数据结构2-集合类ArrayList与洗牌算法
文章目录
- ★引言:
- 一. MyArrayList模拟实现
-
- (一)IList
- (二)MyArrayList
-
- (1)add(T data)
- (2)add(int pos, T data)
- (3)IllgalPosException
- (4)indexOf(Object toFind)
- (5)contains(Object toFind)
- (6)get(int pos)
- (7)set(int pos, T value)
- (8)remove(Object toRemove)
- (9)size()
- (10)clear()
- (11)display()
- (12)remove(int pos)
- (13)EmptyException
- 二. 洗牌算法
-
- (一)Card
- (二)CardArrayList
-
- (1)buyCard()
- (2)shuffle(MyArrayList cardList)
- (3)swap(MyArrayList cardList,int i,int j)
- 三. 测试
★引言:
该篇博客带大家一起模拟实现一个简易版集合ArrayList,并结合洗牌算法来验证正确性,喜欢的话可以点赞和收藏
一. MyArrayList模拟实现
(一)IList
- 查看ArrayList源码可以发现:ArrayList继承了抽象类AbstractList,而AbstractList又实现了List接口
- 这里我们省去AbstractList的过程,直接实现一个IList接口,让ArrayList重写接口当中的方法
package list;/** * Created with IntelliJ IDEA. * Description: * User: 32309 * Date: 2025-07-20 * Time: 15:57 */public interface IList<T> { // 新增元素,默认在数组最后新增 public void add(T data) ; public void add(int pos, T data) ; public boolean contains(Object toFind) ; public int indexOf(Object toFind) ; // 获取 pos 位置的元素 public Tget(int pos) ; public void set(int pos, T value) ; //删除第⼀次出现的关键字key public boolean remove(Object toRemove) ; // 获取顺序表⻓度 public int size() ; // 清空顺序表 public void clear() ; // 打印顺序表,注意:该⽅法并不是顺序表中的⽅法,为了⽅便看测试结果给出的 public void display();}(二)MyArrayList
- 首先我们要创建一个Object数组,用来接收所有类型,以及实际使用数量count和默认容量DEFAULT_CAPACITY
public class MyArrayList<T> implements IList<T> { private Object[] array; private int count; private final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10;}
- 提供两个构造方法,带容量参数initcapacity,new一个用户想要容量的数组,与不带参数的构造方法,new默认容量的数组
/** * Created with IntelliJ IDEA. * Description: * User: 32309 * Date: 2025-07-20 * Time: 15:55 */public class MyArrayList<T> implements IList<T> { private Object[] array; private int count; private final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10; // 默认构造⽅法 public MyArrayList() { array = new Object[DEFAULT_CAPACITY]; } // 将顺序表的底层容量设置为initcapacity public MyArrayList(int initcapacity) { if (initcapacity > 0) { array = new Object[initcapacity]; return; } array = new Object[DEFAULT_CAPACITY]; }}(1)add(T data)
- 这里我们默认采用尾插法,尾插法的时间复杂度为O(1),更为快捷
- 在插入数据之前我们首先要判断的就是,数组是否满了 isFull,满了就要扩容 grow
// 默认尾插 @Override public void add(T data) { if (isFull()) { grow(); } array[count++] = data; } // 扩容 private void grow() { array = Arrays.copyOf(array,count << 1); } // 判满 private boolean isFull() { return count == array.length; }(2)add(int pos, T data)
- 指定下标插入,是add的重载方法
- 插入之前同样要判满与扩容
- 检查下标是否合法 checkPos1
- 下标不合法要抛出异常 IllgalPosException
- 插入时采用从后向前覆盖的方式,给pos位置留出位置
// 在 pos 位置新增元素 @Override public void add(int pos, T data) { if (isFull()) { grow(); } if (checkPos(pos)) { throw new IllgalPosException(\"pos下标不合法:\" + pos); } // 从后往前覆盖 for (int i = count - 1; i >= pos; i--) { array[i + 1] = array[i]; } array[pos] = data; count++; } // 检查下标是否合法 private boolean checkPos1(int pos) { if (pos < 0 || pos > count) { return true; } return false; }(3)IllgalPosException
下标不合法异常
package list;/** * Created with IntelliJ IDEA. * Description: * User: 32309 * Date: 2025-07-20 * Time: 16:41 */public class IllgalPosException extends RuntimeException{ public IllgalPosException() { } public IllgalPosException(String message) { super(message); }}(4)indexOf(Object toFind)
- 查找对应位置传入值的下标
- 遍历数组查找到返回下标,找不到返回-1,因为数组下标没有-1
- 注意:这里面比较值是否相等要调用 equals方法,不能用 **==**直接比较
// 查找某个元素对应的位置 @Override public int indexOf(Object toFind) { for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) { if (array[i].equals(toFind)) { return i; } } return -1; }(5)contains(Object toFind)
- 查找数组中是否有这个值
- 直接调用 indexOf方法,根据返回的下标来判断是否存在
// 判定是否包含某个元素 @Override public boolean contains(Object toFind) { int index = indexOf(toFind); return index != -1; }(6)get(int pos)
- 获取 pos 位置的元素的方法
- 判断 pos位置是否合法,不合法抛出异常,合法就返回该下标的值
// 判断下标知否合法 private boolean checkPos2(int pos) { if (pos < 0 || pos >= count) { return true; } return false; } // 获取 pos 位置的元素 @Override public T get(int pos) { if (checkPos2(pos)) { throw new IllgalPosException(\"下标位置不合法!!!\"); }else { return (T) array[pos]; } }(7)set(int pos, T value)
- 给 pos 位置的元素设为 value的方法
- 先判断 pos 是否合法,再设置值
// 给 pos 位置的元素设为 value @Override public void set(int pos, T value) { if (checkPos2(pos)) { throw new IllgalPosException(\"下标位置不合法!!!\"); } array[pos] = value; }(8)remove(Object toRemove)
- 删除第⼀次出现的关键字key的方法
- 先判断数组有没有这个值
- 采用从前向后覆盖方式,同时注意将末尾位置置为null
// 删除第⼀次出现的关键字key @Override public boolean remove(Object toRemove) { int index = indexOf(toRemove); if (index == -1) { System.out.println(\"没有你要删除的值!!!\"); return false; } for (int i = index; i < count - 1; i++) { array[i] = array[i + 1]; } array[count--] = null; return true; }(9)size()
返回顺序表长度
// 获取顺序表⻓度 @Override public int size() { return count; }(10)clear()
清空顺序表,注意:需要将数组中所有元素都置为null
// 清空顺序表 @Override public void clear() { for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) { array[i] = null; } count = 0; }(11)display()
打印顺序表
// 打印顺序表 @Override public void display() { for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) { System.out.print(array[i] + \" \"); } System.out.println(); }(12)remove(int pos)
- remove 的重载方法,该方法可以返回删除位置的元素
- 需要验证数组中是否是空的,以及pos位置是否合法
public T remove(int pos) { if (isEmpty()) { throw new EmptyException(\"空数组异常!!!\"); } if (checkPos2(pos)) { throw new IllgalPosException(\"pos 下标非法!!!\"); } T t = get(pos); remove(t); return t; }(13)EmptyException
空数组异常
package list;public class EmptyException extends RuntimeException { public EmptyException() { } public EmptyException(String message) { super(message); }}二. 洗牌算法
(一)Card
一张扑克牌上的属性有花色 suit 与 数字 rank
package card;/** * Created with IntelliJ IDEA. * Description: * User: 32309 * Date: 2025-07-20 * Time: 9:55 */public class Card { private String suit; private int rank; public Card(String suit, int rank) { this.suit = suit; this.rank = rank; } public String getSuit() { return suit; } public void setSuit(String suit) { this.suit = suit; } public int getRank() { return rank; } public void setRank(int rank) { this.rank = rank; } @Override public String toString() { return \"{\" + suit + rank + \"}\"; }}(二)CardArrayList
- 所有扑克牌放到该集合中
- 使用我们刚写好的MyArrayList
- 分为三部分:买牌 buyCard,洗牌 shuffle,交换 swap
- 设置号四种花色
(1)buyCard()
54张扑克牌,1~13,每张花色不同,外加小王与大王
private static final String[] suits = {\"♥\",\"♠\",\"♦\",\"♣\"}; public static MyArrayList<Card> buyCard() { MyArrayList<Card> cards = new MyArrayList<>(54); for (int i = 1; i <= 13; i++) { int rank = i; for (int j = 0; j < 4; j++) { String suit = suits[j]; Card card = new Card(suit,rank); cards.add(card); } } Card card1 = new Card(\"大王🃏\",999); cards.add(card1); Card card2= new Card(\"小王🃏\",888); cards.add(card2); return cards; }(2)shuffle(MyArrayList cardList)
通过设置随机数,从末尾开始来交换,来达到洗牌目的
public static void shuffle(MyArrayList<Card> cardList) { Random random = new Random(); for (int i = cardList.size() - 1; i > 0; i--) { int index = random.nextInt(i); swap(cardList,i,index); } }(3)swap(MyArrayList cardList,int i,int j)
作为洗牌的辅助方法
private static void swap(MyArrayList<Card> cardList,int i,int j) { Card card = cardList.get(i); cardList.set(i, cardList.get(j)); cardList.set(j,card); }三. 测试
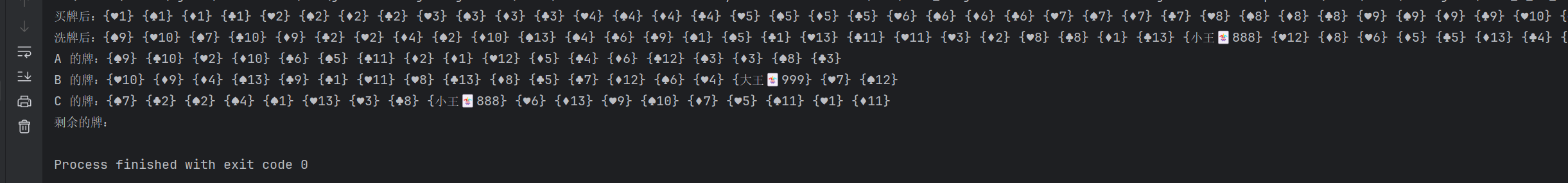
- 分别调用买牌 buyCard,洗牌 shuffle,这两二方法来打印牌的信息来测试方法是否正确
- 三个人轮流揭牌,把所有牌全部揭完
package list;import card.Card;import card.CardArrayList;public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { MyArrayList<Card> cards = CardArrayList.buyCard(); System.out.print(\"买牌后:\"); cards.display(); System.out.print(\"洗牌后:\"); CardArrayList.shuffle(cards); cards.display(); // 三个人轮流抓五张牌 MyArrayList<MyArrayList<Card>> hands = new MyArrayList<>(); hands.add(new MyArrayList<>()); hands.add(new MyArrayList<>()); hands.add(new MyArrayList<>()); // 抓牌 for (int i = 0; i < 18; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) { // 获取第几个人 hands.get(j).add(cards.remove(0)); } } System.out.print(\"A 的牌:\"); hands.get(0).display(); System.out.print(\"B 的牌:\"); hands.get(1).display(); System.out.print(\"C 的牌:\"); hands.get(2).display(); System.out.print(\"剩余的牌:\"); cards.display(); }}