Java Map和Set_java map查找
文章目录
- Map和Set
-
- 二叉搜索树
-
- 查找
- 分析:
- 插入
- 删除
- Map
-
- Map的使用
- Set
-
- Set的使用
- 哈希表
-
- 负载因子的调节(重点)
- 闭散列
- 开散列
- HashMap和HashSet
- 面试题
- HashMap的源码

Map和Set
- map和set用于搜索
- 搜索树,二叉搜索树 -> AVL树 -> 红黑树
- AVL树:高度平衡的二叉搜索树
- TreeMap和TreeSet底层是红黑树,每次存储元素都得进行大小比较
二叉搜索树
- 二叉搜索树:如果左子树不为空,那么左子树所有节点都小于根节点,如果右子树不为空,那么右子树所有节点都大于根节点,它的左右子树都是二叉搜索树
- 二叉搜索树的中序遍历是有序的
查找
- 比key大往右找,比key小往左找
// 查找 public boolean search(int key){ TreeNode cur = root; while(cur != null){ if(cur.val > key){ cur = cur.left; }else if(cur.val < key){ cur = cur.right; }else{ return true; } } return false; }分析:
- 时间复杂度:
最好情况:O(logN),完全二叉树
最坏情况:O(N),单分支的二叉树
插入
// 插入 public boolean insert(int key){ TreeNode node = new TreeNode(key); TreeNode parent = null; if(root == null){ root = node; return true; } TreeNode cur = root; while(cur != null){ if(cur.val < key){ parent = cur; cur = cur.right; }else if(cur.val > key){ parent = cur; cur = cur.left; }else{ // 在二叉搜索树中只能不能有相同的数字,比如5,有一个5就可以了,只要有这个数就可以了 return false; } } if(parent.val < key){ parent.right= node; }else{ parent.left = node; } return true; }删除
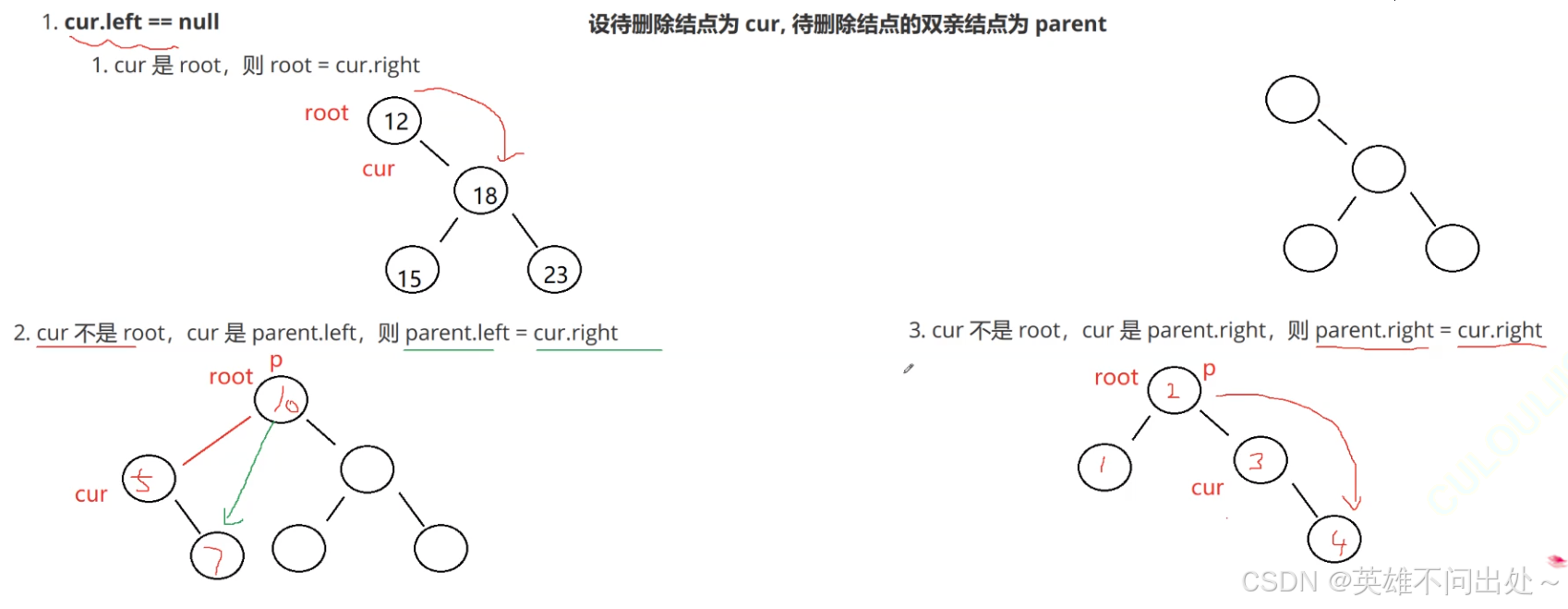
- 第一种情况:cur.left == null
要删除的节点是cur
cur是根节点
cur是某个节点的左边
cur是某个节点的右边
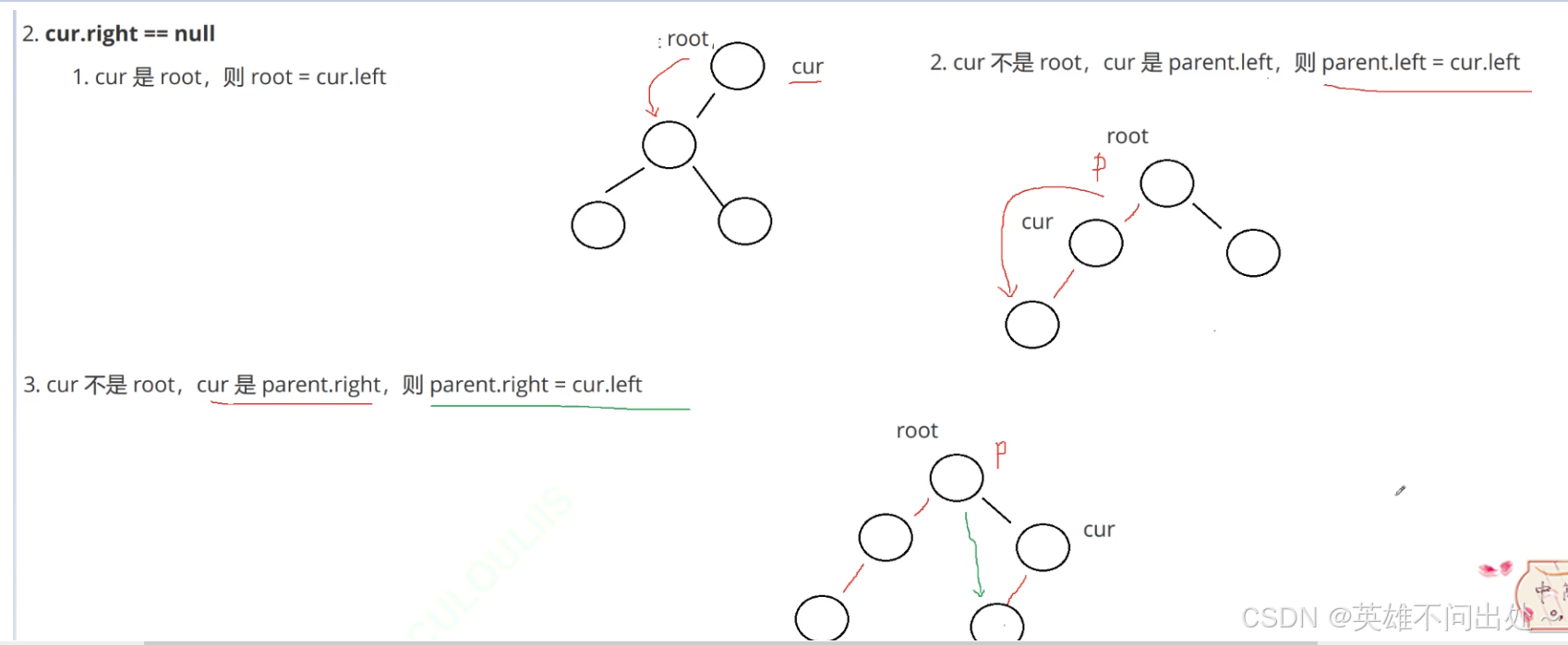
2. 第二种情况:cur.right == null
要删除的节点是cur
cur是根节点
cur是某个节点的左边
cur是某个节点的右边
3. 第三种情况:cur.left != null && cur.right != null
使用替换法进行删除
替换为左树中最大的值
或者是右树中最小的值
替换完之后删除这个去替换的值
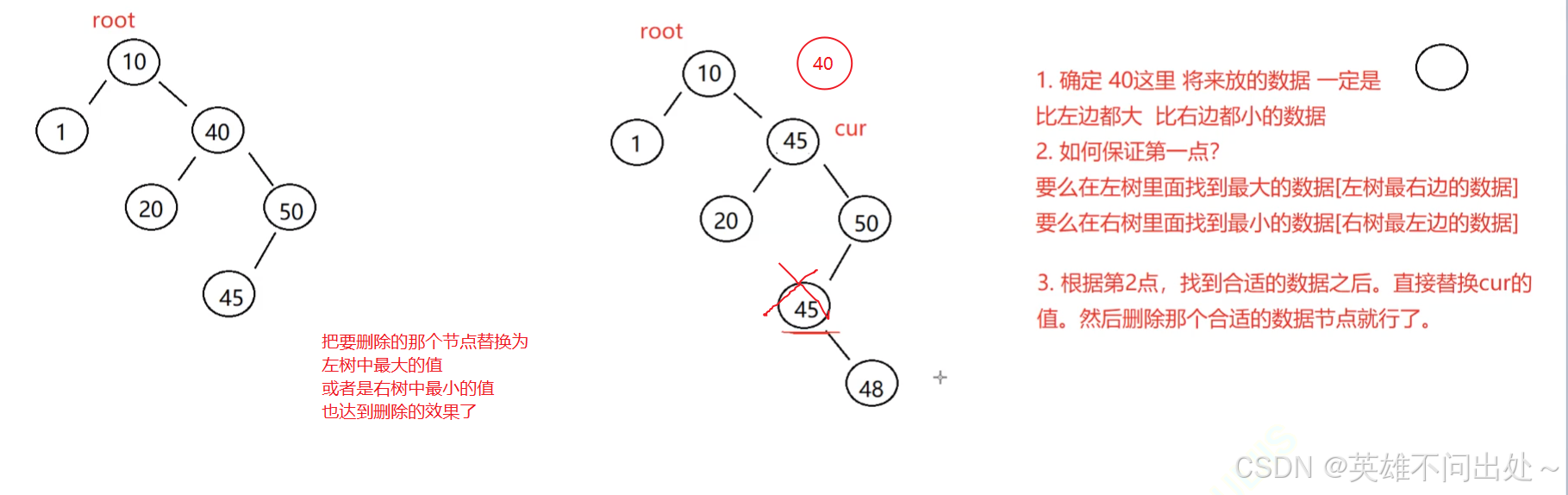
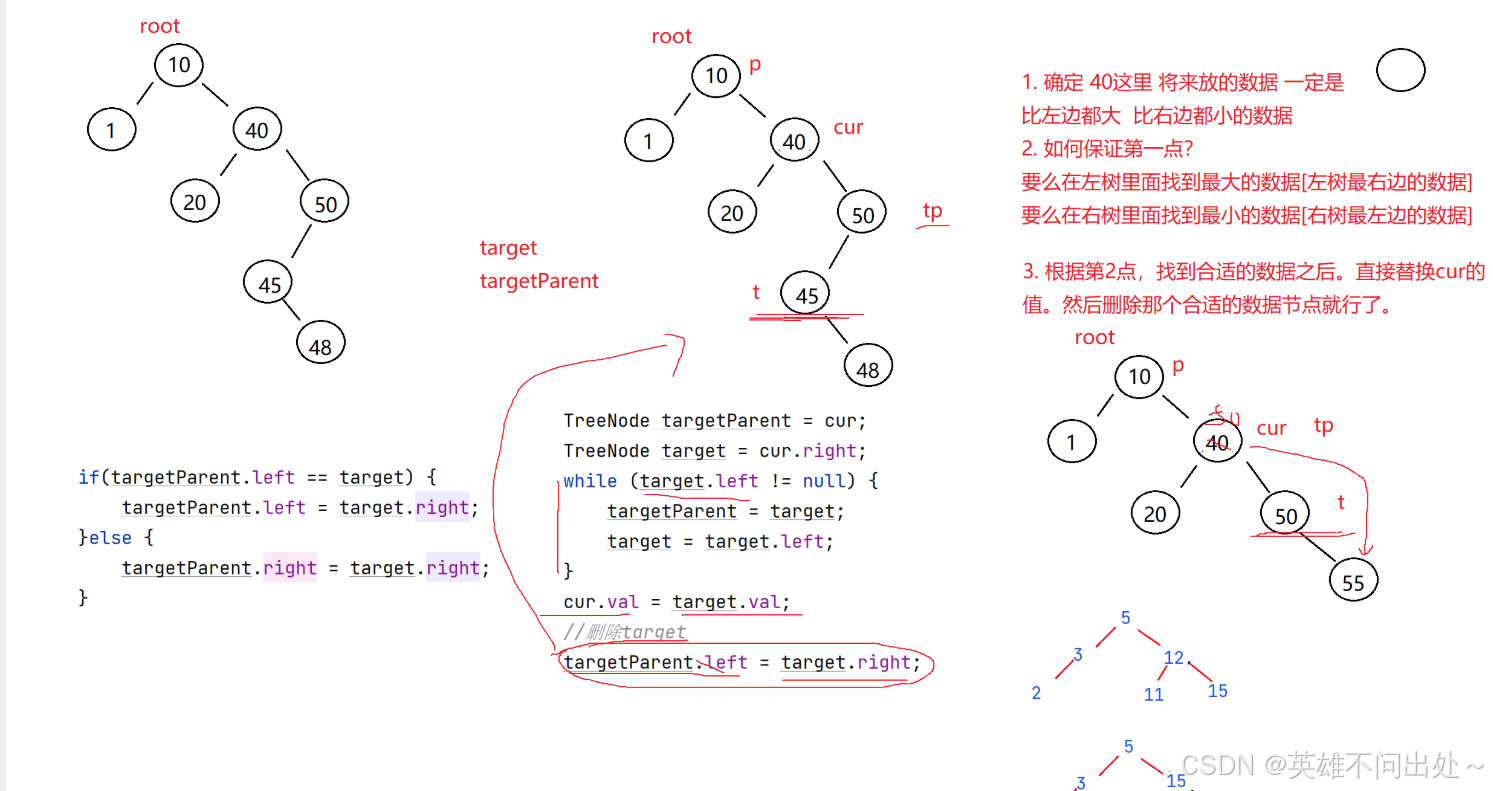
// 删除 private void removeNode(TreeNode cur, TreeNode parent) { if(cur.left == null){ // 要删除的是根节点 if(cur == root){ root = cur.right; }else if(cur == parent.left){ parent.left = cur.right; }else{ parent.right = cur.right; } }else if(cur.right == null){ if(cur == root){ root = cur.left; }else if(cur == parent.left){ parent.left = cur.left; }else{ parent.right = cur.left; } }else{ // cur.left != null && cur.right != null TreeNode parentTarget = cur; TreeNode target = cur.right; // 在右树中找最小值 while(target.left != null){ parentTarget = target; target = target.left; } // 直到找到右树中的最左边的树 cur.val = target.val; // 删除target if(parentTarget.left == target) { parentTarget.left = target.right; }else{ // parentTarget.right == target parentTarget.right = target.right; } } }Map
- map是一种(k,v)结构的数据结构
- map可以进行去重,TreeMap不可以插入null的key,HashMap可以插入null的key,因为红黑树是要进行比较的,哈希表是不进行比较的
Map<String,Integer> map = new TreeMap<>();// 底层是红黑树,查找的时间复杂度O(N*logN) Map<String,Integer> map1 = new HashMap<>();// 底层是哈希表,查找的时间复杂度O(1) // 哈希表 = 数组 + 链表 + 红黑树Map的使用
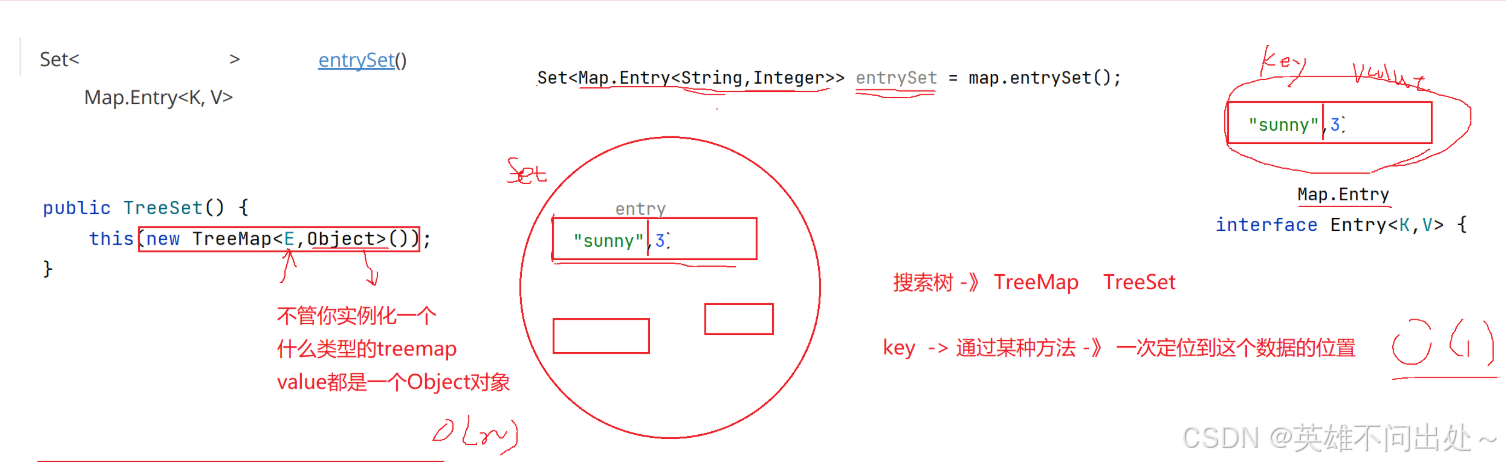
public static void main(String[] args) { Map<String,Integer> map = new TreeMap<>();// 底层是红黑树,查找的时间复杂度O(N*logN) // 插入元素 map.put(\"push\",3);// push出现了3次 // 获取元素,给定一个key值可以获取它的value值 Integer val = map.get(\"push\"); Integer val1 = map.get(\"aaa\");// null // 获取val值,如果没有这个值,返回一个默认值 Integer val2 = map.getOrDefault(\"bbb\",99999); System.out.println(val); // 删除key值 // map.remove(\"push\"); // 把所有的key放入一个集合中 Set<String> set = map.keySet(); System.out.println(set); // 获取values中的所有值 ArrayList<Integer> value = new ArrayList(map.values()); System.out.println(value); // 把Map.Entry当做Set中的一个节点 // map.entrySet()用于获取这种节点 Set<Map.Entry<String,Integer>> entrySet = map.entrySet(); for(Map.Entry<String,Integer> entry : entrySet){ System.out.println(\"key: \" + entry.getKey() + \" value: \" + entry.getValue()); } // boolean map.containsKey(\"push\"); 判断是否含有key // boolean map.containsValue(3); 判断是否含有value Map<String,Integer> map1 = new HashMap<>();// 底层是哈希表,查找的时间复杂度O(1) // 哈希表 = 数组 + 链表 + 红黑树 }Set
- set是一种只有key的模型
Set的使用
- Set是要进行去重的
- TreeSet不可以插入null的key,HashSet可以插入null的key,因为红黑树是要进行比较的,哈希表是不进行比较的
public static void main(String[] args) { Set<String> set = new TreeSet<>(); set.add(\"push\"); set.add(\"hello\"); set.add(\"world\"); // set是无序的 System.out.println(set); Iterator<String> it = set.iterator(); while(it.hasNext()){ System.out.println(it.next()); } }哈希表
- 查找可以一次定位到该元素,时间复杂度为O(1)
- 哈希冲突(碰撞):不同的key通过相同的哈希函数得到相同的值
哈希冲突是必然产生的,我们要做的是降低冲突的概率
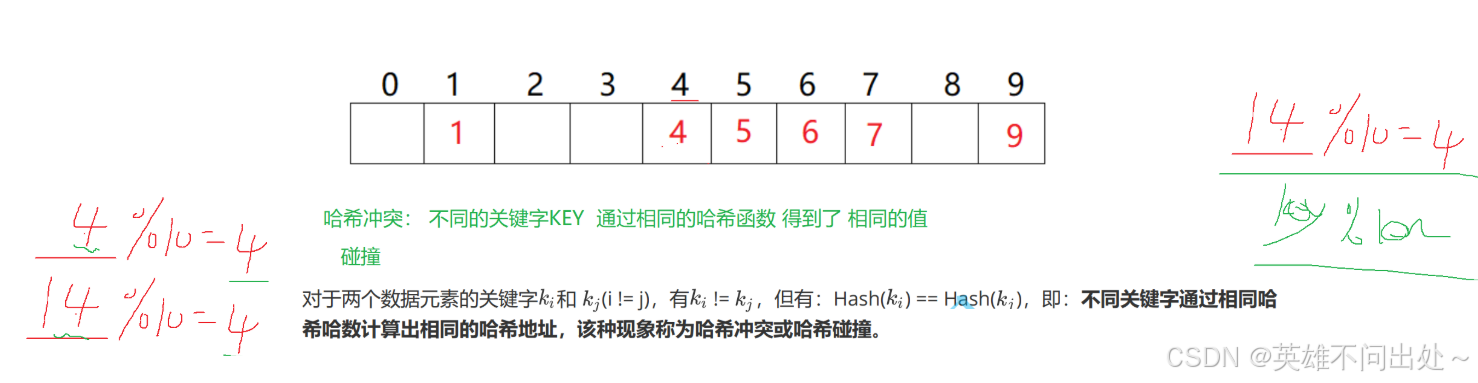
解决哈希冲突:哈希函数的设计要合理
哈希函数要简单
哈希表中要均匀分到数组中去
哈希表的范围要合理,比如有m个地址,存储位置就是[0,m-1]

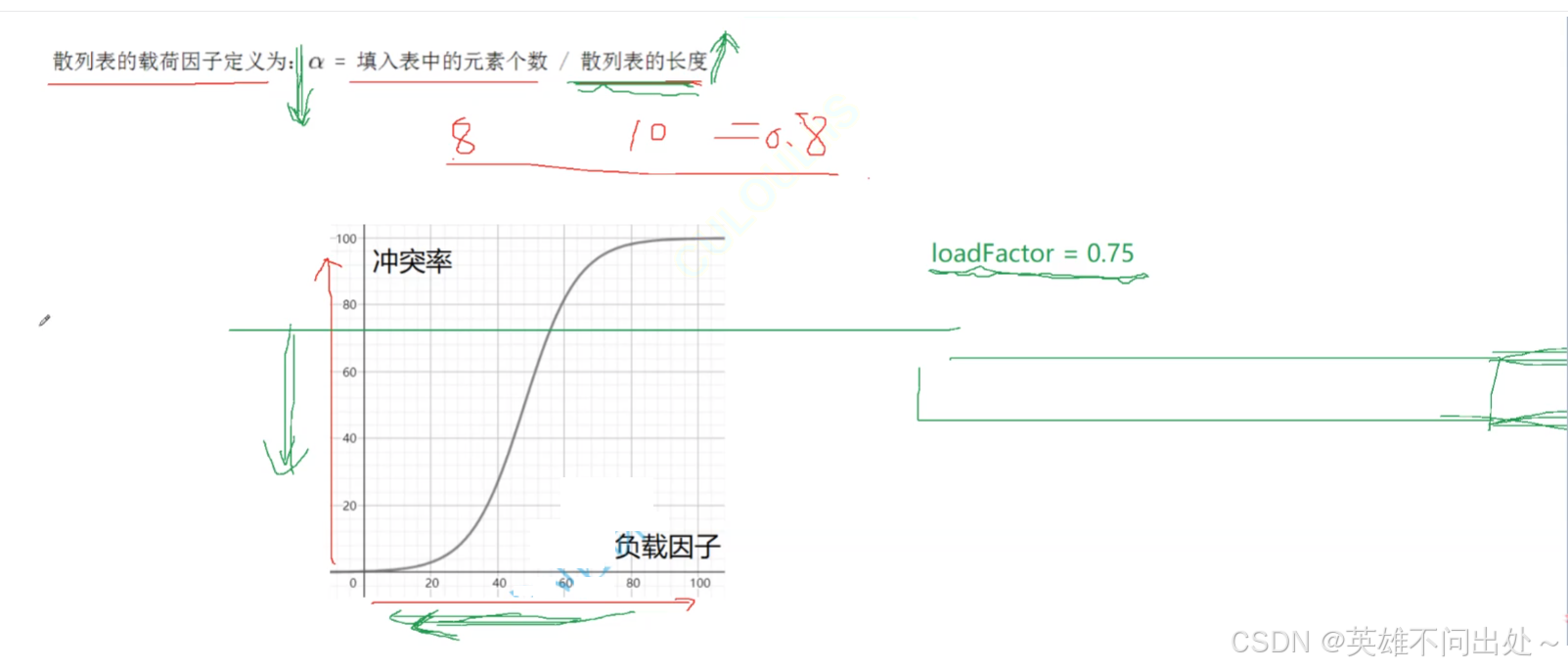
负载因子的调节(重点)
- 负载因子影响了哈希冲突,负载因子越大冲突率越高
- 哈希表中的负载因子定义为:
a = 填入表中的元素个数 / 哈希表的长度
比如:a = 8 / 10 = 0.8 - 如果降低冲突率就要降低负载因子,因此要扩容哈希表的大小,不增加插入的元素是不现实的,给定一个阈值,如果超过了就扩大哈希表的容量
闭散列
- 开放定址法,如果没有达到阈值,但是冲突了,就放到冲突的下一个空的位置上,这个也叫线性探测
- 线性探测的缺点:把冲突的元素都集中放到了一起
- 二次探测:为了解决线性探测的缺点,通过公式进行处理,H0是当前冲突的位置,i是出现冲突的次数,m是哈希表的大小,Hi表示冲突后,下一次要放的位置
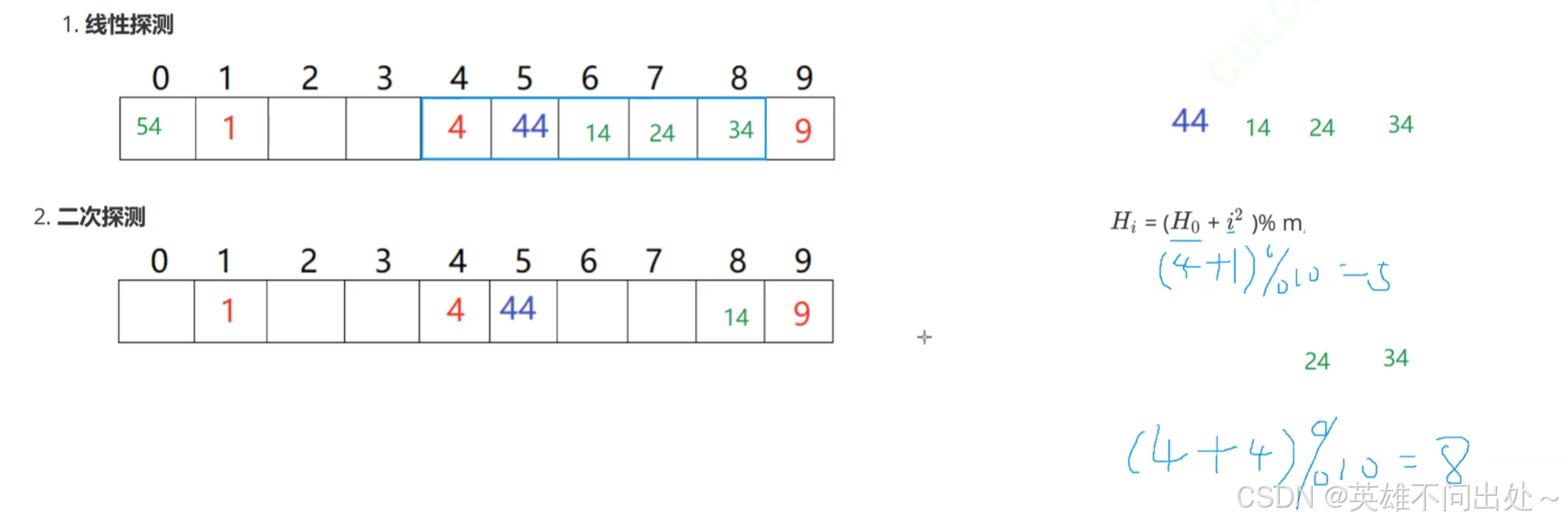
4. 线性探测对于空间的利用率不高
开散列
- 开散列:又叫链地址法,为了解决空间利用率不高的问题,开散列是数组 + 链表 + 红黑树的模式
- 把冲突的元素挂到同一个空间下的链表上
- Java是采用开散列的方式实现的

4. 扩容之后需要重新哈希,因为数组长度变了,要重新计算节点存放的位置
5. 遍历哈希数组中每个数组元素,都要重新计算节点位置
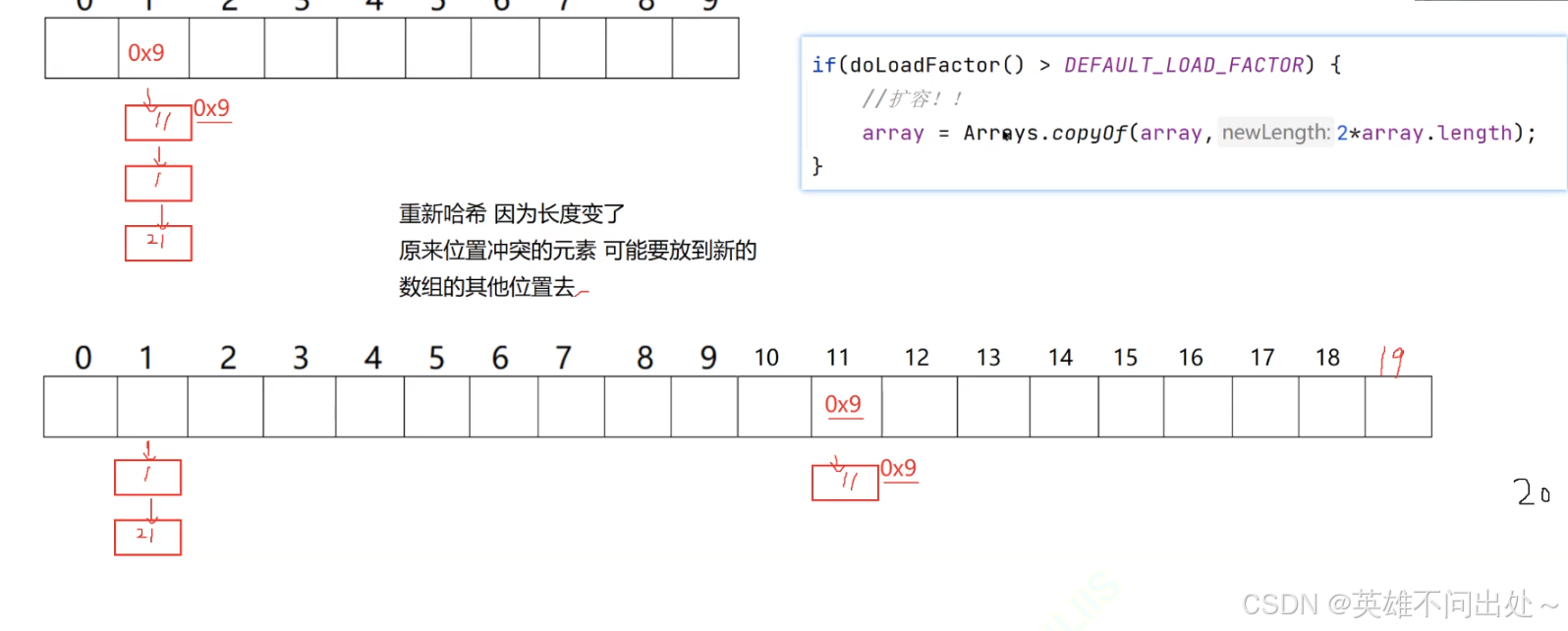
package Demo1;import java.util.Arrays;public class HashBuck { // 链表数组,数组中的每一个元素都时链表的头结点 public class Node{ public int key; public int val; public Node next; public Node(int key, int val) { this.key = key; this.val = val; } } public Node[] array; public int usedSize; public static final float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f; public HashBuck(){ array = new Node[10]; } public void put(int key,int value){ int index = key % array.length; // 遍历index下标的链表 是否存在key 存在就更新value 不存在就头插这个节点 Node node = new Node(key,value); // 该链表的头结点 Node cur = array[index]; while(cur != null){ if(cur.key == key){ // 如果插入的这个key相同就替换这个key cur.val = value; return; } cur = cur.next; } // 没有找到这个节点就头插 node.next = array[index]; array[index] = node; usedSize++; // 负载因子大于阈值 if(doLoadFactor() > DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR){ // 扩容 // array = Arrays.copyOf(array,2*array.length); resize(); } } private void resize(){ // 建一个新的数组 Node[] newArray = new Node[2*array.length]; for(int i = 0;i < array.length;i++){ Node cur = array[i]; while(cur != null){ Node tmp = cur.next; // 每次都要算新数组的下标因为是一个链表有很多个节点 int newIndex = cur.key % newArray.length; // 头插法 cur.next = newArray[newIndex]; newArray[newIndex] = cur; cur = tmp; } } array = newArray; } // 计算负载因子 private float doLoadFactor(){ return usedSize * 1.0f / array.length; } // 获取对应key的value值 public int get(int key){ int index = key % array.length; Node cur = array[index]; while(cur != null){ if(cur.key == key){ // 如果插入的这个key相同就替换这个key return cur.val; } cur = cur.next; } return -1; }}-
HashMap是线程不安全的,因为采用了头插法,后面采用了尾插法变得安全了,ConcurrentHashMap是线程安全的,之后学到了线程就可以理解了
-
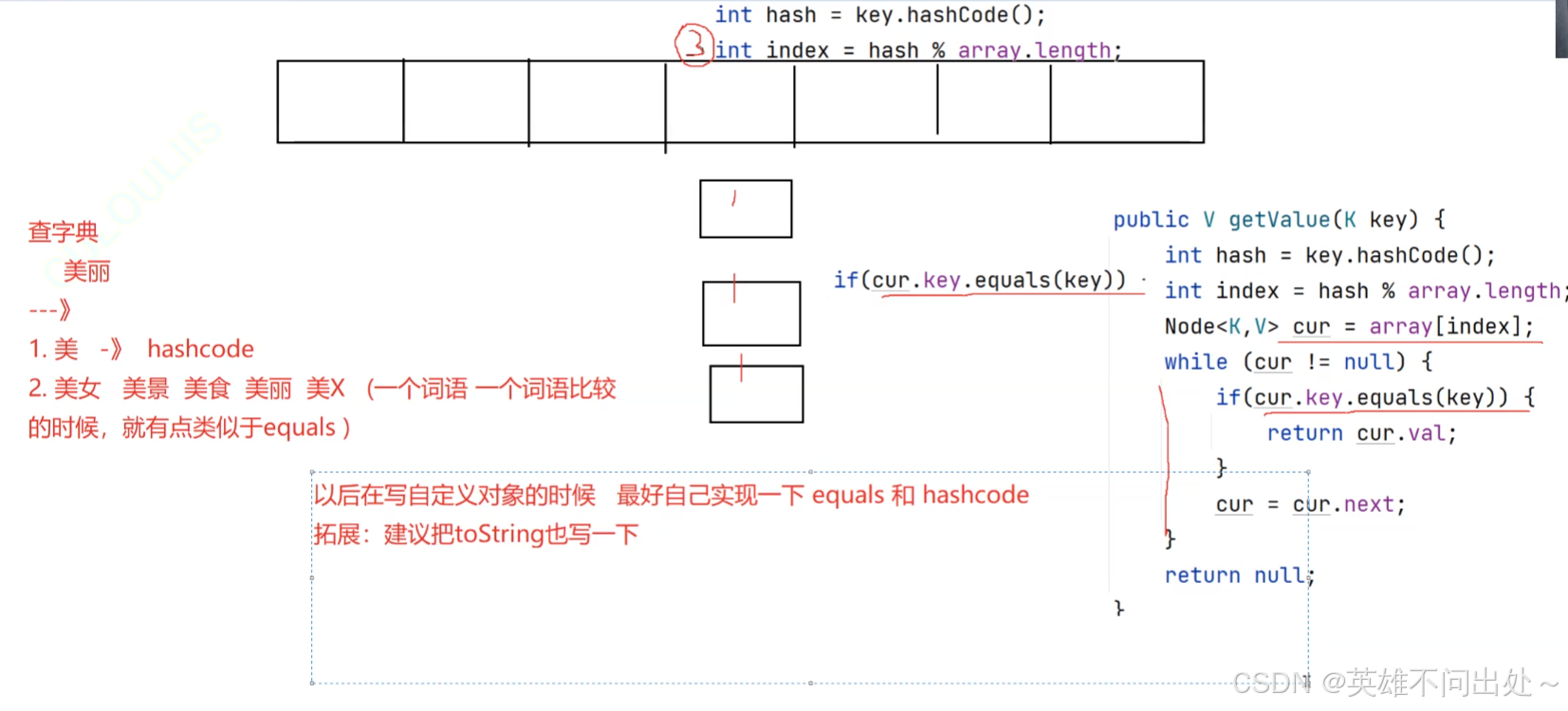
如果key是String,Person类型就不能除以数组的长度了,该怎么找到对应的下标呢?
可以用hashcode来将自定义类型转化为整形类型
hashCode和equals
HashMap和HashSet
public static void main(String[] args) { HashMap<String,Integer> hashMap = new HashMap<>(); hashMap.put(\"hello\",2); hashMap.put(\"abcde\",10); hashMap.put(\"abc\",11); Integer val = hashMap.get(\"hello\"); System.out.println(val); // 遍历map System.out.println(hashMap); for(Map.Entry<String,Integer> entry : hashMap.entrySet()){ System.out.println(\"key:\" + entry.getKey() + \" value:\" + entry.getValue()); } // Map不支持迭代器遍历,Set支持迭代器遍历 // 可以将Map转化为Set进行迭代器遍历 HashMap<Student,Integer> hashMap1 = new HashMap<>(); hashMap1.put(new Student(),2); hashMap1.put(new Student(),2); hashMap1.put(null,2); // TreeMap hashMap2 = new TreeMap(); // hashMap2.put(new Student(),3); // hashMap2.put(new Student(),3); // Sutdent不能进行比较 // set可以去重,Set的底层是HashMap // 每次存储元素的时候,默认的value都是一个Object对象 HashSet<String> set = new HashSet<>(); set.add(\"hello\"); set.add(\"world\"); set.add(\"hello\"); System.out.println(set); }面试题
只出现一次的数字
宝石与石头
旧键盘
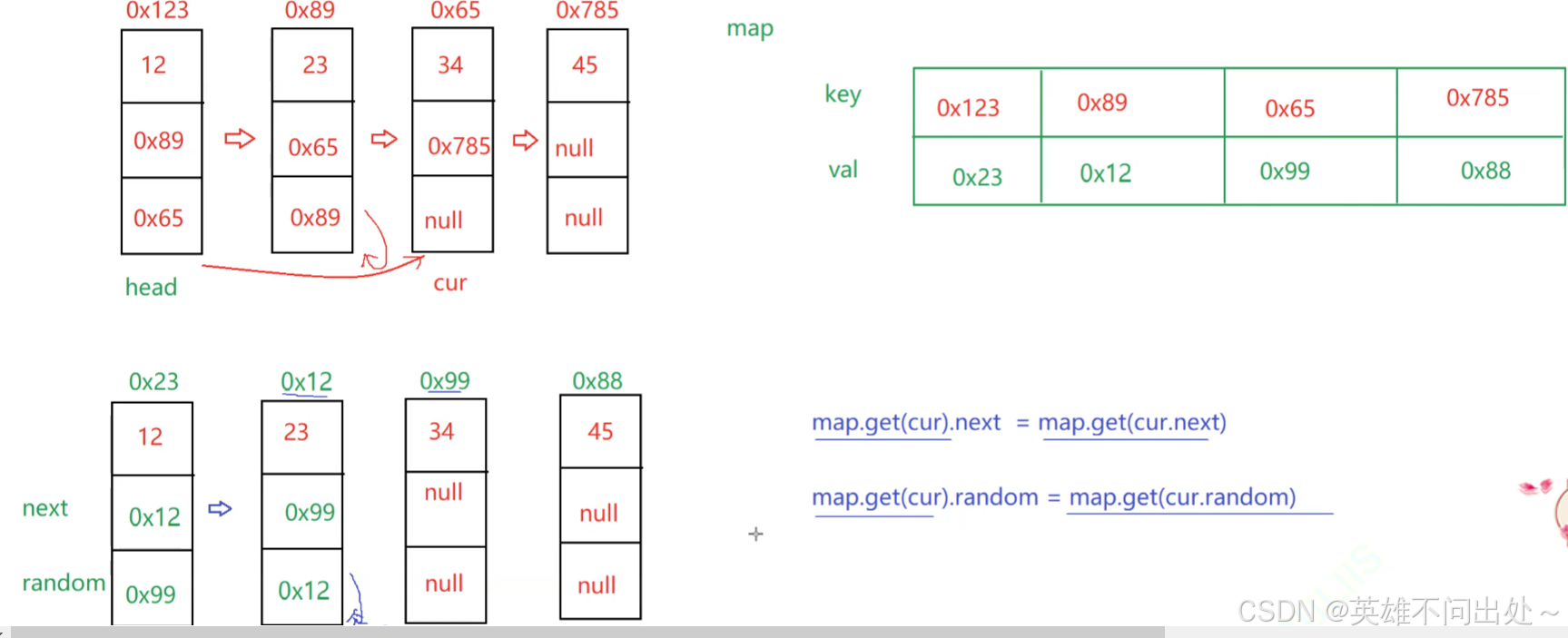
随机链表的复制
统计6个数中数字出现的次数
public static void main(String[] args) { int[] array = {1,1,2,2,3,3}; HashMap<Integer,Integer> map = new HashMap<>(); for(int i = 0;i < array.length;i++){ if(!map.containsKey(array[i])){ map.put(array[i],1); }else{ int k = map.get(array[i]); k++; map.put(array[i],k); } } System.out.println(map); }前k个高频单词

如果频率相同放入堆中要使用大根堆,要让love排在i的前面
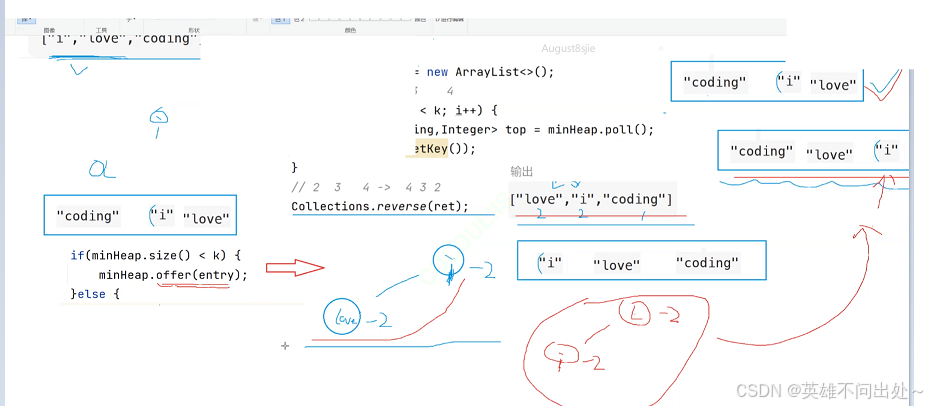
class Solution { public List<String> topKFrequent(String[] words, int k) { // 1. 统计单词出现的次数 Map<String,Integer> map = new HashMap<>(); for(String s : words){ if(!map.containsKey(s)){ map.put(s,1); }else{ int val = map.get(s); map.put(s,val+1); } } // 2. 把单词和出现的次数当做一个整体放入小根堆中 PriorityQueue<Map.Entry<String,Integer>> minHeap = new PriorityQueue<>( new Comparator<Map.Entry<String,Integer>>(){ public int compare(Map.Entry<String,Integer> o1,Map.Entry<String,Integer> o2){ // 放元素的时候,如果频率相同,我们转变为大根堆 -> 按照单词的字典序进行排序 if(o1.getValue().compareTo(o2.getValue()) == 0){ return o2.getKey().compareTo(o1.getKey()); } return o1.getValue().compareTo(o2.getValue()); } }); for(Map.Entry<String,Integer> entry : map.entrySet()){ if(minHeap.size() < k){ // 没有放满小根堆 minHeap.add(entry); }else{ // 放满了和堆顶元素比较大小 // 如果比堆顶元素还大,就入堆 int v = minHeap.peek().getValue(); if(v < entry.getValue()){ minHeap.poll(); minHeap.offer(entry); }else{ // 出现频率相同,比较字典序大小 if(v == entry.getValue()){ if(minHeap.peek().getKey().compareTo(entry.getKey()) > 0){ minHeap.poll(); minHeap.offer(entry); } } } } } // 2 3 4 -> 4 3 2 List<String> arr = new ArrayList<>(); for(int i = 0;i < k;i++){ Map.Entry<String,Integer> top = minHeap.poll(); arr.add(top.getKey()); } // 逆置 Collections.reverse(arr); return arr; }}HashMap的源码
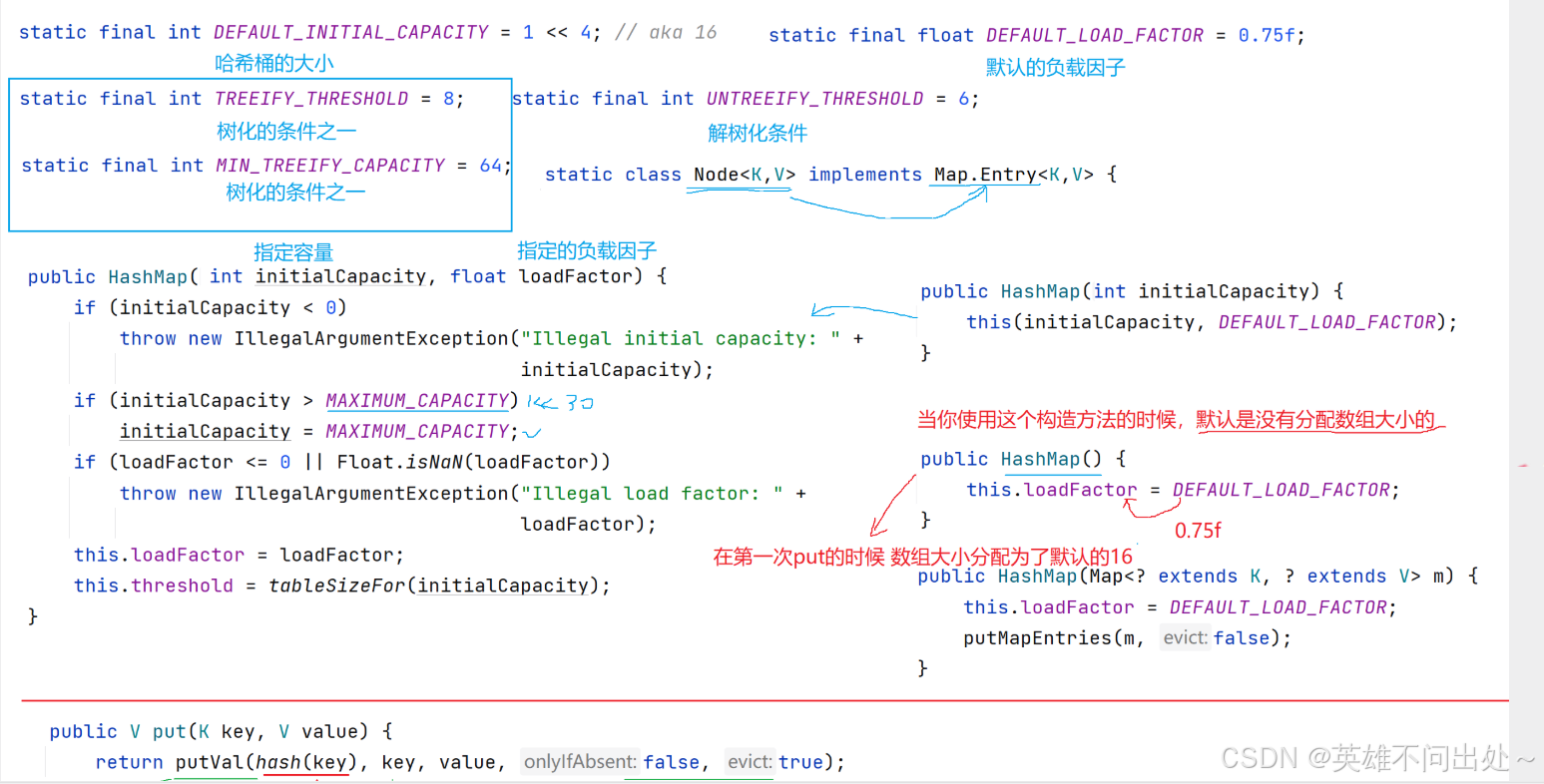
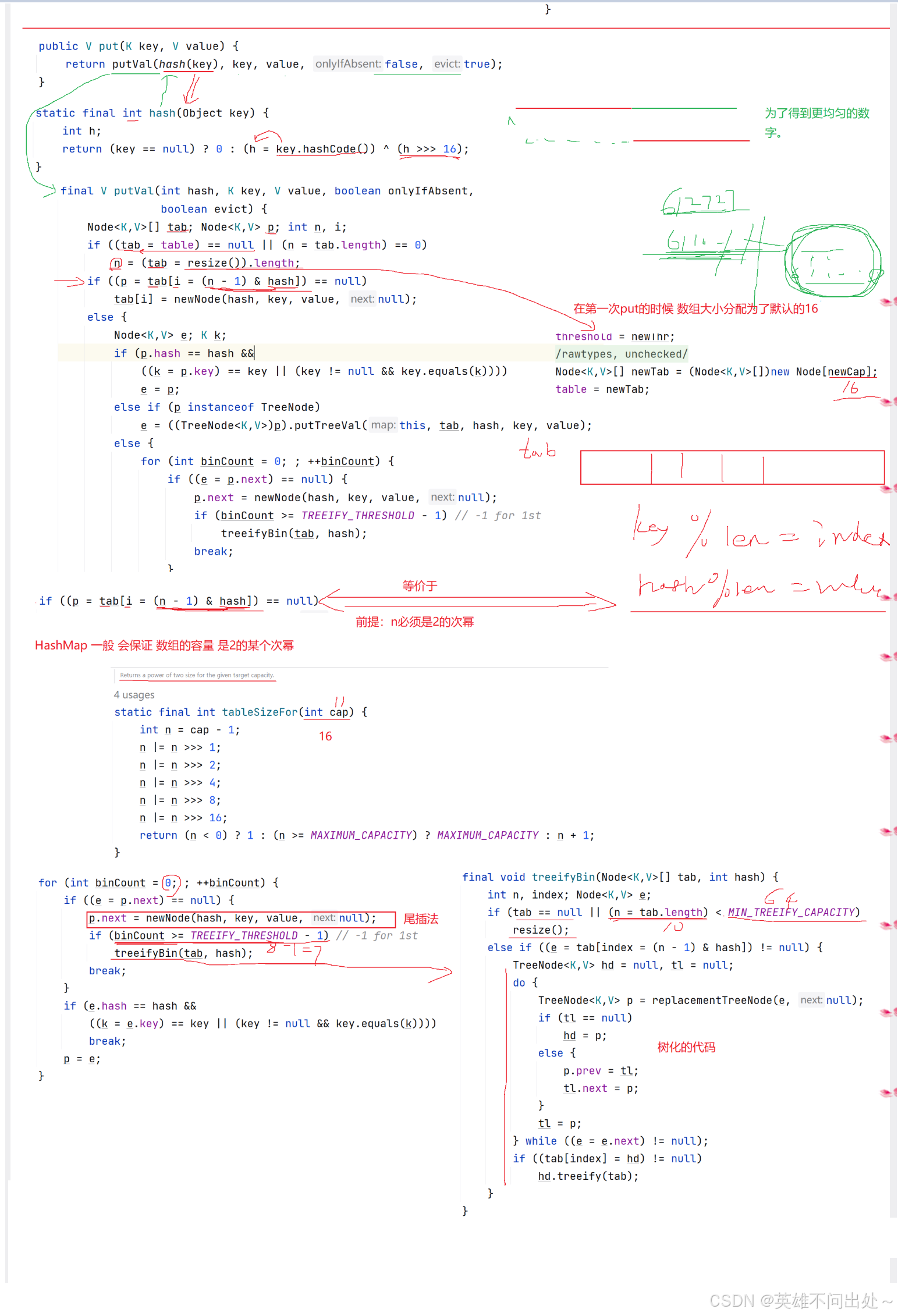
- 如果达到一定条件会把哈希表编程红黑树:如果链表的长度大于8并且数组的长度大于64就会进行树化