【c++】STL容器-unordered_map/unordered_set的封装(逐步完善讲解)
小编个人主页详情<—请点击
小编个人gitee代码仓库<—请点击
c++系列专栏<—请点击
倘若命中无此运,孤身亦可登昆仑,送给屏幕面前的读者朋友们和小编自己!
目录
-
- 前言
- 一、哈希表模板参数以及节点的改造
- 二、哈希表的普通迭代器
-
- 普通迭代器
- 哈希表的普通迭代器
- 三、unordered_set基本框架
-
-
- 测试
-
- 四、unordered_map基本框架
-
-
- 测试
-
- 五、如何限制unordered_set的key值不被修改
-
-
- 测试
- 给哈希表添加const迭代器
- const迭代器
- 哈希表的const迭代器
- 修改unordered_set
-
- 测试
- 测试
- 修改迭代器
-
- 测试
-
- 六、如何限制unordered_map的key值不被修改
-
- 修改unordered_map
-
- 测试
- 七、给unordered_map添加operator[ ]
-
- Find
- Erase
- Insert
- 修改unordered_set中函数的返回值
- 修改unordered_map中函数的返回值以及编写operator[ ]
-
- 测试
- 八、源代码
-
- UnOrderedSet.h
- UnOrderedMap.h
- HashTable.h
- Test.cpp
- 总结
前言
【c++】STL容器-哈希概念介绍、哈希冲突的解决(闭散列和开散列)——书接上文 详情请点击<——
本文由小编为大家介绍——STL容器-unordered_map/unordered_set的封装
本文的unordered_map/unordered_set的封装的底层封装的是哈希表,哈希表我们采用开散列(链地址法\\哈希桶)的方式实现,本文是基于开散列文章的基础上进行讲解,其中使用到的相关概念以及源代码和开散列文章的相关性极大,所以在阅读学习本文前,请读者友友先阅读学习哈希冲突的解决(开散列) 详情请点击<——
同样的,unordered_map/unordered_set的封装和红黑树封装map/set在很多地方都具有相似之处,例如哈希表模板参数K,T,KeyOfT的设置,unordered_map/unordered_set中限制key不能修改的措施等,都可以参考【c++】STL容器——使用红黑树模拟实现map和set(由浅入深逐步完善3w字详解)详情请点击<—— 进行学习,小编基于红黑树模拟实现map/set的文章的基础上进行讲解
一、哈希表模板参数以及节点的改造
- 哈希表的模板参数中的K是key,用于erase和find的函数参数进行设计,T是节点中实际存储的类型,对于unordered_map则是pair,对于unordered_set则是key
- KeyOfT是仿函数,用于提取key,和map/set的相同类似,详细细节请点击后方蓝字学习 详情请点击<——
template<class K, class T, class KeyOfT, class HashFunC = DefaultHashFunc<K>>class HashTable- 那么哈希表的节点的模板参数就要改成T,为了模板泛型考虑适用于unordered_map/unordered_set,更改如下
template<class T>struct HashNode{T _data;HashNode<T>* _next;HashNode(const T& data):_data(data),_next(nullptr){}};二、哈希表的普通迭代器
普通迭代器
- 迭代器的本质就是模拟指针的行为,哈希表的迭代器类似于list,封装一个节点的指针,使用运算符重载,模拟指针的行为
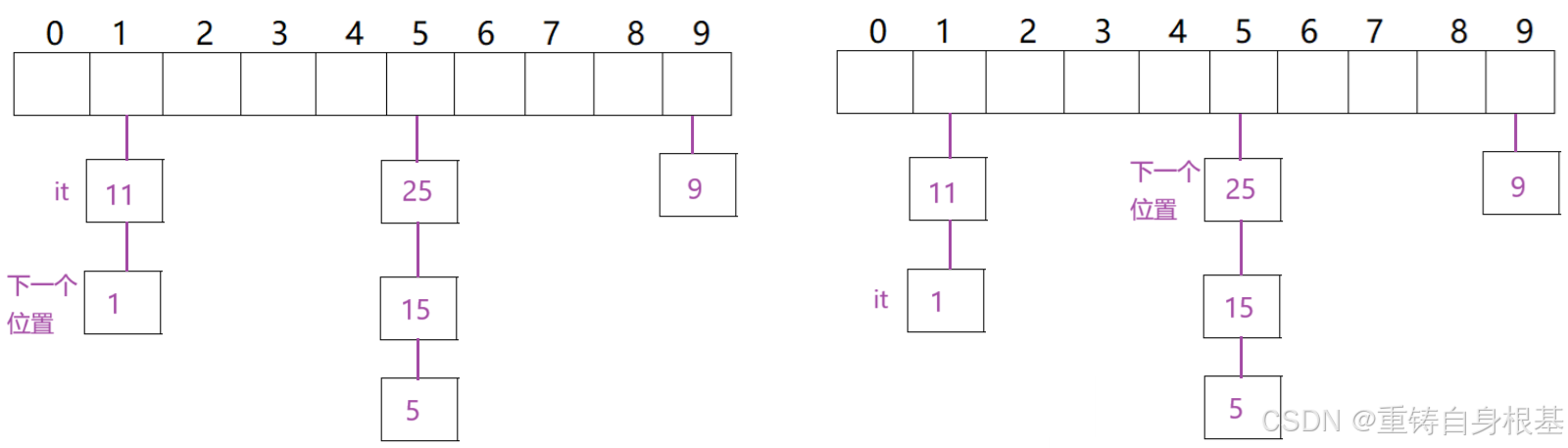
- 以上图的左图为例,如果it位于11节点这个位置,那么进行++仅需要将节点指向它的下一个1节点即可
- 以上图的右图为例,如果it位于1这个位置,那么进行++需要指针指向25这个节点,那么我们该如何做到呢?如果仅凭借当前这个指向1的节点的指针是断然没有办法进行++的,因为它的下一个位置的指针就是空nullptr了,这时候我们就要思考,如何做?
- 我们知道1这个节点,可以提取出它的关键码,使用哈希函数算出它当前的哈希地址,可是仅仅有哈希地址也没有办法在表中去找下一个存储节点指针不为空的位置,此时小编有一个大胆的想法,我们能否将哈希表的指针传过去,那么这样就什么都不缺了,应有尽有,此时我们就可以利用我们算出的1的这个节点的哈希地址去在表中向后去找下一个存储节点指针不为空的位置了,找到了让迭代器的指针指向那个节点指针不为空的位置上存储节点的指针,如果找不到节点指针不为空的位置,那么就说明此时哈希表已经遍历完成,我们采用空nullptr来标志结束,让迭代器的指针指向空即可
- 那么我们就可以实现出一个普通版本的迭代器了
- 但是还需要特别注意一点,迭代器中有使用的哈希表,哈希表中又对迭代器进行了使用,那么这样就形成了相互依赖关系,那么编译器在编译迭代器的时候,只会默认向前去找哈希表,而哈希表的代码又是在迭代器后面,那么我们应该使用一个模板声明,让编译器在编译的时候先不要报错,打一针安定剂,等到后面哈希表模板实例化后再去后面去找
template<class K, class T, class KeyOfT, class HashFunC>//这里必须去掉缺省值class HashTable;//哈希表模板的声明template<class K, class T, class KeyOfT, class HashFunC>struct HTIterator{typedef HashNode<T> Node;typedef HTIterator<K, T, KeyOfT, HashFunC> Self;Node* _node;HashTable<K, T, KeyOfT, HashFunC>* _pht;HTIterator(Node* node, HashTable<K, T, KeyOfT, HashFunC>* pht):_node(node), _pht(pht){}Self& operator++(){if (_node->_next){_node = _node->_next;return *this;}else{HashFunC hf;KeyOfT kot;size_t hashi = hf(kot(_node->_data)) % _pht->_table.size();hashi++;while (hashi < _pht->_table.size()){if (_pht->_table[hashi]){_node = _pht->_table[hashi];return *this;}else{hashi++;}}_node = nullptr;}return *this;}bool operator!=(const Self& it){return _node != it._node;}T& operator*(){return _node->_data;}T* operator->(){return &_node->_data;}};哈希表的普通迭代器
- 由于普通迭代器中使用了哈希表的指针去访问哈希表的表_table,_table表又是哈希表的私有成员变量,在类外无法访问,所以我们要让普通迭代器成为哈希表的朋友,即在哈希表中添加普通迭代器类模板的友元声明,注意,类模板的友元声明要将模板参数一并带上
- 对于迭代器begin返回的应该是哈希表中第一个不为空的节点指针的迭代器,那么我们遍历表_table去寻找即可,有一点值得注意,如果找到了那么返回由那个节点的指针和this指针构造的迭代器即可,这个this指针实际上就是我们要传入迭代器的哈希表的指针
- 对于迭代器的end返回空节点和this构造的迭代器即可
template<class K, class T, class KeyOfT, class HashFunC = DefaultHashFunc<K>>class HashTable{typedef HashNode<T> Node;template<class K, class T, class KeyOfT, class HashFunC>friend struct HTIterator;public:typedef HTIterator<K, T, KeyOfT, HashFunC> iterator;iterator begin(){for (size_t i = 0; i < _table.size(); i++){if (_table[i]){return iterator(_table[i], this);}}return iterator(nullptr, this);}iterator end(){return iterator(nullptr, this);}private:vector<Node*> _table;size_t _n = 0;};那么我们后续的任务就是先把unordered_map/unordered_set这两个容器的框架搭起来,简单封装一下哈希表的迭代器以及插入接口,让我们普通迭代器可以跑起来
三、unordered_set基本框架
- 同样的对于unordered_set,我们需要类似set的形式,写一个SetKeyOfT的仿函数去提取哈希表节点中存储的key,这里其实对于unordered_set来讲哈希表节点中存储的本身就是key,这里是我们接收到后返回即可,其实这里是为了兼容unordered_map
- 那么我们取出哈希表中的迭代器在unordered_set中将其使用typedef重命名为iterator,同时由于哈希表中的迭代器编译器不能确定哈希表中的迭代器究竟是内嵌类型(typedef的和内部类)还是静态成员变量,所以我们需要使用typename进行声明告诉编译器取出的哈希表中的迭代器是类型,在进行语法检查的时候你先跳过,等到哈希表模板实例化后再去检查是否是类型
- 那么接下来我们封装一下插入,查找,删除即可
- unordered_set中封装一个私有成员变量哈希表_ht即可,哈希表中的模板参数T的类型对应到unordered_set中是K
#pragma once#include \"HashTable.h\"namespace wzx{template<class K>class unordered_set{public:struct SetKeyOfT{const K& operator()(const K& key){return key;}};typedef typename hash_bucket::HashTable<K, K, SetKeyOfT>::iterator iterator;iterator begin(){return _ht.begin();}iterator end(){return _ht.end();}bool Insert(const K& key){return _ht.Insert(key);}hash_bucket::HashNode<const K>* Find(const K& key){return _ht.Find(key);}bool Erase(const K& key){return _ht.Erase(key);}private:hash_bucket::HashTable<K, K, SetKeyOfT> _ht;};}测试
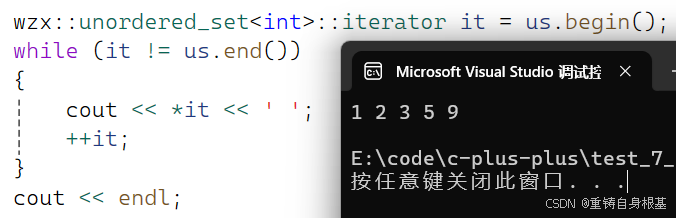
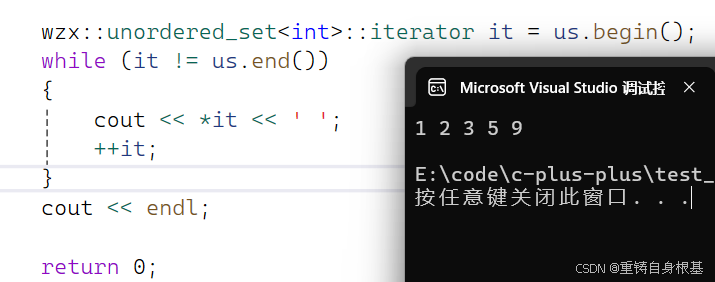
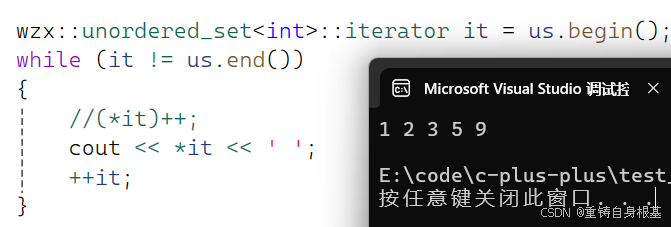
- 我们使用如下代码测试unordered_set的迭代器是否可以正常运行
#include #include using namespace std;#include \"HashTable.h\"#include \"UnorderedMap.h\"#include \"UnorderedSet.h\"int main(){wzx::unordered_set<int> us;us.Insert(1);us.Insert(5);us.Insert(2);us.Insert(9);us.Insert(3);wzx::unordered_set<int>::iterator it = us.begin();while (it != us.end()){cout << *it << \' \';++it;}cout << endl;return 0;}测试结果如下,正确
四、unordered_map基本框架
- unordered_map中需要我们编写一个MapKeyOfT将哈希表节点中存储的kv的first即key取出进行返回
- 和unordered_set类似的套路取出并重命名哈希表中的迭代器作为unordered_map的迭代器iterator
- 那么接下来我们封装一下插入,查找,删除即可
- unordered_map中封装一个私有成员变量哈希表_ht即可,哈希表中的模板参数T的类型对应到unordered_map中是pair
#pragma once#include \"HashTable.h\"namespace wzx{template<class K, class V>class unordered_map{public:struct MapKeyOfT{const K& operator()(const pair<K, V>& kv){return kv.first;}};typedef typename hash_bucket::HashTable<K, pair<K, V>, MapKeyOfT>::iterator iterator;iterator begin(){return _ht.begin();}iterator end(){return _ht.end();}bool Insert(const pair<K, V>& kv){return _ht.Insert(kv);}hash_bucket::HashNode<const pair<K, V>>* Find(const K& key){return _ht.Find(key);}bool Erase(const K& key){return _ht.Erase(key);}private:hash_bucket::HashTable<K, pair<K, V>, MapKeyOfT> _ht;};}测试
- 我们使用如下代码测试unordered_set的迭代器是否可以正常运行
int main(){wzx::unordered_map<int, int> um;um.Insert(make_pair(11, 11));um.Insert(make_pair(22, 22));um.Insert(make_pair(323, 323));um.Insert(make_pair(113, 113));um.Insert(make_pair(55, 55));um.Insert(make_pair(66, 66));um.Insert(make_pair(56, 56));um.Insert(make_pair(44, 44));um.Insert(make_pair(89, 89));um.Insert(make_pair(98, 98));um.Insert(make_pair(1, 1));um.Insert(make_pair(12, 12));for (auto& kv : um){cout << kv.first << \':\' << kv.second << endl;}return 0;}运行结果如下,正确
五、如何限制unordered_set的key值不被修改
测试
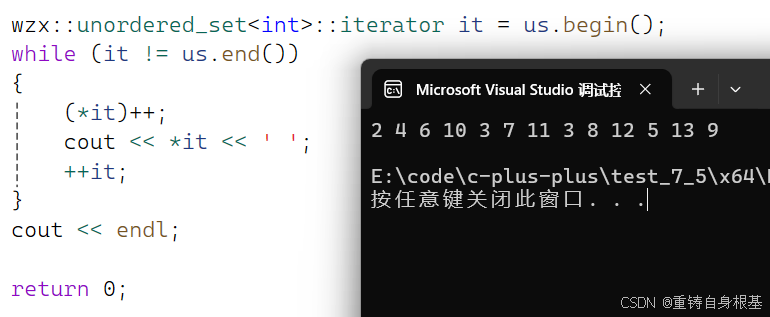
int main(){wzx::unordered_set<int> us;us.Insert(1);us.Insert(5);us.Insert(2);us.Insert(9);us.Insert(3);wzx::unordered_set<int>::iterator it = us.begin();while (it != us.end()){(*it)++;cout << *it << \' \';++it;}cout << endl;return 0;}同样是上述unordered_set的迭代器的测试代码,小编可以给*it进行++,我们知道unordered_set的key值是不能修改的,所以我们的迭代器不应该出现 (*it) 进行++,如果出现了那么要直接给报错,那么我们应该如何才能进行限制呢?
给哈希表添加const迭代器
参照set的限制方式,其set限制key不能修改的使用红黑树的const迭代器作为set的普通迭代器,所以这里我们的unordered_set中限制key不能修改也应该要使用哈希表的const迭代器作为unordered_set的普通迭代器,那么接下来我们就要给哈希表添加const迭代器
const迭代器
- 添加方式也很简单,无非就是新增加两个模板参数Ptr, Ref即可,同时给operator*的返回值给上Ref,operator->的返回值给上Ptr即可完成同一份模板类,给不同的类型就可以实例化出普通迭代器也可以实例化出const迭代器
template<class K, class T, class KeyOfT, class HashFunC>class HashTable;template<class K, class T, class Ptr, class Ref, class KeyOfT, class HashFunC>struct HTIterator{typedef HashNode<T> Node;typedef HTIterator<K, T, Ptr, Ref, KeyOfT, HashFunC> Self;Node* _node;HashTable<K, T, KeyOfT, HashFunC>* _pht;HTIterator(Node* node, HashTable<K, T, KeyOfT, HashFunC>* pht):_node(node), _pht(pht){}Self& operator++(){if (_node->_next){_node = _node->_next;return *this;}else{HashFunC hf;KeyOfT kot;size_t hashi = hf(kot(_node->_data)) % _pht->_table.size();hashi++;while (hashi < _pht->_table.size()){if (_pht->_table[hashi]){_node = _pht->_table[hashi];return *this;}else{hashi++;}}_node = nullptr;}return *this;}bool operator!=(const Self& it){return _node != it._node;}Ref operator*(){return _node->_data;}Ptr operator->(){return &_node->_data;}};哈希表的const迭代器
- 使用typedef并且传入不同参数的Iterator类去实例化出不同的迭代器进行重命名为普通迭代器和const迭代器即可
- 同时添加const迭代器版本的begin和end即可
- 同时由于Iterator的模板参数增加了Ptr和Ref所以由于Iterator是哈希表的友元类,所以Iterator在哈希表中的友元声明要更改
template<class K, class T, class KeyOfT, class HashFunC = DefaultHashFunc<K>>class HashTable{typedef HashNode<T> Node;template<class K, class T,class Ptr, class Ref, class KeyOfT, class HashFunC>friend struct HTIterator;public:typedef HTIterator<K, T, T*, T&, KeyOfT, HashFunC> iterator;typedef HTIterator<K, T, const T*, const T&, KeyOfT, HashFunC> const_iterator;iterator begin(){for (size_t i = 0; i < _table.size(); i++){if (_table[i]){return iterator(_table[i], this);}}return iterator(nullptr, this);}iterator end(){return iterator(nullptr, this);}const_iterator begin() const{for (size_t i = 0; i < _table.size(); i++){if (_table[i]){return const_iterator(_table[i], this);}}return const_iterator(nullptr, this);}const_iterator end() const{return const_iterator(nullptr, this);}private:vector<Node*> _table;size_t _n = 0;};修改unordered_set
- 那么我们将哈希表的const迭代器作为unordered_set的普通迭代器,将哈希表的const迭代器作为unordered_set的const迭代器即可
- 同时将unordered_set中的begin和end函数加上const修饰适配普通迭代器和const迭代器即可
template<class K>class unordered_set{public:typedef typename hash_bucket::HashTable<K, K, SetKeyOfT>::const_iterator iterator;typedef typename hash_bucket::HashTable<K, K, SetKeyOfT>::const_iterator const_iterator;iterator begin() const{return _ht.begin();}iterator end() const{return _ht.end();}};测试
进行测试一下我们修改后的迭代器,对于我们在循环内修改key值的操作被编译器报错了,成功的限制了key值不能被修改
测试
小编循环内修改key值的语句去掉,测试迭代器能否正常运行
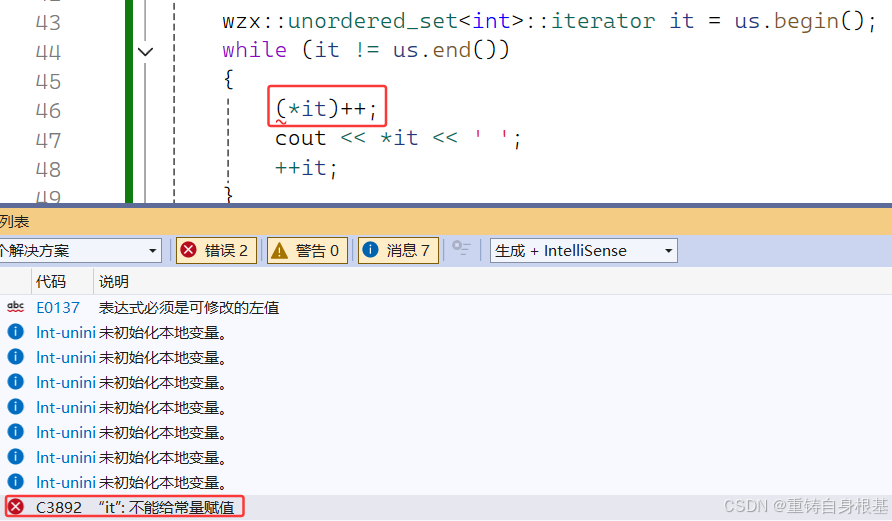
- 运行结果如下,迭代器运行失败
- 那么我们思考一下为什么运行失败

修改迭代器
- 所以小编就根据上面的推论将迭代器类模板进行修改
template<class K, class T, class Ptr, class Ref, class KeyOfT, class HashFunC>struct HTIterator{typedef HashNode<T> Node;typedef HTIterator<K, T, Ptr, Ref, KeyOfT, HashFunC> Self;Node* _node;const HashTable<K, T, KeyOfT, HashFunC>* _pht;HTIterator(Node* node, const HashTable<K, T, KeyOfT, HashFunC>* pht):_node(node), _pht(pht){}};测试
- 修改完成迭代器后,我们继续进行测试,这一次迭代器可以正常运行了
测试结果如下,正常
六、如何限制unordered_map的key值不被修改
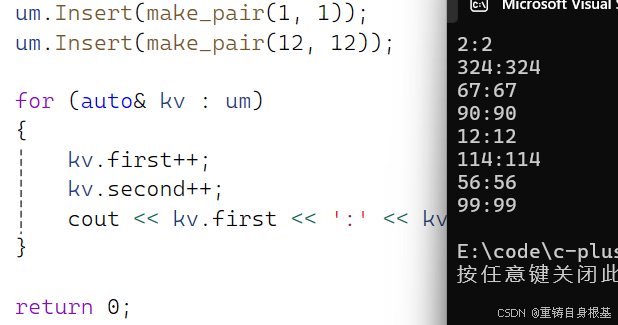
- 我们使用如下代码测试小编当前编写的unordered_map是否可以修改key值
int main(){wzx::unordered_map<int, int> um;um.Insert(make_pair(11, 11));um.Insert(make_pair(22, 22));um.Insert(make_pair(323, 323));um.Insert(make_pair(113, 113));um.Insert(make_pair(55, 55));um.Insert(make_pair(66, 66));um.Insert(make_pair(56, 56));um.Insert(make_pair(44, 44));um.Insert(make_pair(89, 89));um.Insert(make_pair(98, 98));um.Insert(make_pair(1, 1));um.Insert(make_pair(12, 12));for (auto& kv : um){kv.first++;kv.second++;cout << kv.first << \':\' << kv.second << endl;}return 0;}运行结果如下
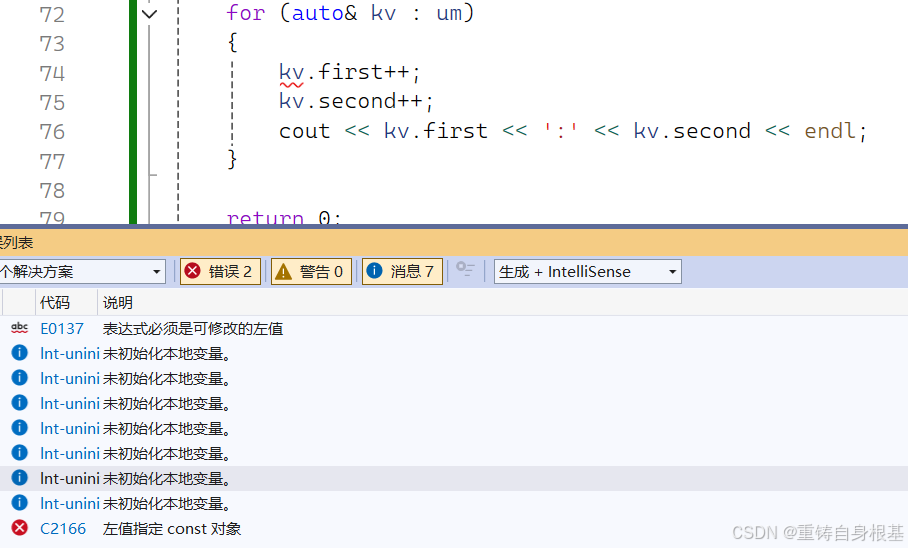
- 可以进行修改key值和value值,那么我们应该如何做才能限制key值的修改,同时让value值可以被修改呢?
我们可以类似于map中在pair中的第一个key加上const进行修饰,那么就可以进行限制,同时value值可以进行修改
修改unordered_map
- 小编给unordered_map中的pair的key使用const进行修饰,同时添加const迭代器
#pragma once#include \"HashTable.h\"namespace wzx{template<class K, class V>class unordered_map{public:struct MapKeyOfT{const K& operator()(const pair<const K, V>& kv){return kv.first;}};typedef typename hash_bucket::HashTable<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyOfT>::iterator iterator;typedef typename hash_bucket::HashTable<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyOfT>::const_iterator const_iterator;iterator begin(){return _ht.begin();}iterator end(){return _ht.end();}iterator begin() const{return _ht.begin();}iterator end() const{return _ht.end();}bool Insert(const pair<const K, V>& kv){return _ht.Insert(kv);}hash_bucket::HashNode<const pair<const K, V>>* Find(const K& key){return _ht.Find(key);}bool Erase(const K& key){return _ht.Erase(key);}private:hash_bucket::HashTable<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyOfT> _ht;};}测试
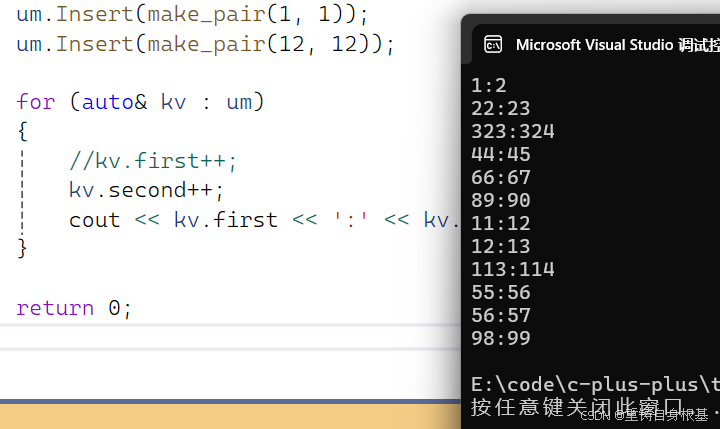
- 再次进行测试,能否限制key值的修改
运行结果如下,正确,可以限制key值的修改
- 将修改key的操作去掉看能否正常运行,同时让value值可以被修改
运行结果如下,正确,value值可以被修改
七、给unordered_map添加operator[ ]
我们知道库中的operator[ ]是复用的Insert,其中Insert的返回值是一个pair,小编编写的Insert是bool类型,所以要进行修改Insert,但是Insert中有调用的Find,那么库中的Find的返回值是一个迭代器,那么我们就要先修改一下Find的返回值,Find的返回值修改好之后顺带修改一下Erase中调用的Find,由于哈希表中的底层接口的返回值都进行了修改,那么上层的unordered_map和unordered_set的函数的返回值也要一并进行修改,连锁反应,下面小编带领大家逐一进行修改
Find
- Find的返回值应该是一个迭代器,所以我们进行如下修改即可
iterator Find(const K& key){HashFunC hf;size_t hashi = hf(key) % _table.size();if (_table[hashi]){Node* cur = _table[hashi];KeyOfT kot;while (cur){if (kot(cur->_data) == key){return iterator(cur, this);}cur = cur->_next;}}return iterator(nullptr, this);}Erase
- Erase中只需要使用迭代器接收一下Find进行判断即可
bool Erase(const K& key){iterator it = Find(kot(key));if (it._node == nullptr){return false;}HashFunC hf;size_t hashi = hf(key) % _table.size();KeyOfT kot;Node* prev = nullptr;Node* cur = _table[hashi];while (cur){if (kot(cur->_data) == key){if (prev == nullptr){_table[hashi] = nullptr;}else{prev->_next = cur->_next;}delete cur;_n--;break;}prev = cur;cur = cur->_next;}return true;}Insert
- 使用迭代器接收一下Find进行判断
- 返回值使用make_pair进行返回
pair<iterator, bool> Insert(const T& data){KeyOfT kot;iterator it = Find(kot(data));if (it._node){return make_pair(it, false);}HashFunC hf;if (_n == _table.size()){size_t newsize = _table.size() * 2;vector<Node*> newtable;newtable.resize(newsize, nullptr);for (int i = 0; i < _table.size(); i++){Node* cur = _table[i];while (cur){Node* next = cur->_next;size_t hashi = hf(kot(cur->_data)) % newtable.size();cur->_next = newtable[hashi];newtable[hashi] = cur;cur = next;}_table[i] = nullptr;}_table.swap(newtable);}size_t hashi = hf(kot(data)) % _table.size();Node* cur = new Node(data);cur->_next = _table[hashi];_table[hashi] = cur;_n++;return make_pair(iterator(cur, this), true);}修改unordered_set中函数的返回值
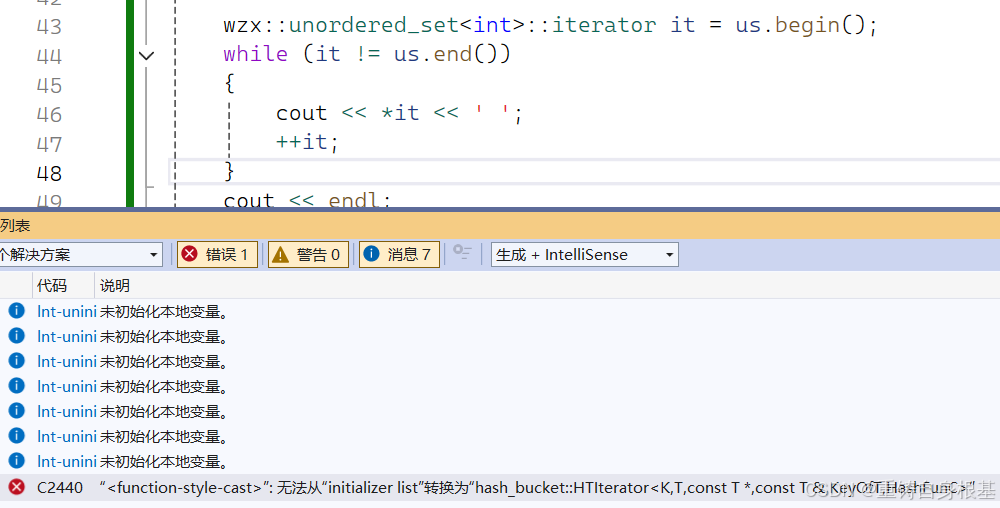
- 修改插入,删除,查找如下,关于插入由于类型和哈希表的插入的返回值类型不匹配,所以要先使用一个相同类型pair的进行接收,接着调用pair的构造函数构造出和插入的返回值相同类型的pair进行返回,关于插入下面紧接着就是详细讲解,请读者友友继续向下阅读
#pragma once#include \"HashTable.h\"namespace wzx{template<class K>class unordered_set{public:struct SetKeyOfT{const K& operator()(const K& key){return key;}};typedef typename hash_bucket::HashTable<K, K, SetKeyOfT>::const_iterator iterator;typedef typename hash_bucket::HashTable<K, K, SetKeyOfT>::const_iterator const_iterator;iterator begin() const{return _ht.begin();}iterator end() const{return _ht.end();}pair<iterator, bool> Insert(const K& key){pair<typename hash_bucket::HashTable<K, K, SetKeyOfT>::iterator, bool> kv = _ht.Insert(key);return pair<iterator, bool>(kv.first, kv.second);}iterator Find(const K& key){return _ht.Find(key);}bool Erase(const K& key){return _ht.Erase(key);}private:hash_bucket::HashTable<K, K, SetKeyOfT> _ht;};}- 在unordered_set由于其普通迭代器和const迭代器都是const迭代器,所以在unordered_set中的Insert的返回值返回的pair实际上的迭代器是const迭代器
- _ht调用Insert的返回值的是pair,其中的迭代器是普通迭代器,那么这里就会出现类型不匹配,报错结果如下
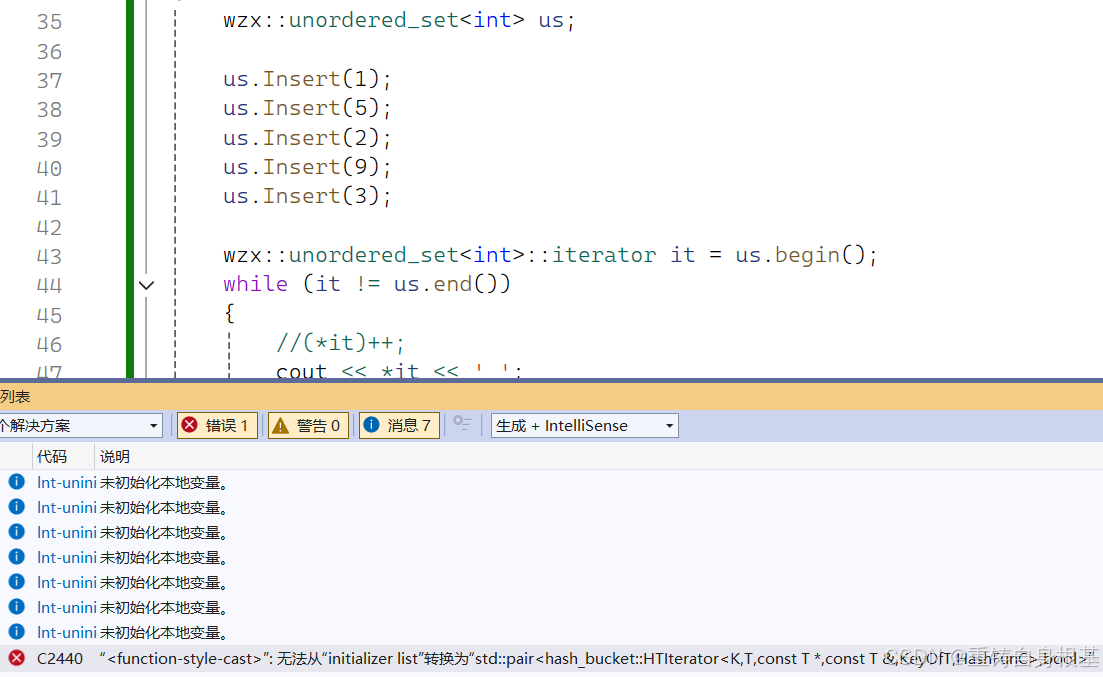
- 那么我们接下来就要对哈希表的迭代器进行修改,添加一个普通迭代器类型,编写一个构造函数,即可以让普通迭代器转化构造出const迭代器,那么当迭代器模板类实例化为const迭代器的时候,我们的构造该构造函数就是构造函数,当迭代器模板类实例化为普通迭代器的时候,我们该构造函数就是拷贝构造函数
template<class K, class T, class Ptr, class Ref, class KeyOfT, class HashFunC>struct HTIterator{typedef HashNode<T> Node;typedef HTIterator<K, T, Ptr, Ref, KeyOfT, HashFunC> Self;typedef HTIterator<K, T, T*, T&, KeyOfT, HashFunC> Iterator;//普通迭代器类型Node* _node;const HashTable<K, T, KeyOfT, HashFunC>* _pht;HTIterator(Node* node, const HashTable<K, T, KeyOfT, HashFunC>* pht):_node(node), _pht(pht){}HTIterator(const Iterator& it)//模板类被实例化为普通迭代器的时候就是拷贝构造函数:_node(it._node) //模板类被实例化为const迭代器的时候就是构造函数,_pht(it._pht){}};此时经过改进之后我们的代码就可以正常跑了
修改unordered_map中函数的返回值以及编写operator[ ]
- 将插入,删除,查找的函数的返回值进行修改即可
- 同时调用插入编写operator[ ],返回value即可
#pragma once#include \"HashTable.h\"namespace wzx{template<class K, class V>class unordered_map{public:struct MapKeyOfT{const K& operator()(const pair<const K, V>& kv){return kv.first;}};typedef typename hash_bucket::HashTable<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyOfT>::iterator iterator;typedef typename hash_bucket::HashTable<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyOfT>::const_iterator const_iterator;iterator begin(){return _ht.begin();}iterator end(){return _ht.end();}iterator begin() const{return _ht.begin();}iterator end() const{return _ht.end();}pair<iterator, bool> Insert(const pair<const K, V>& kv){return _ht.Insert(kv);}V& operator[](const K& key){pair<iterator, bool> kv = Insert(make_pair(key, V()));return kv.first->second;}iterator Find(const K& key){return _ht.Find(key);}bool Erase(const K& key){return _ht.Erase(key);}private:hash_bucket::HashTable<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyOfT> _ht;};}测试
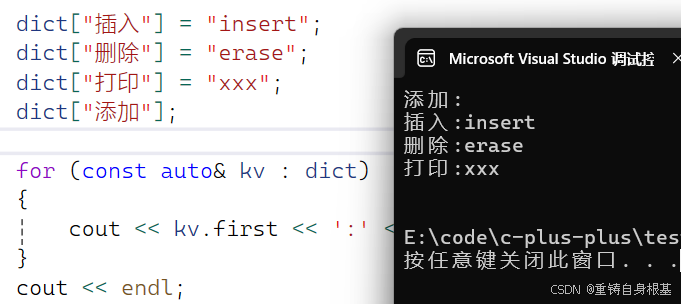
- 我们使用如下代码测试,小编编写的unordered_map的operator[ ]是否可以正常运行
int main(){wzx::unordered_map<string, string> dict;dict[\"插入\"] = \"insert\";dict[\"删除\"] = \"erase\";dict[\"打印\"] = \"xxx\";dict[\"添加\"];for (const auto& kv : dict){cout << kv.first << \':\' << kv.second << endl;}cout << endl;return 0;}运行结果如下,正确
八、源代码
UnOrderedSet.h
#pragma once#include \"HashTable.h\"namespace wzx{template<class K>class unordered_set{public:struct SetKeyOfT{const K& operator()(const K& key){return key;}};typedef typename hash_bucket::HashTable<K, K, SetKeyOfT>::const_iterator iterator;typedef typename hash_bucket::HashTable<K, K, SetKeyOfT>::const_iterator const_iterator;iterator begin() const{return _ht.begin();}iterator end() const{return _ht.end();}pair<iterator, bool> Insert(const K& key){pair<typename hash_bucket::HashTable<K, K, SetKeyOfT>::iterator, bool> kv = _ht.Insert(key);return pair<iterator, bool>(kv.first, kv.second);}iterator Find(const K& key){return _ht.Find(key);}bool Erase(const K& key){return _ht.Erase(key);}private:hash_bucket::HashTable<K, K, SetKeyOfT> _ht;};}UnOrderedMap.h
#pragma once#include \"HashTable.h\"namespace wzx{template<class K, class V>class unordered_map{public:struct MapKeyOfT{const K& operator()(const pair<const K, V>& kv){return kv.first;}};typedef typename hash_bucket::HashTable<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyOfT>::iterator iterator;typedef typename hash_bucket::HashTable<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyOfT>::const_iterator const_iterator;iterator begin(){return _ht.begin();}iterator end(){return _ht.end();}iterator begin() const{return _ht.begin();}iterator end() const{return _ht.end();}pair<iterator, bool> Insert(const pair<const K, V>& kv){return _ht.Insert(kv);}V& operator[](const K& key){pair<iterator, bool> kv = Insert(make_pair(key, V()));return kv.first->second;}iterator Find(const K& key){return _ht.Find(key);}bool Erase(const K& key){return _ht.Erase(key);}private:hash_bucket::HashTable<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyOfT> _ht;};}HashTable.h
#pragma oncetemplate<class K>struct DefaultHashFunc{size_t operator()(const K& key){return key;}};template<>struct DefaultHashFunc<string>{size_t operator()(const string str){size_t ret = 0;for (size_t i = 0; i < str.size(); i++){ret *= 131;ret += str[i];}return ret;}};namespace hash_bucket{template<class T>struct HashNode{T _data;HashNode<T>* _next;HashNode(const T& data):_data(data), _next(nullptr){}};template<class K, class T, class KeyOfT, class HashFunC>class HashTable;template<class K, class T, class Ptr, class Ref, class KeyOfT, class HashFunC>struct HTIterator{typedef HashNode<T> Node;typedef HTIterator<K, T, Ptr, Ref, KeyOfT, HashFunC> Self;typedef HTIterator<K, T, T*, T&, KeyOfT, HashFunC> Iterator;Node* _node;const HashTable<K, T, KeyOfT, HashFunC>* _pht;HTIterator(Node* node, const HashTable<K, T, KeyOfT, HashFunC>* pht):_node(node), _pht(pht){}HTIterator(const Iterator& it):_node(it._node),_pht(it._pht){}Self& operator++(){if (_node->_next){_node = _node->_next;return *this;}else{HashFunC hf;KeyOfT kot;size_t hashi = hf(kot(_node->_data)) % _pht->_table.size();hashi++;while (hashi < _pht->_table.size()){if (_pht->_table[hashi]){_node = _pht->_table[hashi];return *this;}else{hashi++;}}_node = nullptr;}return *this;}bool operator!=(const Self& it){return _node != it._node;}Ref operator*(){return _node->_data;}Ptr operator->(){return &_node->_data;}};template<class K, class T, class KeyOfT, class HashFunC = DefaultHashFunc<K>>class HashTable{typedef HashNode<T> Node;template<class K, class T,class Ptr, class Ref, class KeyOfT, class HashFunC>friend struct HTIterator;public:typedef HTIterator<K, T, T*, T&, KeyOfT, HashFunC> iterator;typedef HTIterator<K, T, const T*, const T&, KeyOfT, HashFunC> const_iterator;iterator begin(){for (size_t i = 0; i < _table.size(); i++){if (_table[i]){return iterator(_table[i], this);}}return iterator(nullptr, this);}iterator end(){return iterator(nullptr, this);}const_iterator begin() const{for (size_t i = 0; i < _table.size(); i++){if (_table[i]){return const_iterator(_table[i], this);}}return const_iterator(nullptr, this);}const_iterator end() const{return const_iterator(nullptr, this);}HashTable(){_table.resize(10, nullptr);}~HashTable(){for (int i = 0; i < _table.size(); i++){Node* cur = _table[i];while (cur){Node* next = cur->_next;delete cur;cur = next;}_table[i] = nullptr;}}pair<iterator, bool> Insert(const T& data){KeyOfT kot;iterator it = Find(kot(data));if (it._node){return make_pair(it, false);}HashFunC hf;if (_n == _table.size()){size_t newsize = _table.size() * 2;vector<Node*> newtable;newtable.resize(newsize, nullptr);for (int i = 0; i < _table.size(); i++){Node* cur = _table[i];while (cur){Node* next = cur->_next;size_t hashi = hf(kot(cur->_data)) % newtable.size();cur->_next = newtable[hashi];newtable[hashi] = cur;cur = next;}_table[i] = nullptr;}_table.swap(newtable);}size_t hashi = hf(kot(data)) % _table.size();Node* cur = new Node(data);cur->_next = _table[hashi];_table[hashi] = cur;_n++;return make_pair(iterator(cur, this), true);}iterator Find(const K& key){HashFunC hf;size_t hashi = hf(key) % _table.size();if (_table[hashi]){Node* cur = _table[hashi];KeyOfT kot;while (cur){if (kot(cur->_data) == key){return iterator(cur, this);}cur = cur->_next;}}return iterator(nullptr, this);}bool Erase(const K& key){iterator it = Find(kot(key));if (it._node == nullptr){return false;}HashFunC hf;size_t hashi = hf(key) % _table.size();KeyOfT kot;Node* prev = nullptr;Node* cur = _table[hashi];while (cur){if (kot(cur->_data) == key){if (prev == nullptr){_table[hashi] = nullptr;}else{prev->_next = cur->_next;}delete cur;_n--;break;}prev = cur;cur = cur->_next;}return true;}private:vector<Node*> _table;size_t _n = 0;};}Test.cpp
#include #include using namespace std;#include \"HashTable.h\"#include \"UnorderedMap.h\"#include \"UnorderedSet.h\"//int main()//{//wzx::unordered_set us;////us.Insert(1);//us.Insert(3);//us.Erase(1);//cout << us.Find(1) << endl;//////wzx::unordered_map dict;////dict.Insert(make_pair(\"sort\", \"\"));//dict.Insert(make_pair(\"insert\", \"xxx\"));//hash_bucket::HashNode<pair>* ret = dict.Find(\"insert\");////ret->_data.second = \"\";////return 0;//}//int main()//{//wzx::unordered_set us;////us.Insert(1);//us.Insert(5);//us.Insert(2);//us.Insert(9);//us.Insert(3);////wzx::unordered_set::iterator it = us.begin();//while (it != us.end())//{////(*it)++;//cout << *it << \' \';//++it;//}//cout << endl;////return 0;//}//int main()//{//wzx::unordered_map um;////um.Insert(make_pair(11, 11));//um.Insert(make_pair(22, 22));//um.Insert(make_pair(323, 323));//um.Insert(make_pair(113, 113));//um.Insert(make_pair(55, 55));//um.Insert(make_pair(66, 66));//um.Insert(make_pair(56, 56));//um.Insert(make_pair(44, 44));//um.Insert(make_pair(89, 89));//um.Insert(make_pair(98, 98));//um.Insert(make_pair(1, 1));//um.Insert(make_pair(12, 12));////for (auto& kv : um)//{////kv.first++;//kv.second++;//cout << kv.first << \':\' << kv.second << endl;//}////return 0;//}int main(){wzx::unordered_map<string, string> dict;dict[\"插入\"] = \"insert\";dict[\"删除\"] = \"erase\";dict[\"打印\"] = \"xxx\";dict[\"添加\"];for (const auto& kv : dict){cout << kv.first << \':\' << kv.second << endl;}cout << endl;return 0;}总结
以上就是今天的博客内容啦,希望对读者朋友们有帮助
水滴石穿,坚持就是胜利,读者朋友们可以点个关注
点赞收藏加关注,找到小编不迷路!