分布式微服务架构日志处理解决方案: SpringBoot使用Ttl框架增强MDC,实现traceId在子线程的传递_微服务日志框架
如果你目前只关注解决方案请点击这里直接跳转: SpringBoot2.x 使用TTL框架增强MDC实现TraceId传递
前置知识介绍
TTL(TransmittableThreadLocal)
TTL(TransmittableThreadLocal)是阿里巴巴开源的一个Java线程间传递数据的框架,它是对Java标准库中ThreadLocal的增强版本。
核心概念
ThreadLocal的局限性
标准的ThreadLocal存在一个主要问题:当使用线程池时,由于线程复用,ThreadLocal的值会从一个任务\"泄漏\"到下一个任务,导致数据污染。
TTL的解决方案
TTL框架通过\"可传递的ThreadLocal\"概念解决了这个问题,它能够在以下场景中正确传递线程本地变量:
- 线程池任务提交
- 异步调用
- 跨线程调用链
主要特性
- 线程池兼容:正确处理线程池场景下的ThreadLocal传递
- 透明使用:与标准ThreadLocal API兼容,易于迁移
- 框架集成:支持与各种异步框架(如RxJava、Hystrix等)集成
- 性能优化:相比其他方案(如InheritableThreadLocal)有更好的性能
使用场景
- 分布式跟踪系统中的调用链跟踪
- 多线程环境下的上下文传递
- 异步编程中的上下文保持
- 需要在线程池中传递上下文信息的任何场景
基本用法
1. 添加依赖
<dependency> <groupId>com.alibaba</groupId> <artifactId>transmittable-thread-local</artifactId> <version>2.12.6</version> </dependency>2. 基本使用示例
// 创建TTL实例TransmittableThreadLocal<String> context = new TransmittableThreadLocal<>();// 设置值context.set(\"value-in-parent\");// 在子线程或线程池任务中获取值ExecutorService executor = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();executor.execute(() -> { System.out.println(context.get()); // 输出\"value-in-parent\"});// 清除context.remove();3. 与线程池集成
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();// 使用TtlExecutors装饰线程池ExecutorService ttlExecutorService = TtlExecutors.getTtlExecutorService(executorService);TransmittableThreadLocal<String> context = new TransmittableThreadLocal<>();context.set(\"value-in-parent\");ttlExecutorService.execute(() -> { System.out.println(context.get()); // 正确获取父线程的值});高级用法
1. 自定义拷贝策略
TransmittableThreadLocal<MyObject> ttl = new TransmittableThreadLocal<MyObject>() { @Override protected MyObject copy(MyObject parentValue) { return parentValue.clone(); // 自定义拷贝逻辑 }};2. 与异步框架集成
// 例如与RxJava集成TransmittableThreadLocal<String> context = new TransmittableThreadLocal<>();context.set(\"value-in-parent\");Observable.create(...) .subscribeOn(Schedulers.io()) .subscribe(result -> { System.out.println(context.get()); // 正确获取上下文 });实现原理
TTL的核心实现机制:
- 通过Java Agent或手动装饰Runnable/Callable来捕获任务提交时的ThreadLocal值
- 在任务执行前恢复捕获的ThreadLocal值
- 在任务执行后清理恢复的值
学习资源
- GitHub仓库 - 官方文档和源码
- 阿里巴巴中间件博客 - 有TTL的设计原理解析
- 官方示例代码 - 仓库中的example目录
注意事项
- 性能考虑:虽然TTL做了优化,但仍比普通ThreadLocal有额外开销
- 对象序列化:传递的对象需要是可序列化的(如果需要在分布式环境中传递)
- 内存泄漏:与ThreadLocal一样,需要及时remove避免内存泄漏
TTL是处理Java异步编程中上下文传递问题的优秀解决方案,特别适合在复杂的多线程和异步调用场景中使用。
MDC与TraceId详解:分布式系统日志追踪基础
1. MDC (Mapped Diagnostic Context) - 映射诊断上下文
什么是MDC?
MDC是日志框架(如Logback、Log4j)提供的一种机制,允许开发者在日志中存储上下文信息,这些信息会随着当前线程的日志输出自动附加。
MDC的核心特点:
- 线程绑定:信息与当前线程绑定
- 自动传递:在同一个线程内自动传递
- 日志集成:自动添加到每一条日志中
MDC的基本使用(以Logback为例):
// 放入上下文信息MDC.put(\"userId\", \"user123\");MDC.put(\"requestId\", UUID.randomUUID().toString());// 日志输出时会自动包含这些信息logger.info(\"Processing payment\"); // 输出示例: [user123] [a1b2c3d4] Processing payment// 使用完成后清除MDC.clear();MDC的典型应用场景:
- Web请求跟踪:记录用户ID、会话ID等
- 事务追踪:记录事务ID
- 系统间调用:保持调用链标识
2. TraceId - 跟踪标识符
什么是TraceId?
TraceId是分布式系统中用于唯一标识一个完整请求链路的标识符,贯穿于整个调用链的所有服务。
TraceId的特点:
- 全局唯一:通常使用UUID或类似算法生成
- 跨服务传递:通过HTTP头、RPC上下文等方式传递
- 调用链聚合:用于将所有相关日志串联起来
TraceId的作用:
- 请求追踪:跟踪一个请求在分布式系统中的完整路径
- 问题排查:快速定位故障点
- 性能分析:分析请求在各服务的耗时情况
3. MDC与TraceId的关系
在实际应用中,TraceId通常会被放入MDC中,实现日志的自动标记:
// 在请求入口处生成traceIdString traceId = generateTraceId(); MDC.put(\"traceId\", traceId);// 所有日志都会自动带上traceIdlogger.info(\"Request started\");logger.debug(\"Processing step 1\");logger.error(\"Something went wrong\");// 输出示例:// [traceId:abc123] Request started// [traceId:abc123] Processing step 1// [traceId:abc123] Something went wrong4. 分布式系统中的完整实现示例
4.1 服务入口(如Spring Boot Controller)
@RestControllerpublic class MyController { @GetMapping(\"/api\") public ResponseEntity<?> handleRequest(HttpServletRequest request) { // 从请求头获取或生成traceId String traceId = request.getHeader(\"X-Trace-Id\"); if(traceId == null) { traceId = UUID.randomUUID().toString(); } // 放入MDC MDC.put(\"traceId\", traceId); try { logger.info(\"Request received\"); // 处理请求... return ResponseEntity.ok(\"Success\"); } finally { MDC.clear(); // 确保清除 } }}4.2 服务间调用(如Feign Client)
@FeignClient(name = \"other-service\")public interface OtherServiceClient { @GetMapping(\"/other\") String callOtherService();}// 配置Feign拦截器传递traceIdpublic class FeignTraceInterceptor implements RequestInterceptor { @Override public void apply(RequestTemplate template) { String traceId = MDC.get(\"traceId\"); if(traceId != null) { template.header(\"X-Trace-Id\", traceId); } }}4.3 日志配置(logback.xml示例)
<appender name=\"STDOUT\" class=\"ch.qos.logback.core.ConsoleAppender\"> <encoder> <pattern>%d{yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss} [%thread] [traceId:%X{traceId}] %-5level %logger{36} - %msg%n</pattern> </encoder></appender>5. 常见问题
Q: MDC在线程池中会丢失吗?
A: 是的,直接使用线程池会导致MDC丢失,需要使用TTL等解决方案。
Q: TraceId和SpanId有什么区别?
A: TraceId标识整个调用链,SpanId标识单个服务内的调用段,一个Trace包含多个Span。
Q: 生产环境应该用什么生成TraceId?
A: 通常使用UUID或基于时间戳+机器标识+序列号的算法(如Snowflake)。
希望这些信息能帮助你理解MDC和TraceId的基本概念!这是现代分布式系统开发中非常重要的基础知识。
为什么要使用TTL框架增强MDC实现TraceId传递
理解这个问题需要先明白MDC在并发环境中的局限性,以及TTL框架如何解决这些问题。下面我会从基础到深入逐步解释。
一、MDC在单线程中的工作方式
MDC(Mapped Diagnostic Context)本质上是基于ThreadLocal实现的:
// 伪代码表示MDC原理public class MDC { private static ThreadLocal<Map<String, String>> context = new ThreadLocal<>(); public static void put(String key, String val) { context.get().put(key, val); }}在单线程中工作完美:
主线程:MDC.put(\"traceId\", \"123\") → 子任务执行 → 日志输出[traceId:123]二、问题场景:线程池中的MDC丢失
当引入线程池时会出现问题:
// 线程池示例ExecutorService pool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2);MDC.put(\"traceId\", \"123\"); // 主线程设置pool.execute(() -> { // 子线程中MDC.get(\"traceId\") == null ❌ logger.info(\"Processing...\"); });问题根源:
- 线程复用:线程池线程可能执行过其他任务
- ThreadLocal隔离:子线程无法自动获取父线程的ThreadLocal值
- 任务提交/执行分离:MDC值在任务提交时存在,但执行时可能已清除
三、TTL的解决方案原理
TTL(TransmittableThreadLocal)通过三种方式解决这个问题:
1. 值捕获(Capture)
在任务提交时(如execute()调用时):
// 伪代码public class TtlRunnable implements Runnable { private final Runnable runnable; private final Map<TransmittableThreadLocal<?>, ?> captured; TtlRunnable(Runnable runnable) { this.captured = TransmittableThreadLocal.capture(); // 捕获当前值 this.runnable = runnable; }}2. 值回放(Replay)
在任务执行时:
public void run() { Map<TransmittableThreadLocal<?>, ?> backup = TransmittableThreadLocal.replay(captured); try { runnable.run(); // 执行实际任务 } finally { TransmittableThreadLocal.restore(backup); // 恢复原值 }}3. 线程池装饰
通过TtlExecutors包装线程池:
ExecutorService ttlPool = TtlExecutors.getTtlExecutorService(pool);四、关键优势对比
五、生产环境最佳实践
-
初始化时机:在应用启动时尽早初始化TTL适配器
-
TraceId生成:
public class TraceContext { private static final TransmittableThreadLocal<String> traceIdHolder = new TransmittableThreadLocal<>(); public static void startTrace() { traceIdHolder.set(\"trace-\" + UUID.randomUUID()); } public static String getTraceId() { return traceIdHolder.get(); }} -
与异步框架集成:
// Reactor示例Hooks.onEachOperator(TracingSubscriber.asHook());// RxJava示例RxJavaPlugins.setScheduleHandler(TtlSchedulers::wrap); -
清理策略:
try { // 业务代码} finally { MDC.clear(); TransmittableThreadLocal.clear();}
六、常见问题解决方案
问题1:TTL导致内存泄漏?
- 解决方案:确保在finally块中清理TTL
问题2:与某些框架不兼容?
- 解决方案:检查框架是否提供了线程装饰器接口(如Spring的TaskDecorator)
问题3:性能下降明显?
- 解决方案:减少TTL中存储的数据量,避免存储大对象
通过TTL增强的MDC实现,可以确保traceId在复杂的异步编程场景中依然能正确传递,这对分布式系统的问题排查和调用链追踪至关重要。
SpringBoot2.x 使用TTL框架增强MDC实现TraceId传递
在介绍SpringBoot3.x 实现TTL框架增强MDC实现TraceId传递的解决方案时需要先介绍一下现在很多网上说的教程。网上说的教程都是针对于SpringBoot2.x版本的实现,如果你使用的是2.x就可以用这里的方案。如果不是这里你可以直接跳过,感兴趣也可以了解一下。
初始化示例项目
项目pom.xml文件如下
<project xmlns=\"http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0\" xmlns:xsi=\"http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance\" xsi:schemaLocation=\"http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd\"> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <parent> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId> <version>2.7.18</version> </parent> <groupId>org.tgr</groupId> <artifactId>ttl-log-demo</artifactId> <version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version> <packaging>jar</packaging> <name>ttl-log-demo</name> <properties> <project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding> </properties> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId> <artifactId>lombok</artifactId> </dependency> </dependencies></project>实现原理
为了实现在线程池中可以传递traceId,我们需要做以下两个操作:
- 自定义MDCAdapter,使用TTL替换原先的Thread Local;
- 利用SpringBoot中的spi机制,加载MDCAdapter
自定义MDCAdapter
网上能搜出一大推,我这里给一份网上可用的代码
其实主要有以下关键的改动:
- 将ThreadLocal 变为 TransmittableThreadLocal
- 新增一个静态属性 TtlMDCAdapter mtcMDCAdapter以及一个静态方法块
- 新增一个静态方法 getInstance()
注意: 这里很多教程都要求你将自定义的MDCAdapter放在org.slf4j这个路径下。却不说为什么这么做。实际上是因为在静态代码块中使用到了MDC.mdcAdapter,MDC的mdcAdapter使用的是默认访问权限(default/package-private),只允许在同一个包下使用。因此我们的MDCAdapter必须与MDC在同一个包名下才可以通过 MDC.mdcAdapter = mtcMDCAdapter;直接赋值
package org.slf4j;import ch.qos.logback.classic.util.LogbackMDCAdapter;import com.alibaba.ttl.TransmittableThreadLocal;import org.slf4j.helpers.ThreadLocalMapOfStacks;import org.slf4j.spi.MDCAdapter;import java.util.*;/** * 重构{@link LogbackMDCAdapter}类,搭配TransmittableThreadLocal实现父子线程之间的数据传递 * */public class TtlMDCAdapter implements MDCAdapter { final ThreadLocal<Map<String, String>> readWriteThreadLocalMap = new TransmittableThreadLocal<>(); final ThreadLocal<Map<String, String>> readOnlyThreadLocalMap = new TransmittableThreadLocal<>(); private final ThreadLocalMapOfStacks threadLocalMapOfDeques = new ThreadLocalMapOfStacks(); private static TtlMDCAdapter mtcMDCAdapter; static { mtcMDCAdapter = new TtlMDCAdapter(); MDC.mdcAdapter = mtcMDCAdapter; } public static MDCAdapter getInstance() { return mtcMDCAdapter; } public void put(String key, String val) throws IllegalArgumentException { if (key == null) { throw new IllegalArgumentException(\"key cannot be null\"); } Map<String, String> current = readWriteThreadLocalMap.get(); if (current == null) { current = new HashMap<>(); readWriteThreadLocalMap.set(current); } current.put(key, val); nullifyReadOnlyThreadLocalMap(); } /** * Get the context identified by the key parameter. * * * This method has no side effects. */ @Override public String get(String key) { Map<String, String> hashMap = readWriteThreadLocalMap.get(); if ((hashMap != null) && (key != null)) { return hashMap.get(key); } else { return null; } } /** * Remove the context identified by the key parameter. *
*/ @Override public void remove(String key) { if (key == null) { return; } Map<String, String> current = readWriteThreadLocalMap.get(); if (current != null) { current.remove(key); nullifyReadOnlyThreadLocalMap(); } } private void nullifyReadOnlyThreadLocalMap() { readOnlyThreadLocalMap.set(null); } /** * Clear all entries in the MDC. */ @Override public void clear() { readWriteThreadLocalMap.set(null); nullifyReadOnlyThreadLocalMap(); } /** * Get the current thread\'s MDC as a map. This method is intended to be used * internally.
* * The returned map is unmodifiable (since version 1.3.2/1.4.2). */ @SuppressWarnings(\"unchecked\") public Map<String, String> getPropertyMap() { Map<String, String> readOnlyMap = readOnlyThreadLocalMap.get(); if (readOnlyMap == null) { Map<String, String> current = readWriteThreadLocalMap.get(); if (current != null) { final Map<String, String> tempMap = new HashMap<>(current); readOnlyMap = Collections.unmodifiableMap(tempMap); readOnlyThreadLocalMap.set(readOnlyMap); } } return readOnlyMap; } /** * Return a copy of the current thread\'s context map. Returned value may be * null. */ public Map getCopyOfContextMap() { Map<String, String> readOnlyMap = getPropertyMap(); if (readOnlyMap == null) { return null; } else { return new HashMap<>(readOnlyMap); } } /** * Returns the keys in the MDC as a {@link Set}. The returned value can be * null. */ public Set<String> getKeys() { Map<String, String> readOnlyMap = getPropertyMap(); if (readOnlyMap != null) { return readOnlyMap.keySet(); } else { return null; } } @SuppressWarnings(\"unchecked\") public void setContextMap(Map contextMap) { if (contextMap != null) { readWriteThreadLocalMap.set(new HashMap<String, String>(contextMap)); } else { readWriteThreadLocalMap.set(null); } nullifyReadOnlyThreadLocalMap(); } @Override public void pushByKey(String key, String value) { threadLocalMapOfDeques.pushByKey(key, value); } @Override public String popByKey(String key) { return threadLocalMapOfDeques.popByKey(key); } @Override public Deque<String> getCopyOfDequeByKey(String key) { return threadLocalMapOfDeques.getCopyOfDequeByKey(key); } @Override public void clearDequeByKey(String key) { threadLocalMapOfDeques.clearDequeByKey(key); }}利用SpringBoot中的spi机制,加载MDCAdapter
1. 自定义类实现 ApplicationContextInitializer接口
我找一个网上可以使用的代码贴在这里
package com.central.log.config;import org.slf4j.TtlMDCAdapter;import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextInitializer;import org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext;/** * 初始化TtlMDCAdapter实例,并替换MDC中的adapter对象 * */public class TtlMDCAdapterInitializer implements ApplicationContextInitializer<ConfigurableApplicationContext> { @Override public void initialize(ConfigurableApplicationContext applicationContext) { //加载TtlMDCAdapter实例 TtlMDCAdapter.getInstance(); }}这里它使用了一个getInstance(),不知道是哪个天才想出来的方法。上面的TtlMDCAdapter的getInstance()只是获取mtcMDCAdapter属性而已,怎么和加载挂上钩了呢?怎么替换的MDCAdapter呢?
实际上它是通过调用这个静态方法,然后触发类加载,执行TtlMDCAdapter中的静态代码块,在静态代码块中new一个TtlMDCAdapter并把这个对象的值设置给了MDC.mdcAdapterstatic { mtcMDCAdapter = new TtlMDCAdapter(); MDC.mdcAdapter = mtcMDCAdapter; } public static MDCAdapter getInstance() { return mtcMDCAdapter; }实际上完成不需要这么麻烦,可以换一种方式实现同时也更直观,
TtlMDCAdapter改造后的代码如下public class TtlMDCAdapter implements MDCAdapter { public static void initTtlMDCAdapter() { System.out.println(\"TtlMDCAdapter initTtlMDCAdapter\"); MDC.mdcAdapter = new TtlMDCAdapter(); } // 其他代码与原来保持一致即可 ...
TtlMDCAdapterInitializer改造后的代码如下:public class TtlMDCAdapterInitializer implements ApplicationContextInitializer<ConfigurableApplicationContext> { @Override public void initialize(ConfigurableApplicationContext applicationContext) { TtlMDCAdapter.initTtlMDCAdapter(); }}
2. 配置spring.factories让springboot能够扫描到自定义的类
创建spring.factories文件,放在resources/META-INF/目录下
文件内容如下:
# Application Context Initializersorg.springframework.context.ApplicationContextInitializer=\\org.tgr.ttl.log.demo.initializer.TtlMDCAdapterInitializer通过Springboot提供的SPI加载机制,让项目在启动的最开始就执行TtlMDCAdapter.initTtlMDCAdapter();从而将MDC中的mdcAdapter 替换成自定义的MdcAdapter ,这样后续的MDC相关操作都会使用自己增强好的MdcAdapter
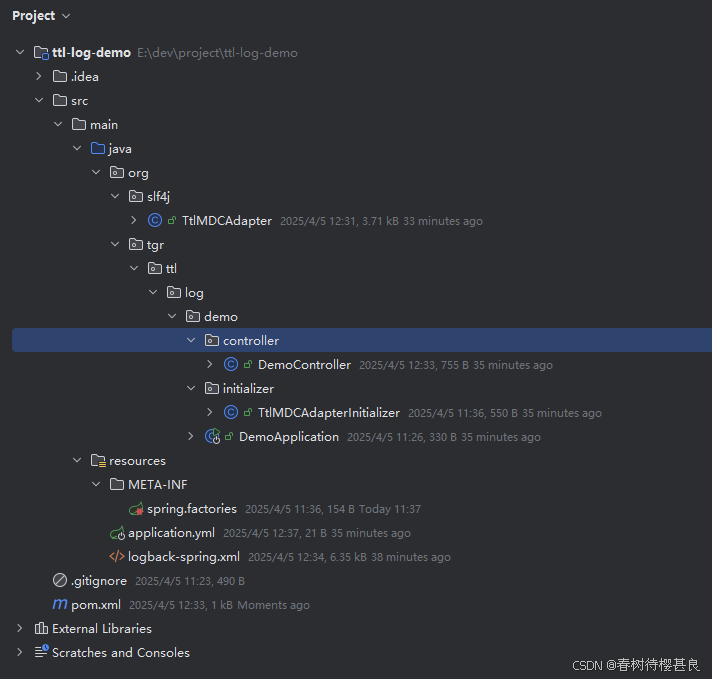
项目完成结构如下
SpringBoot3.x 使用TTL框架增强MDC实现TraceId传递
前面介绍到的2.x使用的方法在SpringBoot3.x后其实无法生效。这里针对Springboot3.x再进行一次介绍
初始化示例项目
pom.xml文件如下
<project xmlns=\"http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0\" xmlns:xsi=\"http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance\" xsi:schemaLocation=\"http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd\"> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <parent> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId> <version>3.1.12</version> </parent> <groupId>org.tgr</groupId> <artifactId>ttl-log-demo-17</artifactId> <version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version> <packaging>jar</packaging> <name>ttl-log-demo-17</name> <properties> <project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding> </properties> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId> <artifactId>lombok</artifactId> </dependency> </dependencies></project>实现原理
为了实现在线程池中可以传递traceId,我们需要做以下两个操作:
- 自定义MDCAdapter,使用TTL替换原先的Thread Local;
- 自定义LogbackServiceProvider替换默认的LogbackServiceProvider
自定义MDCAdapter
package org.slf4j;import ch.qos.logback.classic.util.LogbackMDCAdapter;import com.alibaba.ttl.TransmittableThreadLocal;import org.slf4j.helpers.ThreadLocalMapOfStacks;import java.util.*;/** * 重构{@link LogbackMDCAdapter}类,搭配TransmittableThreadLocal实现父子线程之间的数据传递 * */public class TtlMDCAdapter extends LogbackMDCAdapter { // BEWARE: Keys or values placed in a ThreadLocal should not be of a type/class // not included in the JDK. See also https://jira.qos.ch/browse/LOGBACK-450 final ThreadLocal<Map<String, String>> readWriteThreadLocalMap = new TransmittableThreadLocal<>(); final ThreadLocal<Map<String, String>> readOnlyThreadLocalMap = new TransmittableThreadLocal<>(); private final ThreadLocalMapOfStacks threadLocalMapOfDeques = new ThreadLocalMapOfStacks(); /** * Put a context value (the val parameter) as identified with the * key parameter into the current thread\'s context map. Note that * contrary to log4j, the val parameter can be null. * * * If the current thread does not have a context map it is created as a side * effect of this call. * * * Each time a value is added, a new instance of the map is created. This is * to be certain that the serialization process will operate on the updated * map and not send a reference to the old map, thus not allowing the remote * logback component to see the latest changes. * * @throws IllegalArgumentException in case the \"key\" parameter is null */ public void put(String key, String val) throws IllegalArgumentException { if (key == null) { throw new IllegalArgumentException(\"key cannot be null\"); } Map<String, String> current = readWriteThreadLocalMap.get(); if (current == null) { current = new HashMap<String, String>(); readWriteThreadLocalMap.set(current); } current.put(key, val); nullifyReadOnlyThreadLocalMap(); } /** * Get the context identified by the key parameter. * * * This method has no side effects. */ @Override public String get(String key) { Map<String, String> hashMap = readWriteThreadLocalMap.get(); if ((hashMap != null) && (key != null)) { return hashMap.get(key); } else { return null; } } /** * Remove the context identified by the key parameter. *
*/ @Override public void remove(String key) { if (key == null) { return; } Map<String, String> current = readWriteThreadLocalMap.get(); if (current != null) { current.remove(key); nullifyReadOnlyThreadLocalMap(); } } private void nullifyReadOnlyThreadLocalMap() { readOnlyThreadLocalMap.set(null); } /** * Clear all entries in the MDC. */ @Override public void clear() { readWriteThreadLocalMap.remove(); nullifyReadOnlyThreadLocalMap(); } /** * Get the current thread\'s MDC as a map. This method is intended to be used * internally.
* * The returned map is unmodifiable (since version 1.3.2/1.4.2). */ @SuppressWarnings(\"all\") public Map<String, String> getPropertyMap() { Map<String, String> readOnlyMap = readOnlyThreadLocalMap.get(); if (readOnlyMap == null) { Map<String, String> current = readWriteThreadLocalMap.get(); if (current != null) { final Map<String, String> tempMap = new HashMap<>(current); readOnlyMap = Collections.unmodifiableMap(tempMap); readOnlyThreadLocalMap.set(readOnlyMap); } } return readOnlyMap; } /** * Return a copy of the current thread\'s context map. Returned value may be * null. */ public Map getCopyOfContextMap() { Map<String, String> readOnlyMap = getPropertyMap(); if (readOnlyMap == null) { return null; } else { return new HashMap<>(readOnlyMap); } } /** * Returns the keys in the MDC as a {@link Set}. The returned value can be * null. */ public Set<String> getKeys() { Map<String, String> readOnlyMap = getPropertyMap(); if (readOnlyMap != null) { return readOnlyMap.keySet(); } else { return null; } } @SuppressWarnings(\"unchecked\") public void setContextMap(Map contextMap) { if (contextMap != null) { readWriteThreadLocalMap.set(new HashMap<String, String>(contextMap)); } else { readWriteThreadLocalMap.set(null); } nullifyReadOnlyThreadLocalMap(); } @Override public void pushByKey(String key, String value) { threadLocalMapOfDeques.pushByKey(key, value); } @Override public String popByKey(String key) { return threadLocalMapOfDeques.popByKey(key); } @Override public Deque<String> getCopyOfDequeByKey(String key) { return threadLocalMapOfDeques.getCopyOfDequeByKey(key); } @Override public void clearDequeByKey(String key) { threadLocalMapOfDeques.clearDequeByKey(key); }}自定义LogbackServiceProvider
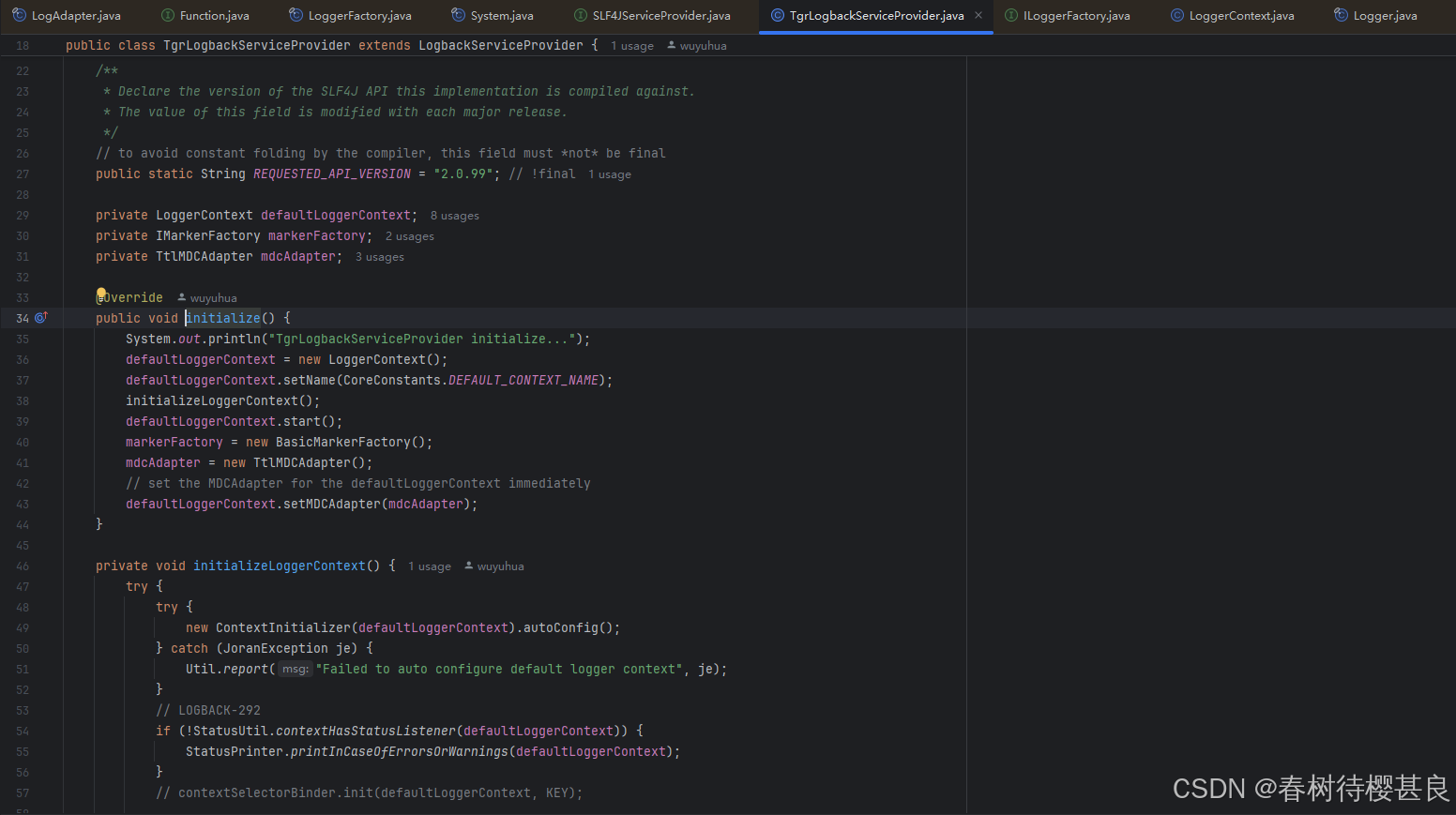
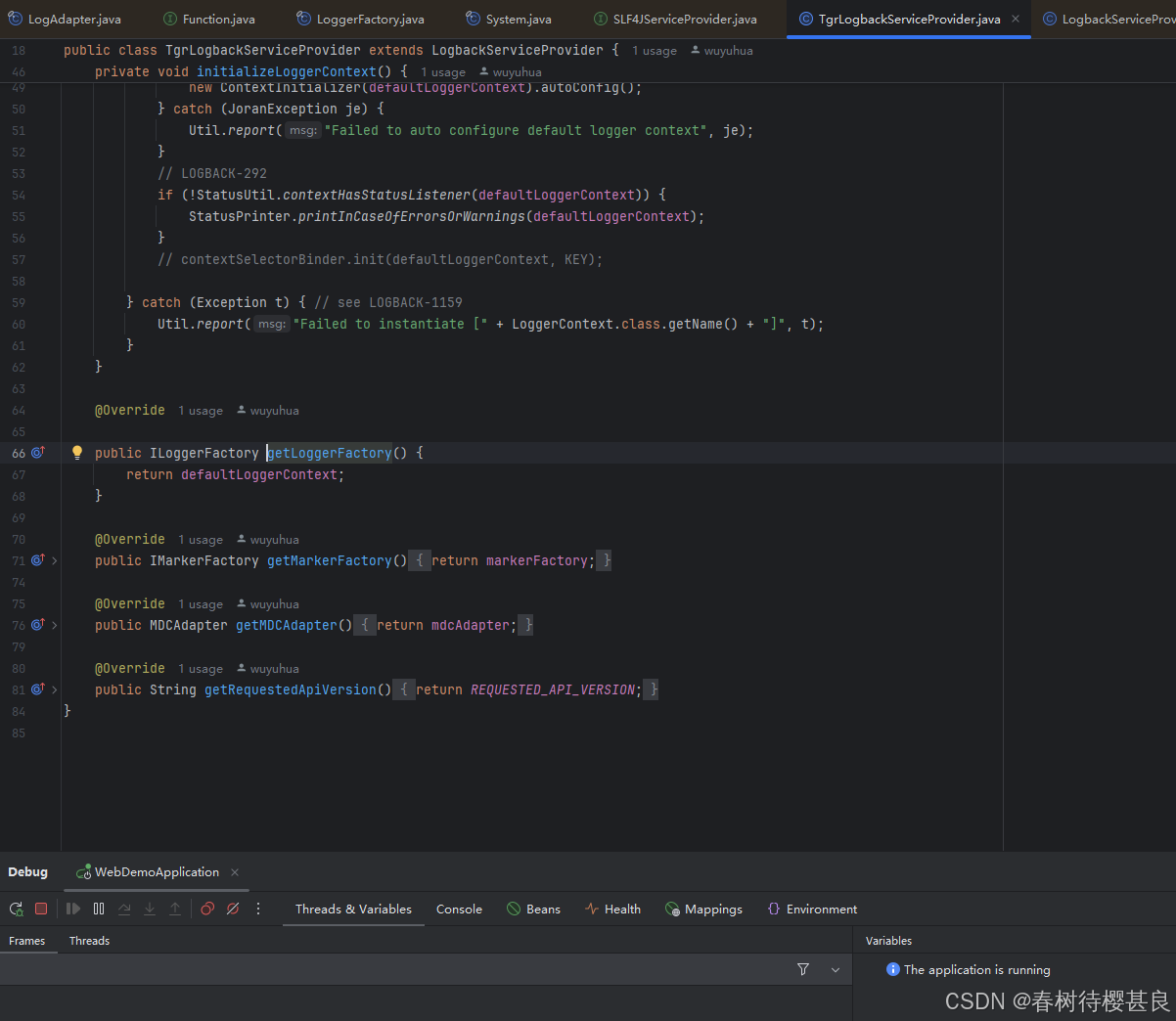
package org.slf4j;import ch.qos.logback.classic.LoggerContext;import ch.qos.logback.classic.spi.LogbackServiceProvider;import ch.qos.logback.classic.util.ContextInitializer;import ch.qos.logback.core.CoreConstants;import ch.qos.logback.core.joran.spi.JoranException;import ch.qos.logback.core.status.StatusUtil;import ch.qos.logback.core.util.StatusPrinter;import org.slf4j.helpers.BasicMarkerFactory;import org.slf4j.helpers.Util;import org.slf4j.spi.MDCAdapter;import org.slf4j.spi.SLF4JServiceProvider;/** * 重写 LogbackServiceProvider */public class TgrLogbackServiceProvider extends LogbackServiceProvider { final static String NULL_CS_URL = CoreConstants.CODES_URL + \"#null_CS\"; /** * Declare the version of the SLF4J API this implementation is compiled against. * The value of this field is modified with each major release. */ // to avoid constant folding by the compiler, this field must *not* be final public static String REQUESTED_API_VERSION = \"2.0.99\"; // !final private LoggerContext defaultLoggerContext; private IMarkerFactory markerFactory; private TtlMDCAdapter mdcAdapter; @Override public void initialize() { System.out.println(\"TgrLogbackServiceProvider initialize...\"); defaultLoggerContext = new LoggerContext(); defaultLoggerContext.setName(CoreConstants.DEFAULT_CONTEXT_NAME); initializeLoggerContext(); defaultLoggerContext.start(); markerFactory = new BasicMarkerFactory(); mdcAdapter = new TtlMDCAdapter(); // set the MDCAdapter for the defaultLoggerContext immediately defaultLoggerContext.setMDCAdapter(mdcAdapter); } private void initializeLoggerContext() { try { try { new ContextInitializer(defaultLoggerContext).autoConfig(); } catch (JoranException je) { Util.report(\"Failed to auto configure default logger context\", je); } // LOGBACK-292 if (!StatusUtil.contextHasStatusListener(defaultLoggerContext)) { StatusPrinter.printInCaseOfErrorsOrWarnings(defaultLoggerContext); } // contextSelectorBinder.init(defaultLoggerContext, KEY); } catch (Exception t) { // see LOGBACK-1159 Util.report(\"Failed to instantiate [\" + LoggerContext.class.getName() + \"]\", t); } } @Override public ILoggerFactory getLoggerFactory() { return defaultLoggerContext; } @Override public IMarkerFactory getMarkerFactory() { return markerFactory; } @Override public MDCAdapter getMDCAdapter() { return mdcAdapter; } @Override public String getRequestedApiVersion() { return REQUESTED_API_VERSION; }}使用SpringBoot的Spi机制 加载TgrLogbackServiceProvider
在resources/META-INF/services/目录下新建org.slf4j.spi.SLF4JServiceProvider文件。内容如下:
# 这里的值应该是你自定义的LogbackServiceProvider类的全路径限定名org.slf4j.TgrLogbackServiceProvider项目启动后日志打印会出现一些警告
SLF4J: Class path contains multiple SLF4J providers.
SLF4J: Found provider [org.slf4j.TgrLogbackServiceProvider@2a3046da]
SLF4J: Found provider [ch.qos.logback.classic.spi.LogbackServiceProvider@2a098129]
SLF4J: See https://www.slf4j.org/codes.html#multiple_bindings for an explanation.
SLF4J: Actual provider is of type [org.slf4j.TgrLogbackServiceProvider@2a3046da]
这样就表示加载成功,需要注意的是你自定义的LogbackServiceProvider必须是第一个加载的,这样才会生效。否则将不会生效
这里的警告意思就是扫描到了两个SLF4J providers,最终使用的providers 是 [org.slf4j.TgrLogbackServiceProvider@2a3046da]
你也可以通过java命令行参数的方式强制指定要使用的providers
java -jar -Dslf4j.provider=org.slf4j.TgrLogbackServiceProvider ...这种方式同样可以实现,日志会打印出如下内容:
SLF4J: Attempting to load provider “org.slf4j.TgrLogbackServiceProvider” specified via “slf4j.provider” system property
表示使用命令行参数强制指定Provider的实现为org.slf4j.TgrLogbackServiceProvider
到这里就结束了。为什么springboot2.x 和 springboot3.x的实现方式完全不一样呢?这里需要牵扯到Springboot中默认日志框架logback各个版本的实现差异。下面一章通过源码的方式介绍二者之间的差异
原因
Spring Boot 2.x
我使用的是2.7.14. 它自动引入的logback依赖是 1.2.12

为了搞明白为什么同样的代码在SpringBoot2.x就能生效但是到了SpringBoot3.x却没有用,我们要先了解他们日志框架是怎么将我们日志中的%X{traceId} 这种占位符替换成具体的值的呢。
我们在SpringBoot2.x的应用中通过改变MDC.mdcAdapter的属性来实现日志打印的增强,那么这个占位符替换具体的值就肯定是和我们的MDCAdapter有关系了。我们可以看到MDCAdapter接口有哪些方法
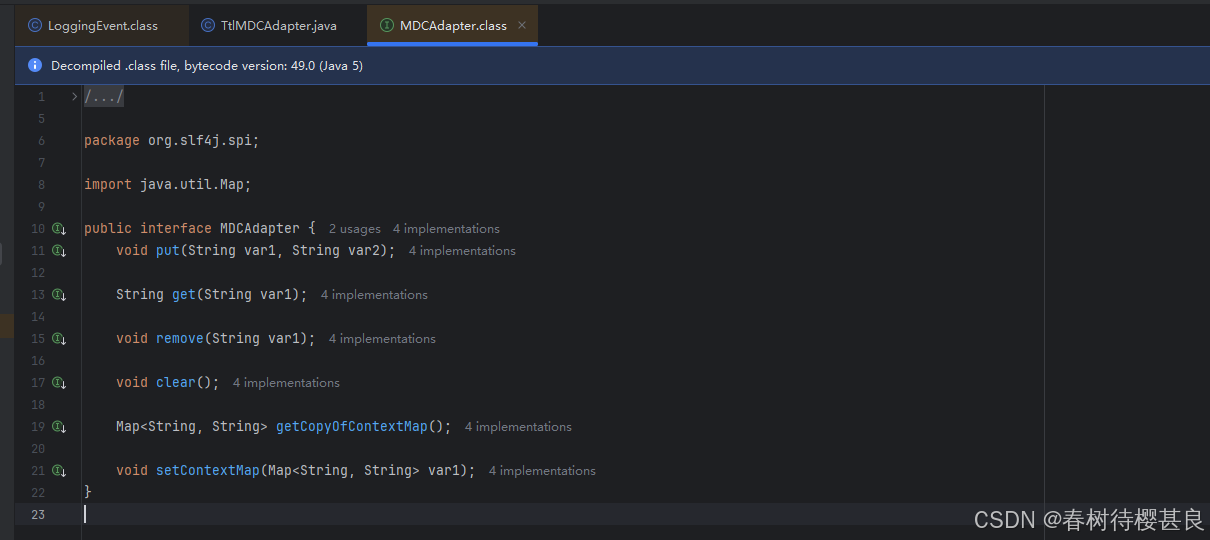
很明显,put是设置一个键值对,那将占位符替换成具体的值肯定涉及到一个get操作,所以要么是get方法 要么就是getCopyOfContextMap方法了。get明显就是获取一个key 的值 getCopyOfContexntMap的方法应该就是获取Map,Map包含所有设置进去的所有键值对了。
通过Debug,实际上是调用了getCopyOfContexntMap()方法
因为springboot采用的日志框架是logback,因为我们找到Logback的实现 LogbackMDCAdapter
public Map<String, String> getCopyOfContextMap() { Map<String, String> hashMap = (Map)this.copyOnThreadLocal.get(); return hashMap == null ? null : new HashMap(hashMap); }这个方法实际上就是将存在当前线程的threadlocal中的map拿出来而已。
那很显然,如果我们想让我们的MDCAdapter生效,就得让MDCAdapter的具体实现变成我们自己的MDCAdapter。
通过堆栈,我们再往前看是谁调用了MDCAdapter的getCopyOfContextMap(),找一下是在哪里选择具体的实现类的。
往上找我们会找到一个LoggingEvent的类下的getMDCPropertyMap()方法。
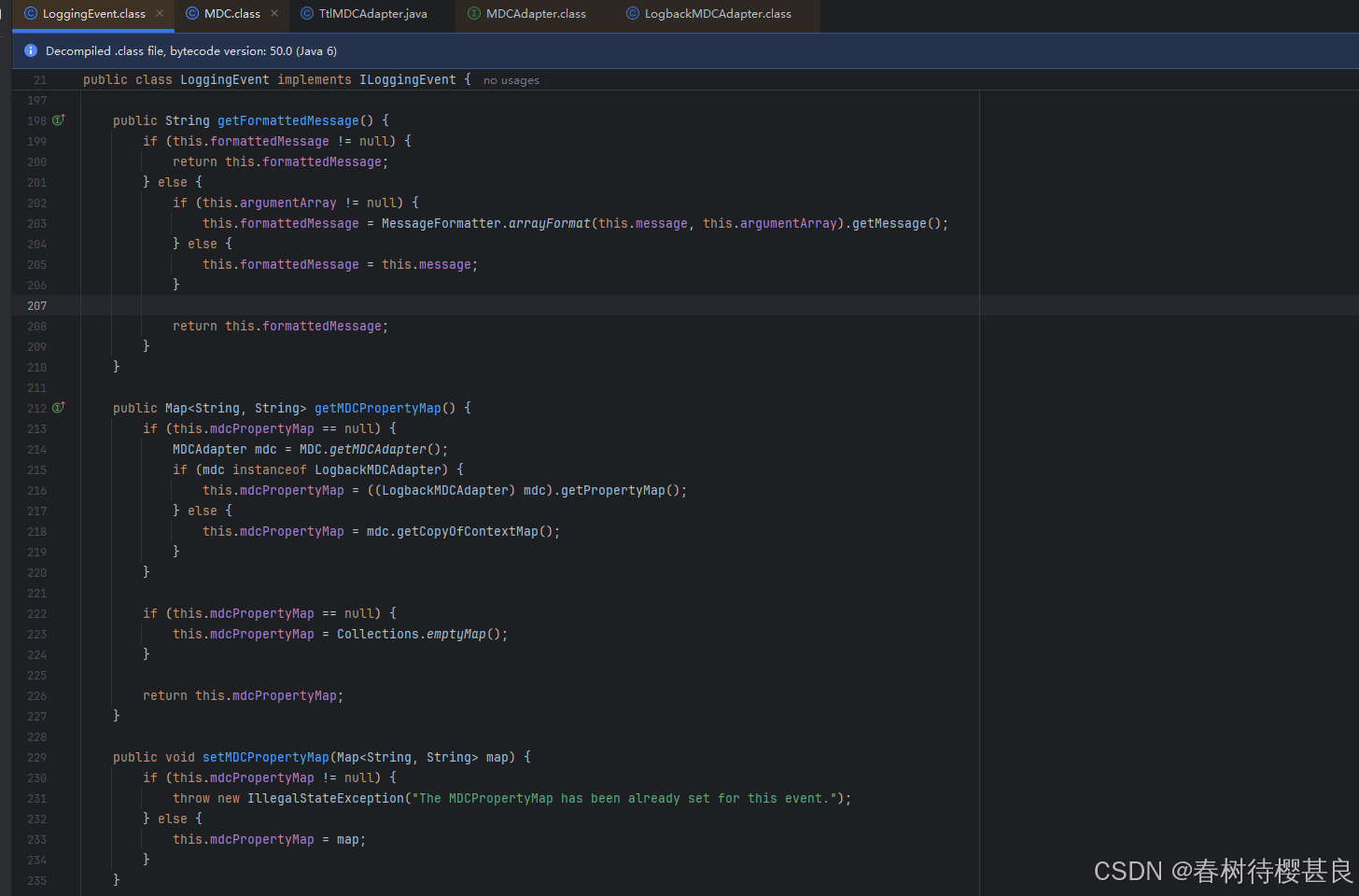
我们在这里就能很清楚的看到 它使用了MDC.getMDCAdapter()方法获取MDCAdapter 的具体实现类。
我们再看这个方法里的实现
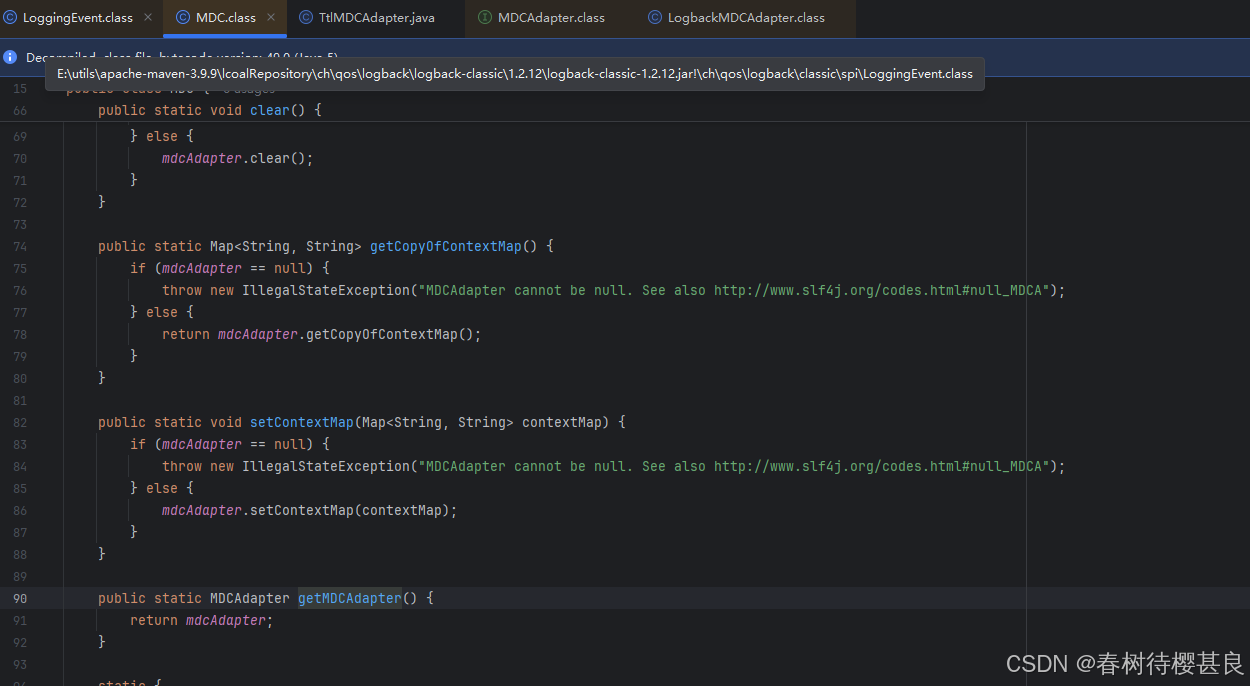
它实际上返回了MDC的mdcAdapter属性,到这里就很明显了。我们增强的时候不是刚好设置了这个属性吗
回顾网上的代码
static { mtcMDCAdapter = new TtlMDCAdapter(); MDC.mdcAdapter = mtcMDCAdapter; } public static MDCAdapter getInstance() { return mtcMDCAdapter; }其实就是设置了 MDC.mdcAdapter 的值,然后保证这个方法能在项目的最开始去执行就可以了。那这就是SpringBoot2.x 中自定义MDCAdapter的实现原理。
Spring Boot 3.x
我们来到SpringBoot3.x的版本再看,首先可以看到logback的版本已经发生了变化 版本是1.4.11
同样的流程,我这回就直接到LoggingEvent的类下的getMDCPropertyMap()方法。看看新版本的实现是什么

我们可以看到,新版的getMDCPropertyMap()方法已经更新了,不再使用MDC的mtcAdapter属性了。而是使用了一个loggerContext的对象中的getMDCAdapter()方法。
我们点进去看看这个方法的实现是什么
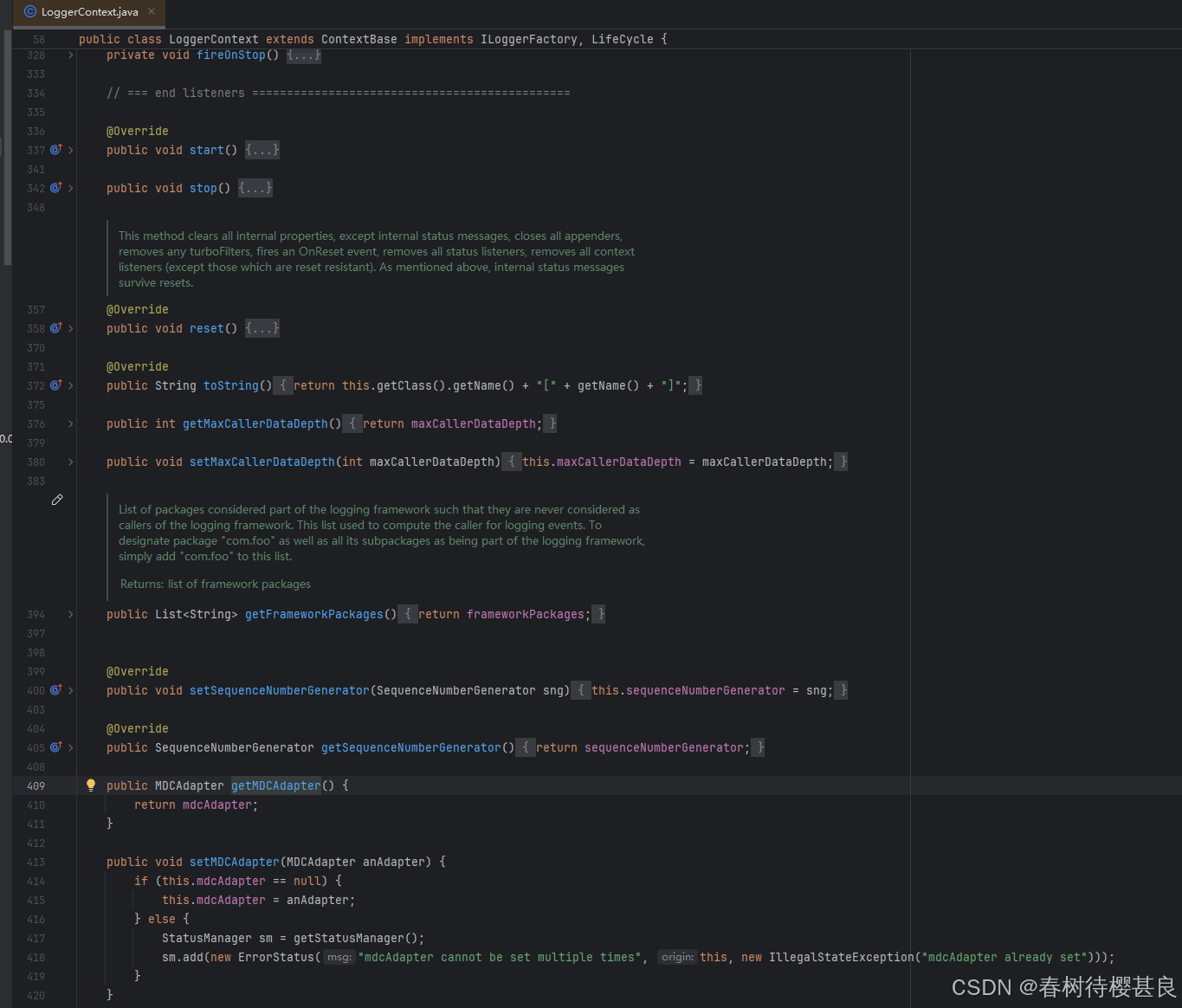
还是一样使用了自己的mdcAdapter属性。那我们下一步就是找这个属性是怎么赋值
经过 我的一系列排查,发现这个属性只有一个setMDCAdapter()方法,在这个类中并没有找到有设置MDCAdapter的地方,构造方法中也没有。
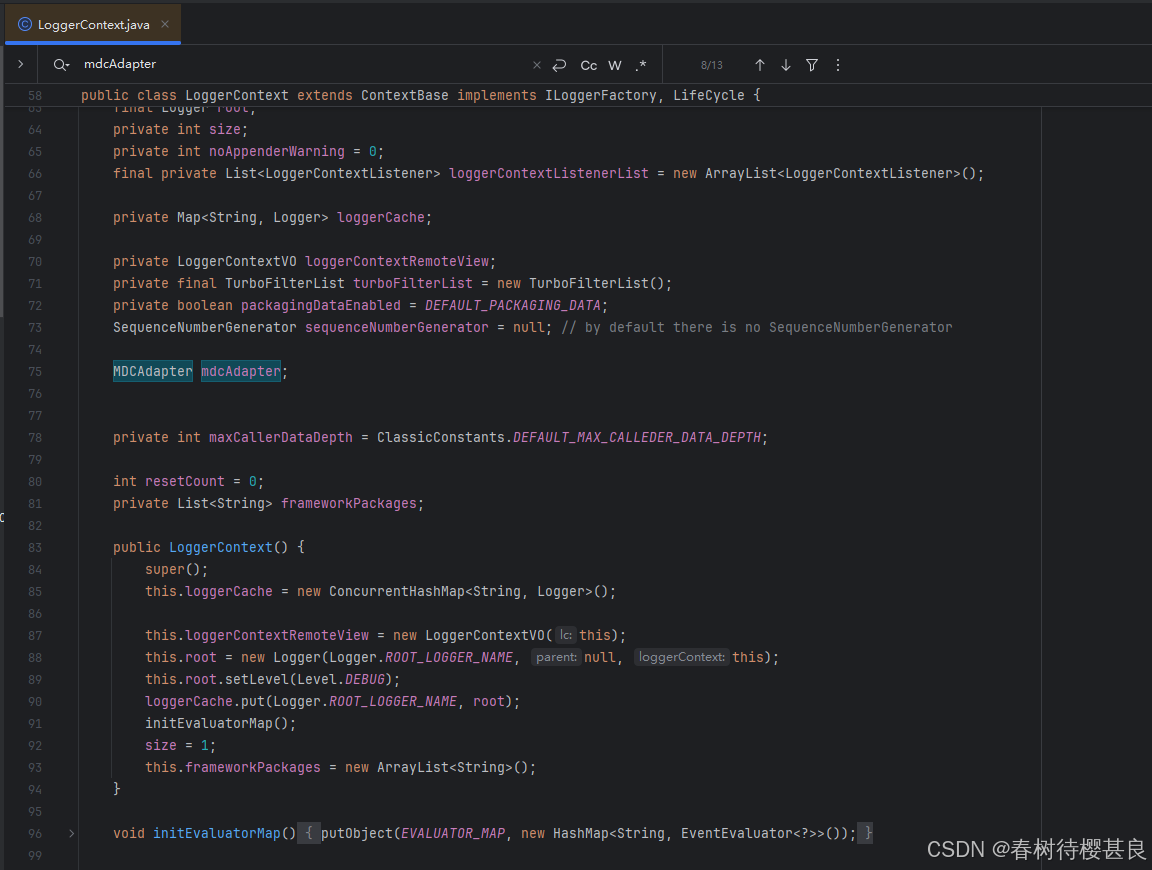
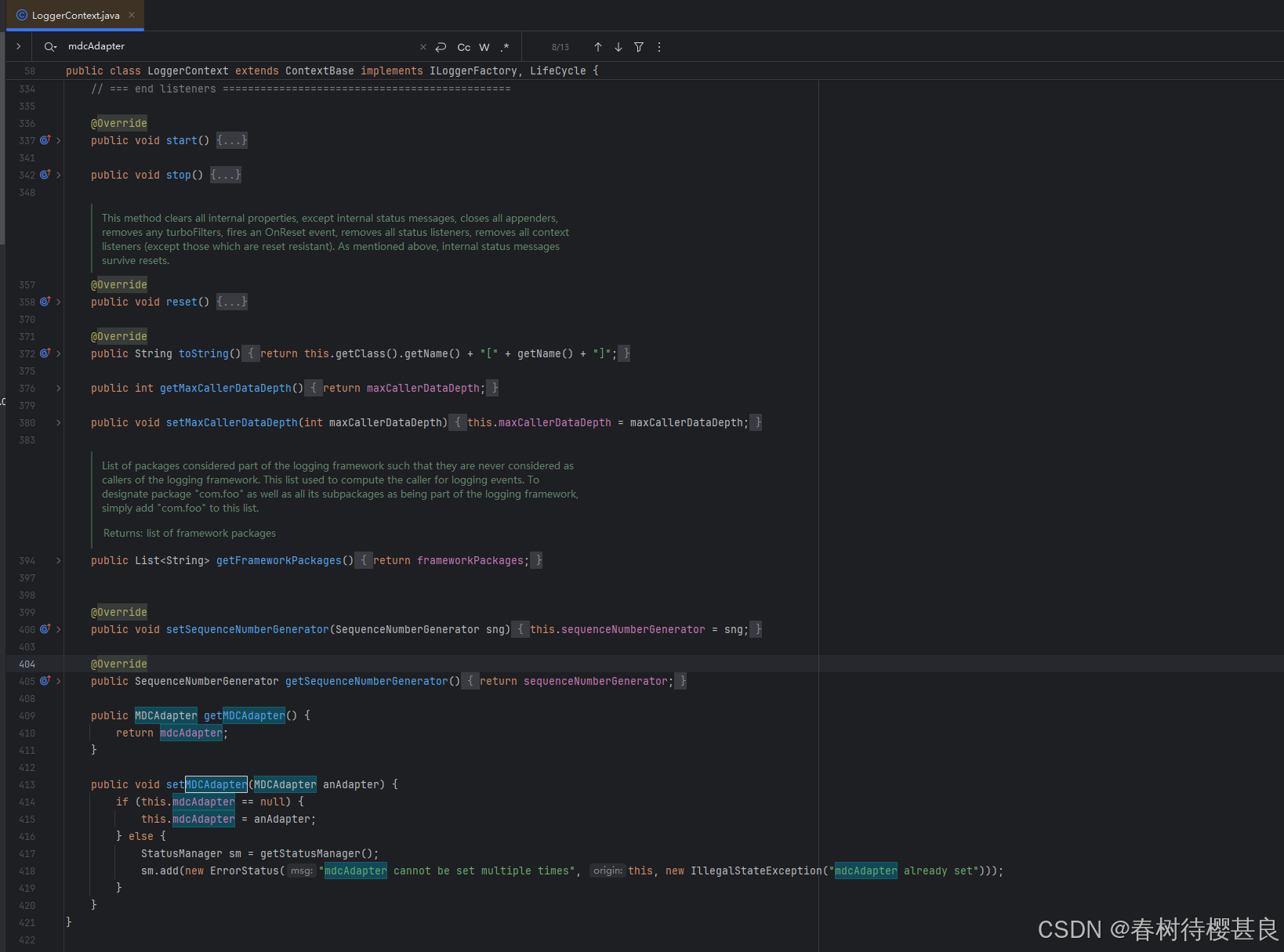 那我们再往上找一层,看看是哪里初始化这个
那我们再往上找一层,看看是哪里初始化这个loggerContext的,在初始化的地方应该会有设置的方法
在这里我跳过排查的过程,直接给大家展示调用链
首先在SpringApplication类中有一个Log类型的属性logger
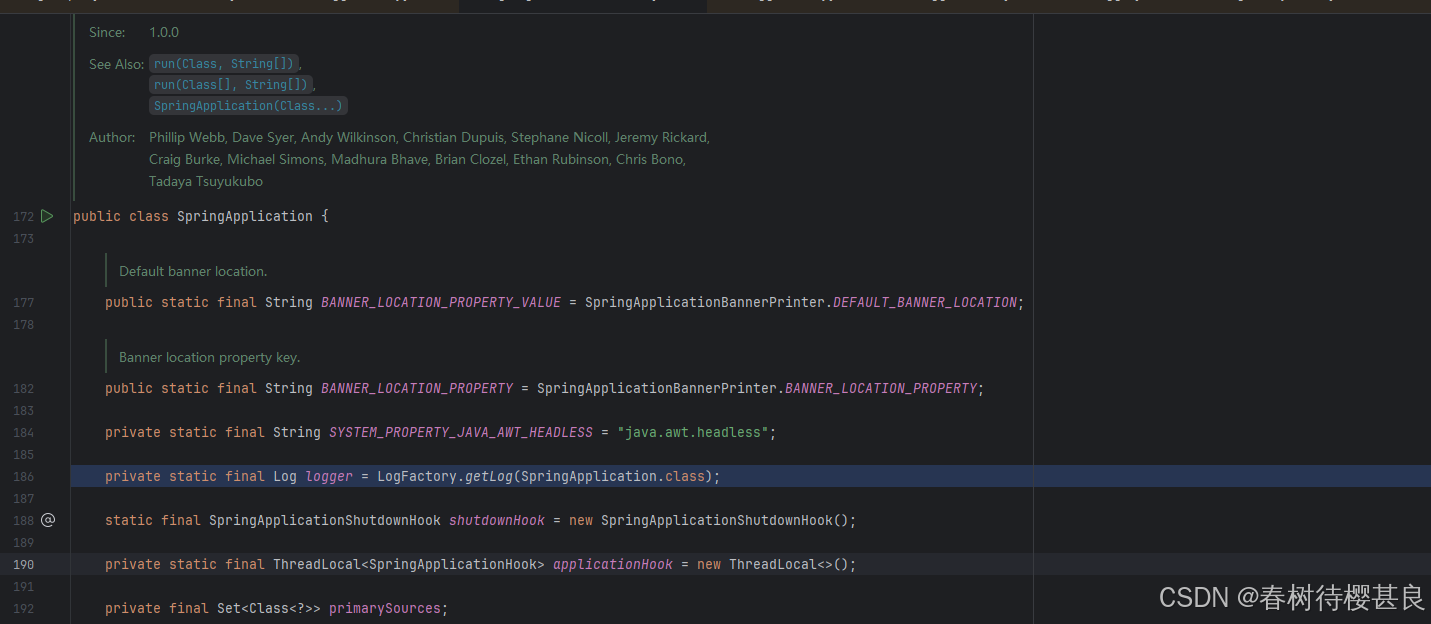
它通过LogFactory的getLog方法获取Log对象。在LogFactory这个抽象类中getLog方法实际用到了LogAdapter的静态方法createLog创建日志对象
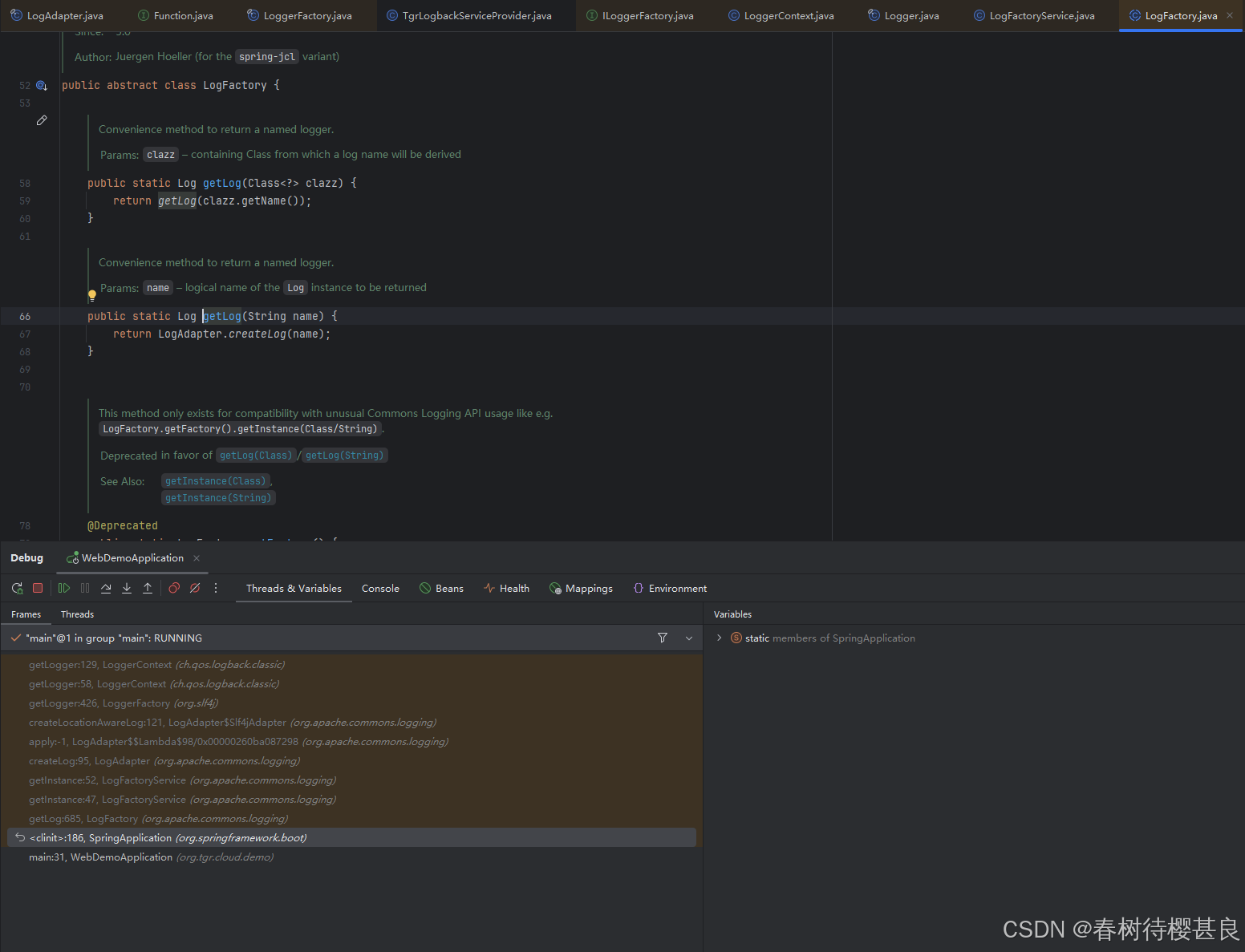
在LogAdapter.createLog()方法中使用到了一个属性createLog,它是一个static final的函数式接口,并在静态代码块中设置
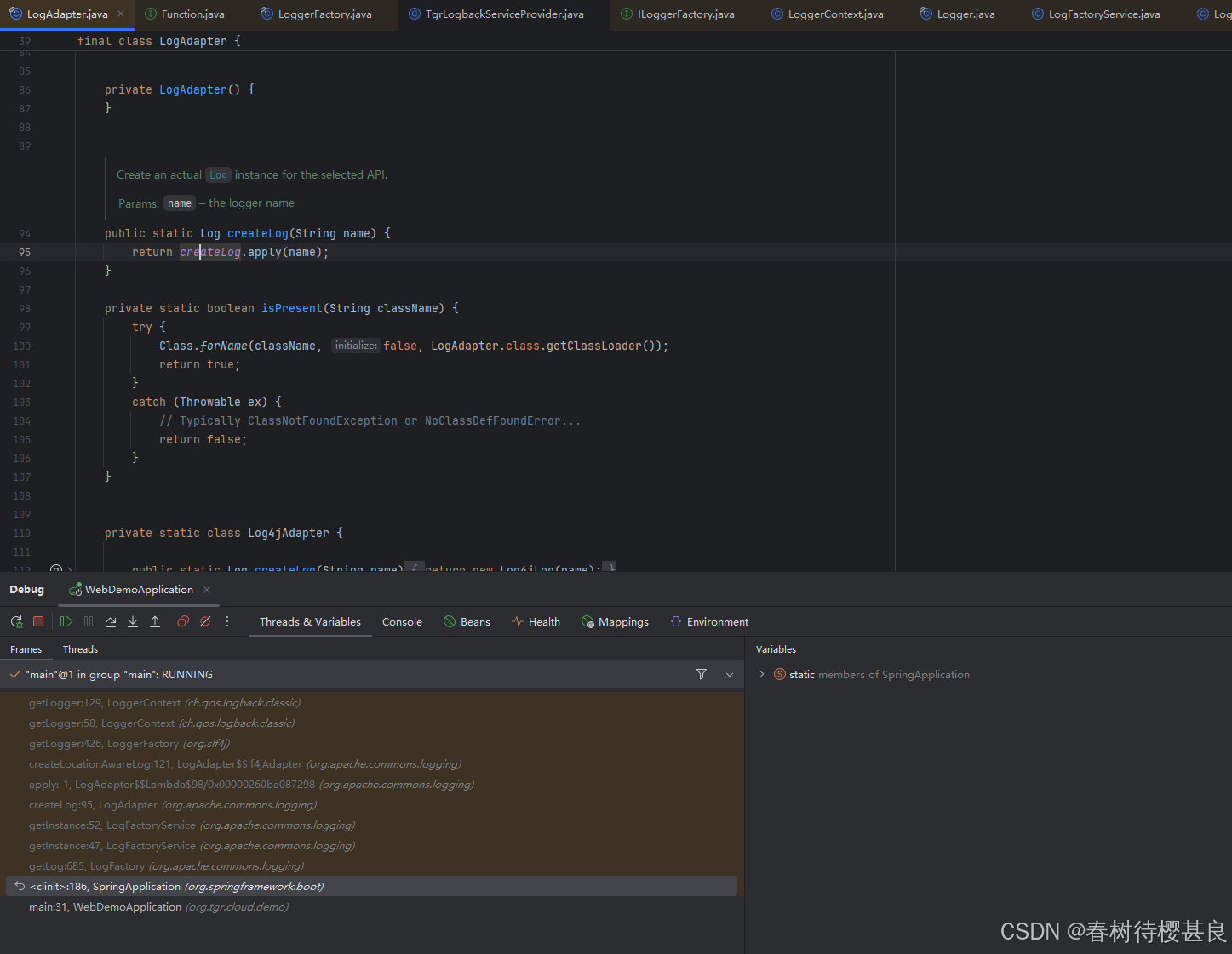
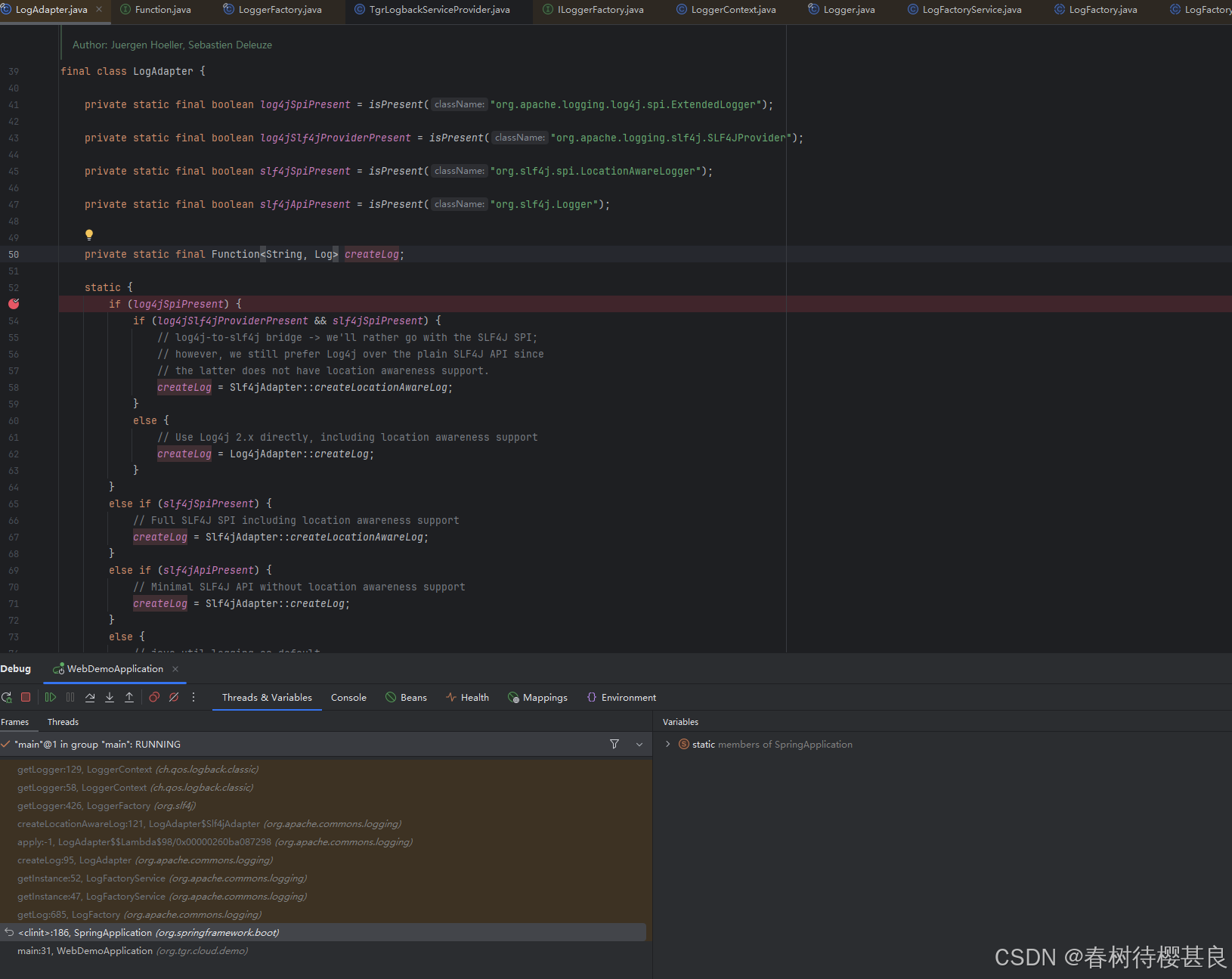
在这个静态代码块中,通过debug最终发现createLog的值是Slf4jAdapter::createLocationAwareLog;这个方法。顺着这个方法点进去。它的内部实现是通过LoggerFactory.getLogger()方法拿到Logger对象,并最终将其转成Log返回。
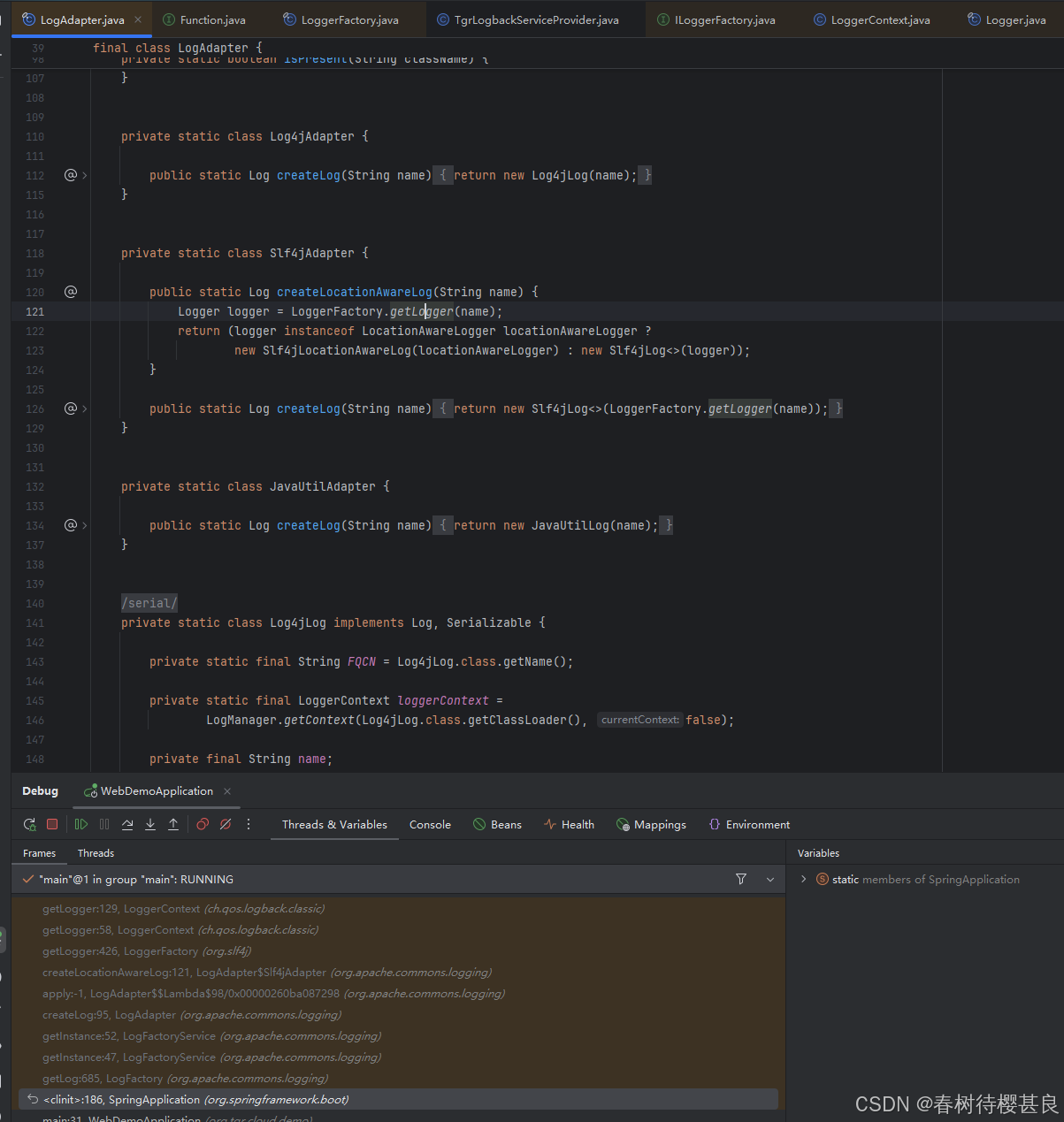
我们再点进LoggerFactory.getLogger()方法的实现
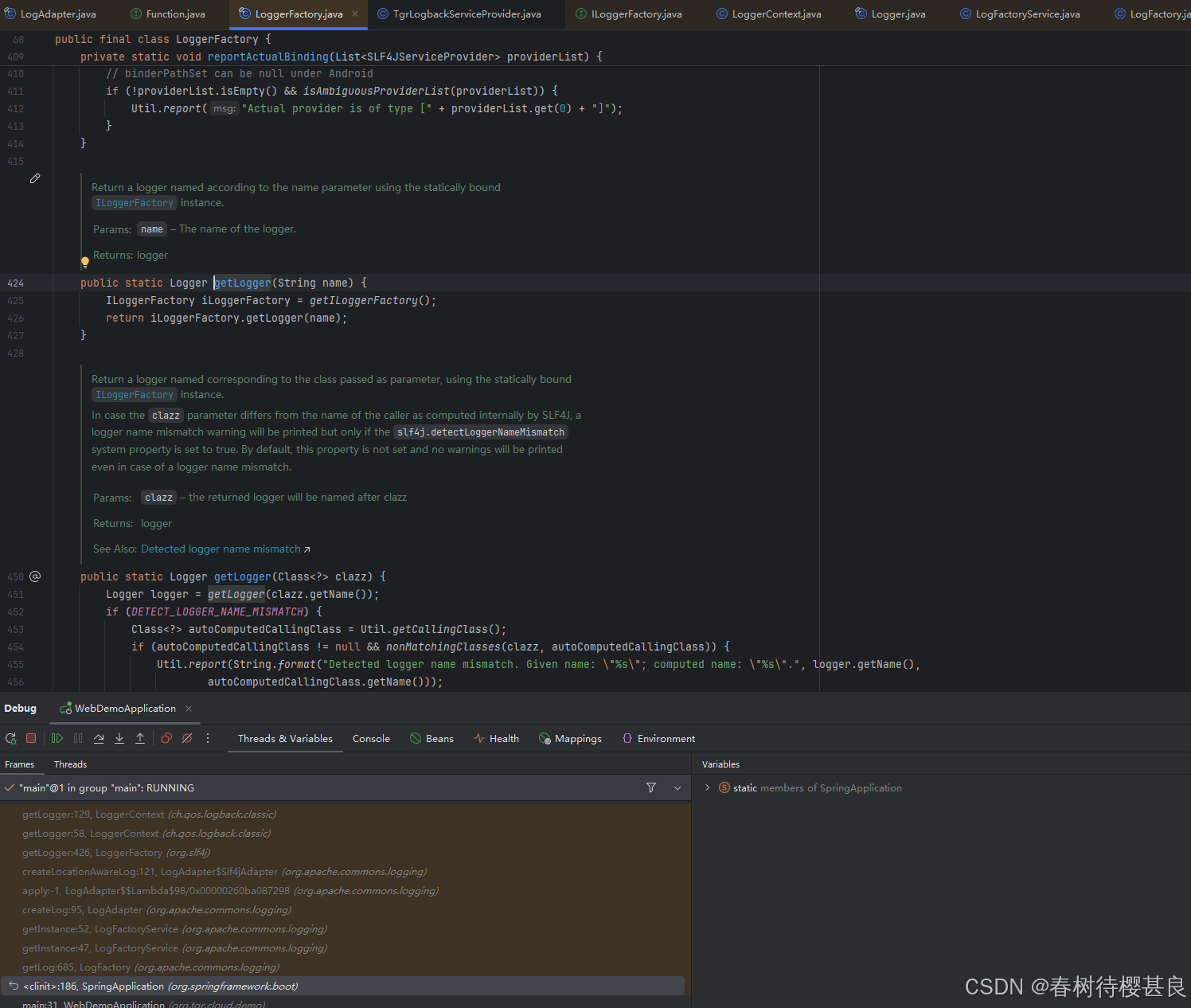
这个方法的实现实际上是通过getILoggerFactory()获取一个ILoggerFactory实例.那这个ILoggerFactory是什么呢 ,它实际上是一个接口,它的定义如下:
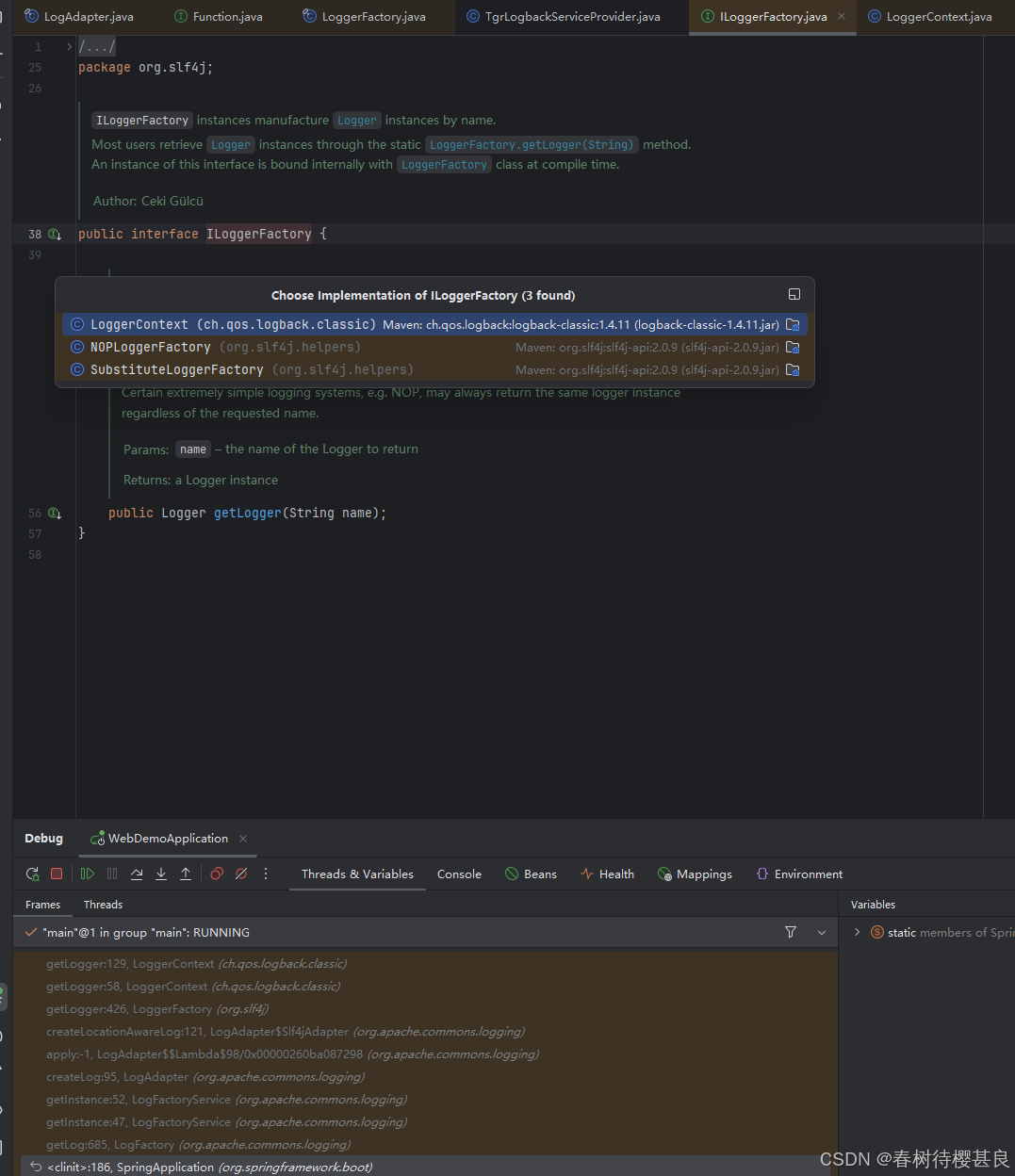
我们在这里发现了之前找到的那个LoggerContext类的身影,这个接口只有一个getLogger的方法。我们先不管这个getLogger的实现,先看看SpringBoot是怎么确认使用LoggerContext作为ILoggerFactory的实现类的
回到LoggerFactory.getLogger()这个方法的定义这里,点进去看看这个getLogger方法实际上做了什么
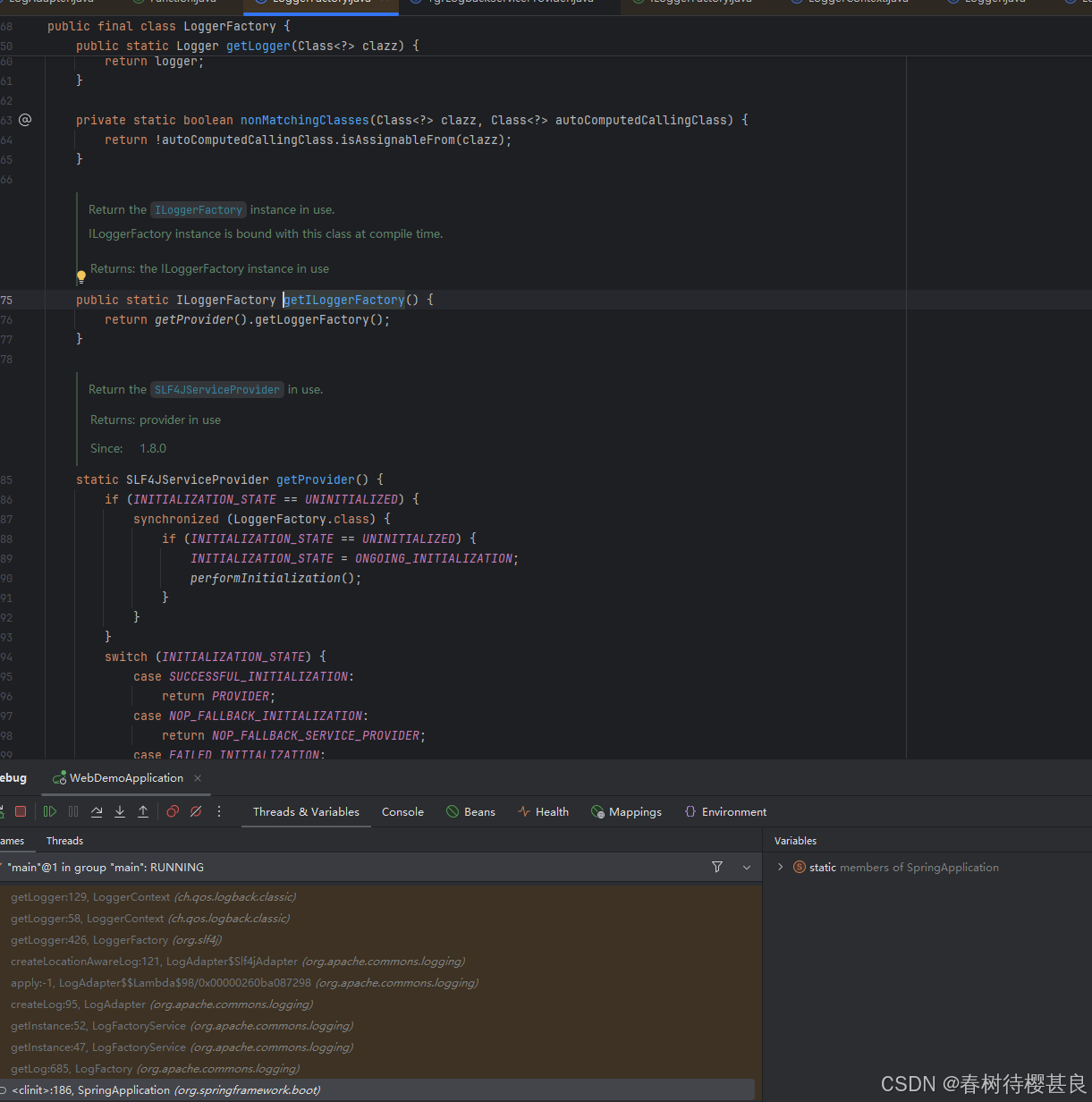
方法的实现很简单,调用了getProvider()获取到一个对象并且调用了获取到的对象的getLoggerFactory方法
在看看getProvider方法的实现
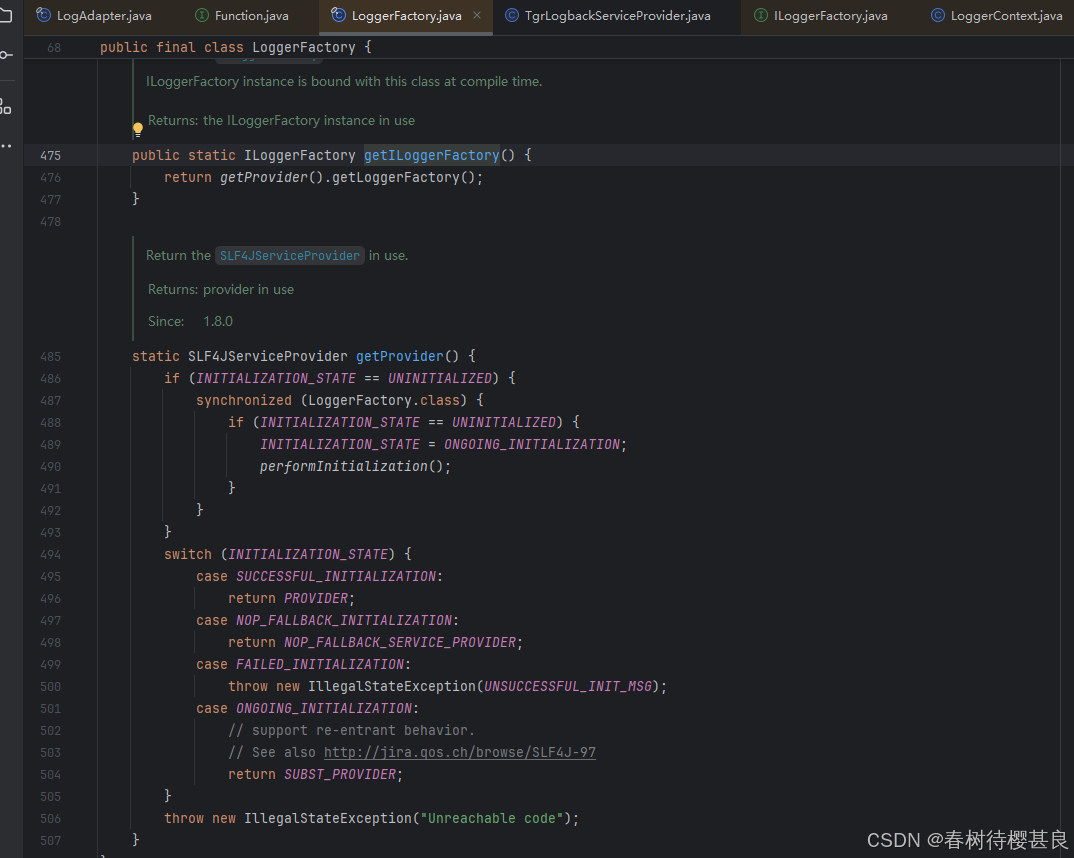
通过debug,SpringBoot实际上会到SUCCESSFUL_INITIALIZATION这个分支,具体为什么会走这个分支,感兴趣的可以自己了解一下,我这里就没有深入了,大概应该是引入了日志框架后,加载了一些SLF4JServiceProvider接口实现类就会到这里
这个分支实际是返回了一个静态属性PROVIDER,SpringBoot通过调用PROVIDER的 getILoggerFactory()最终确定了ILoggerFactory的实现类
我们继续跟进,看看这个静态属性又是在哪里赋值的。最终找到了bind方法
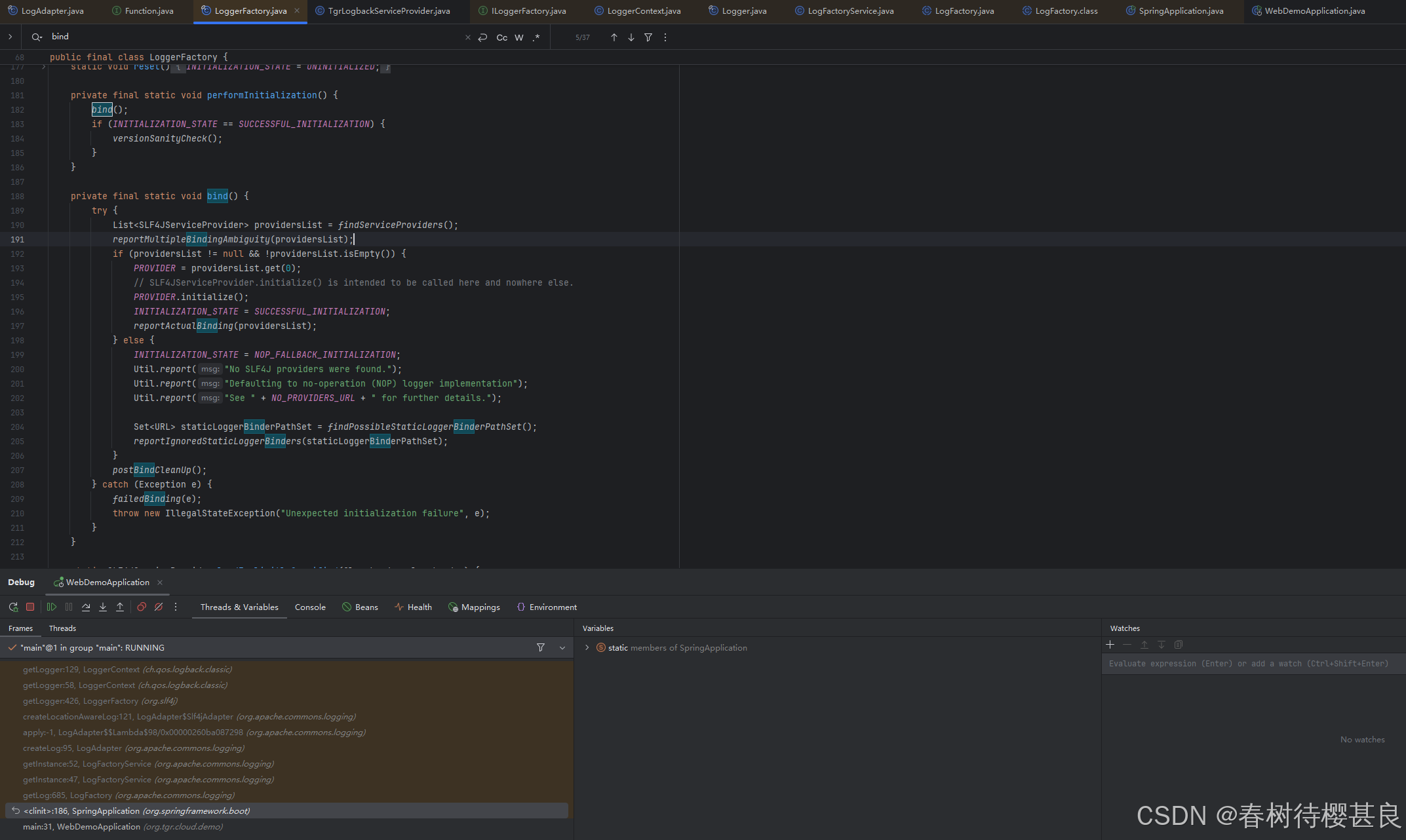
bind方法调用了findServiceProviders()查询到了所有SLF4JServiceProvider类实例列表,我们点进去看看这个SLF4JServiceProvider是什么东西,记性好的就能联想到,我们之前实现Springboot3.x增强MDCAdapter的时候就是自定义了一个类并实现了这个SLF4JSerivceProvider。
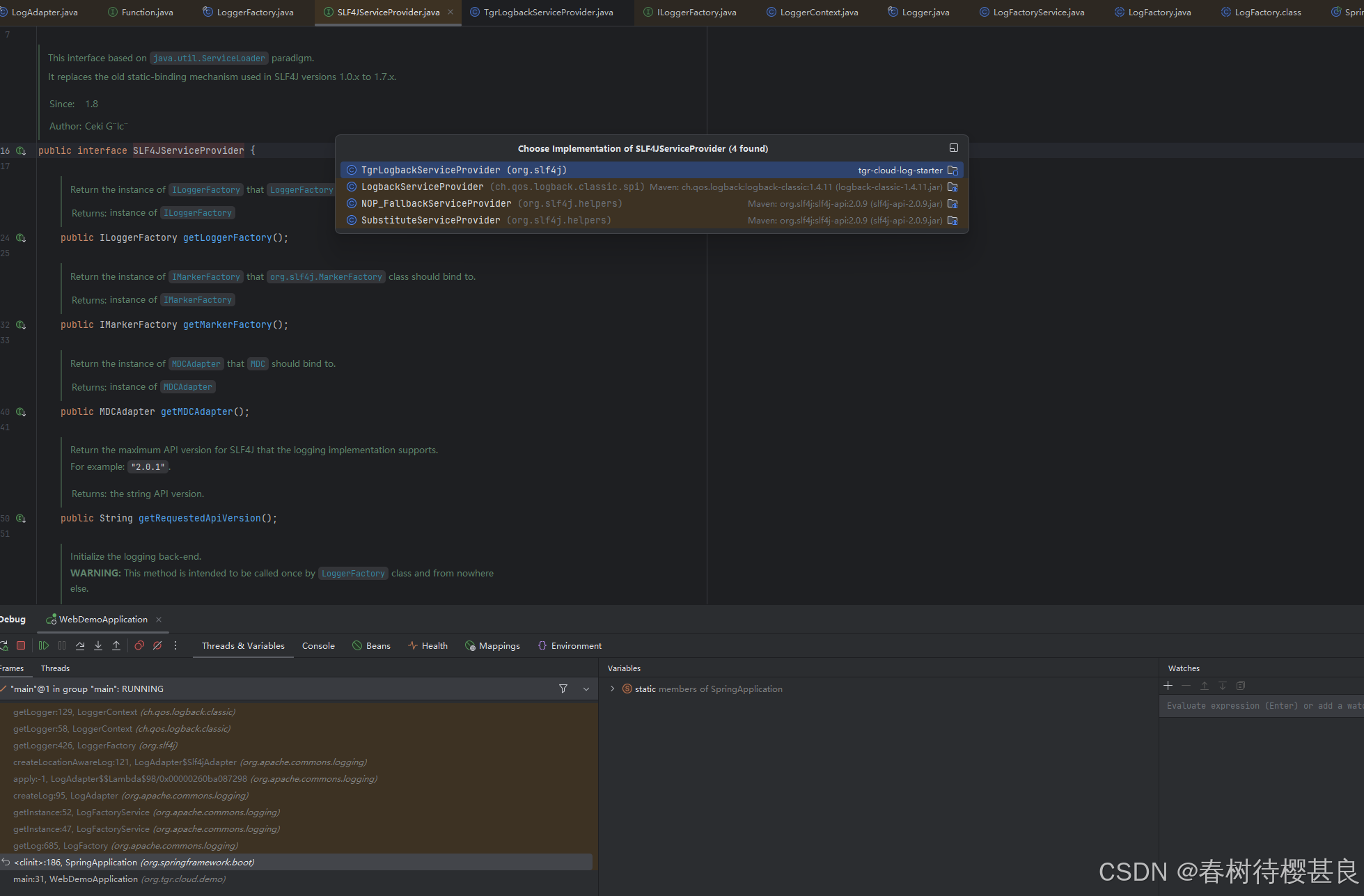
通过这个接口的定义我们就能看到,它有一个getLoggerFactory()的方法以及一个看着和MDC增强密切相关的方法getMDCAdapter()方法。可以看到我们自定义的实现排在第一位,而在第二位的就是LogbackServiceProvider,实际上这个就是SpringBoot的日志框架logback的默认实现了。
已经知道了SLF4JServiceProvider是什么后,我们再回到bind方法
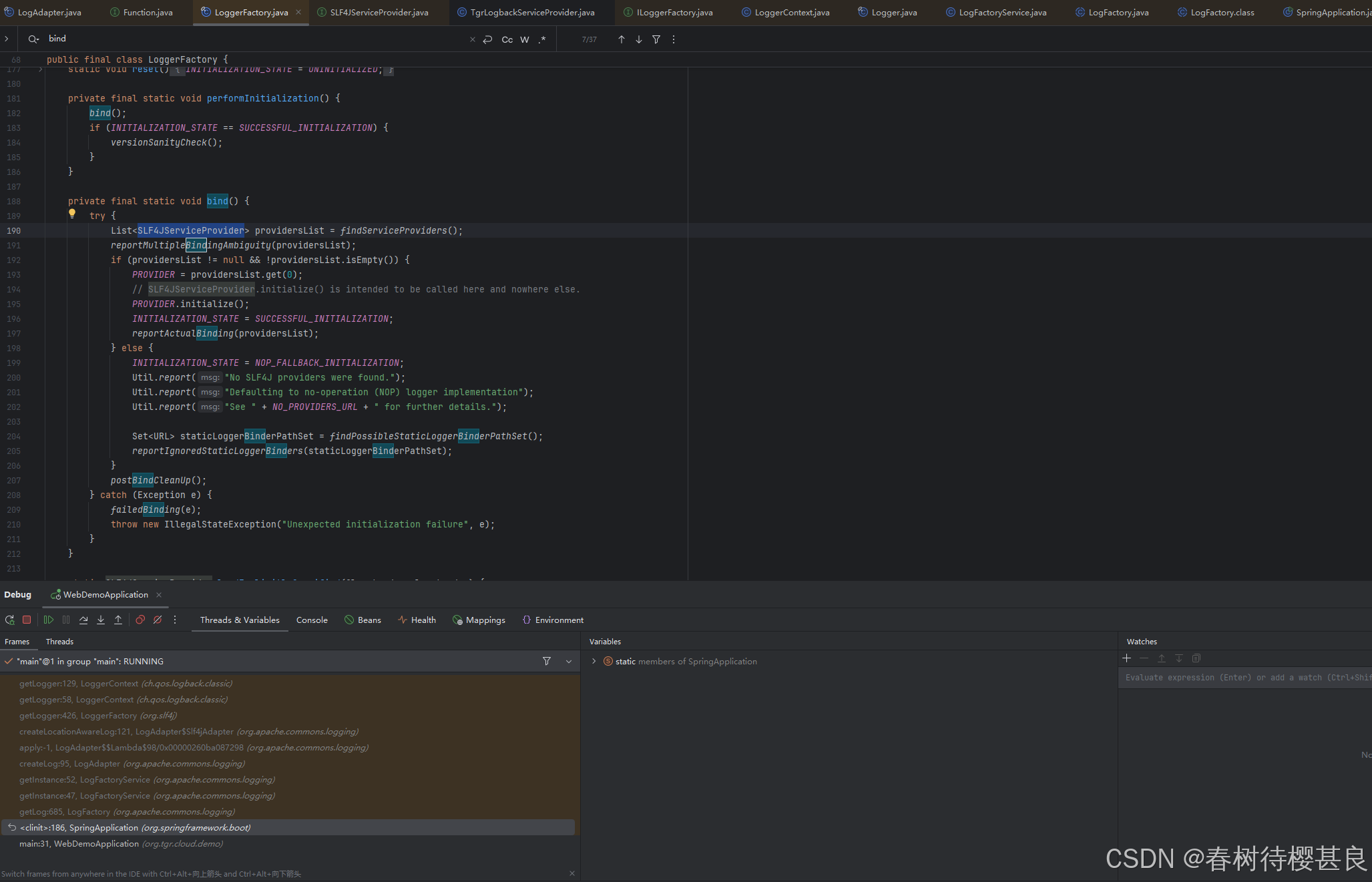
可以看到它首先查询了全部的SLF4JServiceProvider的实现类列表,最后把列表的第一个元素赋值给了静态属性PROVIDER,PROVIDER再调用它的initialize完成了初始化。那这就是为什么我们之前自定义SLF4JServiceProvider实现类提到的要保证我们自己的类是第一个加载的原因了。因为在框架中它只会取第一个实现类,为了保证PROVIDER的类型是我们自己的,就得保证我们自己类的加载顺序是在第一位.
接下来我们再看看findServiceProviders()这个方法是怎么查询到项目中SLF4JServiceProvider的实现类的。
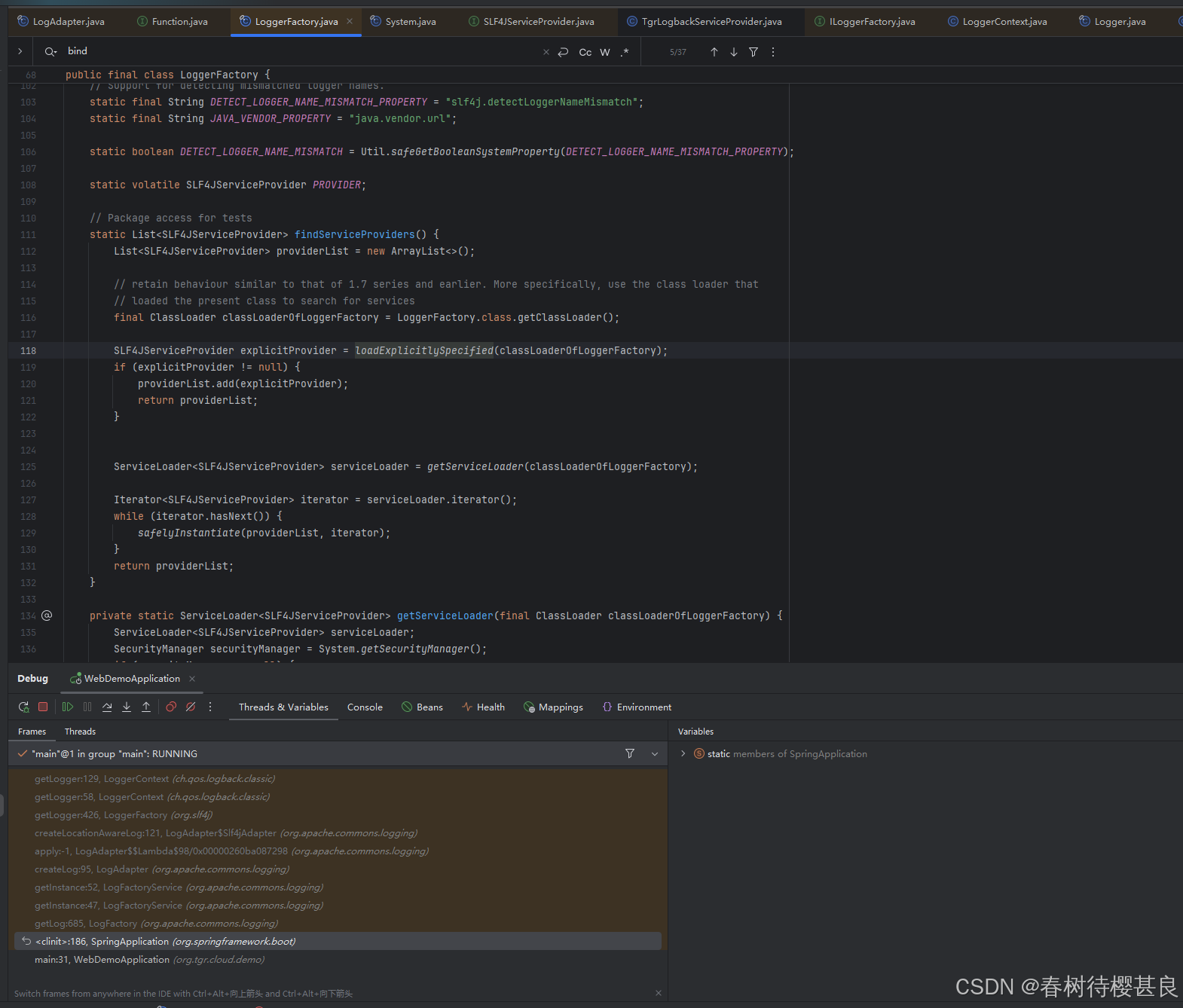
它的实现又涉及到了另外两个方法loadExplicitlySpecified和getServiceLoader.,这两个方法才是实际去加载类的执行流程.我就带大家看看第一个方法吧,第二个大家可以自行研究,第二个大致就是通过SPI机制加载类。
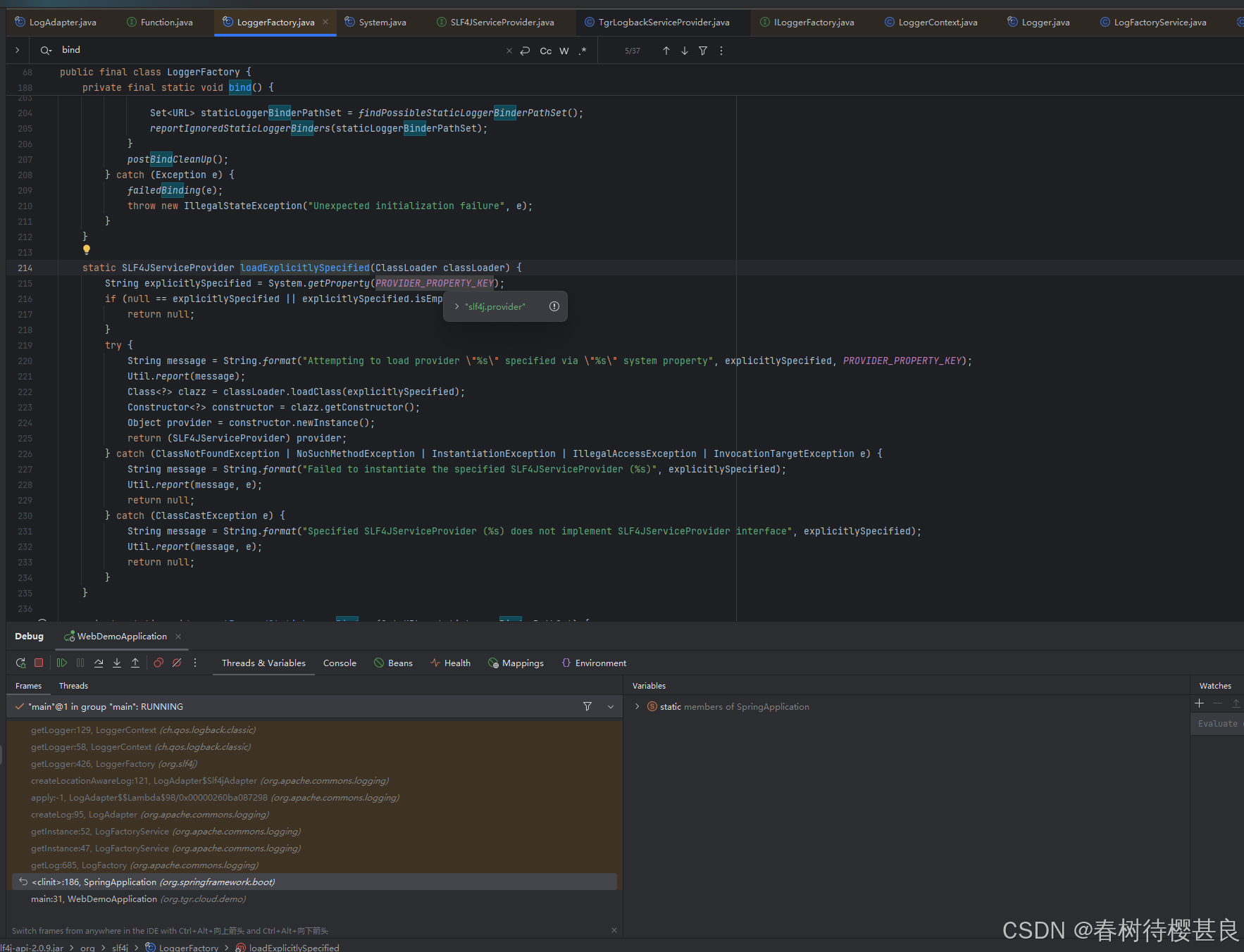
在这里方法的实现中,我们就发现了它实际读取了系统属性slf4j.provider,很明显,我们的那个虚拟机参数
-Dslf4j.provider=org.slf4j.TgrLogbackServiceProvider就是从这里得到的。
到这里我们就知道了如何让LoggerFactory的PROVIDER变成我们自己的实现类TgrLogbackServiceProvider
再回到bind方法
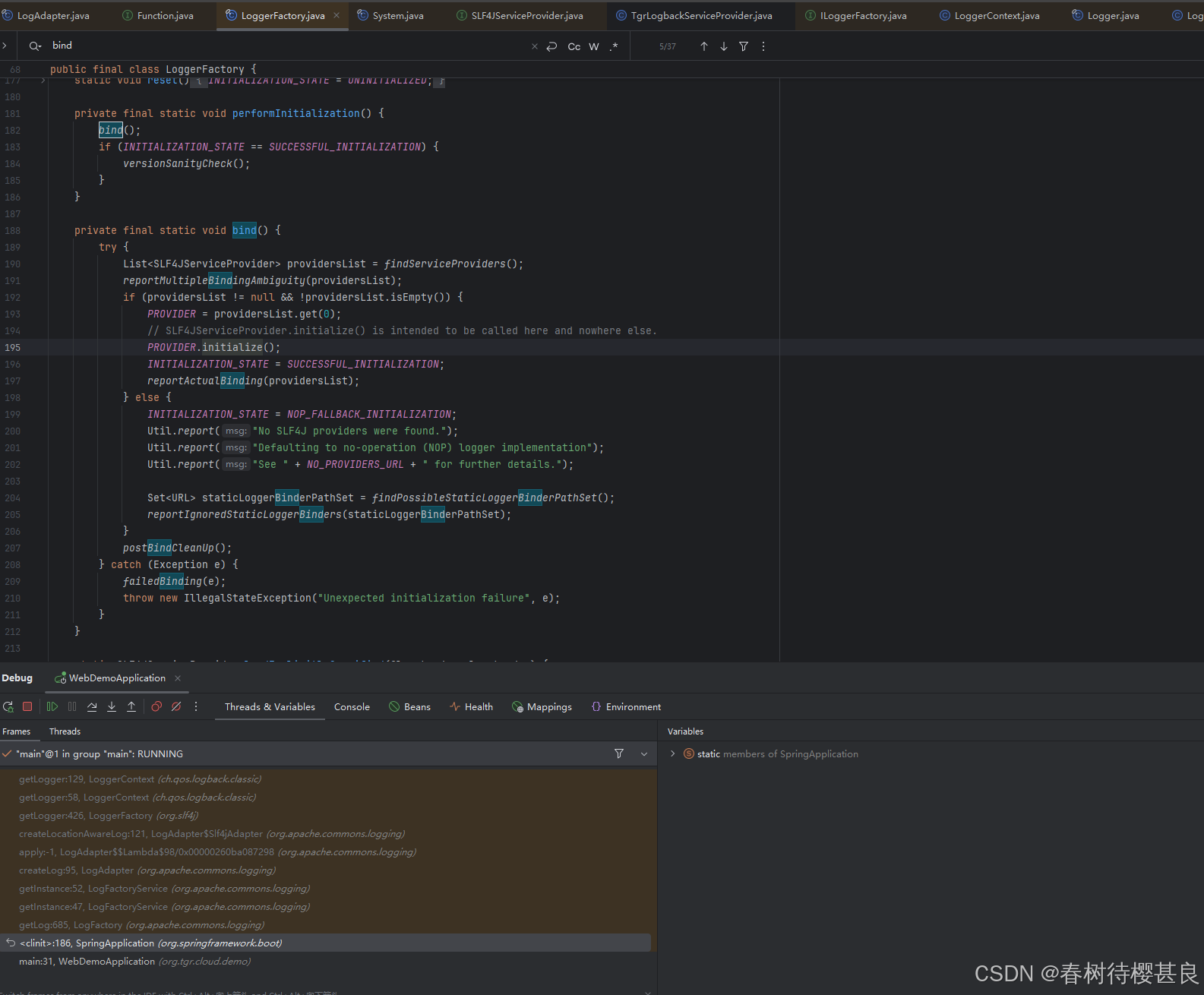
看看initialize()这个方法。这里我展示我们自定义的 和SpringBoot默认的Logback实现类的initialize()方法实现。
TgrLogbackServiceProvider
LogbackServiceProvider
可以看到就是在这个方法中设置了MdcAdapter,那我们就是在这个方法中将原来的LogbackMDCAdapter替换成了我们自己的TtlMDCAdapter
同时我们也终于看到了那个LoggerContext.很显然,关键的代码就是在initialize()这里,这里给LoggerContext进行了实例化,并调用了setMDCAdapter()方法设置LoggerContext中的MdcAdapter,然后日志在打印时再调用LoggerContext中的MdcAdapter属性获取用于替换占位符的属性map。
最后我们只需要确认这个LoggerContext是怎么返回的就可以了。还记得LoggerContext是一个ILoggerFactory接口吗,以及LoggerFactory的getILoggerFactory()的实现
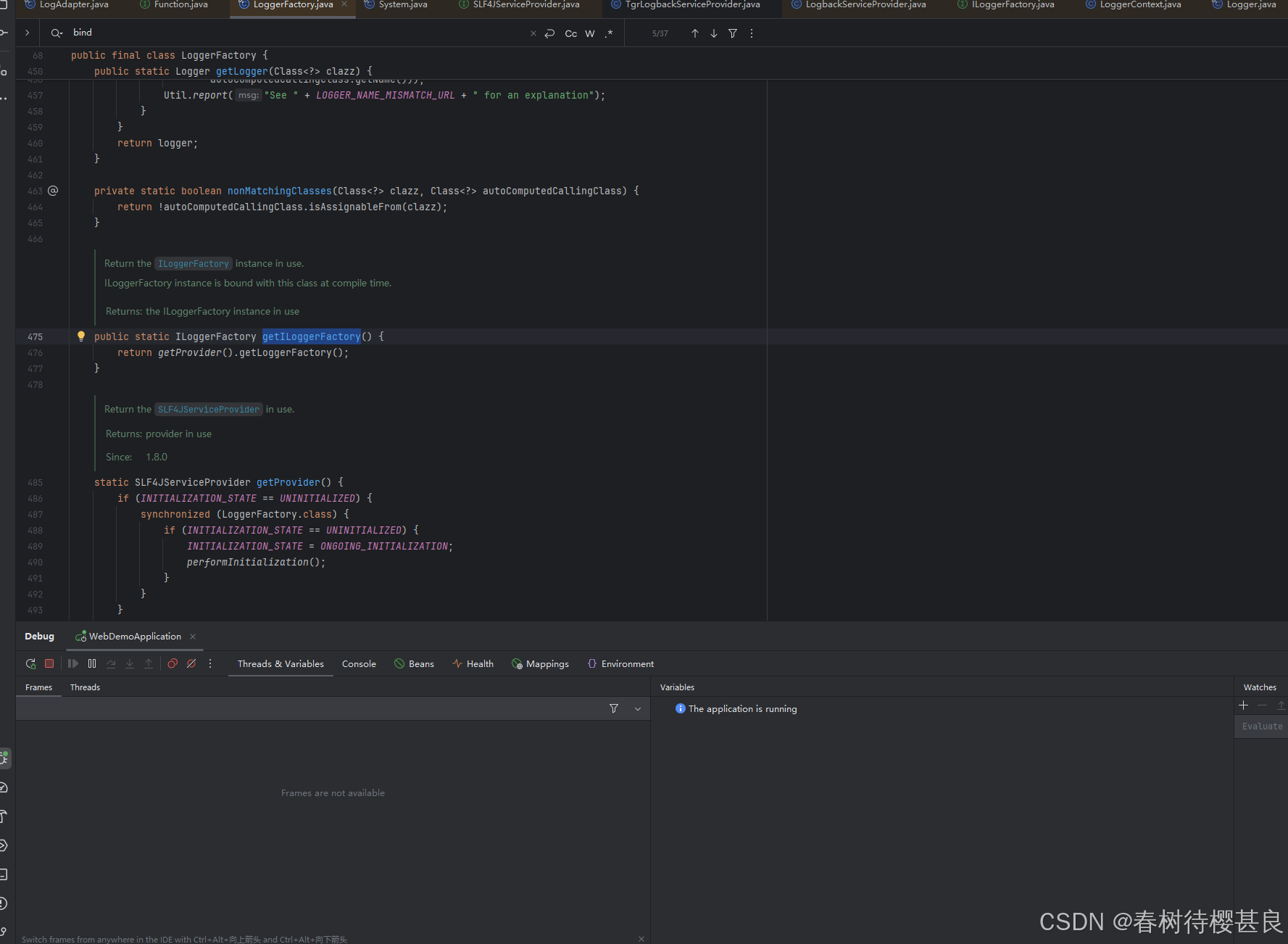
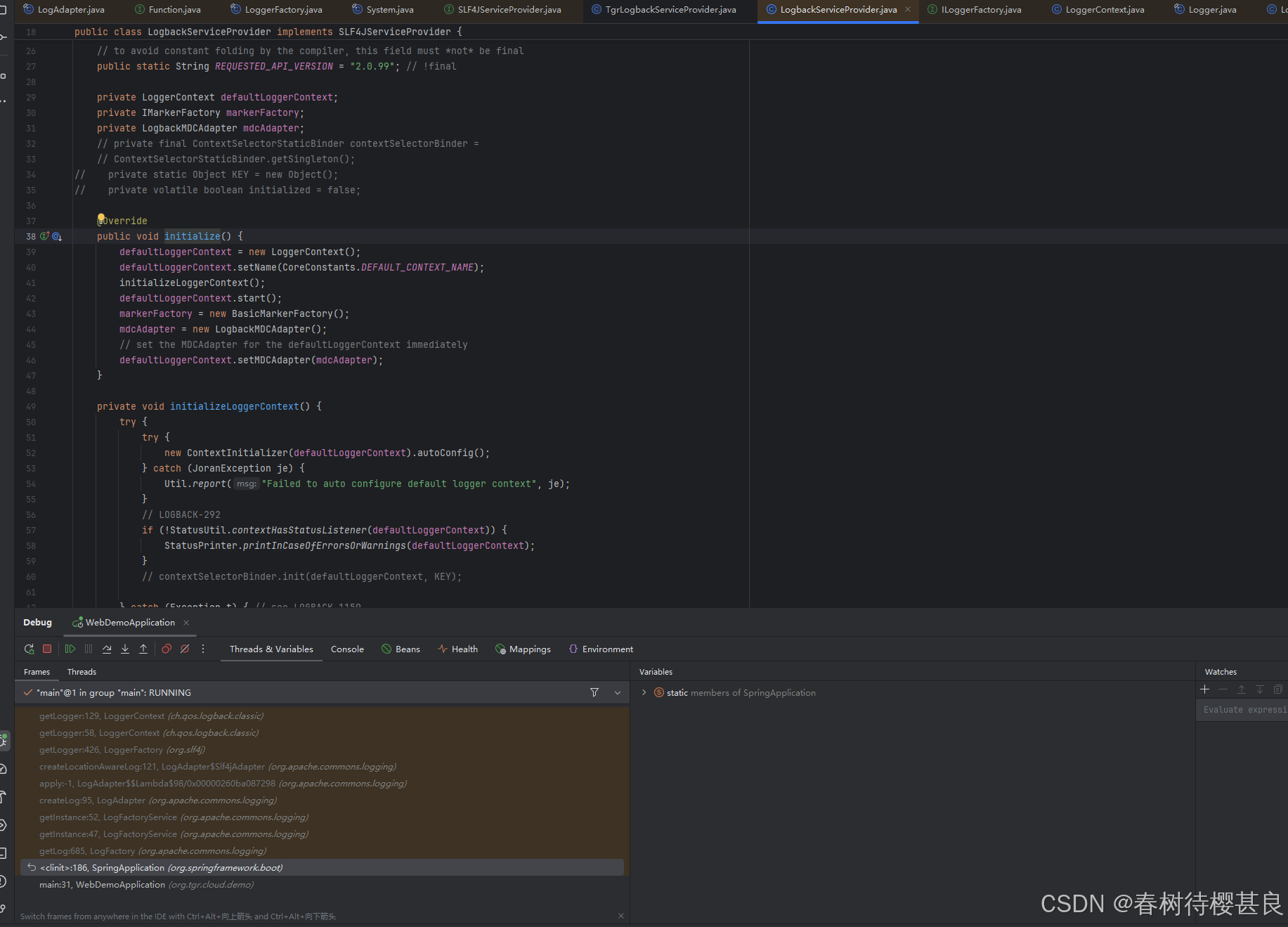
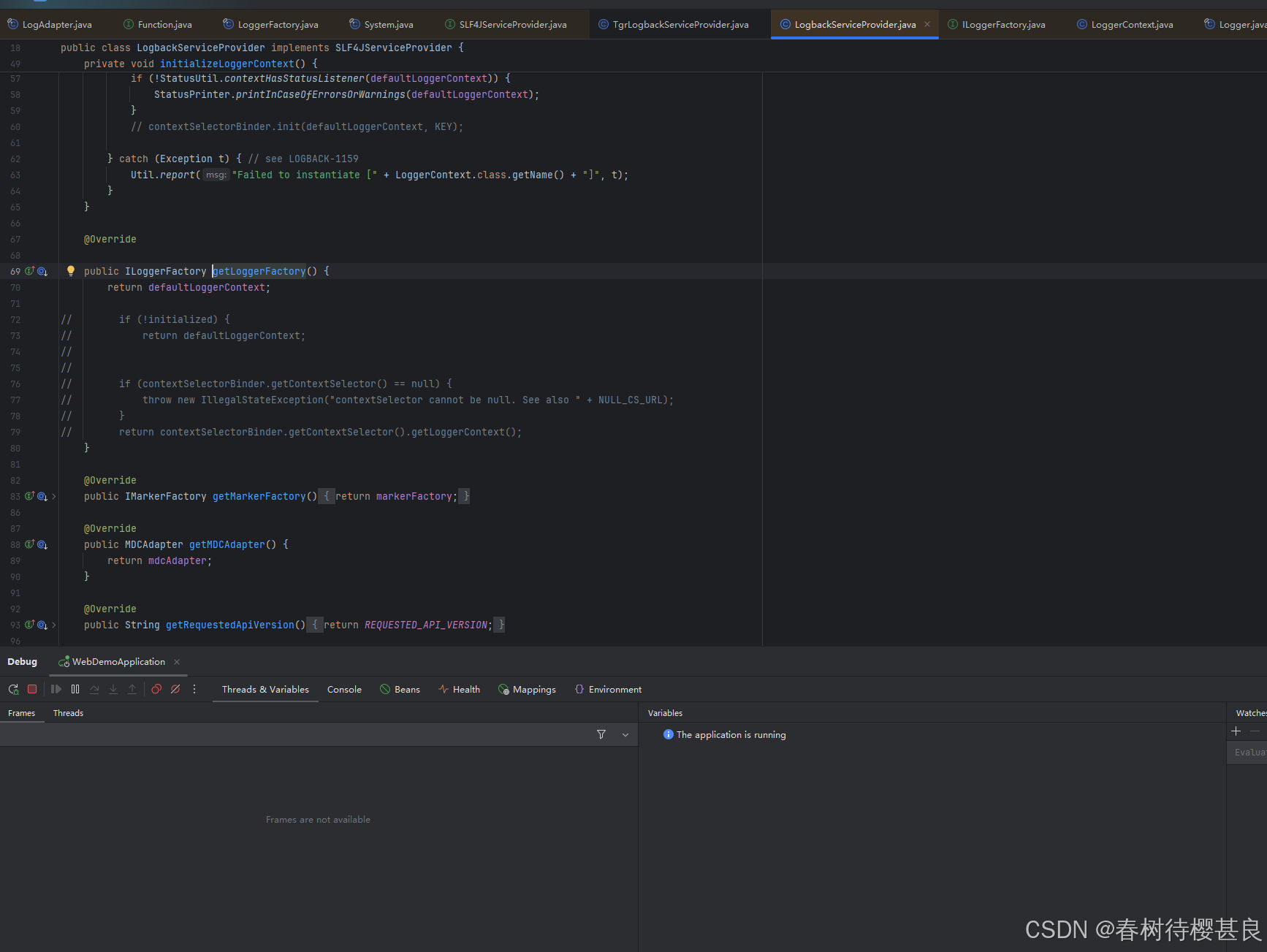
回到这里,我们此时就知道了getProvider()最终会拿到我们自己的TgrLogbackServiceProvider,如果我们没有自定义的话,那这里就是拿到SpringBoot的默认实现LogbackServiceProvider,我们看看两个实现类中这个方法是怎么实现的
TgrLogbackServiceProvider
LogbackServiceProvider
可以看到两个实现都是单纯的返回了自己的defaultLoggerContext属性,而这个属性就是在initialize()方法中进行初始化的。只不过我们自定义的defaultLoggerContext它调用的setMDCAdapter()传入的是我们自己定义的TtlMDCAdapter.我们就是通过这样实现了MDCAdapter的增强
自此整个源码分析就结束了,如果我哪里说的不清楚或者有错误的希望大家都够在评论区指出,我在这感激不尽.