LeetCode 85:最大矩形
LeetCode 85:最大矩形
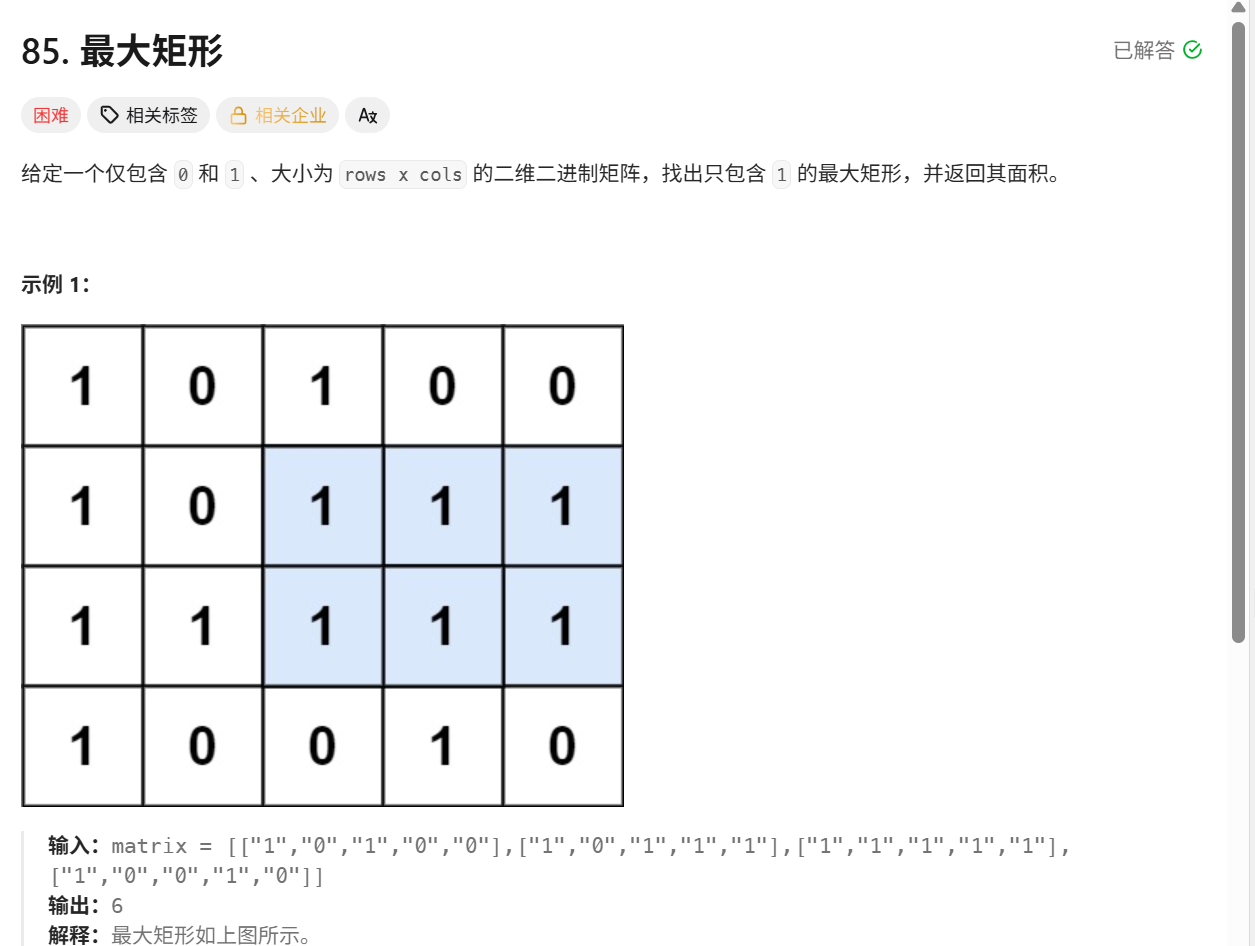
问题本质与核心挑战
给定仅含 0 和 1 的二维矩阵,需找到全由 1 组成的最大矩形面积。核心挑战:
- 直接枚举所有矩形(
O(n²m²))效率极低; - 需通过 “逐行构建柱状图 + 单调栈求最大面积” 优化,将复杂度降为
O(rows×cols)。
核心思路:二维 → 一维的转化
1. 柱状图的构建
对矩阵的每一行,计算以该行作为底边的“柱状图高度”:
- 若当前单元格为
1,则高度为上方连续1的个数 + 1(继承上一行的高度); - 若当前单元格为
0,则高度重置为0(无法形成垂直连续的1)。
2. 复用柱状图最大面积算法(LeetCode 84题)
对每一行构建的柱状图,使用 单调栈 快速计算其最大矩形面积(时间复杂度 O(cols)),最终取所有行的最大值。
算法步骤详解(以示例 matrix = [[1,0,1,0,0],[1,0,1,1,1],[1,1,1,1,1],[1,0,0,1,0]] 为例)
步骤 1:初始化变量与高度数组
int rows = matrix.length; // 行数(4)int cols = matrix[0].length; // 列数(5)int[] height = new int[cols]; // 记录当前行的柱状图高度int maxArea = 0; // 全局最大面积步骤 2:逐行构建柱状图,计算最大面积
遍历每一行,更新 height 数组,并调用 largestRectangleArea 计算当前行的最大面积:
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++) { // 更新当前行的高度数组 for (int j = 0; j < cols; j++) { height[j] = (matrix[i][j] == \'1\') ? height[j] + 1 : 0; } // 计算当前柱状图的最大面积,更新全局最大值 maxArea = Math.max(maxArea, largestRectangleArea(height));}示例演示(行2的 height 构建):
- 行2的
matrix为[\"1\",\"1\",\"1\",\"1\",\"1\"]:j=0:matrix[2][0]=\'1\'→height[0] = height[0](2) + 1 = 3;j=1:matrix[2][1]=\'1\'→height[1] = height[1](0) + 1 = 1;- 最终
height = [3,1,3,2,2](对应柱状图高度)。
步骤 3:单调栈计算柱状图最大面积(复用LeetCode 84题逻辑)
private int largestRectangleArea(int[] heights) { Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>(); // 存储索引,保持高度递增 int max = 0; int n = heights.length; for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { // 当前高度 < 栈顶高度 → 弹出栈顶,计算面积 while (!stack.isEmpty() && heights[i] < heights[stack.peek()]) { int top = stack.pop(); int h = heights[top]; int left = stack.isEmpty() ? -1 : stack.peek(); // 左边界 int right = i; // 右边界 max = Math.max(max, h * (right - left - 1)); } stack.push(i); // 当前索引入栈 } // 处理栈中剩余元素(右边界为n) while (!stack.isEmpty()) { int top = stack.pop(); int h = heights[top]; int left = stack.isEmpty() ? -1 : stack.peek(); int right = n; max = Math.max(max, h * (right - left - 1)); } return max;}示例演示(行2的 height = [3,1,3,2,2]):
i=0(height=3)[0]0i=1(height=1)[1]3×(1-(-1)-1)=333i=2(height=3)[1,2]3i=3(height=2)[1,3]3×(3-1-1)=3;弹出1 → 面积 1×(3-(-1)-1)=33,33i=4(height=2)[3,4]3[]2×(5-3-1)=2;弹出3 → 面积 2×(5-1-1)=62,66完整代码(Java)
import java.util.Stack;class Solution { public int maximalRectangle(char[][] matrix) { if (matrix == null || matrix.length == 0) { return 0; } int rows = matrix.length; int cols = matrix[0].length; int[] height = new int[cols]; // 记录当前行的柱状图高度 int maxArea = 0; for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++) { // 逐列更新高度:当前为\'1\'则累加,否则置0 for (int j = 0; j < cols; j++) { height[j] = (matrix[i][j] == \'1\') ? height[j] + 1 : 0; } // 计算当前行的最大矩形面积,更新全局最大值 maxArea = Math.max(maxArea, largestRectangleArea(height)); } return maxArea; } // 复用LeetCode 84题的单调栈解法,计算柱状图的最大矩形面积 private int largestRectangleArea(int[] heights) { Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>(); int maxArea = 0; int n = heights.length; for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { // 维护单调递增栈:当前高度 < 栈顶高度时,弹出栈顶计算面积 while (!stack.isEmpty() && heights[i] < heights[stack.peek()]) { int topIndex = stack.pop(); int h = heights[topIndex]; // 左边界:栈空则为-1,否则为新栈顶 int left = stack.isEmpty() ? -1 : stack.peek(); // 右边界:当前索引i int right = i; int width = right - left - 1; maxArea = Math.max(maxArea, h * width); } stack.push(i); // 当前索引入栈 } // 处理栈中剩余元素(右边界为n) while (!stack.isEmpty()) { int topIndex = stack.pop(); int h = heights[topIndex]; int left = stack.isEmpty() ? -1 : stack.peek(); int right = n; int width = right - left - 1; maxArea = Math.max(maxArea, h * width); } return maxArea; }}关键逻辑解析
1. 柱状图的构建逻辑
- 若当前单元格为
1,高度继承自上一行同列的高度(height[j] += 1),形成垂直连续的1; - 若为
0,高度重置为0(垂直连续中断)。
2. 单调栈的作用
- 维护递增的高度索引,确保每次弹出栈顶时,其左右边界是第一个比它矮的柱子,从而快速计算以该高度为高的矩形面积。
3. 时间复杂度
- 每行处理:
O(cols)(更新高度 + 单调栈操作,每个元素入栈、出栈各一次); - 总复杂度:
O(rows×cols),可处理题目中rows, cols ≤ 200的规模。
该方法通过二维转一维的巧妙转化,将复杂的二维矩形问题拆解为多个一维柱状图问题,再利用单调栈高效求解,体现了算法优化中降维思想与经典模板复用的精髓。


