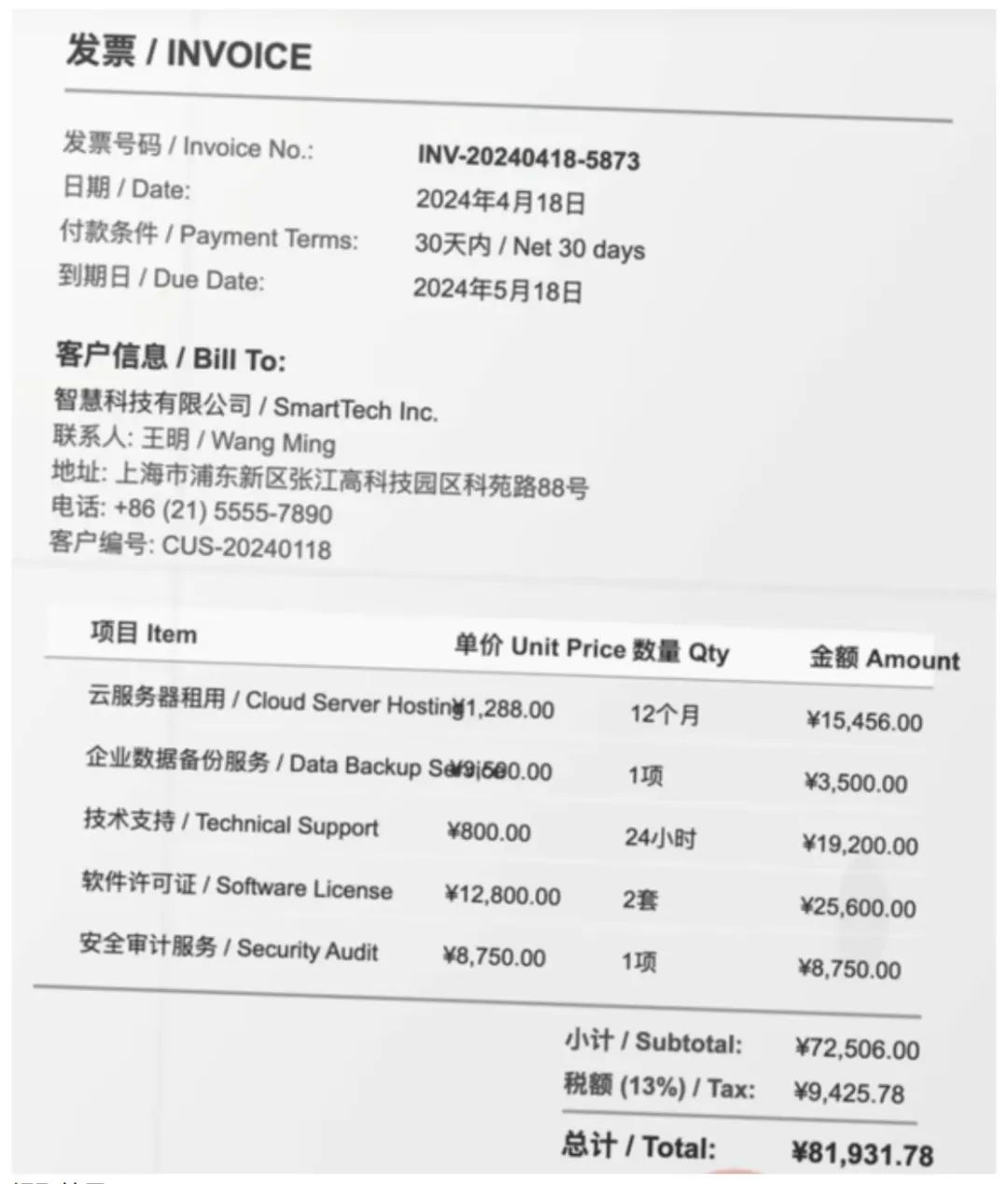
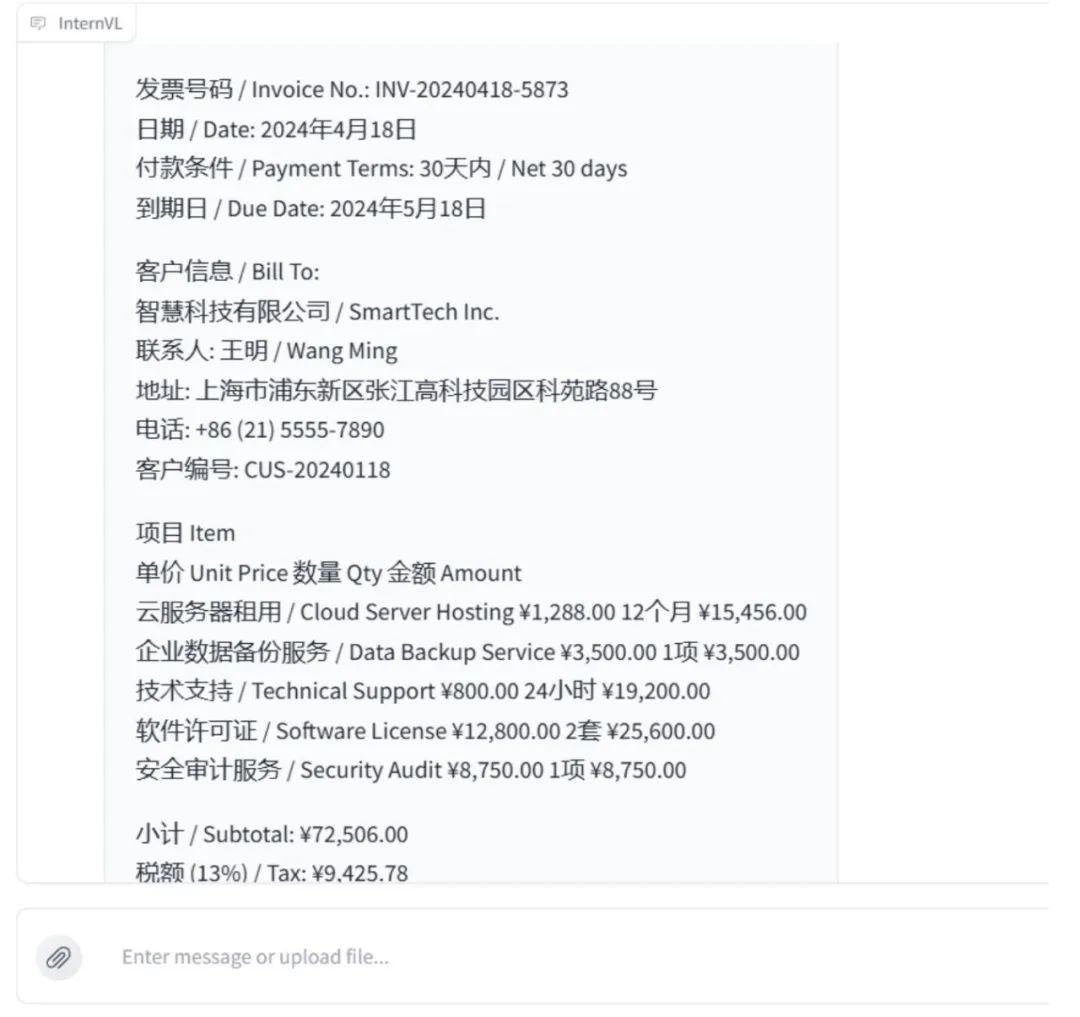
提取结果:
模糊的PDF识别:

使用模型:
模型加载
1、16 位(bf16 / fp16)
import torch
from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModel
path = \"OpenGVLab/InternVL3-14B\"
model = AutoModel.from_pretrained(
path,
torch_dtype=torch.bfloat16,
low_cpu_mem_usage=True,
use_flash_attn=True,
trust_remote_code=True).eval().cuda()
2、BNB 8 位量化
import torch
from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModel
path = \"OpenGVLab/InternVL3-14B\"
model = AutoModel.from_pretrained(
path,
torch_dtype=torch.bfloat16,
load_in_8bit=True,
low_cpu_mem_usage=True,
use_flash_attn=True,
trust_remote_code=True).eval()
多块 GPU:
import math
import torch
from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModel
def split_model(model_name):
device_map = {}
world_size = torch.cuda.device_count()
config = AutoConfig.from_pretrained(model_path, trust_remote_code=True)
num_layers = config.llm_config.num_hidden_layers
# Since the first GPU will be used for ViT, treat it as half a GPU.
num_layers_per_gpu = math.ceil(num_layers / (world_size - 0.5))
num_layers_per_gpu = [num_layers_per_gpu] * world_size
num_layers_per_gpu[0] = math.ceil(num_layers_per_gpu[0] * 0.5)
layer_cnt = 0
for i, num_layer in enumerate(num_layers_per_gpu):
for j in range(num_layer):
device_map[f\'language_model.model.layers.{layer_cnt}\'] = i
layer_cnt += 1
device_map[\'vision_model\'] = 0
device_map[\'mlp1\'] = 0
device_map[\'language_model.model.tok_embeddings\'] = 0
device_map[\'language_model.model.embed_tokens\'] = 0
device_map[\'language_model.output\'] = 0
device_map[\'language_model.model.norm\'] = 0
device_map[\'language_model.model.rotary_emb\'] = 0
device_map[\'language_model.lm_head\'] = 0
device_map[f\'language_model.model.layers.{num_layers - 1}\'] = 0
return device_map
path = \"OpenGVLab/InternVL3-14B\"
device_map = split_model(\'InternVL3-14B\')
model = AutoModel.from_pretrained(
path,
torch_dtype=torch.bfloat16,
low_cpu_mem_usage=True,
use_flash_attn=True,
trust_remote_code=True,
device_map=device_map).eval()
Transformer:
import math
import numpy as np
import torch
import torchvision.transforms as T
from decord import VideoReader, cpu
from PIL import Image
from torchvision.transforms.functional import InterpolationMode
from transformers import AutoModel, AutoTokenizer
IMAGENET_MEAN = (0.485, 0.456, 0.406)
IMAGENET_STD = (0.229, 0.224, 0.225)
def build_transform(input_size):
MEAN, STD = IMAGENET_MEAN, IMAGENET_STD
transform = T.Compose([
T.Lambda(lambda img: img.convert(\'RGB\') if img.mode != \'RGB\' else img),
T.Resize((input_size, input_size), interpolation=InterpolationMode.BICUBIC),
T.ToTensor(),
T.Normalize(mean=MEAN, std=STD)
])
return transform
def find_closest_aspect_ratio(aspect_ratio, target_ratios, width, height, image_size):
best_ratio_diff = float(\'inf\')
best_ratio = (1, 1)
area = width * height
for ratio in target_ratios:
target_aspect_ratio = ratio[0] / ratio[1]
ratio_diff = abs(aspect_ratio - target_aspect_ratio)
if ratio_diff < best_ratio_diff:
best_ratio_diff = ratio_diff
best_ratio = ratio
elif ratio_diff == best_ratio_diff:
if area > 0.5 * image_size * image_size * ratio[0] * ratio[1]:
best_ratio = ratio
return best_ratio
def dynamic_preprocess(image, min_num=1, max_num=12, image_size=448, use_thumbnail=False):
orig_width, orig_height = image.size
aspect_ratio = orig_width / orig_height
# calculate the existing image aspect ratio
target_ratios = set(
(i, j) for n in range(min_num, max_num + 1) for i in range(1, n + 1) for j in range(1, n + 1) if
i * j = min_num)
target_ratios = sorted(target_ratios, key=lambda x: x[0] * x[1])
# find the closest aspect ratio to the target
target_aspect_ratio = find_closest_aspect_ratio(
aspect_ratio, target_ratios, orig_width, orig_height, image_size)
# calculate the target width and height
target_width = image_size * target_aspect_ratio[0]
target_height = image_size * target_aspect_ratio[1]
blocks = target_aspect_ratio[0] * target_aspect_ratio[1]
# resize the image
resized_img = image.resize((target_width, target_height))
processed_images = []
for i in range(blocks):
box = (
(i % (target_width // image_size)) * image_size,
(i // (target_width // image_size)) * image_size,
((i % (target_width // image_size)) + 1) * image_size,
((i // (target_width // image_size)) + 1) * image_size
)
# split the image
split_img = resized_img.crop(box)
processed_images.append(split_img)
assert len(processed_images) == blocks
if use_thumbnail and len(processed_images) != 1:
thumbnail_img = image.resize((image_size, image_size))
processed_images.append(thumbnail_img)
return processed_images
def load_image(image_file, input_size=448, max_num=12):
image = Image.open(image_file).convert(\'RGB\')
transform = build_transform(input_size=input_size)
images = dynamic_preprocess(image, image_size=input_size, use_thumbnail=True, max_num=max_num)
pixel_values = [transform(image) for image in images]
pixel_values = torch.stack(pixel_values)
return pixel_values
def split_model(model_name):
device_map = {}
world_size = torch.cuda.device_count()
config = AutoConfig.from_pretrained(model_path, trust_remote_code=True)
num_layers = config.llm_config.num_hidden_layers
# Since the first GPU will be used for ViT, treat it as half a GPU.
num_layers_per_gpu = math.ceil(num_layers / (world_size - 0.5))
num_layers_per_gpu = [num_layers_per_gpu] * world_size
num_layers_per_gpu[0] = math.ceil(num_layers_per_gpu[0] * 0.5)
layer_cnt = 0
for i, num_layer in enumerate(num_layers_per_gpu):
for j in range(num_layer):
device_map[f\'language_model.model.layers.{layer_cnt}\'] = i
layer_cnt += 1
device_map[\'vision_model\'] = 0
device_map[\'mlp1\'] = 0
device_map[\'language_model.model.tok_embeddings\'] = 0
device_map[\'language_model.model.embed_tokens\'] = 0
device_map[\'language_model.output\'] = 0
device_map[\'language_model.model.norm\'] = 0
device_map[\'language_model.model.rotary_emb\'] = 0
device_map[\'language_model.lm_head\'] = 0
device_map[f\'language_model.model.layers.{num_layers - 1}\'] = 0
return device_map
# If you set `load_in_8bit=True`, you will need two 80GB GPUs.
# If you set `load_in_8bit=False`, you will need at least three 80GB GPUs.
path = \'OpenGVLab/InternVL3-14B\'
device_map = split_model(\'InternVL3-14B\')
model = AutoModel.from_pretrained(
path,
torch_dtype=torch.bfloat16,
load_in_8bit=False,
low_cpu_mem_usage=True,
use_flash_attn=True,
trust_remote_code=True,
device_map=device_map).eval()
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(path, trust_remote_code=True, use_fast=False)
# set the max number of tiles in `max_num`
pixel_values = load_image(\'./examples/image1.jpg\', max_num=12).to(torch.bfloat16).cuda()
generation_config = dict(max_new_tokens=1024, do_sample=True)
# pure-text conversation (纯文本对话)
question = \'Hello, who are you?\'
response, history = model.chat(tokenizer, None, question, generation_config, history=None, return_history=True)
print(f\'User: {question}\\nAssistant: {response}\')
question = \'Can you tell me a story?\'
response, history = model.chat(tokenizer, None, question, generation_config, history=history, return_history=True)
print(f\'User: {question}\\nAssistant: {response}\')
# single-image single-round conversation (单图单轮对话)
question = \'\\nPlease describe the image shortly.\'
response = model.chat(tokenizer, pixel_values, question, generation_config)
print(f\'User: {question}\\nAssistant: {response}\')
# single-image multi-round conversation (单图多轮对话)
question = \'\\nPlease describe the image in detail.\'
response, history = model.chat(tokenizer, pixel_values, question, generation_config, history=None, return_history=True)
print(f\'User: {question}\\nAssistant: {response}\')
question = \'Please write a poem according to the image.\'
response, history = model.chat(tokenizer, pixel_values, question, generation_config, history=history, return_history=True)
print(f\'User: {question}\\nAssistant: {response}\')
# multi-image multi-round conversation, combined images (多图多轮对话,拼接图像)
pixel_values1 = load_image(\'./examples/image1.jpg\', max_num=12).to(torch.bfloat16).cuda()
pixel_values2 = load_image(\'./examples/image2.jpg\', max_num=12).to(torch.bfloat16).cuda()
pixel_values = torch.cat((pixel_values1, pixel_values2), dim=0)
question = \'\\nDescribe the two images in detail.\'
response, history = model.chat(tokenizer, pixel_values, question, generation_config,
history=None, return_history=True)
print(f\'User: {question}\\nAssistant: {response}\')
question = \'What are the similarities and differences between these two images.\'
response, history = model.chat(tokenizer, pixel_values, question, generation_config,
history=history, return_history=True)
print(f\'User: {question}\\nAssistant: {response}\')
# multi-image multi-round conversation, separate images (多图多轮对话,独立图像)
pixel_values1 = load_image(\'./examples/image1.jpg\', max_num=12).to(torch.bfloat16).cuda()
pixel_values2 = load_image(\'./examples/image2.jpg\', max_num=12).to(torch.bfloat16).cuda()
pixel_values = torch.cat((pixel_values1, pixel_values2), dim=0)
num_patches_list = [pixel_values1.size(0), pixel_values2.size(0)]
question = \'Image-1: \\nImage-2: \\nDescribe the two images in detail.\'
response, history = model.chat(tokenizer, pixel_values, question, generation_config,
num_patches_list=num_patches_list,
history=None, return_history=True)
print(f\'User: {question}\\nAssistant: {response}\')
question = \'What are the similarities and differences between these two images.\'
response, history = model.chat(tokenizer, pixel_values, question, generation_config,
num_patches_list=num_patches_list,
history=history, return_history=True)
print(f\'User: {question}\\nAssistant: {response}\')
# batch inference, single image per sample (单图批处理)
pixel_values1 = load_image(\'./examples/image1.jpg\', max_num=12).to(torch.bfloat16).cuda()
pixel_values2 = load_image(\'./examples/image2.jpg\', max_num=12).to(torch.bfloat16).cuda()
num_patches_list = [pixel_values1.size(0), pixel_values2.size(0)]
pixel_values = torch.cat((pixel_values1, pixel_values2), dim=0)
questions = [\'\\nDescribe the image in detail.\'] * len(num_patches_list)
responses = model.batch_chat(tokenizer, pixel_values,
num_patches_list=num_patches_list,
questions=questions,
generation_config=generation_config)
for question, response in zip(questions, responses):
print(f\'User: {question}\\nAssistant: {response}\')
# video multi-round conversation (视频多轮对话)
def get_index(bound, fps, max_frame, first_idx=0, num_segments=32):
if bound:
start, end = bound[0], bound[1]
else:
start, end = -100000, 100000
start_idx = max(first_idx, round(start * fps))
end_idx = min(round(end * fps), max_frame)
seg_size = float(end_idx - start_idx) / num_segments
frame_indices = np.array([
int(start_idx + (seg_size / 2) + np.round(seg_size * idx))
for idx in range(num_segments)
])
return frame_indices
def load_video(video_path, bound=None, input_size=448, max_num=1, num_segments=32):
vr = VideoReader(video_path, ctx=cpu(0), num_threads=1)
max_frame = len(vr) - 1
fps = float(vr.get_avg_fps())
pixel_values_list, num_patches_list = [], []
transform = build_transform(input_size=input_size)
frame_indices = get_index(bound, fps, max_frame, first_idx=0, num_segments=num_segments)
for frame_index in frame_indices:
img = Image.fromarray(vr[frame_index].asnumpy()).convert(\'RGB\')
img = dynamic_preprocess(img, image_size=input_size, use_thumbnail=True, max_num=max_num)
pixel_values = [transform(tile) for tile in img]
pixel_values = torch.stack(pixel_values)
num_patches_list.append(pixel_values.shape[0])
pixel_values_list.append(pixel_values)
pixel_values = torch.cat(pixel_values_list)
return pixel_values, num_patches_list
video_path = \'./examples/red-panda.mp4\'
pixel_values, num_patches_list = load_video(video_path, num_segments=8, max_num=1)
pixel_values = pixel_values.to(torch.bfloat16).cuda()
video_prefix = \'\'.join([f\'Frame{i+1}: \\n\' for i in range(len(num_patches_list))])
question = video_prefix + \'What is the red panda doing?\'
# Frame1: \\nFrame2: \\n...\\nFrame8: \\n{question}
response, history = model.chat(tokenizer, pixel_values, question, generation_config,
num_patches_list=num_patches_list, history=None, return_history=True)
print(f\'User: {question}\\nAssistant: {response}\')
question = \'Describe this video in detail.\'
response, history = model.chat(tokenizer, pixel_values, question, generation_config,
num_patches_list=num_patches_list, history=history, return_history=True)
print(f\'User: {question}\\nAssistant: {response}\')
流式输出:
from transformers import TextIteratorStreamer
from threading import Thread
# Initialize the streamer
streamer = TextIteratorStreamer(tokenizer, skip_prompt=True, skip_special_tokens=True, timeout=10)
# Define the generation configuration
generation_config = dict(max_new_tokens=1024, do_sample=False, streamer=streamer)
# Start the model chat in a separate thread
thread = Thread(target=model.chat, kwargs=dict(
tokenizer=tokenizer, pixel_values=pixel_values, question=question,
history=None, return_history=False, generation_config=generation_config,
))
thread.start()
# Initialize an empty string to store the generated text
generated_text = \'\'
# Loop through the streamer to get the new text as it is generated
for new_text in streamer:
if new_text == model.conv_template.sep:
break
generated_text += new_text
print(new_text, end=\'\', flush=True) # Print each new chunk of generated text on the same line
多图像推理:
当处理多张图像时,可以将它们全部放入一个列表中。请注意,多张图像会导致输入标记的数量增加,因此通常需要增加上下文窗口的大小。
from lmdeploy import pipeline, TurbomindEngineConfig, ChatTemplateConfig
from lmdeploy.vl import load_image
from lmdeploy.vl.constants import IMAGE_TOKEN
model = \'OpenGVLab/InternVL3-14B\'
pipe = pipeline(model, backend_config=TurbomindEngineConfig(session_len=16384, tp=1), chat_template_config=ChatTemplateConfig(model_name=\'internvl2_5\'))
image_urls=[
\'https://raw.githubusercontent.com/open-mmlab/mmdeploy/main/demo/resources/human-pose.jpg\',
\'https://raw.githubusercontent.com/open-mmlab/mmdeploy/main/demo/resources/det.jpg\'
]
images = [load_image(img_url) for img_url in image_urls]
# Numbering images improves multi-image conversations
response = pipe((f\'Image-1: {IMAGE_TOKEN}\\nImage-2: {IMAGE_TOKEN}\\ndescribe these two images\', images))
print(response.text)
开源地址:https://huggingface.co/OpenGVLab/InternVL3-14B#ocr-chart-and-document-understanding
大模型&AI产品经理如何学习
求大家的点赞和收藏,我花2万买的大模型学习资料免费共享给你们,来看看有哪些东西。

1.学习路线图

第一阶段: 从大模型系统设计入手,讲解大模型的主要方法;
第二阶段: 在通过大模型提示词工程从Prompts角度入手更好发挥模型的作用;
第三阶段: 大模型平台应用开发借助阿里云PAI平台构建电商领域虚拟试衣系统;
第四阶段: 大模型知识库应用开发以LangChain框架为例,构建物流行业咨询智能问答系统;
第五阶段: 大模型微调开发借助以大健康、新零售、新媒体领域构建适合当前领域大模型;
第六阶段: 以SD多模态大模型为主,搭建了文生图小程序案例;
第七阶段: 以大模型平台应用与开发为主,通过星火大模型,文心大模型等成熟大模型构建大模型行业应用。
2.视频教程
网上虽然也有很多的学习资源,但基本上都残缺不全的,这是我自己整理的大模型视频教程,上面路线图的每一个知识点,我都有配套的视频讲解。


(都打包成一块的了,不能一一展开,总共300多集)
因篇幅有限,仅展示部分资料,需要点击下方图片前往获取
3.技术文档和电子书
这里主要整理了大模型相关PDF书籍、行业报告、文档,有几百本,都是目前行业最新的。

4.LLM面试题和面经合集
这里主要整理了行业目前最新的大模型面试题和各种大厂offer面经合集。

👉学会后的收获:👈
• 基于大模型全栈工程实现(前端、后端、产品经理、设计、数据分析等),通过这门课可获得不同能力;
• 能够利用大模型解决相关实际项目需求: 大数据时代,越来越多的企业和机构需要处理海量数据,利用大模型技术可以更好地处理这些数据,提高数据分析和决策的准确性。因此,掌握大模型应用开发技能,可以让程序员更好地应对实际项目需求;
• 基于大模型和企业数据AI应用开发,实现大模型理论、掌握GPU算力、硬件、LangChain开发框架和项目实战技能, 学会Fine-tuning垂直训练大模型(数据准备、数据蒸馏、大模型部署)一站式掌握;
• 能够完成时下热门大模型垂直领域模型训练能力,提高程序员的编码能力: 大模型应用开发需要掌握机器学习算法、深度学习框架等技术,这些技术的掌握可以提高程序员的编码能力和分析能力,让程序员更加熟练地编写高质量的代码。

1.AI大模型学习路线图
2.100套AI大模型商业化落地方案
3.100集大模型视频教程
4.200本大模型PDF书籍
5.LLM面试题合集
6.AI产品经理资源合集***
👉获取方式:
😝有需要的小伙伴,可以保存图片到wx扫描二v码免费领取【保证100%免费】🆓



