【C++】字符串处理标准库函数大全_c++字符串处理库
在 C++ 编程中,字符串处理是一项非常基础且重要的操作。C++ 继承了 C 语言的字符串处理函数,同时也拥有功能更强大的标准库 string 类。本文将全面介绍 C++ 中常用的字符串处理标准库函数,包括 C 风格字符串函数和 C++ 标准库 string 类的相关函数。
目录
一、C 风格字符串函数
1.1 字符串长度计算函数
1.2 字符串复制函数
1.3 字符串连接函数
1.4 字符串比较函数
1.5 字符串查找函数
1.6 其他常用 C 风格字符串函数
二、C++ 标准库 string 类
2.1 string 类的构造函数
2.2 string 类的赋值操作
2.3 string 类的字符串拼接
2.4 string 类的字符串比较
2.5 string 类的字符访问
2.6 string 类的子串操作
2.7 string 类的查找操作
2.8 string 类的替换操作
2.9 string 类的插入操作
2.10 string 类的删除操作
2.11 string 类与 C 风格字符串的转换
2.12 string 类的其他常用函数
三、其他字符串处理相关函数
3.1 字符分类和转换函数()
3.2 算法库中的字符串操作函数()
一、C 风格字符串函数
C 风格字符串是以空字符 \'\\0\' 结尾的字符数组,C++ 继承了 C 语言中用于处理这类字符串的大量函数,这些函数声明在头文件中。
1.1 字符串长度计算函数
strlen 函数
strlen 函数用于计算字符串的长度,它的参数是一个 const char * 类型的指针,指向要计算长度的字符串。返回值是 size_t 类型,表示字符串中字符的个数,不包括结束符 \'\\0\'。
例如,对于字符串 \"hello\",strlen 的返回值是 5。需要注意的是,strlen 和 sizeof 不同,sizeof 计算的是变量所占用的内存大小,对于字符数组来说,包括结束符 \'\\0\'。
示例代码:
#include #include using namespace std;int main() { char str[] = \"hello\"; cout << \"strlen(str) = \" << strlen(str) << endl; // 输出5 cout << \"sizeof(str) = \" << sizeof(str) << endl; // 输出6,包含\'\\0\' return 0;}
1.2 字符串复制函数
①strcpy 函数
strcpy 函数用于将源字符串复制到目标字符串中,其原型为 char* strcpy (char* dest, const char* src)。它会把 src 指向的字符串(包括 \'\\0\')复制到 dest 指向的数组中。但要注意,若 dest 指向的数组空间不够大,可能会导致缓冲区溢出,造成程序错误。
示例代码:
#include #include using namespace std;int main() { char dest[10]; char src[] = \"hello\"; strcpy(dest, src); cout << dest << endl; // 输出hello return 0;}
②strncpy 函数
为了避免 strcpy 函数可能导致的缓冲区溢出问题,引入了 strncpy 函数,其原型为 char* strncpy (char* dest, const char* src, size_t n)。该函数将 src 指向的字符串中前 n 个字符复制到 dest 指向的数组中。
如果源字符串长度小于 n,则会在 dest 的剩余位置填充 \'\\0\';如果源字符串长度大于等于 n,则不会自动添加结束符 \'\\0\',此时需要手动添加,否则可能导致字符串处理错误。
示例代码:
#include #include using namespace std;int main() { char dest[10]; char src[] = \"helloworld\"; strncpy(dest, src, 5); dest[5] = \'\\0\'; // 手动添加结束符 cout << dest << endl; // 输出hello return 0;}
1.3 字符串连接函数
①strcat 函数
strcat 函数用于将源字符串连接到目标字符串的末尾,其原型为 char* strcat (char* dest, const char* src)。它会将 src 指向的字符串(包括 \'\\0\')添加到 dest 指向的字符串的后面,连接后的字符串以 \'\\0\' 结尾。使用该函数时,必须保证 dest 指向的数组有足够的空间容纳连接后的字符串,否则会导致缓冲区溢出。
示例代码:
#include #include using namespace std;int main() { char dest[20] = \"hello\"; char src[] = \"world\"; strcat(dest, src); cout << dest << endl; // 输出helloworld return 0;}
②strncat 函数
strncat 函数相对更安全,其原型为 char* strncat (char* dest, const char* src, size_t n)。它将 src 指向的字符串中前 n 个字符连接到 dest 指向的字符串末尾,并自动添加结束符 \'\\0\'。即使 src 的长度大于 n,也只会连接 n 个字符,且会添加结束符。
示例代码:
#include #include using namespace std;int main() { char dest[20] = \"hello\"; char src[] = \"world123\"; strncat(dest, src, 3); cout << dest << endl; // 输出hellowor return 0;}
1.4 字符串比较函数
①strcmp 函数
strcmp 函数用于比较两个字符串的大小,其原型为 int strcmp (const char* str1, const char* str2)。比较规则是按照 ASCII 码值逐个字符进行比较,直到出现不同的字符或遇到 \'\\0\' 为止。
如果 str1 等于 str2,返回 0;如果 str1 大于 str2,返回一个正数;如果 str1 小于 str2,返回一个负数。
示例代码:
#include #include using namespace std;int main() { char str1[] = \"apple\"; char str2[] = \"banana\"; int result = strcmp(str1, str2); if (result < 0) { cout << \"str1小于str2\" < 0) { cout << \"str1大于str2\" << endl; } else { cout << \"str1等于str2\" << endl; } return 0;}
\"apple\" 和 \"banana\" 比较,第一个字符 \'a\' 的 ASCII 码小于 \'b\',所以 result 为负数,输出 “str1 小于 str2”。
②strncmp 函数
strncmp 函数用于比较两个字符串的前 n 个字符,其原型为 int strncmp (const char* str1, const char* str2, size_t n)。比较规则与 strcmp 类似,但只比较前 n 个字符。
示例代码:
#include #include using namespace std;int main() { char str1[] = \"apple\"; char str2[] = \"appletree\"; int result = strncmp(str1, str2, 5); if (result == 0) { cout << \"前5个字符相等\" << endl; } else { cout << \"前5个字符不相等\" << endl; } return 0;}
这里比较前 5 个字符,\"apple\" 和 \"appletree\" 的前 5 个字符都是 \"apple\",所以输出 “前 5 个字符相等”。
1.5 字符串查找函数
①strchr 函数
strchr 函数用于在字符串中查找指定字符第一次出现的位置,其原型为 char* strchr (const char* str, int c)。其中 c 是要查找的字符(以 ASCII 码形式传入)。如果找到该字符,返回指向该字符的指针;如果未找到,返回 NULL。
示例代码:
#include #include using namespace std;int main() { char str[] = \"hello world\"; char* ptr = strchr(str, \'o\'); if (ptr != NULL) { cout << \"找到字符\'o\',位置在:\" << ptr - str << endl; // 输出4 } else { cout << \"未找到字符\'o\'\" << endl; } return 0;}
②strrchr 函数
strrchr 函数用于在字符串中查找指定字符最后一次出现的位置,其原型为 char* strrchr (const char* str, int c)。用法与 strchr 类似,只是查找方向是从字符串末尾开始。
示例代码:
#include #include using namespace std;int main() { char str[] = \"hello world\"; char* ptr = strrchr(str, \'o\'); if (ptr != NULL) { cout << \"最后一次出现字符\'o\'的位置在:\" << ptr - str << endl; // 输出7 } else { cout << \"未找到字符\'o\'\" << endl; } return 0;}
③strstr 函数
strstr 函数用于在一个字符串中查找另一个字符串第一次出现的位置,其原型为 char* strstr (const char* haystack, const char* needle)。如果找到,返回指向第一次出现位置的指针;如果未找到,返回 NULL。
示例代码:
#include #include using namespace std;int main() { char haystack[] = \"hello world, welcome to the world\"; char needle[] = \"world\"; char* ptr = strstr(haystack, needle); if (ptr != NULL) { cout << \"找到子串,位置在:\" << ptr - haystack << endl; // 输出6 } else { cout << \"未找到子串\" << endl; } return 0;}
1.6 其他常用 C 风格字符串函数
①strtok 函数
strtok 函数用于将字符串分割成多个子串,其原型为 char* strtok (char* str, const char* delim)。第一次调用时,str 指向要分割的字符串,后续调用时,str 设为 NULL,delim 是分隔符集合。
该函数会修改原字符串,将分隔符替换为 \'\\0\',并返回指向当前子串的指针。当没有更多子串时,返回 NULL。
示例代码:
#include #include using namespace std;int main() { char str[] = \"apple,banana,orange\"; const char* delim = \",\"; char* token = strtok(str, delim); while (token != NULL) { cout << token << endl; token = strtok(NULL, delim); } return 0;}
②memset 函数
memset 函数用于将一块内存区域的内容设置为指定的值,其原型为 void* memset (void* ptr, int value, size_t num)。常用来初始化字符数组,将其所有元素设置为某个字符(通常是 \'\\0\')。
示例代码:
#include #include using namespace std;int main() { char str[10]; memset(str, \'\\0\', sizeof(str)); // 将数组所有元素设为\'\\0\' cout << \"字符串长度:\" << strlen(str) << endl; // 输出0 return 0;}
二、C++ 标准库 string 类
C++ 标准库中的 string 类封装了字符串的操作,提供了更安全、更便捷的字符串处理方式,声明在头文件中。string 类重载了许多运算符,并提供了丰富的成员函数。
2.1 string 类的构造函数
string 类有多种构造函数,可以满足不同的初始化需求:
- 默认构造函数:string (),创建一个空字符串。
- string (const char* s):用 C 风格字符串 s 初始化。
- string (size_t n, char c):创建一个包含 n 个字符 c 的字符串。
- string (const string& str):拷贝构造函数,用另一个 string 对象初始化。
- string (const string& str, size_t pos, size_t len):用 str 中从 pos 位置开始的 len 个字符初始化。
示例代码:
#include #include using namespace std;int main() { string s1; // 空字符串 string s2(\"hello\"); // 用C风格字符串初始化 string s3(5, \'a\'); // 包含5个\'a\'的字符串 string s4(s2); // 拷贝构造 string s5(s2, 1, 3); // 用s2中从位置1开始的3个字符初始化,即\"ell\" cout << \"s2: \" << s2 << endl; cout << \"s3: \" << s3 << endl; cout << \"s4: \" << s4 << endl; cout << \"s5: \" << s5 << endl; return 0;}
2.2 string 类的赋值操作
1. 直接赋值:使用 = 运算符,如 string s; s = \"hello\";。
2. assign 成员函数:
- string& assign (const char* s):用 C 风格字符串 s 赋值。
- string& assign (const char* s, size_t n):用 s 的前 n 个字符赋值。
- string& assign (const string& str):用另一个 string 对象赋值。
- string& assign (const string& str, size_t pos, size_t len):用 str 中从 pos 位置开始的 len 个字符赋值。
- string& assign (size_t n, char c):赋值为 n 个字符 c。
示例代码:
#include #include using namespace std;int main() { string s; s = \"world\"; // 直接赋值 cout << \"s: \" << s << endl; s.assign(\"hello\", 3); // 用\"hello\"的前3个字符赋值,即\"hel\" cout << \"s after assign: \" << s << endl; string s2 = \"welcome\"; s.assign(s2, 2, 4); // 用s2中从位置2开始的4个字符赋值,即\"lcom\" cout << \"s after another assign: \" << s << endl; return 0;}
2.3 string 类的字符串拼接
1. 使用 + 运算符:可以将两个 string 对象或 string 对象与 C 风格字符串、字符拼接。
2. 使用 append 成员函数:
- string& append (const char* s):将 C 风格字符串 s 拼接到当前字符串后。
- string& append (const char* s, size_t n):将 s 的前 n 个字符拼接到当前字符串后。
- string& append (const string& str):将另一个 string 对象拼接到当前字符串后。
- string& append (const string& str, size_t pos, size_t len):将 str 中从 pos 位置开始的 len 个字符拼接到当前字符串后。
- string& append (size_t n, char c):在当前字符串后添加 n 个字符 c。
示例代码:
#include #include using namespace std;int main() { string s1 = \"hello\"; string s2 = \"world\"; string s3 = s1 + \" \" + s2; // 使用+运算符拼接 cout << \"s3: \" << s3 << endl; // 输出hello world s1.append(\" there\"); // 拼接C风格字符串 cout << \"s1 after append: \" << s1 << endl; // 输出hello there s1.append(3, \'!\'); // 添加3个\'!\' cout << \"s1 after another append: \" << s1 << endl; // 输出hello there!!! return 0;}
2.4 string 类的字符串比较
1. 使用关系运算符:==、!=、、=,可以直接比较两个 string 对象或 string 对象与 C 风格字符串。
2. 使用 compare 成员函数:int compare (const string& str) const,比较当前字符串与 str。返回值规则与 strcmp 类似,0 表示相等,正数表示当前字符串大,负数表示当前字符串小。
此外,compare 还有其他重载形式,如比较子串等。
示例代码:
#include #include using namespace std;int main() { string s1 = \"apple\"; string s2 = \"banana\"; if (s1 < s2) { cout << \"s1小于s2\" << endl; } int result = s1.compare(s2); if (result < 0) { cout << \"s1.compare(s2)返回负数,s1小于s2\" << endl; } string s3 = \"apple\"; if (s1 == s3) { cout << \"s1等于s3\" << endl; } return 0;}
2.5 string 类的字符访问
1. 使用 [] 运算符:char& operator [](size_t pos),可以访问或修改指定位置的字符,不进行越界检查。
2. 使用 at 成员函数:char& at (size_t pos),与 [] 类似,但会进行越界检查,若越界会抛出 out_of_range 异常。
示例代码:
#include #include using namespace std;int main() { string s = \"hello\"; cout << s[1] << endl; // 输出e s[1] = \'E\'; cout << s << endl; // 输出hEllo try { cout << s.at(10) << endl; // 越界访问 } catch (out_of_range& e) { cout << \"异常:\" << e.what() << endl; } return 0;}2.6 string 类的子串操作
substr 成员函数用于获取子串,原型为 string substr (size_t pos = 0, size_t len = npos) const,其中 npos 是一个静态常量,表示直到字符串末尾。该函数返回从 pos 位置开始,长度为 len 的子串。
示例代码:
#include #include using namespace std;int main() { string s = \"hello world\"; string sub1 = s.substr(6); // 从位置6开始到末尾的子串,即\"world\" string sub2 = s.substr(0, 5); // 从位置0开始,长度为5的子串,即\"hello\" cout << \"sub1: \" << sub1 << endl; cout << \"sub2: \" << sub2 << endl; return 0;}
2.7 string 类的查找操作
string 类提供了多个查找相关的成员函数,用于查找字符或子串:
1. find:从字符串开头查找,返回第一次出现的位置,若未找到返回 npos。
- size_t find (const string& str, size_t pos = 0) const:从 pos 位置开始查找子串 str。
- size_t find (const char* s, size_t pos = 0) const:从 pos 位置开始查找 C 风格字符串 s。
- size_t find (char c, size_t pos = 0) const:从 pos 位置开始查找字符 c。
2. rfind:从字符串末尾开始查找,返回最后一次出现的位置。
3. find_first_of:查找字符串中第一次出现指定字符集中任何一个字符的位置。
4. find_last_of:查找字符串中最后一次出现指定字符集中任何一个字符的位置。
5. find_first_not_of:查找字符串中第一次出现不在指定字符集中的字符的位置。
6. find_last_not_of:查找字符串中最后一次出现不在指定字符集中的字符的位置。
示例代码:
#include #include using namespace std;int main() { string s = \"hello world, welcome to the world\"; size_t pos1 = s.find(\"world\"); // 查找\"world\"第一次出现的位置 cout << \"pos1: \" << pos1 << endl; // 输出6 size_t pos2 = s.rfind(\"world\"); // 查找\"world\"最后一次出现的位置 cout << \"pos2: \" << pos2 << endl; // 输出29 size_t pos3 = s.find_first_of(\"aeiou\"); // 查找第一次出现元音字母的位置 cout << \"pos3: \" << pos3 << endl; // 输出1(\'e\'的位置) return 0;}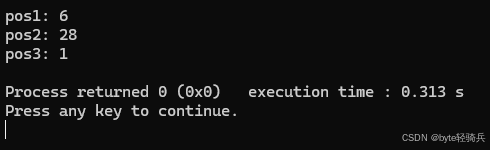
2.8 string 类的替换操作
replace 成员函数用于替换字符串中的部分内容,有多种重载形式:
- string& replace (size_t pos, size_t len, const char* s):将从 pos 位置开始的 len 个字符替换为 s。
- string& replace (size_t pos, size_t len, const string& str):将从 pos 位置开始的 len 个字符替换为 str。
- string& replace (size_t pos, size_t len, size_t n, char c):将从 pos 位置开始的 len 个字符替换为 n 个字符 c。
- 还有其他基于迭代器范围的替换形式。
示例代码:
#include #include using namespace std;int main() { string s = \"hello world\"; s.replace(6, 5, \"there\"); // 将从位置6开始的5个字符(\"world\")替换为\"there\" cout << s << endl; // 输出hello there s.replace(0, 5, 3, \'x\'); // 将从位置0开始的5个字符替换为3个\'x\' cout << s << endl; // 输出xxx there return 0;}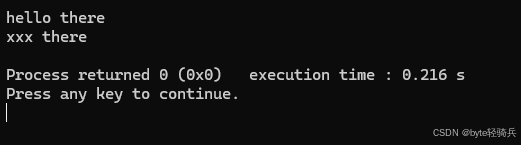
2.9 string 类的插入操作
insert 成员函数用于在字符串中插入内容,有多种重载形式:
- string& insert (size_t pos, const char* s):在 pos 位置插入 C 风格字符串 s。
- string& insert (size_t pos, const string& str):在 pos 位置插入 string 对象 str。
- string& insert (size_t pos, size_t n, char c):在 pos 位置插入 n 个字符 c。
- 基于迭代器的插入形式。
示例代码:
#include #include using namespace std;int main() { string s = \"hello\"; s.insert(5, \" world\"); // 在位置5插入\" world\" cout << s << endl; // 输出hello world s.insert(0, 3, \'!\'); // 在位置0插入3个\'!\' cout << s << endl; // 输出!!!hello world return 0;}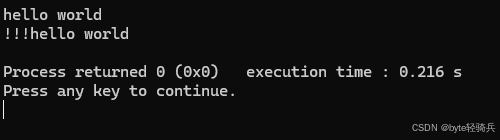
2.10 string 类的删除操作
erase 成员函数用于删除字符串中的部分内容:
- string& erase (size_t pos = 0, size_t len = npos):删除从 pos 位置开始的 len 个字符。
- 基于迭代器的删除形式。
示例代码:
#include #include using namespace std;int main() { string s = \"hello world\"; s.erase(5, 1); // 删除从位置5开始的1个字符(空格) cout << s << endl; // 输出helloworld s.erase(5); // 删除从位置5开始到末尾的字符 cout << s << endl; // 输出hello return 0;}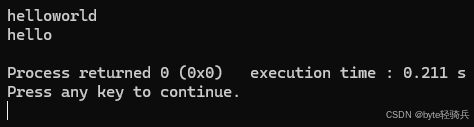
2.11 string 类与 C 风格字符串的转换
- c_str () 成员函数:返回一个指向 C 风格字符串的 const char * 指针,该指针指向的字符串以 \'\\0\' 结尾。
- data () 成员函数:在 C++11 之后,与 c_str () 功能相同,返回 const char * 指针。
- copy (char* s, size_t len, size_t pos = 0) const:将字符串中从 pos 位置开始的 len 个字符复制到字符数组 s 中,不会自动添加 \'\\0\',需要手动添加。
示例代码:
#include #include #include using namespace std;int main() { string s = \"hello\"; const char* cstr = s.c_str(); cout << cstr << endl; // 输出hello char arr[10]; s.copy(arr, 5, 0); arr[5] = \'\\0\'; // 手动添加结束符 cout << arr << endl; // 输出hello return 0;}
2.12 string 类的其他常用函数
- size () 和 length ():都返回字符串的长度,即字符的个数,不包括结束符(string 内部管理,用户无需关心),功能相同。
- empty ():判断字符串是否为空,若为空返回 true,否则返回 false。
- clear ():清空字符串,使之为空。
- reserve (size_t n):预留 n 个字符的存储空间,避免频繁的内存分配,但不会改变字符串的实际长度。
- capacity ():返回当前字符串在重新分配内存之前所能容纳的最大字符数。
- resize (size_t n, char c = \'\\0\'):调整字符串的长度为 n,若 n 大于当前长度,用字符 c 填充;若 n 小于当前长度,截断字符串。
示例代码:
#include #include using namespace std;int main() { string s = \"hello\"; cout << \"size: \" << s.size() << endl; // 输出5 cout << \"length: \" << s.length() << endl; // 输出5 cout << \"empty: \" << (s.empty() ? \"true\" : \"false\") << endl; // 输出false s.clear(); cout << \"after clear, empty: \" << (s.empty() ? \"true\" : \"false\") << endl; // 输出true s = \"hello\"; s.reserve(20); cout << \"capacity: \" << s.capacity() << endl; // 可能输出20(具体实现可能不同) s.resize(8, \'x\'); cout << s << endl; // 输出helloxxx return 0;}
三、其他字符串处理相关函数
除了上述 C 风格字符串函数和 string 类的成员函数外,C++ 标准库中还有一些与字符串处理相关的函数,主要在头文件和中。
3.1 字符分类和转换函数()
- isalpha (int c):判断字符 c 是否为字母(a-z 或 A-Z)。
- isdigit (int c):判断字符 c 是否为数字(0-9)。
- isalnum (int c):判断字符 c 是否为字母或数字。
- islower (int c):判断字符 c 是否为小写字母。
- isupper (int c):判断字符 c 是否为大写字母。
- tolower (int c):将字符 c 转换为小写字母(若为大写字母)。
- toupper (int c):将字符 c 转换为大写字母(若为小写字母)。
这些函数的参数是 int 类型,通常传入字符的 ASCII 码,若传入的不是 unsigned char 范围内的值且不是 EOF,行为未定义。
示例代码:
#include #include using namespace std;int main() { char c = \'A\'; cout << isalpha(c) << endl; // 非0,表示是字母 cout << isdigit(c) << endl; // 0,表示不是数字 cout << (char)tolower(c) << endl; // 输出a char d = \'3\'; cout << isalnum(d) << endl; // 非0,表示是字母或数字 return 0;}
3.2 算法库中的字符串操作函数()
- reverse:反转字符串,可以用于 string 对象或字符数组。对于 string 对象,reverse (s.begin (), s.end ()) 可以反转字符串。
- swap:交换两个 string 对象的值,swap (s1, s2)。
示例代码:
#include #include #include using namespace std;int main() { string s = \"hello\"; reverse(s.begin(), s.end()); cout << s << endl; // 输出olleh string s1 = \"abc\", s2 = \"def\"; swap(s1, s2); cout << \"s1: \" << s1 << \", s2: \" << s2 << endl; // 输出s1: def, s2: abc return 0;}
掌握这些字符串处理函数,能够帮助开发者更高效地进行字符串的各种操作,如复制、连接、比较、查找、替换等。在使用过程中,应根据具体需求选择合适的函数,并注意函数的参数、返回值和可能出现的异常情况,以编写健壮的代码。
中文学习资料


