《黑马笔记》 --- C++ 提高编程
C++ 提高编程
- 本阶段主要针对C++泛型编程>和STL技术的讲解。
1. 模板
1.1 模板的概念
生活中的模板:一寸照片模板,ppt模板,还有求职过程中的简历模板,这可以帮我们在生活中方便很多,C++也是如此。
模板的特点:
- 模板不可以直接使用,他只是一个框架
- 模板的通用并不是万能的
1.2 函数模板
在c++中除了所学过的面向对象的思想之外
- 还有另一种编程思想称为泛型编程,主要利用的技术就是模板。
- c++提供两种模板机制:函数模板和类模板
1.2.1 函数模板语法
建立一个通用函数,其返回值和星形参类型不确定,用一个虚拟的类型来代表。
语法:
template<typename T>函数声明和定义template 声明创建模板
typename 表示其后面的符号是一种数据类型,也可以用class
T 通用的数据类型,名称可换,一般大写。
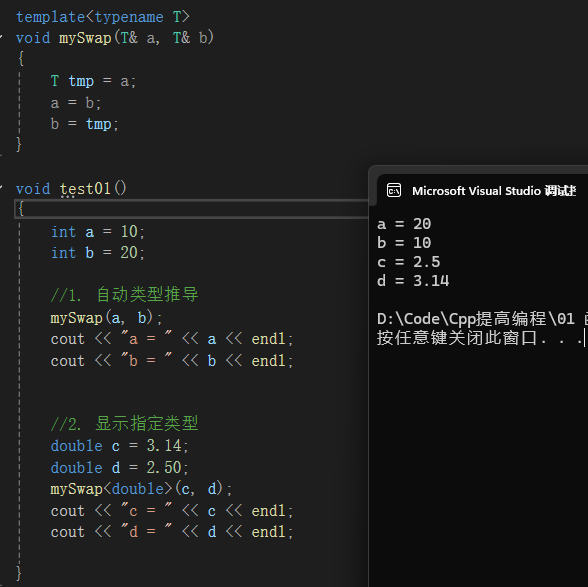
上图所示:我们如果交换的数据类型不止是一个,那按照以前的做法,就得实现两个函数来交换,但是这种模板的思想,我们只需要写一个就好了,而在调用的时候,有两种方式:
- 自动类型推导:编译器自己推导什么类型
- 显示指定类型:我们告诉编译器什么类型
1.2.2 函数模板注意事项
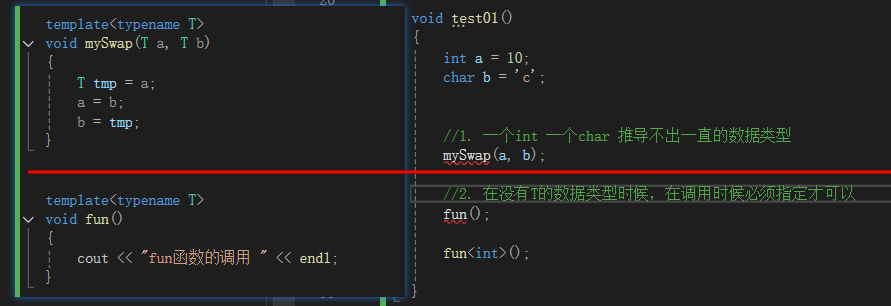
- 自动类型推导,必须推导出一致的数据类型T,才可以使用
- 模板必须要确定出T的数据类型,才可以使用
1.2.3 函数模板案例
写了一个选择排序。
#include using namespace std;template<typename T>void mySwap(T &a, T &b){T tmp = a;a = b;b = tmp;}template<typename T>void mySort(T &arr, int size){for (int i = 0; i < size - 1; i++){int maxIndex = i;for (int j = i + 1; j < size; j++){if (arr[j] > arr[maxIndex])maxIndex = j;}mySwap(arr[i], arr[maxIndex]);}}void test01(){int arr[] = { 1,200,30,400,50 };//char arr[] = \"pkshdas\";int k = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[1]);mySort(arr, k);for (int i = 0; i < k; i++)cout << arr[i] << \" \";}int main(){test01();return 0;}1.2.4 普通函数和函数模板的区别
- 普通函数调用可以发生隐式类型转换
- 函数模板用自动类型推导,不可以发生隐士类型转化。
- 函数模板用显示指定类型,可以发生隐式类型转化。
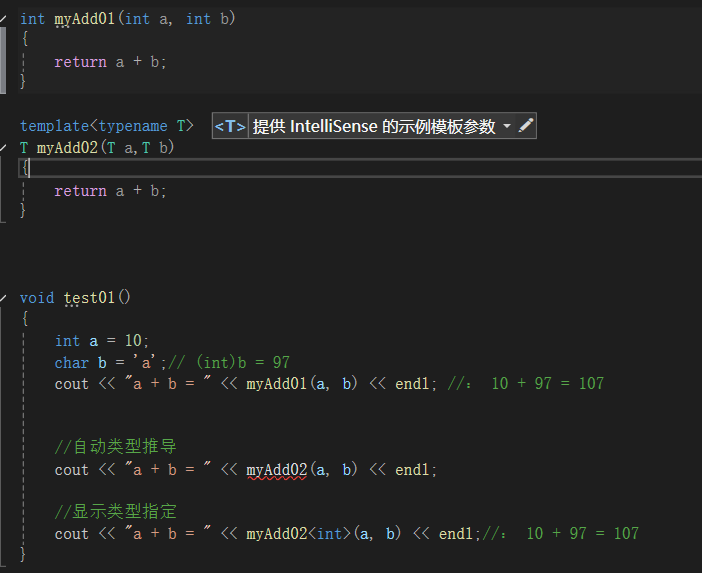
上图中当普通函数调用的时候,会自动将char类型转化成int类型,10 + 97 = 107,而模板函数中的自动类型推导则不会自动转化。
对于显示类型指定,我感觉就是将上述函数模板中T全部编程了int,所以他会和普通函数一样,进行隐式转换。
建议使用显示指定类型的方式,调用函数模板,因为可以自己确定通用类型T。
1.2.5 普通函数与函数模板调用规则
普通函数与函数模板是可以发生重载的。
调用规则:
- 如果普通函数和函数模板都实现,优先调用普通函数。
- 可以通过空模板参数列表来强制调用函数模板
- 函数模板也可以发生重载
- 如果函数模板可以产生更好的匹配,优先调用函数模板。
#include using namespace std;void myPrintf(int a, int b){cout << \"普通函数的调用!\" << endl;}template<typename T>void myPrintf(T a, T b){cout << \"函数模板的调用!\" << endl;}template<typename T>void myPrintf(T a, T b, T c){cout << \"函数模板重载的调用!\" << endl;}//1.如果普通函数和函数模板都实现,优先调用普通函数。void test01(){int a = 0, b = 0;myPrintf(a, b); }//2. 可以通过空模板参数列表来强制调用函数模板//3. 函数模板也可以发生重载void test02(){int a = 0, b = 0;myPrintf<>(a, b);myPrintf<>(a, b, 10);}//4.如果函数模板可以产生更好的匹配,优先调用函数模板//因为如果调用普通函数是需要进行隐式类型转换的。 void test04(){char c1 = \'a\', c2 = \'b\';myPrintf(c1, c2);}int main(){//test01();//test02();test04();return 0;}总结: 既然提供了函数模板,最好就不要提供普通函数,否则容易出现二义性。
1.2.6 模板的局限性
模板的通用性并不是万能的,碰上自定义数据类型,一一般的模板就会出错了。
template<typename T>bool myCompare(T a, T b){return a == b;}void test01(){int a = 10, b = 20;char c1 = \'a\', c2 = \'a\';if (myCompare(a, b))cout << \"a = b\" << endl;elsecout << \"a != b\" << endl;if (myCompare(c1, c2))cout << \"c1 = c2\" << endl;elsecout << \"c1 != c2\" << endl;}这种比较是可以的,但是下面的比较就不行了。
void test02(){Person p1(\"kxq\", 18);Person p2(\"kxq\", 18);if (myCompare(p1, p2))cout << \"p1 = p2\" << endl;elsecout << \"p1 != p2\" << endl;}我们可以用之前所学的将==重载,但如果还要比较大于小于等等其他情况,需要重载的太多了,不太方便。
所以需要添加一个具体化的模板,就可以解决自定义类型的通用化了。
//----------------------------------------template<> bool myCompare(Person a, Person b){return a.name == b.name && a.age == b.age;}//----------------------------------------void test02(){Person p1(\"kxq\", 18);Person p2(\"kxq\", 21);if (myCompare(p1, p2))cout << \"p1 = p2\" << endl;elsecout << \"p1 != p2\" << endl;}1.3 类模板
1.3.1 类模板的语法
类模板的作用:
- 建立一个通用类,类中成员数据类型可以不具体制定,用一个虚拟的类型来代表。
建立一个通用函数,其返回值和星形参类型不确定,用一个虚拟的类型来代表。
语法:
template<typename T>类template 声明创建模板
typename 表示其后面的符号是一种数据类型,也可以用class
T 通用的数据类型,名称可换,一般大写。
- 类模板和函数模板十分像,只是在
template下一行写成类就好了,示例如下:
#include #include using namespace std;//类模板template<class NameType, class AgeType>//可以写多个class Person{public:Person(NameType name, AgeType age){this->m_Name = name;this->m_Age = age;}void showPerson(){cout << \"姓名: \" << this->m_Name << \" 年龄: \" << this->m_Age << endl;}NameType m_Name;AgeType m_Age;};void test01(){Person<string, int> p1(\"kxq\", 18);p1.showPerson();}int main(){test01();return 0;}1.3.2 类模板与函数模板的区别
- 类模板没有自动类型推导的使用方式
//1. 类模板没有自动类型推导使用方式void test01(){//这是错误的,编译器不能够自动推导。Person p1(\"xl\", 18);//只有这一种方式可以。Person<string, int> p1(\"kxq\", 18);p1.showPerson();}int main(){test01();return 0;}- 类模板在模板参数列表中可以有默认参数
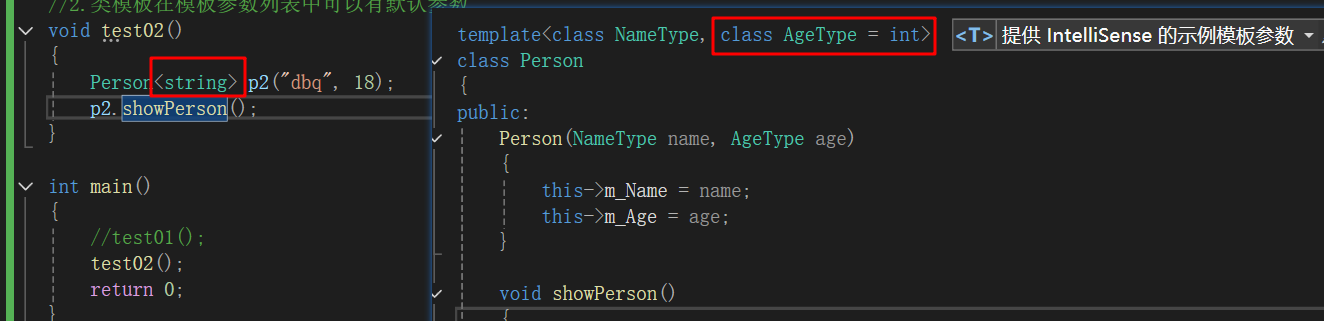
就是说我要是在模板参数列表中有了默认参数,在下面使用时候只需要写出另一个即可。
1.3.3 类模板成员函数创建时机。
- 类模板成员函数在调用时才创建
#include //类模板成员函数创建时机//类模板成员函数在调用时才创建using namespace std;class Person1{public:void showPerson1(){cout << \"Person1 show\" << endl;}};class Person2{public:void showPerson2(){cout << \"Person2 show\" << endl;}};template<class T>class MyClass{public:T obj;//类模板中的成员函数void fun1(){obj.showPerson1();}void fun2(){obj.showPerson2();}};void test01(){MyClass<Person1> m;m.fun1();//m.fun2();//错误。MyClass<Person2> mm;//mm.fun1();//错误。mm.fun2();}int main(){test01();return 0;}- 类模板成员函数并不是一开始就创建的,在调用时才去创建。
1.3.4 类模板对象做函数参数
学习:类模板实例化出对象,向函数传参的方式
一共有三种传入方式:
- 指定传入的类型 — 直接显示对象的数据类型
- 参数模板化 — 将对象中的参数变为模板进行传递
- 整个类模板化 — 将这个对象类型 模板化进行传递
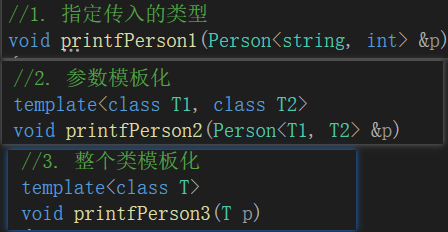
代码示例:
#include using namespace std;template<class T1, class T2>class Person{public:Person(T1 name, T2 age){this->m_Name = name;this->m_Age = age;}void showPerson(){cout << \"姓名: \" << this->m_Name << \" 年龄: \" << this->m_Age << endl;}T1 m_Name;T2 m_Age;};//1. 指定传入的类型void printfPerson1(Person<string, int> &p){p.showPerson();}void test01(){Person<string, int> p(\"xl\", 18);printfPerson1(p);}//2. 参数模板化template<class T1, class T2>void printfPerson2(Person<T1, T2> &p){p.showPerson();cout << \"T1 类型: \" << typeid(T1).name() << endl;cout << \"T2 类型: \" << typeid(T2).name() << endl;}void test02(){Person<string, int> p(\"N9\", 21);printfPerson2(p);}//3. 整个类模板化template<class T>void printfPerson3(T p){p.showPerson();cout << \"T 类型: \" << typeid(T).name() << endl;}void test03(){Person<string, int> p(\"DBQ\", 21);printfPerson3(p);}int main(){test01();test02();test03();return 0;}1.3.5 类模板与继承
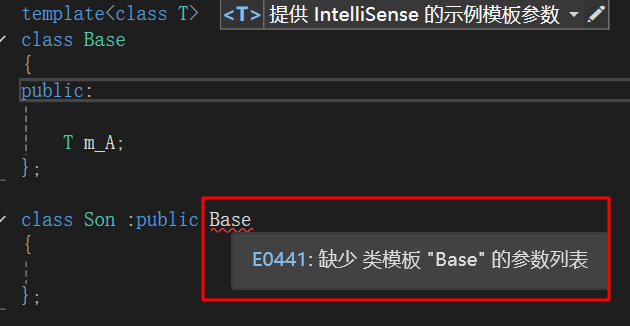
当类模板碰上继承时,需要注意以下几点:
- 当子类继承的父类是一个类模板是,子类在声明的时候,要指定出父类中T的类型
- 如果不指定,编译器无法给予子类分配内存
- 如果想灵活指定出父类中T的类型,子类也需要变为类模板
下图 当我们的父类是一个类模板的时候,正常的方式肯定是不可以的,需要在Base后面写出参数列表。
template<class T>class Base{public:T m_A;};//1. 当子类继承的父类是一个类模板是,子类在声明的时候,要指定出父类中T的类型class Son1 :public Base<int>{};//2. 如果想灵活指定出父类中T的类型,子类也需要变为类模板template<class T1, class T2>class Son2 :public Base<T2>{public:T1 m_A;};总结: 如果父类是类模板,子类需要指定出父类中T的数据类型
1.3.6 类模板成员函数类外实现
- 类模板中成员函数类外实现时,需要加上模板参数列表
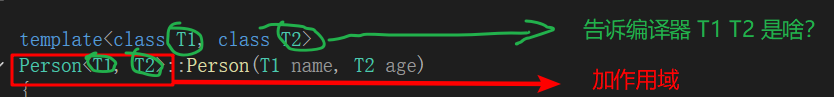
代码示例:
template<class T1, class T2>class Person{public:Person(T1 name, T2 age);void showPerson();T1 m_Name;T2 m_Age;};template<class T1, class T2>Person<T1, T2>::Person(T1 name, T2 age){this->m_Name = name;this->m_Age = age;}template<class T1, class T2>void Person<T1, T2>::showPerson(){cout << \"姓名: \" << this->m_Name << \" 年龄: \" << this->m_Age << endl;}void test01(){Person<string, int> p(\"xl\", 18);p.showPerson();}1.3.7 类模板分文件编写
因为在1.3.3类模板创建时机中学过,类模板成员函数在调用时才创建 所以他和普通的类函数份文件编写不一样。
- 普通的类函数份文件编写只需要保护其
.h文件就好了,而类模板则需要包含类模板函数具体实现的.cpp文件,这是第一种解决方式。 - 第二种解决方式是将
.h文件和.cpp文件写在一起,改为后缀为.hpp的文件
主流的解决方法是第二种解决方法,将类模板成员函数写到一起,并改后缀为.hpp
1.3.8 类模板与友元
额。。。。。全局函数类内实现简单加个friend就好了。
额。。。。。全局函数类外实现。。。。。。。先让编译器知道有这个函数,但是知道这个函数前又必须让编译器知道那个Person类,因为函数中用到了Person类了。
套娃这一块./
左脚踩右脚这一块./
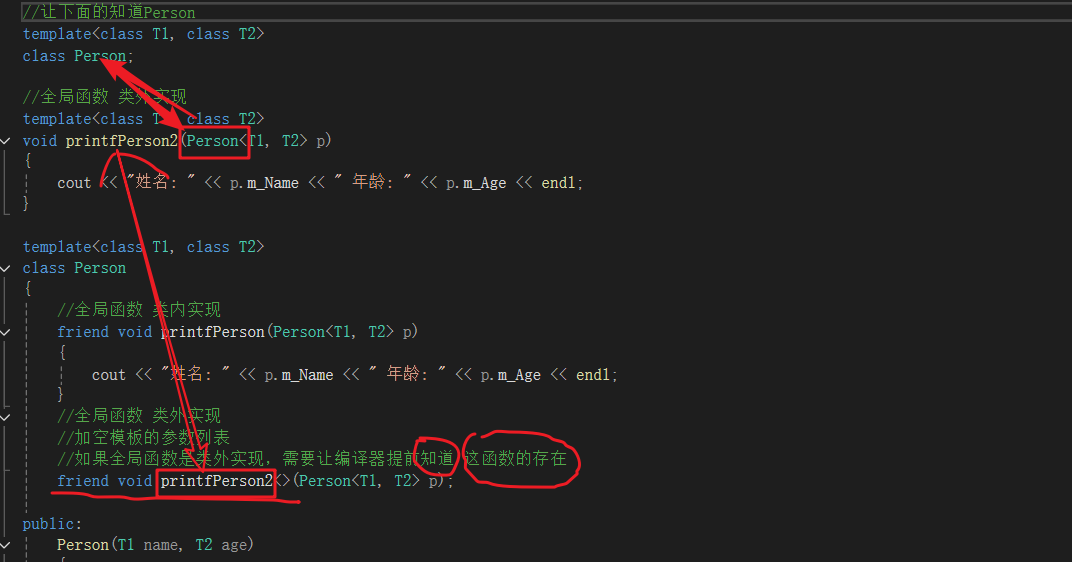
#include #include using namespace std;//让下面的知道Persontemplate<class T1, class T2>class Person;//全局函数 类外实现template<class T1, class T2>void printfPerson2(Person<T1, T2> p){cout << \"姓名: \" << p.m_Name << \" 年龄: \" << p.m_Age << endl;}template<class T1, class T2>class Person{//全局函数 类内实现friend void printfPerson(Person<T1, T2> p){cout << \"姓名: \" << p.m_Name << \" 年龄: \" << p.m_Age << endl;}//全局函数 类外实现//加空模板的参数列表//如果全局函数是类外实现,需要让编译器提前知道 这函数的存在friend void printfPerson2<>(Person<T1, T2> p);public:Person(T1 name, T2 age){this->m_Name = name;this->m_Age = age;}private:T1 m_Name;T2 m_Age;};void test01(){Person<string, int> p(\"xl\", 18);printfPerson(p);Person<string, int> p2(\"n9\", 21);printfPerson2(p2);}int main(){test01();return 0; }建议全局函数做类内实现,用法简单,而且编译器可以直接识别。
2. STL初始
STL,全称为 Standard Template Library(标准模板库),是 C++ 标准库中非常重要且强大的部分。它提供了一系列通用的模板类和函数,让我们能够方便、高效地处理数据结构和算法问题。
STL分为六大组件:
- 容器: 用来存放数据结构
- 算法: 各种各样的算法
- 迭代器:扮演了容器和算法的胶合剂,连接容器和算法,提供统一的访问方式。
- 仿函数:行为类似函数,可以作为算法的某种策略
- 适配器:修饰容器或者仿函数或迭代器接口的东西
- 空间配置器:负责空间的配置管理
2.1 STL的三大组件
- 容器(Containers)
容器是用来存储和组织数据的类模板。常见的容器有:- 顺序容器:如
vector(动态数组)、list(双向链表)、deque(双端队列) - 关联容器:如
set、map(基于红黑树的平衡树结构) - 无序关联容器:如
unordered_set、unordered_map(基于哈希表)
- 顺序容器:如
- 算法(Algorithms)
STL提供了大量的通用算法,如排序、查找、拷贝、合并、差集等。这些算法与容器无关,只要容器支持迭代器,就能使用算法。 - 迭代器(Iterators)
迭代器是连接容器和算法的桥梁,类似于通用指针,能够访问容器中的元素。不同容器支持不同类别的迭代器(输入迭代器、输出迭代器、前向迭代器、双向迭代器、随机访问迭代器),为算法提供灵活的访问方式。
2.2 STL的特点
- 泛型编程
STL基于模板实现,能够支持任意类型的数据,极大地增强了代码的复用性和灵活性。 - 高效性
STL的实现高度优化,许多算法和容器在性能上都接近手写代码。 - 易用性和可维护性
使用STL能大幅减少代码量,避免重复造轮子,提高开发效率和代码的可维护性。 - 标准化
STL是C++标准库的组成部分,跨平台、稳定,广泛被使用和支持。
3. STL常用的容器
3.1 String容器
string 是C++的字符串,而string本质上是一个类。
char*是一个指针string是一个类,类中封装了char*管理了这个字符串,是一个char*型容器
特点:比起C语言来讲,不必担心越界问题以及\'\\0\'问题
3.1.1 string构造函数
构造函数原型:
stirng();创建一个空的字符串string(const char* s)利用字符串s初始化string(const string& str);利用string对象初始化另一个string对象string(int n, char c);使用n个字符c初始化
代码示例:
#include #include using namespace std;/*- `stirng();`创建一个空的字符串 `string(const char* s) `利用字符串s初始化- `string(const string& str);` 利用string对象初始化另一个string对象- `string(int n, char c);` 使用n个字符c初始化*/void test01(){string s1;//默认构造string s2(\"abcdef\");cout << s2 << endl;string s3(s2);cout << s3 << endl;string s4(9, \'n\');cout << s4 << endl;}int main(){test01();return 0;}3.1.2 string赋值操作

代码示例:
#include #include using namespace std;void test01(){//三种等号赋值string str1;str1 = \"N9 is my idol!\";cout << \"str1 = \" << str1 << endl;string str2;str2 = str1;cout << \"str2 = \" << str2 << endl;string str3;str3 = \'y\';cout << \"str3 = \" << str3 << endl;//string str4;str4.assign(\"DBQ is my idol!\");cout << \"str4 = \" << str4 << endl;string str5;str5.assign(\"DBQ is my idol!\", 3);cout << \"str5 = \" << str5 << endl;string str6;str6.assign(str5);cout << \"str6 = \" << str6 << endl;string str7;str7.assign(9, \'N\');cout << \"str7 = \" << str7 << endl;}int main(){test01();return 0;}3.1.3 string字符串拼接
- 实现字符串末尾拼接字符串

代码示例:
#include #include using namespace std;//string 字符串拼接操作。void test01(){//+= 号string str1 = \"N9 \";str1 += \"is my idol\";cout << \"str1 = \" << str1 << endl;str1 += \':\';cout << \"str1 = \" << str1 << endl;string str2 = \"(十年前我是金枪王,十年后我还是金枪王)\";str1 += str2;cout << \"str1 = \" << str1 << endl;//appendstring str3 = \"I\";str3.append(\" love \");cout << \"str3 = \" << str3 << endl;str3.append(\"game abcdef\", 4);cout << \"str3 = \" << str3 << endl;string str4 = \" is cf.\";//str3.append(str4);str3.append(str4, 3, 4);cout << \"str3 = \" << str3 << endl;}int main(){test01();return 0;}3.1.4 string查找和替换
- 替换: 查找指定字符串是否存在
- 替换: 在指定的位置替换字符串

代码示例:
#include #include using namespace std;//字符串查找和替换//1. 查找void test01(){string str1 = \"decdefg\";//find从右往左int pos = str1.find(\"de\");//有返回下标 没有返回-1第一次出现if (pos == -1)cout << \"未找到字符串\" << endl;elsecout << \"pos = \" << pos << endl;//rfind 从左往右 pos = str1.rfind(\"de\");//有返回下标 没有返回-1最后一次出现if (pos == -1)cout << \"未找到字符串\" << endl;elsecout << \"pos = \" << pos << endl;}//2. 替换void test02(){string str1 = \"abcdefg\";//从1号位置起,3个字符替换为\"1111\"str1.replace(1, 3,\"1111\");cout << \"str1 = \" << str1 << endl;}int main(){//test01();test02();return 0;}3.1.5 string字符串比较
- 字符串比较是按照字符的ASCII码进行比较
- 等于返回0
- 大于返回1
- 小于返回-1
代码示例:
#include #include using namespace std;void test01(){string str1 = \"b\";string str2 = \"abcde\";if (str1.compare(str2) == 0){cout << \"str1 == str2\" << endl;}else if (str1.compare(str2) > 0)cout << \"str1 > str2 \" << endl;elsecout << \"str1 < str2\" << endl;}int main(){test01();return 0;}3.1.6 string 字符存取
string 中单个字符存取方式有两种
char& operator[](int n);通过[]的方式取字符char& at(int n);通过at方式获取字符
代码示例:
#include #include using namespace std;void test01(){string str1 = \"abcdefg\";for (int i = 0; i < str1.size(); i++)cout << str1[i] << \" \";cout << endl;for (int i = 0; i < str1.size(); i++)cout << str1.at(i) << \" \";cout << endl;//修改单个字符str1[0] = \'x\';str1.at(1) = \'x\';cout << str1 << endl;}int main(){test01();return 0;}3.1.7 string插入和删除

代码示例:
#include #include using namespace std;void test01(){string str = \"hello\";//插入str.insert(1, \"111\");cout << \"str = \" << str << endl;//删除str.erase(1, 3);cout << \"str = \" << str << endl;}int main(){test01();return 0;}3.1.8 string子串
string subter(int pos = 0, int n = npos)const;返回由pos开始的n个字符组成的字符串。
代码示例:
#include #include using namespace std;void test01(){string str = \"abcdef\";string subStr = str.substr(1, 3);cout << \"subStr = \" << subStr << endl;}//使用操作void test02(){string email = \"xl@code.com\";//从邮件的地址中获取用户的信息int pos = email.find(\'@\');string userName = email.substr(0, pos);cout << \"userName = \" << userName << endl;}int main(){//test01();test02();return 0;}3.2 vector 容器
- vector 数据结构和数组十分相似,也成为单端数组。
- 不同的是:数据是静态的,vector是动态的。
动态扩展,并不是在原有的空间后继续开辟新的空间,而是寻找更大的空间,将原有数据拷贝新空间,释放原空间。
- vector容器的迭代器,是支持随机访问的迭代器。
3.3.1 vector 构造函数

代码示例:
#include #include using namespace std;void myPrint(vector<int> v){for (int i = 0; i < v.size(); i++)cout << v[i] << \" \";cout << endl;}void test01(){//默认构造函数vector<int> v1;for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)v1.push_back(i);myPrint(v1);//区间构造vector<int> v2(v1.begin(), v1.end());myPrint(v1);//n个elemvector<int> v3(10, 6);myPrint(v3);//拷贝构造vector<int> v4(v3);myPrint(v4);}int main(){test01();return 0;}3.3.2 vector 赋值操作

代码示例:
#include #include using namespace std;void printVector(vector<int>& v){for (auto it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++)cout << *it << \" \";cout << endl;}void test01(){vector<int> v1;for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)v1.push_back(i);printVector(v1);//operator=vector<int> v2;v2 = v1;printVector(v2);//assign 区间赋值vector<int> v3;v3.assign(v2.begin(), v2.end());printVector(v3);//assign n个elemvector<int> v4;v4.assign(10, 6);printVector(v4);}int main(){test01();return 0;}3.3.3 vector容量和大小

代码示例:
#include #include using namespace std;void printVector(vector<int>& v1){for (int i = 0; i < v1.size(); i++)cout << v1[i] << \" \";cout << endl;}void test01(){vector<int> v1;for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)v1.push_back(i);printVector(v1);if (v1.empty()){cout << \"v1 为空! \" << endl;}else{cout << \"v1 的容量是: \" << v1.capacity() << endl;cout << \"v1 的大小是: \" << v1.size() << endl;}v1.resize(15);//默认新增的为0printVector(v1);v1.resize(20, 666);//指定新增的为 666printVector(v1);v1.resize(5);printVector(v1);}int main(){test01();return 0;}3.3.4 vector插入和删除

代码示例:
#include #include using namespace std;void printVector(vector<int>& v){for (int i = 0; i < v.size(); i++)cout << v[i] << \" \";cout << endl;}void test01(){vector<int> v1;for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++)v1.push_back(i);printVector(v1);for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)v1.pop_back();printVector(v1);v1.insert(v1.begin(), 10);printVector(v1);v1.insert(v1.begin(), 3, 100);printVector(v1);v1.erase(v1.begin());printVector(v1);v1.erase(v1.begin(), v1.begin() + 3);printVector(v1);v1.clear();printVector(v1);}int main(){test01();return 0;}3.3.5 vector数据存取

#include #include using namespace std;void test01(){vector<int> v1;for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)v1.push_back(i);for (int i = 0; i < v1.size(); i++)cout << v1[i] << \" \";cout << endl;for (int i = 0; i < v1.size(); i++)cout << v1.at(i) << \" \";cout << endl;cout << \"v1 中第一个元素是: \" << v1.front() << endl;cout << \"v1 中最后一个元素是: \" << v1.back() << endl;}int main(){test01();return 0;}3.3.6 vector互换容器
- 实现两个容器内元素进行互换
swqp(vec);//将vect与本身的元素互换
#include #include using namespace std;void printVector(vector<int> v){for (int i = 0; i < v.size(); i++)cout << v[i] << \" \";cout << endl;}//1.基本使用void test01(){vector<int> v1;cout << \"交换前: \" << endl;for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)v1.push_back(i);printVector(v1);vector<int> v2;for (int i = 10; i > 0; i--)v2.push_back(i);printVector(v2);cout << \"交换后: \" << endl;v1.swap(v2);printVector(v1);printVector(v2);} //2.实际用途//巧用swap可以收缩内存空间void test02(){vector<int> v;for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++)v.push_back(i);cout << \"v的容量是: \" << v.capacity() << endl;cout << \"v的大小是: \" << v.size() << endl;cout << endl;v.resize(3);cout << \"v的容量是: \" << v.capacity() << endl;cout << \"v的大小是: \" << v.size() << endl;cout << endl;vector<int>(v).swap(v);//将匿名vector和v互换,然后系统自动释放匿名。cout << \"v的容量是: \" << v.capacity() << endl;cout << \"v的大小是: \" << v.size() << endl;cout << endl;}int main(){//test01();test02();return 0;}3.3.7 vector预留空间
- 可以减少vector在动态扩展容量时的扩展次数
reserve(int len)//容器预留len个元素长度,预留位置不初始化,元素不可访问。
提前开辟可以减少中途新开辟空间,并迁移数据的麻烦。
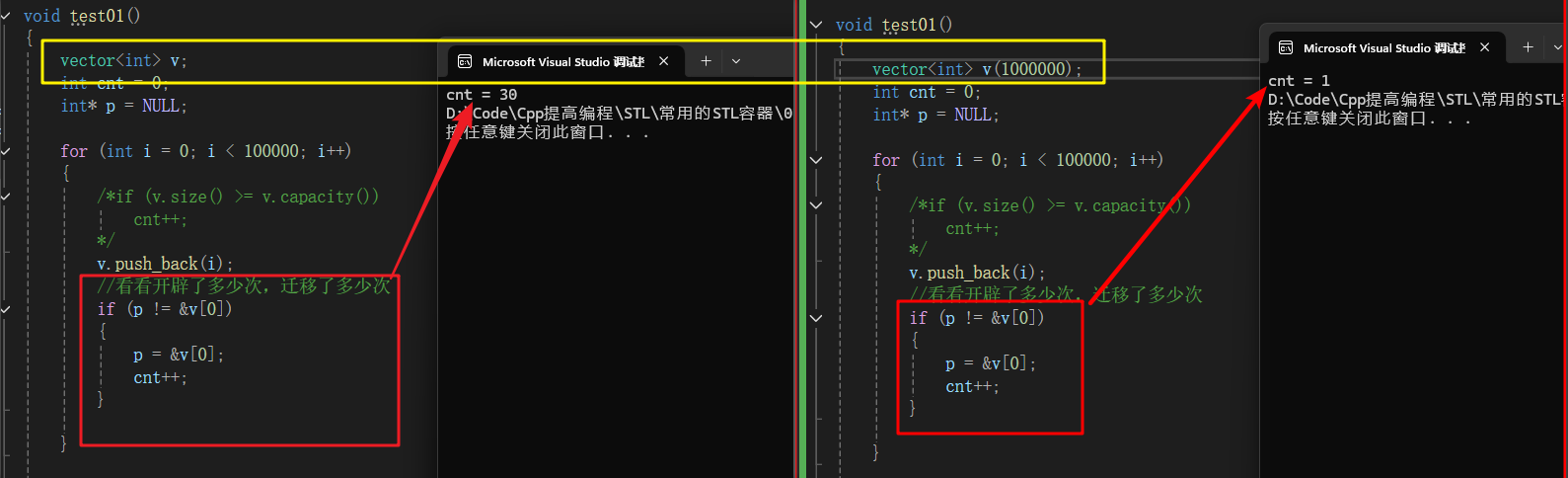
#include #include using namespace std;void test01(){vector<int> v(1000000);int cnt = 0;int* p = NULL;for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++){/*if (v.size() >= v.capacity())cnt++;*/v.push_back(i);//看看开辟了多少次,迁移了多少次if (p != &v[0]){p = &v[0];cnt++;}}cout << \"cnt = \" << cnt;}int main(){test01();return 0;}3.3 deque容器
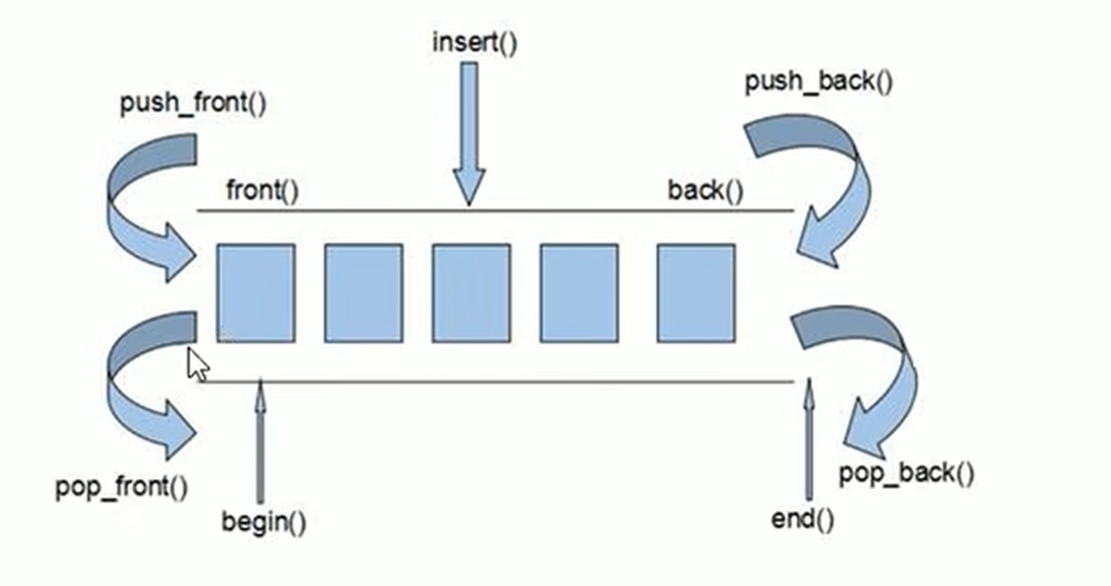
- 双端数组,可以对头端进行插入和删除操作。
- deque相对而言,对头部的插入和删除速度比vector快
- vector访问元素时速度比deque快,这和两者内部实现有关。
3.3.1 deque构造函数

代码示例:
#include #include using namespace std;void printDeque(const deque<int> d){for (auto it = d.begin(); it != d.end(); it++)cout << *it << \" \";cout << endl;}void test01(){deque<int> d1;for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)d1.push_back(i);printDeque(d1);deque<int> d2(d1.begin(), d1.end());printDeque(d2);deque<int> d3(10, 66);printDeque(d3);deque<int> d4(d3);printDeque(d4);}int main(){test01();return 0;}- deque 和 vector 容器的构造方式几乎一致,灵活使用即可。
3.3.2 deque赋值操作
- deque的赋值操作和vector的赋值操作几乎一致。

代码示例:
#include #include using namespace std;void printDeque(const deque<int>& d){for (auto it = d.begin(); it != d.end(); it++)cout << *it << \" \";cout << endl;}void test01(){deque<int> d1;for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)d1.push_back(i);printDeque(d1);deque<int> d2;d2 = d1;printDeque(d2);deque<int> d3;d3.assign(d2.begin(), d2.end());printDeque(d3);deque<int> d4;d4.assign(10, 6);printDeque(d4);}int main(){test01();return 0;}3.3.3 deque大小操作
- 和vector的操作函数区别就少了一个容量,因为deque不需要判断容量,它本身就没有容量限制,可以无限的往后或者往前开辟空间。

3.3.4deque插入和删除

代码示例:
#include #include using namespace std;void printDeque(const deque<int>& d){for (auto it = d.begin(); it != d.end(); it++)cout << *it << \" \";cout << endl;}void test01(){deque<int> d1;//尾插for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)d1.push_back(i);printDeque(d1);//头插for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)d1.push_front(i);printDeque(d1);//尾删d1.pop_back();d1.pop_back();d1.pop_back();printDeque(d1);//头删d1.pop_front();d1.pop_front();d1.pop_front();printDeque(d1);}void test02(){deque<int> d1;d1.push_back(1);d1.push_back(2);d1.push_back(3);printDeque(d1);d1.insert(d1.begin(), 10);d1.insert(d1.begin(), 20);printDeque(d1);d1.insert(d1.begin(), 2, 100);printDeque(d1);// 按照区间进行插入。deque<int> d2;d2.push_back(1);d2.push_back(2);d2.push_back(3);d1.insert(d1.begin(), d2.begin(), d2.end());printDeque(d1);}void test03(){deque<int> d1;d1.push_back(1);d1.push_back(2);d1.push_back(3);d1.push_back(4);printDeque(d1);auto it = d1.begin();it++;d1.erase(it);printDeque(d1);//按照区间删除//d1.erase(d1.begin(), d1.end());d1.clear();printDeque(d1);}int main(){//test01();//test02();test03();return 0;}3.3.5 deque数据存取

代码示例:
#include #include using namespace std;void test01(){deque<int> d;d.push_back(10);d.push_back(20);d.push_back(30);d.push_back(40);d.push_back(50);for (int i = 0; i < d.size(); i++)cout << d[i] << \" \";cout << endl;for (int i = 0; i < d.size(); i++)cout << d.at(i) << \" \";cout << endl;cout << d.front() << endl;cout << d.back() << endl;}int main(){test01();return 0;}3.3.6 deque 排序
算法:
sort(iterator beg, iterator end)// 对beg和end区间元素进行排序。
代码示例:
#include #include #include using namespace std;void printDeque(const deque<int>& d){for (int i = 0; i < d.size(); i++)cout << d[i] << \" \";cout << endl;}void test01(){deque<int> d;d.push_back(10);d.push_back(20);d.push_back(260);d.push_back(9);d.push_back(37);printDeque(d);//排序 默认是升序sort(d.begin(), d.end());printDeque(d);}int main(){test01();return 0;}3.4 stack 容器
- stack – 栈是一种给先进后出的一种数据结构,它是由一个出口。
- 栈只有栈顶可以由外界访问,因此不支持遍历行为。

代码示例:
#include #include using namespace std;void test01(){stack<int> s;s.push(10);s.push(20);s.push(30);s.push(40);s.push(50);cout << \"栈中大小为: \" << s.size() << endl;while (!s.empty()){cout << s.top() << endl;s.pop();}cout << \"栈中大小为: \" << s.size() << endl;}int main(){test01();return 0;}3.5 queue 容器
- queue – 队列是一种先进先出的数据结构,有两个出口.
- 只有对头和队尾可以由外界访问,因此不支持遍历。
#include #include #include using namespace std;class Person{public:Person(string name, int age){this->m_Name = name;this->m_Age = age;}string m_Name;int m_Age;};void test01(){queue<Person> q;Person p1(\"xl\", 18);Person p2(\"N9\", 19);Person p3(\"DBQ\", 20);Person p4(\"XXiao\", 21);Person p5(\"baby\", 22);q.push(p1);q.push(p2);q.push(p3);q.push(p4);q.push(p5);cout << \"队列中的大小为:d \" << q.size() << endl;while (!q.empty()){cout << \"队首元素: \" << \"姓名: \" << q.front().m_Name << \" 年龄: \" << q.front().m_Age << endl;cout << \"队尾元素: \" << \"姓名: \" << q.back().m_Name << \" 年龄: \" << q.back().m_Age << endl;q.pop();}cout << \"队列中的大小为: \" << q.size() << endl;}int main(){test01();return 0;}3.6 list 容器
list 又称链表
- 链表是一种物理存储单元上非连续的存储结构。
- 链表是由一系列节点组成,节点又由数据域和指针域组成的。
- 链表对于增删的效率要比vector高,但是遍历不如vector。
STL中的链表是一个双向循环链表
3.6.1 list 构造函数

代码示例:
#include #include using namespace std;void printList(const list<int>& l1){for (auto it = l1.begin(); it != l1.end(); it++)cout << *it << \" \";cout << endl;}void test01(){list<int> l1;for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)l1.push_back(i);printList(l1);list<int> l2(l1);printList(l2);list<int> l3(l2.begin(), l2.end());printList(l3);list<int> l4(10, 6);printList(l4);}int main(){test01();return 0;}3.6.2 list 赋值和交换
代码示例:
#include #include using namespace std;void printList(const list<int>& l){ for (auto it = l.begin(); it != l.end(); it++) cout << *it << \" \"; cout << endl;}//赋值void test01(){ list<int> l1; for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) l1.push_back(i); printList(l1); list<int> l2; l2 = l1; printList(l2); list <int> l3; l3.assign(l2.begin(), l2.end()); printList(l3); list<int> l4; l4.assign(10, 6); printList(l4);}void test02(){ list<int> l1; for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) l1.push_back(i); list<int> l2; l2.assign(10, 6); cout << \"交换前: \" << endl; printList(l1); printList(l2); swap(l1, l2); cout << \"交换后: \" << endl; printList(l1); printList(l2);}int main(){ //test01(); test02(); return 0;}3.6.3 list 大小操作

代码示例:
#include #include using namespace std;void printList(const list<int>& l){for (auto it = l.begin(); it != l.end(); it++)cout << *it << \" \";cout << endl;}void test01(){list<int> l1;for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)l1.push_back(i);printList(l1);if (l1.empty()){cout << \"l1 为空 \" << endl;}else{cout << \"l1 不为空! \" << endl;cout << \"l1 大小为: \" << l1.size() << endl;}// resizel1.resize(15);printList(l1);l1.resize(20, 66);printList(l1);l1.resize(5);printList(l1);}int main(){test01();return 0;}3.6.4 list 插入和删除

代码示例:
#include #include using namespace std;void printList(const list<int>& l){for (auto it = l.begin(); it != l.end(); it++)cout << *it << \" \";cout << endl;}void test01(){list<int> l1;//尾插l1.push_back(10);l1.push_back(20);l1.push_back(30);//头插l1.push_front(100);l1.push_front(200);l1.push_front(300);printList(l1);//头尾删l1.pop_back();l1.pop_front();printList(l1);auto it = l1.begin();l1.insert(l1.end(), 66);l1.insert(it, 6, 66);printList(l1);//区间插入list<int> l2;for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)l2.push_back(521);it = l1.begin();it++;l1.insert(it, l2.begin(), l2.end());printList(l1);//删除it = l1.begin();l1.erase(it);printList(l1);l1.remove(521);printList(l1);l1.clear();printList(l1);}int main(){test01();return 0;}3.6.5 list 数据存取
front()//返回第一个元素back()//返回最后一个元素
list不支持随机访问
代码示例:
#include #include using namespace std;void test01(){list<int> l1;l1.push_back(10);l1.push_back(20);l1.push_back(30);l1.push_back(40);cout << \"第一个元素为 \" << l1.front() << endl;cout << \"最后一个元素为 \" << l1.back() << endl;//不支持随机访问auto it = l1.begin();it++;it--;//it = it + 1;//error 不支持随机访问}int main(){test01();return 0;}3.3.6 list 反转和排序
- 将容器元素反转以及排序。
函数原型:
reverse();//反转链表srot();//链表排序
代码示例:
#include #include #include using namespace std;void printList(const list<int>& l){for (auto it = l.begin(); it != l.end(); it++)cout << *it << \" \";cout << endl;}bool myCompare(int v1, int v2){//第一个数 大于 第二数 10 9 8 .。。。。 return v1 > v2;//降序}void test01(){list<int> l1;l1.push_back(50);l1.push_back(20);l1.push_back(40);l1.push_back(10);l1.push_back(30);cout << \"反转前: \" << endl;printList(l1);//反转l1.reverse();cout << \"反转后: \" << endl;printList(l1);//排序//sort(l1.begin(), l1.end());//标准算法库中的sort只能对支持随机访问的数据结构进行排序,比如strig vector 等等.cout << \"排序前: \" << endl;printList(l1);l1.sort();cout << \"排序后: \" << endl;printList(l1);l1.sort(myCompare);//降序printList(l1);}int main(){test01();return 0;}3.7 set/ multiset 容器
- set容器中所有元素再插入时自动排序
- set/multiset 属于关联式容器 底层用红黑树实现
- set不允许出现重复的元素,multiset 允许出现重复的元素。
3.7.1 set 构造和赋值

代码示例:
#include #include using namespace std;void printSet(const set<int>& s){for (auto it = s.begin(); it != s.end(); it++)cout << *it << \" \";cout << endl;}void printMultiset(const multiset<int>& s){for (auto it = s.begin(); it != s.end(); it++)cout << *it << \" \";cout << endl;}void test01(){set<int> s1;s1.insert(10);s1.insert(30);s1.insert(60);s1.insert(20);s1.insert(20);s1.insert(20);s1.insert(20);s1.insert(50);//set中不支持重复的元素,只能插入一次//自动排序printSet(s1);set<int> s2(s1);printSet(s2);set<int> s3;s3 = s2;printSet(s3);}void test02(){multiset<int> s1;s1.insert(10);s1.insert(30);s1.insert(60);s1.insert(20);s1.insert(20);s1.insert(20);s1.insert(20);s1.insert(50);//multiset中支持重复的元素,//自动排序printMultiset(s1);multiset<int> s2(s1);printMultiset(s2);multiset<int> s3;s3 = s2;printMultiset(s3);}int main(){//test01();test02();return 0;}3.7.2 set 大小和交换
size();// 返回容器中元素的数目empty();// 判断容器是否为空swap();//交换两个集合容器
#include #include using namespace std;void printSet(const set<int>& s1){for (auto it = s1.begin(); it != s1.end(); it++)cout << *it << \" \";cout << endl;}void test01(){set<int> s1;s1.insert(10);s1.insert(40);s1.insert(20);s1.insert(30);printSet(s1);if (s1.empty()){cout << \"s1 为空!\" << endl;}else{cout << \"s1 不为空! \" << endl;cout << \"s1 大小为: \" << s1.size() << endl;}set<int> s2;s2.insert(100);s2.insert(400);s2.insert(200);s2.insert(300);cout << \"交换前: \" << endl;printSet(s1);printSet(s2);cout << \"交换后: \" << endl;s1.swap(s2);printSet(s1);printSet(s2);}int main(){test01();return 0;}3.7.3 set 插入和删除

#include #include using namespace std;void printSet(const set<int>& s1){for (auto it = s1.begin(); it != s1.end(); it++)cout << *it << \" \";cout << endl;}void test01(){set<int> s1;s1.insert(10);s1.insert(40);s1.insert(30);s1.insert(20);printSet(s1);s1.erase(s1.begin());printSet(s1);s1.erase(30);printSet(s1);//清空//s1.erase(s1.begin(), s1.end());s1.clear();printSet(s1);}int main(){test01();return 0;}3.7.4 set 查找和统计
find(key); // 查找key是否存在,若存在返回改键的元素的迭代器;若不存在,返回set.end();count(key);// 统计key的元素个数。
代码示例:
#include #include using namespace std;void printSet(const set<int>& s1){for (auto it = s1.begin(); it != s1.end(); it++)cout << *it << \" \";cout << endl;}void test01(){set<int> s1;s1.insert(10);s1.insert(40);s1.insert(30);s1.insert(20);s1.insert(20);s1.insert(20);s1.insert(20);s1.insert(20);auto pos = s1.find(20);if (pos == s1.end()){cout << \"没找到!\" << endl;}else{cout << \"找到了!\" << endl;}cout << s1.count(20) << endl;}void test02(){multiset<int> s1;s1.insert(10);s1.insert(40);s1.insert(30);s1.insert(20);s1.insert(20);s1.insert(20);s1.insert(20);s1.insert(20);cout << s1.count(20) << endl;}int main(){//test01();test02();return 0;}3.7.5 set 和 multiset的区别
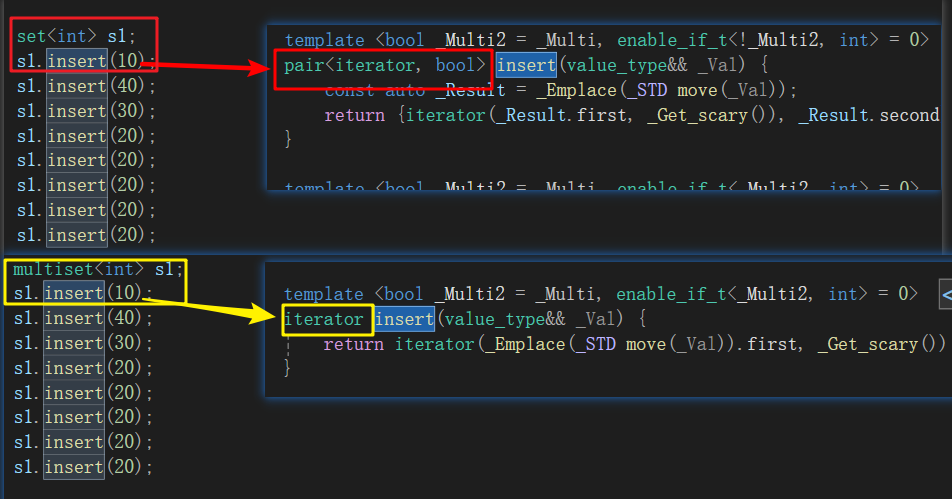
我感觉最大的区别就是 set检测重复的数据,multiset不检测重复的数据。
如下图转到定义会发现: insert的返回值, set比multiset多一个bool型,这个bool就是看是否插入成功的。若书不存在则插入成功,返回true,若数据存在,则插入失败,返回false。
3.7.6 pair 对组创建
- 成对出现的数据,利用对组可以返回两个数据。

代码示例:
#include #include using namespace std;void test01(){pair<string, int>p(\"xl\", 18);cout << \"姓名: \" << p.first << \" 年龄: \" << p.second << endl;pair<string, int> p2 = make_pair(\"N9\", 21);cout << \"姓名: \" << p2.first << \" 年龄: \" << p2.second << endl;}int main(){test01();return 0;}3.7.7 set 容器排序
- set默认是从小到大,学习改变set容器的排序规则
- 利用仿函数可以改变排序规则。
示例:set 存放内置数据类型与set存放自定义数据类型
#include #include using namespace std;class MyCompare{public://重载一下() 注意要加const//不是 const 函数,意思是编译器认为这个函数可能修改类的成员变量,//而标准库是不允许在 const 对象上调用非 const 函数的,于是就报错了。bool operator()(int v1, int v2) const{return v1 > v2;}};class Person{public:Person(string name, int age){this->m_Name = name;this->m_Age = age;}string m_Name;int m_Age;};class comparePerson{public:bool operator()(const Person& p1, const Person& p2) const{return p1.m_Age > p2.m_Age;}};// 1. set 存放内置数据类型void test01(){set<int> s1;//乱序插入s1.insert(10);s1.insert(50);s1.insert(30);s1.insert(40);s1.insert(20);//默认升序排序for (auto it = s1.begin(); it != s1.end(); it++)cout << *it << \" \";cout << endl;//利用仿函数,改为降序排序set<int, MyCompare> s2;s2.insert(10);s2.insert(50);s2.insert(30);s2.insert(40);s2.insert(20);for (auto it = s2.begin(); it != s2.end(); it++)cout << *it << \" \";cout << endl;}// 2. set 存放自定义数据类型void test02(){set<Person,comparePerson> s1;Person p1(\"xl\", 18);Person p2(\"N9\", 21);Person p3(\"Ayom\", 35);Person p4(\"DBQ\", 11);Person p5(\"577\", 25);s1.insert(p1);s1.insert(p2);s1.insert(p3);s1.insert(p4);s1.insert(p5);for (auto it = s1.begin(); it != s1.end(); it++)cout << \"姓名: \" << it->m_Name << \" 年龄: \" << it->m_Age << endl;}int main(){//test01(); //1.set 存放内置数据类型test02();//2.set 存放自定义数据类型return 0;}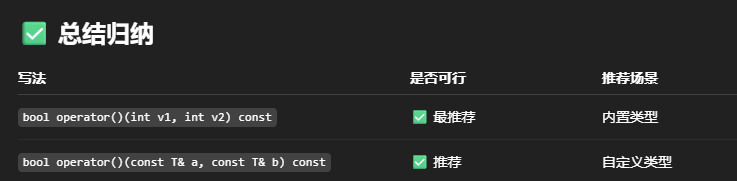
上面这张图片是在重载()时候的注意事项。
3.8 map/ multimap 容器
-
map属于关联式容器 的底层也是红黑树。
-
map中所有的元素都是pari
-
pair中第一个元素为key(键值) 起到索引作用, 第二个元素为value(实值)
-
所有元素会根key值自动排序
优点:
- 可以根据key值快速找到value值。
map和multimap的区别
- map不允许容器中有重复key值元素。
- multimap允许容器中有重复key值元素。
3.8.1 map 构造和赋值
- map容器中插入是以pair形式插入的。

代码示例:
#include #include using namespace std;void printMap(map<int, int> m){for (auto it = m.begin(); it != m.end(); it++)cout << \"key = \" << it->first << \" value = \" << it->second << endl;cout << endl;}void test01(){map<int, int> m;m.insert(pair<int, int>(1, 10));m.insert(pair<int, int>(3, 30));m.insert(pair<int, int>(4, 40));m.insert(pair<int, int>(2, 20));printMap(m);map<int, int> m1(m);printMap(m1);map<int, int> m2;m2 = m1;printMap(m2);}int main(){test01();return 0;}3.8.2 map 大小和交换
size();// 返回容器中元素的数目empty();//判断容器是否为空swap(st);//交换两个集合容器
代码示例:
#include #include using namespace std;void printMap(map<int, int>& m){for (auto it = m.begin(); it != m.end(); it++){cout << \"key = \" << it->first << \" value = \" << it->second << endl;}cout << endl;}void test01(){map<int, int> m1;m1.insert(pair<int, int>(1, 10));m1.insert(pair<int, int>(2, 20));m1.insert(pair<int, int>(3, 30));m1.insert(pair<int, int>(4, 40));if (m1.empty()){cout << \"m1 为空!\" << endl;}else{cout << \"m1 不为空! \" << endl;cout << \"m1 的大小为: \" << m1.size() << endl;}map<int, int> m2;m2.insert(pair<int, int>(10, 100));m2.insert(pair<int, int>(20, 200));m2.insert(pair<int, int>(30, 300));m2.insert(pair<int, int>(40, 400));cout << \"交换前: \" << endl;printMap(m1);printMap(m2);cout << \"交换后: \" << endl;m1.swap(m2);printMap(m1);printMap(m2);}int main(){test01();return 0;}3.8.3 map 插入和删除

代码示例:
#include #include using namespace std;void printMap(map<int, int>& m){for (auto it = m.begin(); it != m.end(); it++){cout << \"key = \" << it->first << \" value = \" << it->second << endl;}cout << endl;}void test01(){map<int, int> m1;//插入 四 种方式m1.insert(pair<int, int>(1, 10));m1.insert(make_pair(2, 20));m1.insert(map<int, int>::value_type(3, 30));m1[4] = 40;cout << m1[5] << endl;//出现m1[5]自动就在map中插入了key为5 value 为0的值。printMap(m1);//删除m1.erase(m1.begin());printMap(m1);m1.erase(5);//按照key删除printMap(m1);//清空//m1.erase(m1.begin(), m1.end());m1.clear();printMap(m1);}int main(){test01();return 0;}3.8.4 map 查找和统计
find();// 查找key是否存在,若存在返回元素的迭代器,否则返回set.end();cout();// 统计key的元素个数
#include #include using namespace std;void test01(){map<int, int> m1;m1[1] = 10;m1[2] = 20;m1[3] = 30;m1[4] = 40;m1.insert(make_pair(3, 30));m1.insert(make_pair(3, 30));m1.insert(make_pair(3, 30));m1.insert(make_pair(3, 30));auto pos = m1.find(4);if (pos != m1.end()){cout << \"找到了!\" << endl;cout << \"key = \" << pos->first << \" value = \" << pos->second << endl;}elsecout << \"没找到!\" << endl;cout << m1.count(3) << endl;multimap<int, int> m2;m2.insert(make_pair(3, 30));m2.insert(make_pair(3, 30));m2.insert(make_pair(3, 30));m2.insert(make_pair(3, 30));m2.insert(make_pair(3, 30));cout << m2.count(3) << endl;}int main(){test01();return 0;}3.8.5 map 排序
也是默认从小到大排序,和set的方式几乎一样。
我们下面将其改为降序排序
#include #include using namespace std;class MyCompare{public:bool operator()(int v1, int v2) const{return v1 > v2;}};void test01(){map<int, int, MyCompare> m1;m1.insert(make_pair(1, 10));m1.insert(make_pair(3, 30));m1.insert(make_pair(2, 20));m1.insert(make_pair(5, 50));m1.insert(make_pair(4, 40));for (auto it = m1.begin(); it != m1.end(); it++){cout << \"key = \" << it->first << \" value = \" << it->second << endl;}}int main(){test01();return 0;}4. STL- 函数对象
4.1 函数对象
4.1.1 函数对象概念
概念:
- 重载函数调用操作符的类,其对象常称为函数对象。
- 函数对象使用重载的()时候,行为类似函数调用,也叫仿函数
本质:
- 函数对象(仿函数)是一个类,不是一个函数。
4.1.2 函数对象的使用
- 函数对象在使用时,可以像普通函数那样调用,可以有参数,可以有返回值。
- 函数对象超出普通函数的概念,函数对象可以有自己的状态。
- 函数对象可以作为参数传递
代码示例:
#include #include using namespace std;/*- 函数对象在使用时,可以像普通函数那样调用,可以有参数,可以有返回值。- 函数对象超出普通函数的概念,函数对象可以有自己的状态。- 函数对象可以作为参数传递*///1. 函数对象在使用时,可以像普通函数那样调用,可以有参数,可以有返回值。class MyAdd{public:int operator()(int v1, int v2){return v1 + v2;}};void test01(){MyAdd myAdd;cout << myAdd(1, 1) << endl;}//2. 函数对象超出普通函数的概念,函数对象可以有自己的状态class MyPrint{public:MyPrint(){count = 0;}void operator()(string test){cout << test << endl;this->count++;}int count;};void test02(){MyPrint myPrint;myPrint(\"hello N9!\");myPrint(\"hello N9!\");myPrint(\"hello N9!\");myPrint(\"hello N9!\");myPrint(\"hello N9!\");cout << \"myPrint 调用次数: \" << myPrint.count << endl;}//3. 函数对象可以作为参数传递void doPrint(MyPrint & mp, string test){mp(test);}void test03(){MyPrint myPrint;doPrint(myPrint, \"hello DBQ\");}int main(){test01();test02();test03();return 0;}4.2 谓词
概念:
- 返回bool类型的仿函数称为谓词
- 如果operatro()接受一个参数,那么称为一元谓词
- 如果operator()接受两个参数,那么称为二元谓词
4.2.1 一元谓词
代码示例:
#include #include #include using namespace std;class CreateFive{public://- 返回bool类型的仿函数称为谓词//-如果operatro()接受一个参数,那么称为一元谓词bool operator()(int val){return val > 5;}};void test01(){vector<int> v;for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)v.push_back(i);auto it = find_if(v.begin(), v.end(), CreateFive());if (it == v.end()){cout << \"没有找到! \" << endl;}else{cout << \"找到了 \" << *it << endl;}}int main(){test01();return 0;}4.2.2 二元谓词
代码示例:
#include #include #include using namespace std;//bool Compare(int v1, int v2)//{//return v1 > v2;//}class ClassCompare{public:bool operator()(int v1, int v2){return v1 > v2;}};void test01(){vector<int> v;v.push_back(10);v.push_back(40);v.push_back(50);v.push_back(30);v.push_back(20);sort(v.begin(), v.end());for (auto it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++)cout << *it << \" \";cout << endl;//sort(v.begin(), v.end(), Compare);sort(v.begin(), v.end(), ClassCompare());for (auto it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++)cout << *it << \" \";cout << endl;}int main(){test01();return 0;}4.3 内建函数对象
4.3.1 内建函数对象意义
- STL提供了一些函数对象
- 算术仿函数
- 关系仿函数
- 逻辑仿函数
这些仿函数所产生的对象,用法和一般函数完全相同,但是使用时候,需要引入头文件#include
4.3.2 算数仿函数

#include #include using namespace std;// 一元仿函数. 取反void test01(){negate<int> n;cout << n(10) << endl;cout << n(-20) << endl;cout << n(666) << endl;}// 二元仿函数 加法void test02(){plus<int> p;cout << p(1, 1) << endl;cout << p(1, 2) << endl;cout << p(1, 3) << endl;}int main(){test01();test02();return 0;}4.3.3 关系仿函数

#include #include #include #include using namespace std;class MyCompare{public:bool operator()(int v1, int v2){return v1 > v2;}};//大于 greatervoid test01(){vector<int> v;v.push_back(10);v.push_back(50);v.push_back(30);v.push_back(40);v.push_back(20);for (auto it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++)cout << *it << \" \";cout << endl;//相同//sort(v.begin(), v.end(), MyCompare());sort(v.begin(), v.end(), greater<int>());for (auto it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++)cout << *it << \" \";}int main(){test01();return 0;}4.3.4 逻辑仿函数
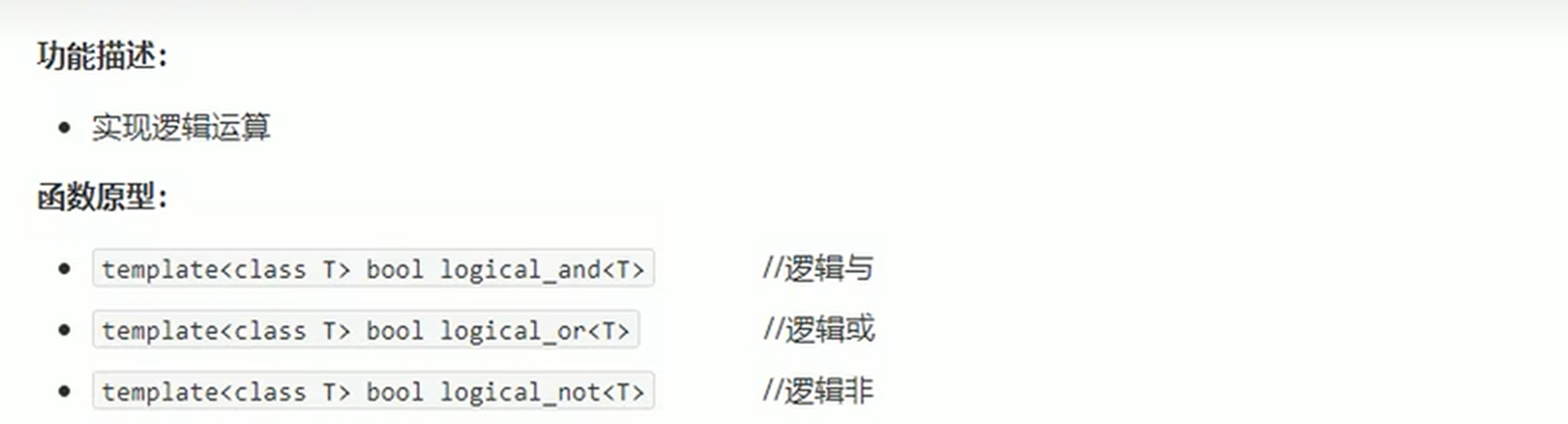
#include #include #include #include using namespace std;//逻辑非 logical_notvoid test01(){vector<bool> v;v.push_back(true);v.push_back(false);v.push_back(true);v.push_back(false);for (auto it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++)cout << *it << \" \";cout << endl;;//利用逻辑非 将容器v搬运到v2中, 并执行取反操作vector<bool> v2;//必须提前开辟空间v2.resize(v.size());transform(v.begin(), v.end(),v2.begin(), logical_not<bool>());for (auto it = v2.begin(); it != v2.end(); it++)cout << *it << \" \";}int main(){test01();return 0;}- 逻辑仿函数实际应用很少,了解即可.
5. STL - 常用算法
- 算法主要由头文件
组成 是所有STL头文件中最大的一个,范围涉及到比较,交换,查找,遍历,复制,修改等等。体积小,只包括几个序列上面进行简单数学运算的模板算法。定义了一些模板类,用以声明函数对象
5.1 常用的遍历算法
掌握常用的遍历算法
for_each遍历容器transform搬运容器到另一个容器中
5.1.1 for_each
-
for_each(iterator beg, iterator end, _func); -
beg开始迭代器,end结束迭代器,_func函数或者函数对象
#include #include #include using namespace std;//普通函数void print01(int val){cout << val << \" \";}void test01(){vector<int> v;for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)v.push_back(i);for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), print01);cout << endl;}// 函数对象(仿函数)class print02{public:void operator()(int val){cout << val << \" \";}};void test02(){vector<int> v;for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)v.push_back(i);for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), print02());cout << endl;}int main(){test01();test01();return 0;}5.1.2 transform
transform(iterator beg1, iterator end1, iterator beg2, _func);- beg1 源容器开始迭代器, end1源容器结束迭代器,beg2 目标容器开始迭代器, _func 函数或者函数对象。
#include #include #include using namespace std;class TransForm{public:int operator()(int val){//支持操作return val%2;}};class MyPrint{public:void operator()(int val){cout << val << \" \";}};void test01(){vector<int> v1;for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)v1.push_back(i);vector<int> v2;//提前开辟空间v2.resize(v1.size());transform(v1.begin(), v1.end(), v2.begin(), TransForm());for_each(v2.begin(), v2.end(), MyPrint());}int main(){test01();return 0;}- 目标容器必须体检开辟空间,否则无法正常搬运。
5.2 常用的查找算法
5.2.1 find
find(iterator beg, iterator end, value)
按值来查找元素,找到返回指定位置迭代器,找不到返回结束迭代器位置
#include #include #include using namespace std;//1. 查找内置数据类型void test01(){vector<int> v;v.push_back(10);v.push_back(20);v.push_back(30);v.push_back(40);v.push_back(50);auto it = find(v.begin(), v.end(), 20);if (it == v.end()){cout << \"没有找到。\" << endl;}else{cout << \"找到了!\" << endl;}}//2. 查找自定义数据类型class Person{public:Person(string name, int age){this->m_Name = name;this->m_Age = age;}bool operator==(const Person& p){return this->m_Name == p.m_Name && this->m_Age == p.m_Age;}string m_Name;int m_Age;};void test02(){vector<Person> v;Person p1(\"aaa\", 11);Person p2(\"bbb\", 12);Person p3(\"ccc\", 13);Person p4(\"ddd\", 14);Person p5(\"eee\", 15);v.push_back(p1);v.push_back(p2);v.push_back(p3);v.push_back(p4);v.push_back(p5);Person pp(\"ccc\", 12);auto it = find(v.begin(), v.end(), pp);if (it == v.end()){cout << \"没有找到。\" << endl;}else{cout << \"找到了!\" << endl;}}int main(){//test01();test02();return 0;}5.2.2 find_if
- 按照条件查找元素
find_if(iterator beg, iterator end, _Pred);
按照 _Pred 的条件来找元素,找到返回迭代器。
_Pred 是一个函数或者谓词(返回bool类型的仿函数)
代码示例:
#include #include #include #include using namespace std;//1. 查找内置数据类型// 函数方式//bool CreateFive(int val)//{//return val > 5;//}//谓词方式class CreateFive{public:bool operator()(int val){return val > 5;}};void test01(){vector<int> v;for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++){v.push_back(i);}auto it = find_if(v.begin(), v.end(), CreateFive());if (it == v.end()){cout << \"找不到\" << endl;}else{cout << \"找到了大于5的数为: \" << *it << endl;}}//2. 查找自定义数据类型class Person{public:Person(string name, int age){this->m_Name = name;this->m_Age = age;}string m_Name;int m_Age;};class Greater20{public:bool operator()(const Person& p){return p.m_Age > 20;}};void test02(){vector<Person> v;Person p1(\"aaa\", 10);Person p2(\"bbb\", 21);Person p3(\"ccc\", 15);Person p4(\"ddd\", 40);v.push_back(p1);v.push_back(p2);v.push_back(p3);v.push_back(p4);auto it = find_if(v.begin(), v.end(), Greater20());if (it == v.end()){cout << \"没找到!\" << endl;}else{cout << \"找到了 姓名: \" << it->m_Name << \" 年龄: \" << it->m_Age << endl;}}int main(){//test01();test02();return 0;}5.2.3 adjacent_find
- 查找相邻重复元素
adjacent_find(iterator beg, iterator end)
查找相邻重复元素,返回相邻元素的第一个位置的迭代器
代码示例:
#include #include #include using namespace std;void test01(){vector<int> v;v.push_back(1);v.push_back(3);v.push_back(4);v.push_back(5);v.push_back(5);auto it = adjacent_find(v.begin(), v.end());if (it == v.end()){cout << \"没有找到! \" << endl;}else{cout << \"找到了他是:\" << *it << endl;}}int main(){test01();return 0;}5.2.4 binary_search
- 查找指定元素是否存在
bool binary_search(iterator beg, iterator end, value);
查找指定的元素,查到返回true,查不到返回false。
注意必须在有序序列中查找。
#include #include #include using namespace std;void test01(){vector<int> v;for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)v.push_back(i);//必须是有序的//无序序列结果未知。if (binary_search(v.begin(), v.end(), 8)){cout << \"找到了 \" << endl;}else{cout << \"没有找到 \" << endl;}}int main(){test01();return 0;}5.2.5 count
- 统计元素个数
count(iterator beg, iterator end, value);
统计在beg到end这个区间内出现的次数。
#include #include #include #include using namespace std;//1. 统计内置数据类型void test01(){vector<int> v;v.push_back(1);v.push_back(1);v.push_back(2);v.push_back(2);v.push_back(2);v.push_back(3);int ret = count(v.begin(), v.end(), 2);cout << ret << endl;}//2. 统计自定义数据类型class Person{public:Person(string name, int age){this->n_Name = name;this->m_Age = age;}bool operator==(const Person& p){return this->m_Age == p.m_Age;}string n_Name;int m_Age;};void test02(){vector<Person> v;Person p1(\"xl\", 21);Person p2(\"N9\", 21);Person p3(\"DBQ\", 21);Person p4(\"Ayom\", 25);v.push_back(p1);v.push_back(p2);v.push_back(p3);v.push_back(p4);Person p5(\"577\", 21);int ret = count(v.begin(), v.end(), p5);cout << \"和\" << p5.n_Name << \"同岁的有: \" << ret << \" 个\" << endl;}int main(){//test01();test02();return 0;}5.2.6 count_if
- 按条件统计元素个数
count_if(iterator beg, iterator end, _Pred);
从beg到end这个区间里面按照谓词_Pred里面的条件统计元素的个数。
#include #include #include #include using namespace std;//1. 内置数据类型class Greater2{public:bool operator()(int v){return v > 2;}};void test01(){vector<int> v;v.push_back(1);v.push_back(2);v.push_back(3);v.push_back(4);v.push_back(5);int ret = count_if(v.begin(), v.end(), Greater2());cout << ret << endl;}//2. 自定义数据类型class Person{public:Person(string name, int age){this->m_Name = name;this->m_Age = age;}string m_Name;int m_Age;};class Greater18{public:bool operator()(const Person& p){return p.m_Age > 18;}};void test02(){vector<Person> v;Person p1(\"aaa\", 13);Person p2(\"bbb\", 18);Person p3(\"ccc\", 22);Person p4(\"ddd\", 25);Person p5(\"ddd\", 31);Person p6(\"ddd\", 100);v.push_back(p1);v.push_back(p2);v.push_back(p3);v.push_back(p4);v.push_back(p5);v.push_back(p6);int ret = count_if(v.begin(), v.end(), Greater18());cout << ret << endl;}int main(){//test01();test02();return 0;}5.3 常用的排序算法
5.3.1 sort
-
给容器排序
-
sort(iterator beg, iterator end, _Pred);
将区间beg到end排序,默认从小到大,_Pred谓词可以改变排序顺序。
#include #include #include #include using namespace std;void Myprint(int val){cout << val << \" \";}void test01(){vector<int> v;v.push_back(2);v.push_back(5);v.push_back(1);v.push_back(3);v.push_back(4);sort(v.begin(), v.end());for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), Myprint);cout << endl;//降序sort(v.begin(), v.end(), greater<int>());for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), Myprint);}int main(){test01();return 0; }5.3.2 random_shuffle
- 洗牌 指定范围内的元素随机调整次序
random_shuffle(iterator beg, iterator end);
#include #include #include #include using namespace std;void test01(){srand((unsigned)time(NULL));vector<int> v;for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)v.push_back(i);random_shuffle(v.begin(), v.end());for (auto it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++)cout << *it << \" \";cout << endl;}int main(){test01();return 0;}用的时候记得加随机数种子
5.3.3 merge
- 将两个容器合并,并存储到另一个容器中
merge(iterator beg1, end1, beg2, end2, dest);
将两个有序的容器合并到dest目标容器。
#include #include #include using namespace std;void test01(){vector<int> v1;vector<int> v2;//有序序列for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++){v1.push_back(i);v2.push_back(i+1);}//必须有足够的空间vector<int> v3;v3.resize(v1.size() + v2.size());merge(v1.begin(), v1.end(), v2.begin(), v2.end(), v3.begin());for (auto it = v3.begin(); it != v3.end(); it++)cout << *it << \" \";cout << endl;}int main(){test01();return 0;}5.3.4 reverse
- 将容器内元素进行反转
reverse(iterator beg, iterator end);
反转beg到end区间内元素。
#include #include #include using namespace std;void test01(){vector<int> v1;for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++){v1.push_back(i);}reverse(v1.begin(), v1.end());for (auto it = v1.begin(); it != v1.end(); it++)cout << *it << \" \";cout << endl;}int main(){test01();return 0;}5.4 常用的拷贝和替换算法
5.4.1 copy
- 拷贝函数
copy(iterator beg, iterator end, iterator dest);
将beg到end区间的元素全部拷贝到dest目标容器中,dest是目标起始迭代器。
#include #include #include using namespace std;void test01(){vector<int> v1;for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)v1.push_back(i);vector<int> v2;v2.resize(v1.size());copy(v1.begin(), v1.end(), v2.begin());for (auto it = v2.begin(); it != v2.end(); it++)cout << *it << \" \";cout << endl;}int main(){test01();return 0;}5.4.2 replace
- 将容器内指定范围的旧元素修改为新元素。
replace(iterator beg, iterator end, oldvalue, newvalue);
将区间beg到end中的oldvalue改为newvalue
#include #include #include using namespace std;void test01(){vector<int> v1;v1.push_back(1);v1.push_back(2);v1.push_back(1);v1.push_back(2);v1.push_back(1);//将1 改为 10//replace(v1.begin(), v1.end(), 1, 10);for (auto it = v1.begin(); it != v1.end(); it++)cout << *it << \" \";cout << endl;}int main(){test01();return 0;}5.4.3 replace_if
- 将区间内满足条件的元素,替换成指定元素。
replace_if(iterator beg, iterator end, _Pred, newvalue);
将去区间内,满足_Pred条件的全部替换为newvalue.
#include #include #include #include using namespace std;class Greater2{public:bool operator()(int val){return val > 2;}};//1. 内置数据类型void test01(){vector<int> v1;v1.push_back(1);v1.push_back(2);v1.push_back(3);v1.push_back(4);v1.push_back(5);for (auto it = v1.begin(); it != v1.end(); it++)cout << *it << \" \";cout << endl;replace_if(v1.begin(), v1.end(), Greater2(), 2);for (auto it = v1.begin(); it != v1.end(); it++)cout << *it << \" \";cout << endl;}//2. 自定义数据类型class Person{public:Person(string name, int age){this->m_Name = name;this->m_Age = age;}string m_Name;int m_Age;};class Greater18{public:bool operator()(const Person& p){return p.m_Age > 18;}};void test02(){vector<Person> v;Person p1(\"aaa\", 18);Person p2(\"aaa\", 21);Person p3(\"aaa\", 30);Person p4(\"aaa\", 12);Person p5(\"aaa\", 13);v.push_back(p1);v.push_back(p2);v.push_back(p3);v.push_back(p4);v.push_back(p5);for (auto it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++)cout << \"姓名:\" << it->m_Name << \" 年龄: \" << it->m_Age;cout << endl;Person pp(\"ccc\", 18);replace_if(v.begin(), v.end(), Greater18(), pp);for (auto it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++)cout << \"姓名:\" << it->m_Name << \" 年龄: \" << it->m_Age;cout << endl;}int main(){//test01();test02();return 0;}5.4.4 swap
- 互换两个相同容器的元素
swap(container c1, container c2)
不仅可以互换容器,还可以互换以下。
int* p1, *p2; std::swap(p1, p2);shared_ptr, unique_ptr)int a[10], int b[10])#include #include #include using namespace std;void myPrint(int val){cout << val << \" \";}void test01(){vector<int> v1, v2;for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++){v1.push_back(i);v2.push_back(i + 10);}cout << \"交换前: \" << endl;for_each(v1.begin(), v1.end(), myPrint);cout << endl;for_each(v2.begin(), v2.end(), myPrint);cout << endl;cout << \"--------------------------------------\" << endl;cout << \"交换后: \" << endl;swap(v1, v2);for_each(v1.begin(), v1.end(), myPrint);cout << endl;for_each(v2.begin(), v2.end(), myPrint);cout << endl;}int main(){test01();return 0;}5.5 常用的算术生成算法
头文件
5.5.1 accumulate
- 计算区间内容器元素积累总和
accumlate(iterator beg, iterator end, value);
将区间内的元素和加起来,value是起始累加值
#include #include #include using namespace std;void test01(){vector<int> v;for (int i = 0; i <= 100; i++)v.push_back(i);int total = accumulate(v.begin(), v.end(), 1000); // + 1000cout << total << endl;}int main(){test01();return 0;}5.5.2 fill
- 向函数中填充指定的元素
fill(iterator beg, iterator end, value);
将区间内的元素填充成value
#include #include #include using namespace std;void test01(){vector<int> v;v.resize(10);//后期填充fill(v.begin(), v.end(), 10);for (auto it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++)cout << *it << \" \";cout << endl;}int main(){test01();return 0;}5.6 常用的集合算法
掌握交集,并集,差集。
5.6.1 set_intersection
-
交集,两个容器共同出现的元素。
-
set_intersection(beg1,end1,beg2,end2,dest)
将两个容器的交集置于目标容器中去,dest为目标容器的起始迭代器, 返回交集最后一个迭代器。
#include #include #include using namespace std;void test01(){vector<int> v1, v2;for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++){v1.push_back(i);v2.push_back(i + 5); // 5~14}vector<int> v3;//最特殊的情况就是一个容器包含另一个容器v3.resize(min(v1.size(), v2.size()));auto itEnd = set_intersection(v1.begin(), v1.end(), v2.begin(), v2.end(), v3.begin());for (auto it = v3.begin(); it != itEnd; it++)cout << *it << \" \";cout << endl;}int main(){test01();return 0;}5.6.2 set_union
- 并集,两个有序容器合并。
set_union(beg1,end1,beg2,end2,dest)
将两个容器取并集,必须是有序容器,然后返回并集后的最后一个迭代器。
#include #include #include using namespace std;void test01(){ vector<int> v1, v2; for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { v1.push_back(i); v2.push_back(i + 5); // 5~14 } vector<int> v3; //最特殊的情况就是两个容器元素全部不一样,需要全部合并。 v3.resize(v1.size() + v2.size()); auto itEnd = set_union(v1.begin(), v1.end(), v2.begin(), v2.end(), v3.begin()); for (auto it = v3.begin(); it != itEnd; it++) cout << *it << \" \"; cout << endl;}int main(){ test01(); return 0;}5.6.3 set_difference
- 差集:属于集合 A 但不属于集合 B 的元素
set_union(beg1,end1,beg2,end2,dest)
将两个容器的差集,放入目标容器中去,但要注意谁与谁的差集。
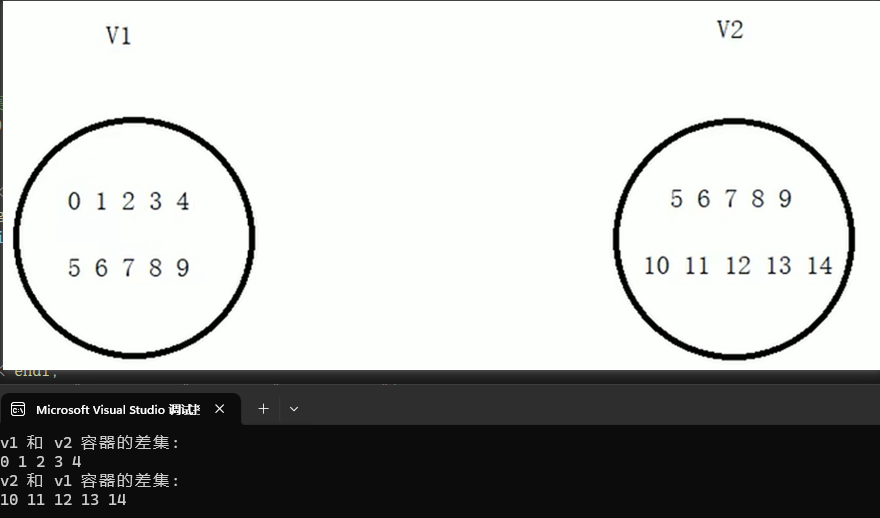
#include #include #include using namespace std;void test01(){vector<int> v1, v2;for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++){v1.push_back(i);v2.push_back(i + 5); // 5~14}vector<int> v3;//最特殊的情况就是两个容器没有交集,取最大的容器即可v3.resize(max(v1.size(), v2.size()));cout << \"v1 和 v2 容器的差集: \" << endl;auto itEnd = set_difference(v1.begin(), v1.end(), v2.begin(), v2.end(), v3.begin());for (auto it = v3.begin(); it != itEnd; it++)cout << *it << \" \";cout << endl;cout << \"v2 和 v1 容器的差集: \" << endl;itEnd = set_difference(v2.begin(), v2.end(), v1.begin(), v1.end(), v3.begin());for (auto it = v3.begin(); it != itEnd; it++)cout << *it << \" \";cout << endl;}int main(){test01();return 0;}课程结束🎉🌸,完美收官!👏🌟


