ES 调优帖:Gateway 批量写入性能优化实践
背景:bulk 优化的应用
在 ES 的写入优化里,bulk 操作被广泛地用于批量处理数据。bulk 操作允许用户一次提交多个数据操作,如索引、更新、删除等,从而提高数据处理效率。bulk 操作的实现原理是,将数据操作请求打包成 HTTP 请求,并批量提交给 Elasticsearch 服务器。这样,Elasticsearch 服务器就可以一次处理多个数据操作,从而提高处理效率。
这种优化的核心价值在于减少了网络往返的次数和连接建立的开销。每一次单独的写入操作都需要经历完整的请求-响应周期,而批量写入则是将多个操作打包在一起,用一次通信完成原本需要多次交互的工作。这不仅仅节省了时间,更重要的是释放了系统资源,让服务器能够专注于真正的数据处理,而不是频繁的协议握手和状态维护。
这样的批量请求的确是可以优化写入请求的效率,让 ES 集群获得更多的资源去做写入请求的集中处理。但是除了客户端与 ES 集群的通讯效率优化,还有其他中间过程能优化么?
Gateway 的优化点
bulk 的优化理念是将日常零散的写入需求做集中化的处理,尽量减低日常请求的损耗,完成资源最大化的利用。简而言之就是“好钢用在刀刃上”。
但是 ES 在收到 bulk 写入请求后,也是需要协调节点根据文档的 id 计算所属的分片来将数据分发到对应的数据节点的。这个过程也是有一定损耗的,如果 bulk 请求中数据分布的很散,每个分片都需要进行写入,原本 bulk 集中写入的需求优势则还是没有得到最理想化的提升。
gateway 的写入加速则对 bulk 的优化理念的最大化补全。
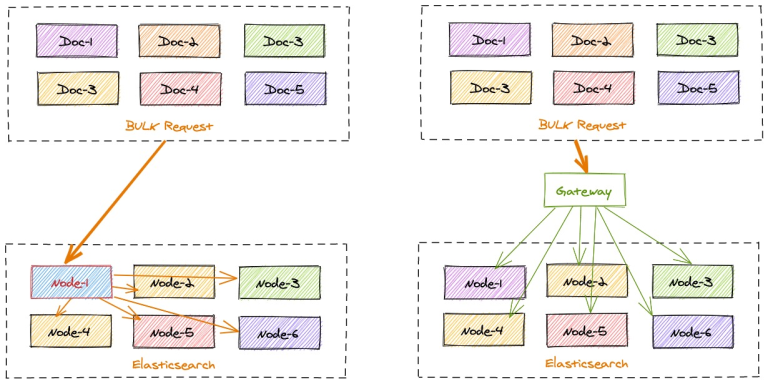
gateway 可以本地计算每个索引文档对应后端 Elasticsearch 集群的目标存放位置,从而能够精准的进行写入请求定位。
在一批 bulk 请求中,可能存在多个后端节点的数据,bulk_reshuffle 过滤器用来将正常的 bulk 请求打散,按照目标节点或者分片进行拆分重新组装,避免 Elasticsearch 节点收到请求之后再次进行请求分发, 从而降低 Elasticsearch 集群间的流量和负载,也能避免单个节点成为热点瓶颈,确保各个数据节点的处理均衡,从而提升集群总体的索引吞吐能力。
整理的优化思路如下图:
优化实践
那我们来实践一下,看看 gateway 能提升多少的写入。
这里我们分 2 个测试场景:
- 基础集中写入测试,不带文档 id,直接批量写入。这个场景更像是日志或者监控数据采集的场景。
- 带文档 id 的写入测试,更偏向搜索场景或者大数据批同步的场景。
2 个场景都进行直接写入 ES 和 gateway 转发 ES 的效率比对。
测试材料除了需要备一个网关和一套 es 外,其余的内容如下:
测试索引 mapping 一致,名称区分:
PUT gateway_bulk_test{ \"settings\": { \"number_of_shards\": 6, \"number_of_replicas\": 0 }, \"mappings\": { \"properties\": { \"timestamp\": { \"type\": \"date\", \"format\": \"strict_date_optional_time\" }, \"field1\": { \"type\": \"keyword\" }, \"field2\": { \"type\": \"keyword\" }, \"field3\": { \"type\": \"keyword\" }, \"field4\": { \"type\": \"integer\" }, \"field5\": { \"type\": \"keyword\" }, \"field6\": { \"type\": \"float\" } } }}PUT bulk_test{ \"settings\": { \"number_of_shards\": 6, \"number_of_replicas\": 0 }, \"mappings\": { \"properties\": { \"timestamp\": { \"type\": \"date\", \"format\": \"strict_date_optional_time\" }, \"field1\": { \"type\": \"keyword\" }, \"field2\": { \"type\": \"keyword\" }, \"field3\": { \"type\": \"keyword\" }, \"field4\": { \"type\": \"integer\" }, \"field5\": { \"type\": \"keyword\" }, \"field6\": { \"type\": \"float\" } } }}gateway 的配置文件如下:
path.data: datapath.logs: logentry: - name: my_es_entry enabled: true router: my_router max_concurrency: 200000 network: binding: 0.0.0.0:8000flow: - name: async_bulk filter: - bulk_reshuffle: when: contains: _ctx.request.path: /_bulk elasticsearch: prod level: node partition_size: 1 fix_null_id: true - elasticsearch: elasticsearch: prod #elasticsearch configure reference name max_connection_per_node: 1000 #max tcp connection to upstream, default for all nodes max_response_size: -1 #default for all nodes balancer: weight refresh: # refresh upstream nodes list, need to enable this feature to use elasticsearch nodes auto discovery enabled: true interval: 60s filter: roles: exclude: - masterrouter: - name: my_router default_flow: async_bulkelasticsearch: - name: prod enabled: true endpoints: - https://127.0.0.1:9221 - https://127.0.0.1:9222 - https://127.0.0.1:9223 basic_auth: username: admin password: adminpipeline: - name: bulk_request_ingest auto_start: true keep_running: true retry_delay_in_ms: 1000 processor: - bulk_indexing: max_connection_per_node: 100 num_of_slices: 3 max_worker_size: 30 idle_timeout_in_seconds: 10 bulk: compress: false batch_size_in_mb: 10 batch_size_in_docs: 10000 consumer: fetch_max_messages: 100 queue_selector: labels: type: bulk_reshuffle测试脚本如下:
#!/usr/bin/env python3\"\"\"ES Bulk写入性能测试脚本\"\"\"import hashlibimport jsonimport randomimport stringimport timefrom typing import List, Dict, Anyimport requestsfrom concurrent.futures import ThreadPoolExecutorfrom datetime import datetimeimport urllib3# 禁用SSL警告urllib3.disable_warnings(urllib3.exceptions.InsecureRequestWarning)class ESBulkTester: def __init__(self): # 配置变量 - 可修改 self.es_configs = [ { \"name\": \"ES直连\", \"url\": \"https://127.0.0.1:9221\", \"index\": \"bulk_test\", \"username\": \"admin\", # 修改为实际用户名 \"password\": \"admin\", # 修改为实际密码 \"verify_ssl\": False # HTTPS需要SSL验证 }, { \"name\": \"Gateway代理\", \"url\": \"http://localhost:8000\", \"index\": \"gateway_bulk_test\", \"username\": None, # 无需认证 \"password\": None, \"verify_ssl\": False } ] self.batch_size = 10000 # 每次bulk写入条数 self.log_interval = 100000 # 每多少次bulk写入输出日志 # ID生成规则配置 - 前2位后5位 self.id_prefix_start = 1 self.id_prefix_end = 999 # 前3位: 01-999 self.id_suffix_start = 1 self.id_suffix_end = 9999 # 后4位: 0001-9999 # 当前ID计数器 self.current_prefix = self.id_prefix_start self.current_suffix = self.id_suffix_start def generate_id(self) -> str: \"\"\"生成固定规则的ID - 前2位后5位\"\"\" id_str = f\"{self.current_prefix:02d}{self.current_suffix:05d}\" # 更新计数器 self.current_suffix += 1 if self.current_suffix > self.id_suffix_end: self.current_suffix = self.id_suffix_start self.current_prefix += 1 if self.current_prefix > self.id_prefix_end: self.current_prefix = self.id_prefix_start return id_str def generate_random_hash(self, length: int = 32) -> str: \"\"\"生成随机hash值\"\"\" random_string = \'\'.join(random.choices(string.ascii_letters + string.digits, k=length)) return hashlib.md5(random_string.encode()).hexdigest() def generate_document(self) -> Dict[str, Any]: \"\"\"生成随机文档内容\"\"\" return { \"timestamp\": datetime.now().isoformat(), \"field1\": self.generate_random_hash(), \"field2\": self.generate_random_hash(), \"field3\": self.generate_random_hash(), \"field4\": random.randint(1, 1000), \"field5\": random.choice([\"A\", \"B\", \"C\", \"D\"]), \"field6\": random.uniform(0.1, 100.0) } def create_bulk_payload(self, index_name: str) -> str: \"\"\"创建bulk写入payload\"\"\" bulk_data = [] for _ in range(self.batch_size): #doc_id = self.generate_id() doc = self.generate_document() # 添加index操作 bulk_data.append(json.dumps({ \"index\": { \"_index\": index_name, # \"_id\": doc_id } })) bulk_data.append(json.dumps(doc)) return \"\\n\".join(bulk_data) + \"\\n\" def bulk_index(self, config: Dict[str, Any], payload: str) -> bool: \"\"\"执行bulk写入\"\"\" url = f\"{config[\'url\']}/_bulk\" headers = { \"Content-Type\": \"application/x-ndjson\" } # 设置认证信息 auth = None if config.get(\'username\') and config.get(\'password\'): auth = (config[\'username\'], config[\'password\']) try: response = requests.post( url, data=payload, headers=headers, auth=auth, verify=config.get(\'verify_ssl\', True), timeout=30 ) return response.status_code == 200 except Exception as e: print(f\"Bulk写入失败: {e}\") return False def refresh_index(self, config: Dict[str, Any]) -> bool: \"\"\"刷新索引\"\"\" url = f\"{config[\'url\']}/{config[\'index\']}/_refresh\" # 设置认证信息 auth = None if config.get(\'username\') and config.get(\'password\'): auth = (config[\'username\'], config[\'password\']) try: response = requests.post( url, auth=auth, verify=config.get(\'verify_ssl\', True), timeout=10 ) success = response.status_code == 200 print(f\"索引刷新{\'成功\' if success else \'失败\'}: {config[\'index\']}\") return success except Exception as e: print(f\"索引刷新失败: {e}\") return False def run_test(self, config: Dict[str, Any], round_num: int, total_iterations: int = 100000): \"\"\"运行性能测试\"\"\" test_name = f\"{config[\'name\']}-第{round_num}轮\" print(f\"\\n开始测试: {test_name}\") print(f\"ES地址: {config[\'url\']}\") print(f\"索引名称: {config[\'index\']}\") print(f\"认证: {\'是\' if config.get(\'username\') else \'否\'}\") print(f\"每次bulk写入: {self.batch_size}条\") print(f\"总计划写入: {total_iterations * self.batch_size}条\") print(\"-\" * 50) start_time = time.time() success_count = 0 error_count = 0 for i in range(1, total_iterations + 1): payload = self.create_bulk_payload(config[\'index\']) if self.bulk_index(config, payload): success_count += 1 else: error_count += 1 # 每N次输出日志 if i % self.log_interval == 0: elapsed_time = time.time() - start_time rate = i / elapsed_time if elapsed_time > 0 else 0 print(f\"已完成 {i:,} 次bulk写入, 耗时: {elapsed_time:.2f}秒, 速率: {rate:.2f} bulk/秒\") end_time = time.time() total_time = end_time - start_time total_docs = total_iterations * self.batch_size print(f\"\\n{test_name} 测试完成!\") print(f\"总耗时: {total_time:.2f}秒\") print(f\"成功bulk写入: {success_count:,}次\") print(f\"失败bulk写入: {error_count:,}次\") print(f\"总文档数: {total_docs:,}条\") print(f\"平均速率: {success_count/total_time:.2f} bulk/秒\") print(f\"文档写入速率: {total_docs/total_time:.2f} docs/秒\") print(\"=\" * 60) return { \"test_name\": test_name, \"config_name\": config[\'name\'], \"round\": round_num, \"es_url\": config[\'url\'], \"index\": config[\'index\'], \"total_time\": total_time, \"success_count\": success_count, \"error_count\": error_count, \"total_docs\": total_docs, \"bulk_rate\": success_count/total_time, \"doc_rate\": total_docs/total_time } def run_comparison_test(self, total_iterations: int = 10000): \"\"\"运行双地址对比测试\"\"\" print(\"ES Bulk写入性能测试开始\") print(f\"测试时间: {datetime.now().strftime(\'%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S\')}\") print(\"=\" * 60) results = [] rounds = 2 # 每个地址测试2轮 # 循环测试所有配置 for config in self.es_configs: print(f\"\\n开始测试配置: {config[\'name\']}\") print(\"*\" * 40) for round_num in range(1, rounds + 1): # 运行测试 result = self.run_test(config, round_num, total_iterations) results.append(result) # 每轮结束后刷新索引 print(f\"\\n第{round_num}轮测试完成,执行索引刷新...\") self.refresh_index(config) # 重置ID计数器 if round_num == 1: # 第1轮:使用初始ID范围(新增数据) print(\"第1轮:新增数据模式\") else: # 第2轮:重复使用相同ID(更新数据模式) print(\"第2轮:数据更新模式,复用第1轮ID\") self.current_prefix = self.id_prefix_start self.current_suffix = self.id_suffix_start print(f\"{config[\'name\']} 第{round_num}轮测试结束\\n\") # 输出对比结果 print(\"\\n性能对比结果:\") print(\"=\" * 80) # 按配置分组显示结果 config_results = {} for result in results: config_name = result[\'config_name\'] if config_name not in config_results: config_results[config_name] = [] config_results[config_name].append(result) for config_name, rounds_data in config_results.items(): print(f\"\\n{config_name}:\") total_time = 0 total_bulk_rate = 0 total_doc_rate = 0 for round_data in rounds_data: print(f\" 第{round_data[\'round\']}轮:\") print(f\" 耗时: {round_data[\'total_time\']:.2f}秒\") print(f\" Bulk速率: {round_data[\'bulk_rate\']:.2f} bulk/秒\") print(f\" 文档速率: {round_data[\'doc_rate\']:.2f} docs/秒\") print(f\" 成功率: {round_data[\'success_count\']/(round_data[\'success_count\']+round_data[\'error_count\'])*100:.2f}%\") total_time += round_data[\'total_time\'] total_bulk_rate += round_data[\'bulk_rate\'] total_doc_rate += round_data[\'doc_rate\'] avg_bulk_rate = total_bulk_rate / len(rounds_data) avg_doc_rate = total_doc_rate / len(rounds_data) print(f\" 平均性能:\") print(f\" 总耗时: {total_time:.2f}秒\") print(f\" 平均Bulk速率: {avg_bulk_rate:.2f} bulk/秒\") print(f\" 平均文档速率: {avg_doc_rate:.2f} docs/秒\") # 整体对比 if len(config_results) >= 2: config_names = list(config_results.keys()) config1_avg = sum([r[\'bulk_rate\'] for r in config_results[config_names[0]]]) / len(config_results[config_names[0]]) config2_avg = sum([r[\'bulk_rate\'] for r in config_results[config_names[1]]]) / len(config_results[config_names[1]]) if config1_avg > config2_avg: faster = config_names[0] rate_diff = config1_avg - config2_avg else: faster = config_names[1] rate_diff = config2_avg - config1_avg print(f\"\\n整体性能对比:\") print(f\"{faster} 平均性能更好,bulk速率高 {rate_diff:.2f} bulk/秒\") print(f\"性能提升: {(rate_diff/min(config1_avg, config2_avg)*100):.1f}%\")def main(): \"\"\"主函数\"\"\" tester = ESBulkTester() # 运行测试(每次bulk 1万条,300次bulk = 300万条文档) tester.run_comparison_test(total_iterations=300)if __name__ == \"__main__\": main()1. 日志场景:不带 id 写入
测试条件:
- bulk 写入数据不带文档 id
- 每批次 bulk 10000 条数据,总共写入 30w 数据
这里把
反馈结果:
性能对比结果:================================================================================ES直连: 第1轮: 耗时: 152.29秒 Bulk速率: 1.97 bulk/秒 文档速率: 19699.59 docs/秒 成功率: 100.00% 平均性能: 总耗时: 152.29秒 平均Bulk速率: 1.97 bulk/秒 平均文档速率: 19699.59 docs/秒Gateway代理: 第1轮: 耗时: 115.63秒 Bulk速率: 2.59 bulk/秒 文档速率: 25944.35 docs/秒 成功率: 100.00% 平均性能: 总耗时: 115.63秒 平均Bulk速率: 2.59 bulk/秒 平均文档速率: 25944.35 docs/秒整体性能对比:Gateway代理 平均性能更好,bulk速率高 0.62 bulk/秒性能提升: 31.7%2. 业务场景:带文档 id 的写入
测试条件:
- bulk 写入数据带有文档 id,两次测试写入的文档 id 生成规则一致且重复。
- 每批次 bulk 10000 条数据,总共写入 30w 数据
这里把 py 脚本中 第 99 行 和 第 107 行的注释打开。
反馈结果:
性能对比结果:================================================================================ES直连: 第1轮: 耗时: 155.30秒 Bulk速率: 1.93 bulk/秒 文档速率: 19317.39 docs/秒 成功率: 100.00% 平均性能: 总耗时: 155.30秒 平均Bulk速率: 1.93 bulk/秒 平均文档速率: 19317.39 docs/秒Gateway代理: 第1轮: 耗时: 116.73秒 Bulk速率: 2.57 bulk/秒 文档速率: 25700.06 docs/秒 成功率: 100.00% 平均性能: 总耗时: 116.73秒 平均Bulk速率: 2.57 bulk/秒 平均文档速率: 25700.06 docs/秒整体性能对比:Gateway代理 平均性能更好,bulk速率高 0.64 bulk/秒性能提升: 33.0%小结
不管是日志场景还是业务价值更重要的大数据或者搜索数据同步场景, gateway 的写入加速都能平稳的节省 25%-30% 的写入耗时。
关于极限网关(INFINI Gateway)

INFINI Gateway 是一个开源的面向搜索场景的高性能数据网关,所有请求都经过网关处理后再转发到后端的搜索业务集群。基于 INFINI Gateway,可以实现索引级别的限速限流、常见查询的缓存加速、查询请求的审计、查询结果的动态修改等等。
官网文档:https://docs.infinilabs.com/gateway
开源地址:https://github.com/infinilabs/gateway
作者:金多安,极限科技(INFINI Labs)搜索运维专家,Elastic 认证专家,搜索客社区日报责任编辑。一直从事与搜索运维相关的工作,日常会去挖掘 ES / Lucene 方向的搜索技术原理,保持搜索相关技术发展的关注。
原文:https://infinilabs.cn/blog/2025/gateway-bulk-write-performance-optimization/


