Java微服务架构设计模式详解
微服务架构已成为现代企业级应用开发的主流选择,它通过将单体应用拆分为一组小型、自治的服务来提高系统的可扩展性、可维护性和弹性。本文将深入探讨Java微服务架构的核心设计模式,结合代码示例、流程图和实际应用场景,帮助开发者构建健壮的微服务系统。
1. 微服务架构概述
微服务架构是一种将应用程序设计为一系列松耦合、可独立部署的服务集合的架构风格。每个服务围绕特定业务功能构建,拥有自己的数据存储,并通过轻量级协议(如HTTP/REST)通信。
微服务架构优势
- 技术异构性:不同服务可使用不同技术栈
- 独立部署:服务可单独部署而不影响整个系统
- 弹性设计:单个服务故障不会导致整个系统崩溃
- 可扩展性:可根据需求独立扩展特定服务
微服务架构挑战
- 分布式系统复杂性
- 服务间通信开销
- 数据一致性管理
- 运维和监控复杂度
2. 核心设计模式详解
2.1 服务拆分模式
服务拆分是微服务架构的基础,需要基于业务领域边界进行合理划分。
领域驱动设计(DDD)拆分策略
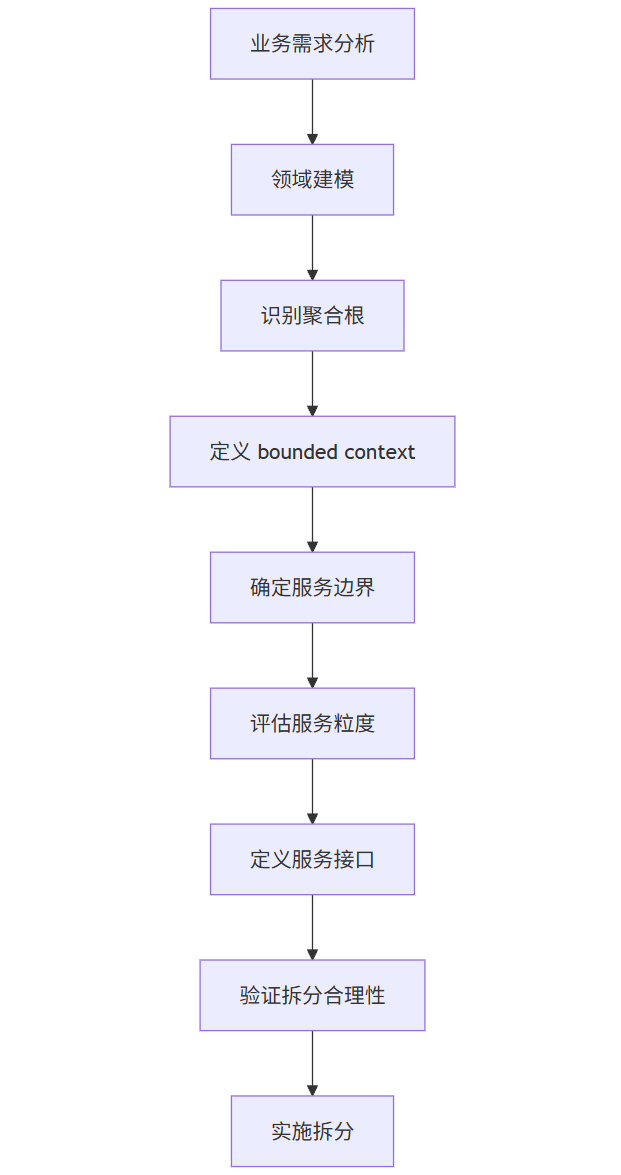
// 领域模型示例 - 订单领域public class Order { private OrderId id; private CustomerId customerId; private List items; private Money totalAmount; private OrderStatus status; public void confirm() { // 业务规则验证 if (status != OrderStatus.PENDING) { throw new IllegalStateException(\"Only pending orders can be confirmed\"); } status = OrderStatus.CONFIRMED; // 发布领域事件 DomainEventPublisher.publish(new OrderConfirmedEvent(id)); }}// 领域服务public class OrderService { private final OrderRepository orderRepository; private final PaymentService paymentService; @Transactional public Order placeOrder(OrderCommand command) { Order order = Order.create(command); orderRepository.save(order); paymentService.processPayment(order.getId(), order.getTotalAmount()); return order; }}服务拆分原则流程图
graph TD
A[业务需求分析] --> B[领域建模]
B --> C[识别聚合根]
C --> D[定义 bounded context]
D --> E[确定服务边界]
E --> F[评估服务粒度]
F --> G[定义服务接口]
G --> H[验证拆分合理性]
H --> I[实施拆分]
2.2 服务发现模式
在动态微服务环境中,服务实例需要动态注册和发现。
Eureka服务发现实现
服务注册中心 (Eureka Server)
@SpringBootApplication@EnableEurekaServerpublic class DiscoveryServerApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(DiscoveryServerApplication.class, args); }}服务提供者 (Eureka Client)
@SpringBootApplication@EnableDiscoveryClientpublic class ProductServiceApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(ProductServiceApplication.class, args); }}// 服务注册配置eureka: client: serviceUrl: defaultZone: http://localhost:8761/eureka/ instance: preferIpAddress: true服务消费者
@Servicepublic class ProductClient { private final LoadBalancerClient loadBalancer; private final RestTemplate restTemplate; public Product getProduct(Long productId) { ServiceInstance instance = loadBalancer.choose(\"PRODUCT-SERVICE\"); String url = String.format(\"http://%s:%s/products/%d\", instance.getHost(), instance.getPort(), productId); return restTemplate.getForObject(url, Product.class); }}服务发现流程图
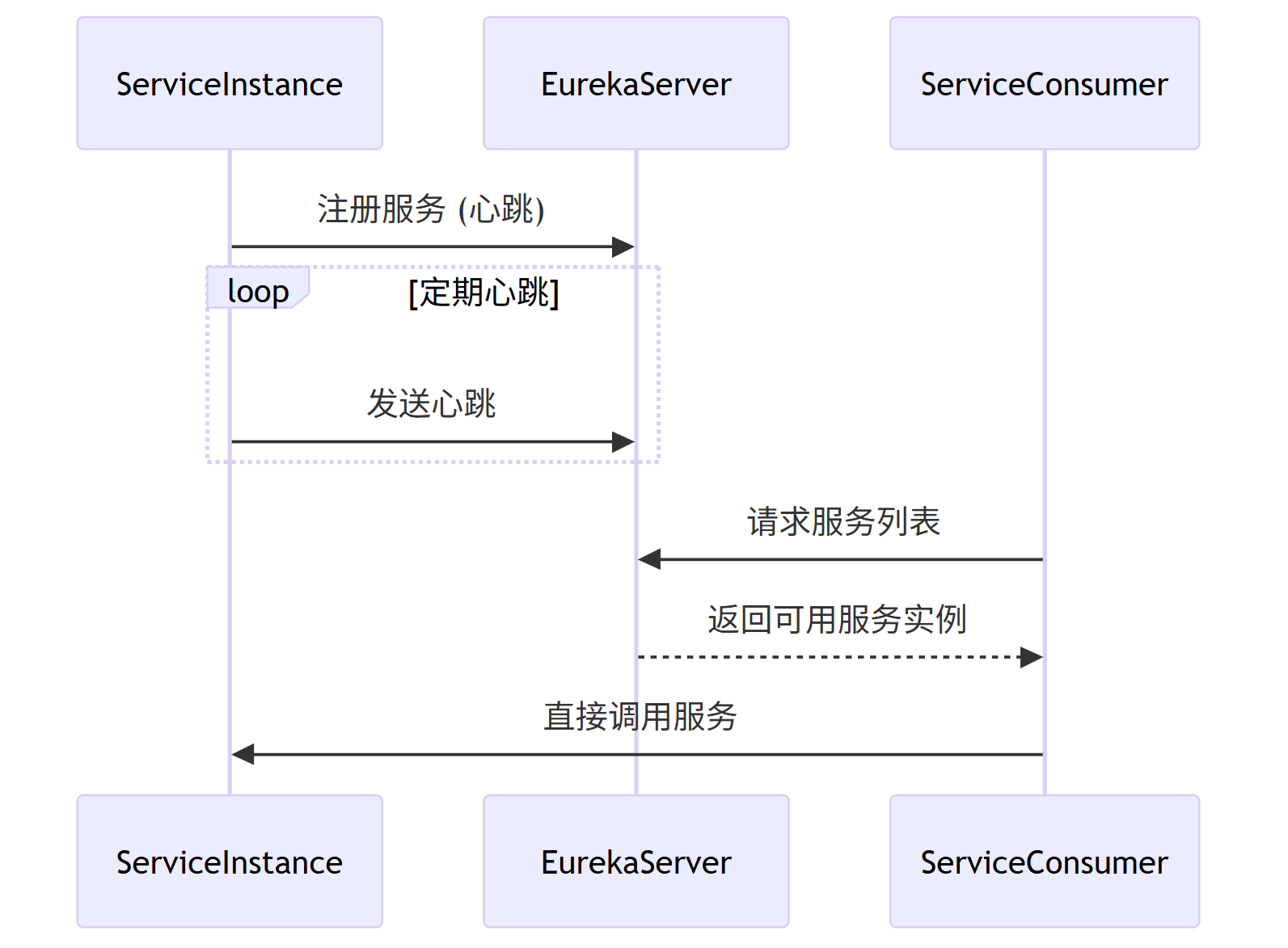
sequenceDiagram
participant ServiceInstance
participant EurekaServer
participant ServiceConsumer
ServiceInstance->>EurekaServer: 注册服务 (心跳)
loop 定期心跳
ServiceInstance->>EurekaServer: 发送心跳
end
ServiceConsumer->>EurekaServer: 请求服务列表
EurekaServer-->>ServiceConsumer: 返回可用服务实例
ServiceConsumer->>ServiceInstance: 直接调用服务
2.3 API网关模式
API网关作为微服务架构的入口点,处理请求路由、认证、限流等横切关注点。
Spring Cloud Gateway实现
@SpringBootApplicationpublic class ApiGatewayApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(ApiGatewayApplication.class, args); }}// 路由配置@Configurationpublic class GatewayConfig { @Bean public RouteLocator customRouteLocator(RouteLocatorBuilder builder) { return builder.routes() .route(\"product-service\", r -> r.path(\"/products/**\") .filters(f -> f.filter(authenticationFilter()) .filter(rateLimiterFilter()) .circuitBreaker(config -> config.setName(\"product-service-cb\"))) .uri(\"lb://PRODUCT-SERVICE\")) .route(\"order-service\", r -> r.path(\"/orders/**\") .filters(f -> f.filter(authenticationFilter())) .uri(\"lb://ORDER-SERVICE\")) .build(); } private GatewayFilter authenticationFilter() { return (exchange, chain) -> { // 认证逻辑 String authHeader = exchange.getRequest().getHeaders().getFirst(\"Authorization\"); if (authHeader == null || !authHeader.startsWith(\"Bearer \")) { exchange.getResponse().setStatusCode(HttpStatus.UNAUTHORIZED); return exchange.getResponse().setComplete(); } return chain.filter(exchange); }; } private GatewayFilter rateLimiterFilter() { return (exchange, chain) -> { // 限流逻辑 String clientId = exchange.getRequest().getHeaders().getFirst(\"X-Client-Id\"); if (rateLimiter.isAllowed(clientId)) { return chain.filter(exchange); } else { exchange.getResponse().setStatusCode(HttpStatus.TOO_MANY_REQUESTS); return exchange.getResponse().setComplete(); } }; }}API网关架构图
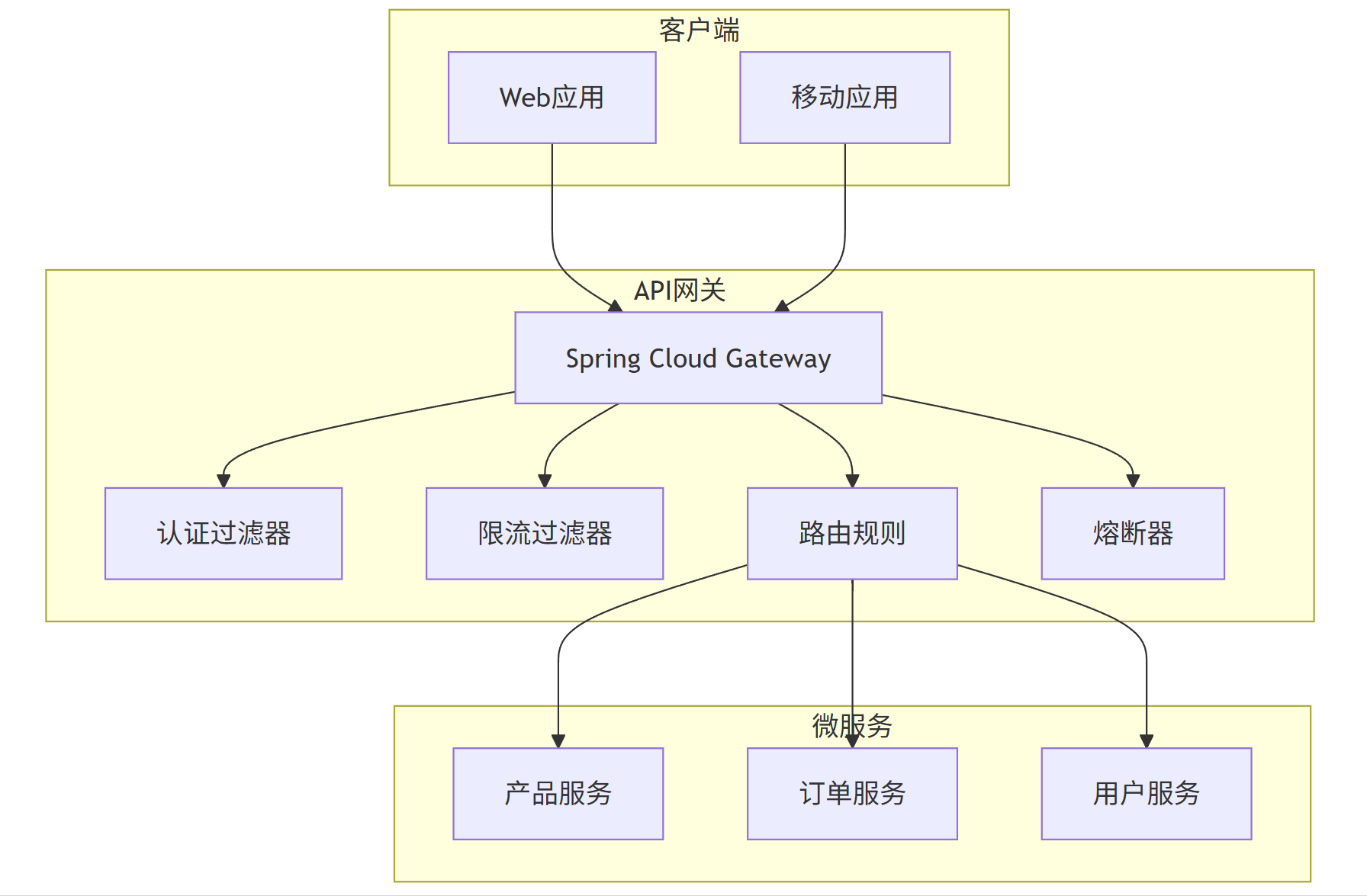
graph TB
subgraph \"客户端\"
A[Web应用]
B[移动应用]
end
subgraph \"API网关\"
C[Spring Cloud Gateway]
D[认证过滤器]
E[限流过滤器]
F[路由规则]
G[熔断器]
end
subgraph \"微服务\"
H[产品服务]
I[订单服务]
J[用户服务]
end
A --> C
B --> C
C --> D
C --> E
C --> F
C --> G
F --> H
F --> I
F --> J
2.4 配置中心模式
集中管理微服务配置,实现配置的动态更新和环境隔离。
Spring Cloud Config实现
配置服务器
@SpringBootApplication@EnableConfigServerpublic class ConfigServerApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(ConfigServerApplication.class, args); }}# 配置服务器配置spring: cloud: config: server: git: uri: https://github.com/your-repo/config-repo search-paths: \'{application}\'配置客户端
@SpringBootApplicationpublic class ProductServiceApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(ProductServiceApplication.class, args); }}# bootstrap.ymlspring: application: name: product-service cloud: config: uri: http://config-server:8888 fail-fast: true retry: initial-interval: 1000 max-interval: 2000 max-attempts: 6动态配置刷新
@RestController@RefreshScopepublic class ProductController { @Value(\"${product.discount.percentage}\") private int discountPercentage; @GetMapping(\"/products/{id}/discount\") public DiscountInfo getDiscount(@PathVariable Long id) { return new DiscountInfo(id, discountPercentage); }}配置中心架构图
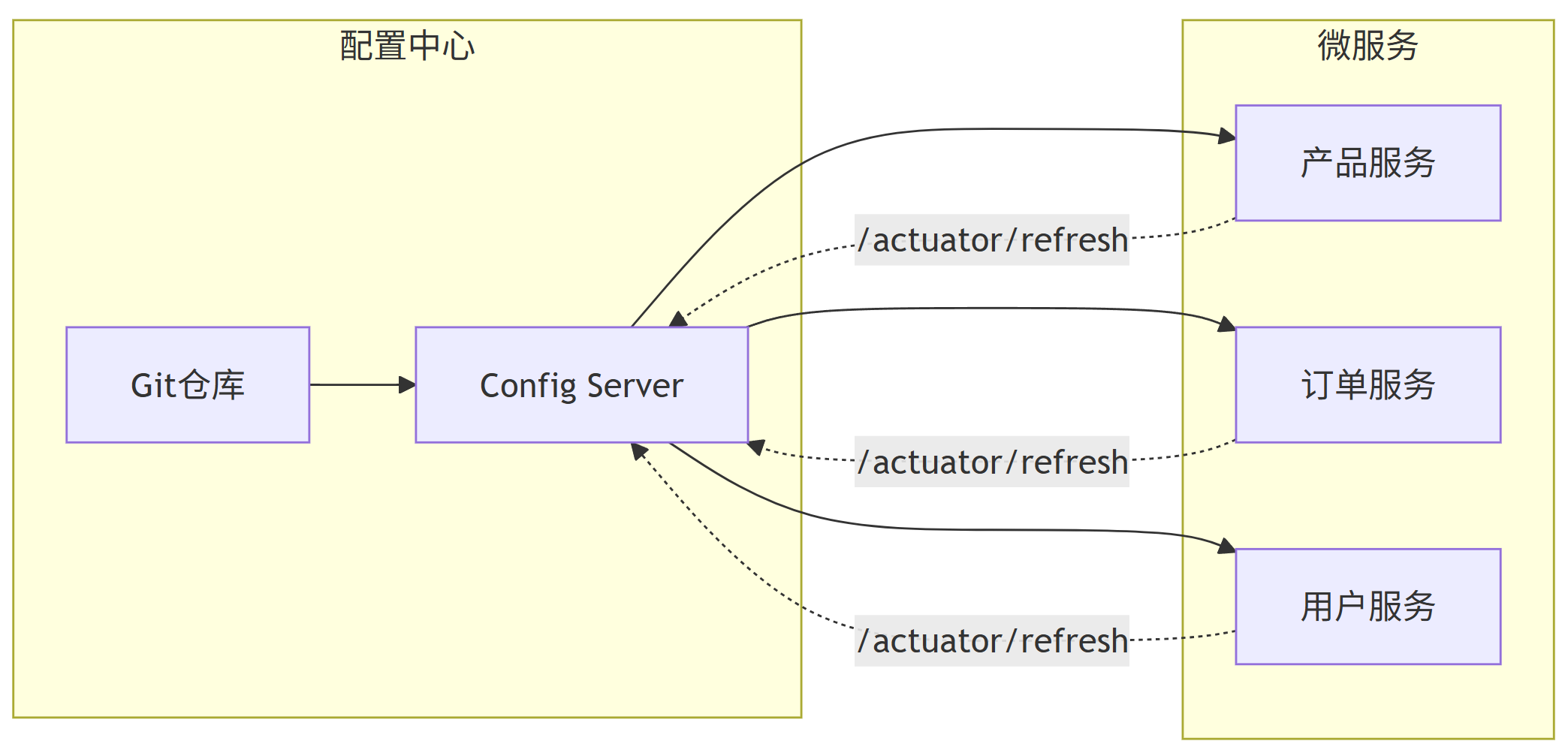
graph LR
subgraph \"配置中心\"
A[Config Server]
B[Git仓库]
end
subgraph \"微服务\"
C[产品服务]
D[订单服务]
E[用户服务]
end
B --> A
A --> C
A --> D
A --> E
C -.->|/actuator/refresh| A
D -.->|/actuator/refresh| A
E -.->|/actuator/refresh| A
2.5 熔断器模式
防止级联故障,提高系统弹性。
Resilience4j熔断器实现
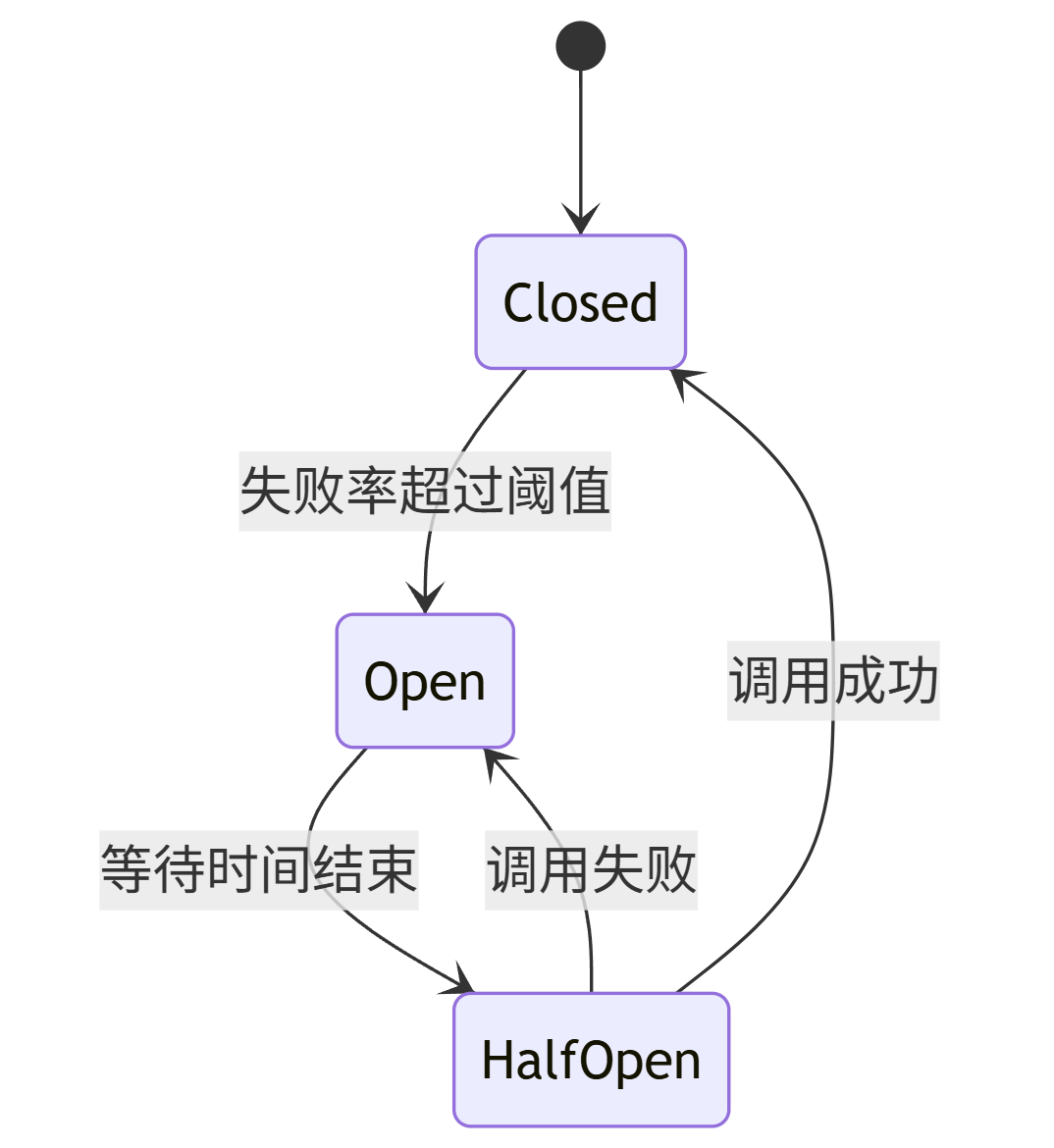
@Configurationpublic class ResilienceConfig { @Bean public CircuitBreaker orderServiceCircuitBreaker() { CircuitBreakerConfig config = CircuitBreakerConfig.custom() .failureRateThreshold(50) .waitDurationInOpenState(Duration.ofMillis(1000)) .slidingWindowSize(10) .build(); return CircuitBreaker.of(\"orderService\", config); }}@Servicepublic class OrderServiceClient { private final CircuitBreaker circuitBreaker; private final RestTemplate restTemplate; public OrderServiceClient(CircuitBreaker circuitBreaker, RestTemplate restTemplate) { this.circuitBreaker = circuitBreaker; this.restTemplate = restTemplate; } public Order getOrder(Long orderId) { return circuitBreaker.executeSupplier(() -> { try { return restTemplate.getForObject( \"http://order-service/orders/\" + orderId, Order.class); } catch (Exception e) { throw new RuntimeException(\"Order service unavailable\", e); } }); } // 降级方法 public Order getOrderFallback(Long orderId) { return new Order(orderId, \"Fallback Order\", Collections.emptyList()); }}熔断器状态转换图
stateDiagram-v2
[*] --> Closed
Closed --> Open: 失败率超过阈值
Open --> HalfOpen: 等待时间结束
HalfOpen --> Closed: 调用成功
HalfOpen --> Open: 调用失败
2.6 分布式追踪模式
跟踪请求在微服务间的完整调用链。
Spring Cloud Sleuth + Zipkin实现
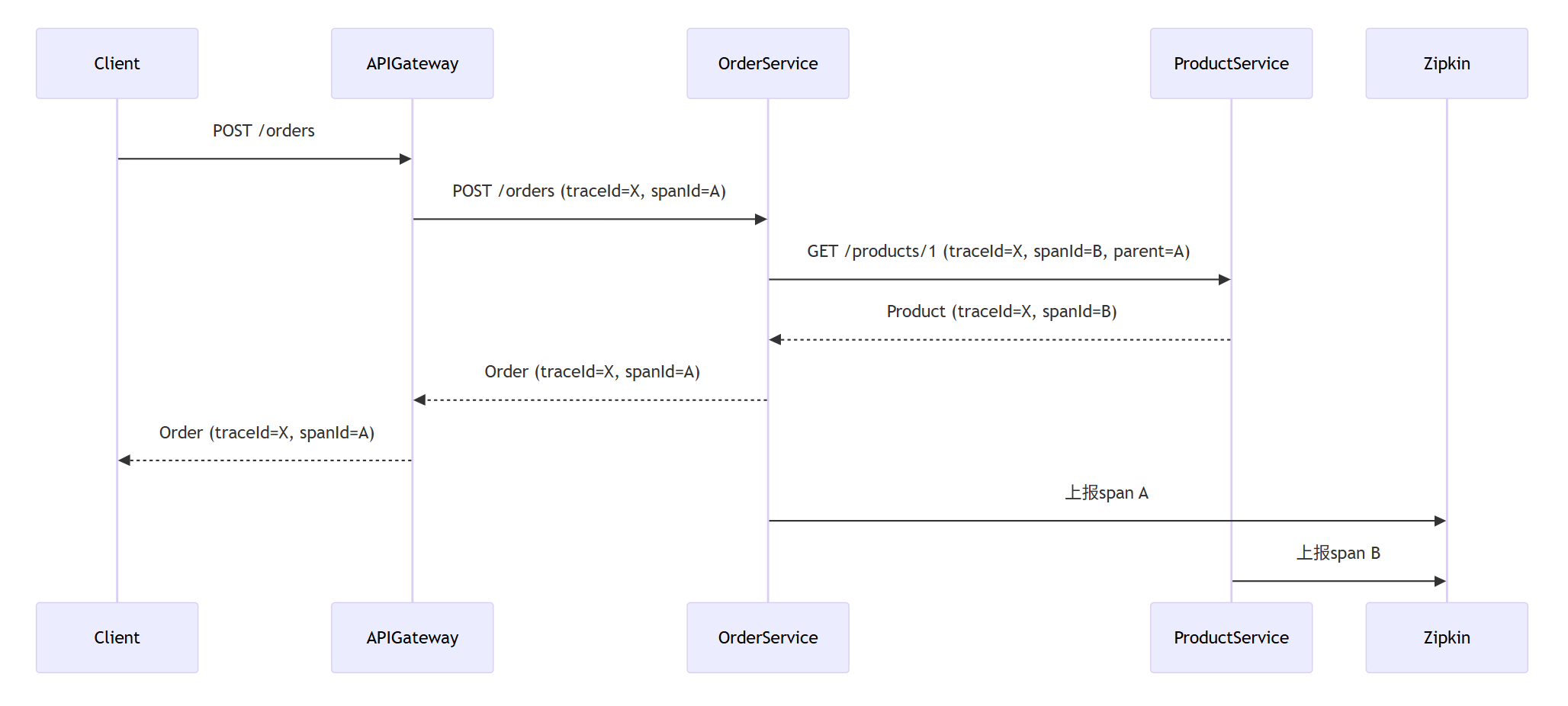
@SpringBootApplicationpublic class OrderServiceApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(OrderServiceApplication.class, args); }}# 配置spring: sleuth: sampler: probability: 1.0 zipkin: base-url: http://zipkin-server:9411/@RestControllerpublic class OrderController { private final ProductServiceClient productClient; private final Tracer tracer; @PostMapping(\"/orders\") public Order createOrder(@RequestBody OrderRequest request) { Span newSpan = tracer.nextSpan().name(\"createOrder\").start(); try (Tracer.SpanInScope ws = tracer.withSpan(newSpan.start())) { // 调用产品服务 Product product = productClient.getProduct(request.getProductId()); // 创建订单 Order order = new Order(request.getCustomerId(), product, request.getQuantity()); // 记录事件 newSpan.event(\"orderCreated\"); return orderRepository.save(order); } finally { newSpan.end(); } }}分布式追踪流程图
sequenceDiagram
participant Client
participant APIGateway
participant OrderService
participant ProductService
participant Zipkin
Client->>APIGateway: POST /orders
APIGateway->>OrderService: POST /orders (traceId=X, spanId=A)
OrderService->>ProductService: GET /products/1 (traceId=X, spanId=B, parent=A)
ProductService-->>OrderService: Product (traceId=X, spanId=B)
OrderService-->>APIGateway: Order (traceId=X, spanId=A)
APIGateway-->>Client: Order (traceId=X, spanId=A)
OrderService->>Zipkin: 上报span A
ProductService->>Zipkin: 上报span B
2.7 事件驱动模式
通过异步事件实现服务间松耦合通信。
Spring Cloud Stream实现
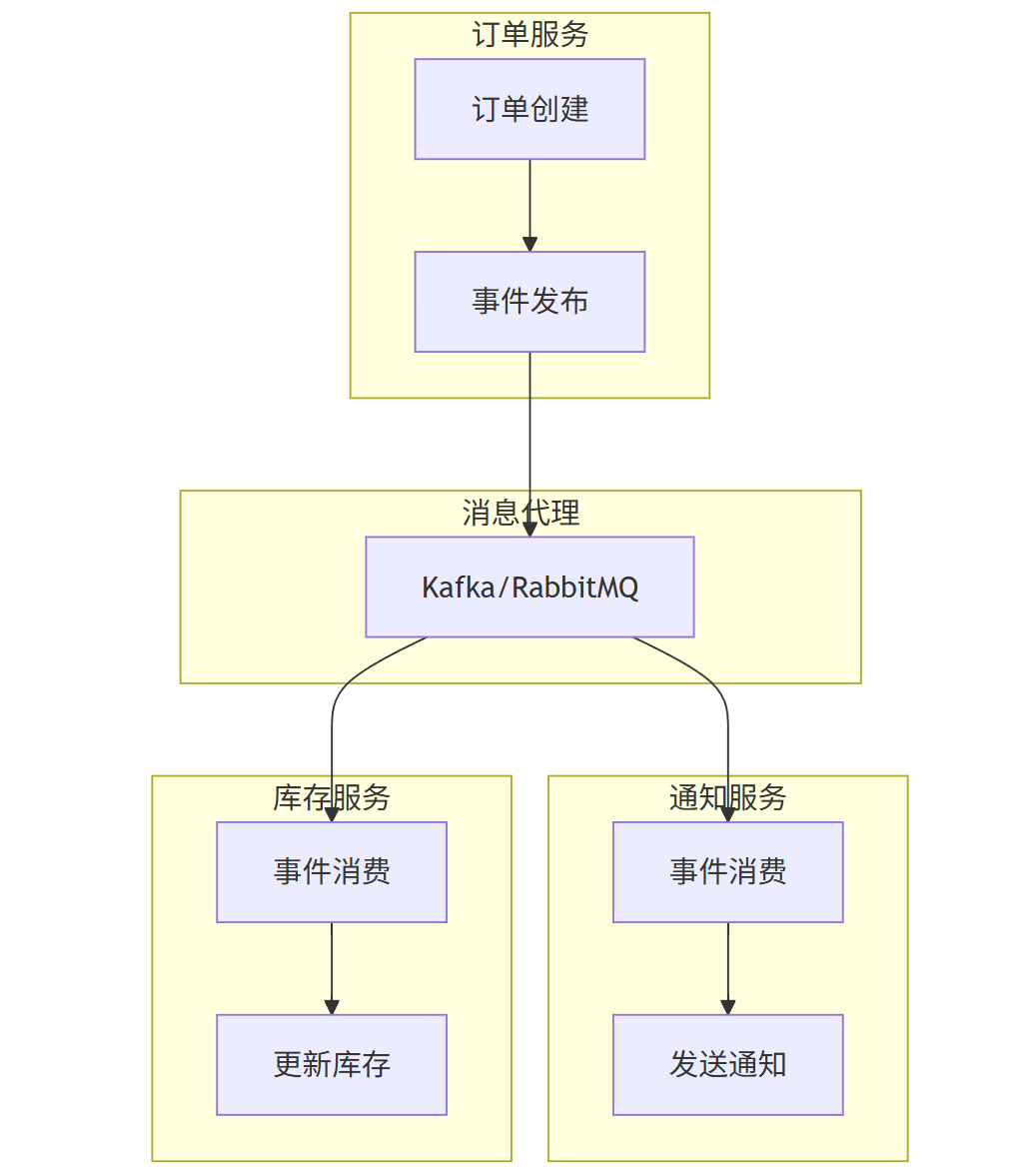
// 事件发布者@Servicepublic class OrderEventPublisher { private final StreamBridge streamBridge; public void publishOrderCreatedEvent(Order order) { OrderCreatedEvent event = new OrderCreatedEvent( order.getId(), order.getCustomerId(), order.getTotalAmount() ); streamBridge.send(\"orderCreated-out-0\", event); }}// 事件消费者@Servicepublic class OrderEventConsumer { private final NotificationService notificationService; @Bean public Consumer orderCreated() { return event -> { notificationService.sendOrderConfirmation( event.getCustomerId(), event.getOrderId() ); }; }}# 配置spring: cloud: stream: bindings: orderCreated-out-0: destination: order-created orderCreated-in-0: destination: order-created group: notification-service事件驱动架构图
graph TB
subgraph \"订单服务\"
A[订单创建]
B[事件发布]
end
subgraph \"消息代理\"
C[Kafka/RabbitMQ]
end
subgraph \"通知服务\"
D[事件消费]
E[发送通知]
end
subgraph \"库存服务\"
F[事件消费]
G[更新库存]
end
A --> B
B --> C
C --> D
D --> E
C --> F
F --> G
3. 微服务架构综合示例
3.1 电商系统微服务架构
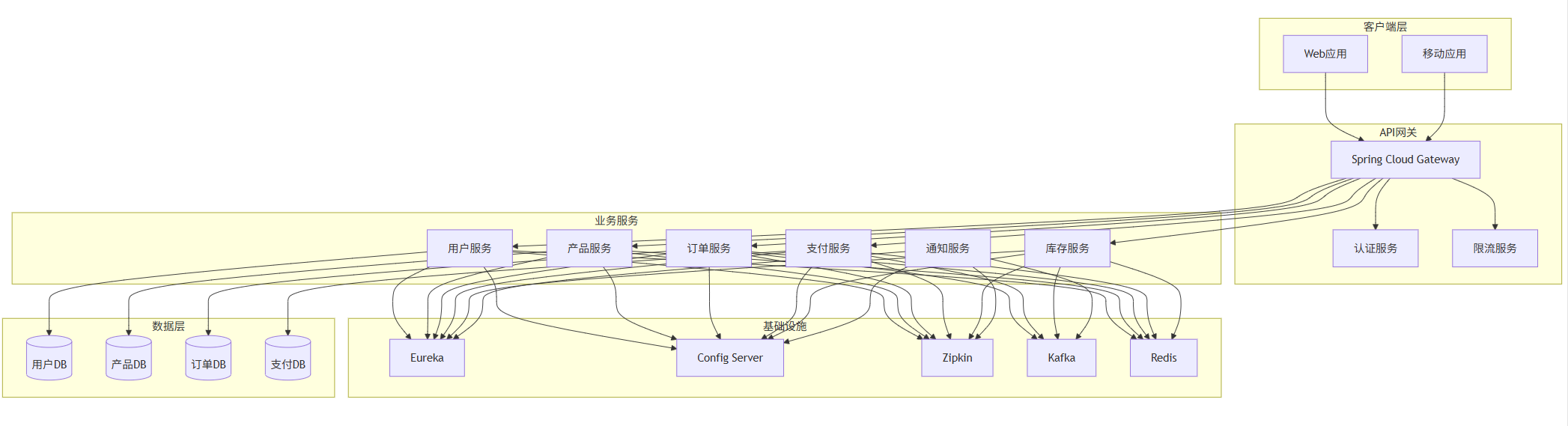
系统架构图
graph TB
subgraph \"客户端层\"
A[Web应用]
B[移动应用]
end
subgraph \"API网关\"
C[Spring Cloud Gateway]
D[认证服务]
E[限流服务]
end
subgraph \"业务服务\"
F[用户服务]
G[产品服务]
H[订单服务]
I[支付服务]
J[库存服务]
K[通知服务]
end
subgraph \"基础设施\"
L[Eureka]
M[Config Server]
N[Zipkin]
O[Kafka]
P[Redis]
end
subgraph \"数据层\"
Q[(用户DB)]
R[(产品DB)]
S[(订单DB)]
T[(支付DB)]
end
A --> C
B --> C
C --> D
C --> E
C --> F
C --> G
C --> H
C --> I
C --> J
F --> L
G --> L
H --> L
I --> L
J --> L
K --> L
F --> M
G --> M
H --> M
I --> M
J --> M
K --> M
F --> N
G --> N
H --> N
I --> N
J --> N
K --> N
H --> O
I --> O
J --> O
K --> O
F --> P
G --> P
H --> P
I --> P
J --> P
F --> Q
G --> R
H --> S
I --> T
3.2 订单处理流程
订单创建流程图
sequenceDiagram
participant Client
participant APIGateway
participant OrderService
participant ProductService
participant InventoryService
participant PaymentService
participant NotificationService
Client->>APIGateway: POST /orders
APIGateway->>OrderService: POST /orders
OrderService->>ProductService: GET /products/{id}
ProductService-->>OrderService: Product details
OrderService->>InventoryService: POST /inventory/reserve
InventoryService-->>OrderService: Reservation confirmed
OrderService->>PaymentService: POST /payments
PaymentService-->>OrderService: Payment processed
OrderService->>OrderService: Create order
OrderService->>NotificationService: Send order confirmation
OrderService-->>APIGateway: Order created
APIGateway-->>Client: Order response
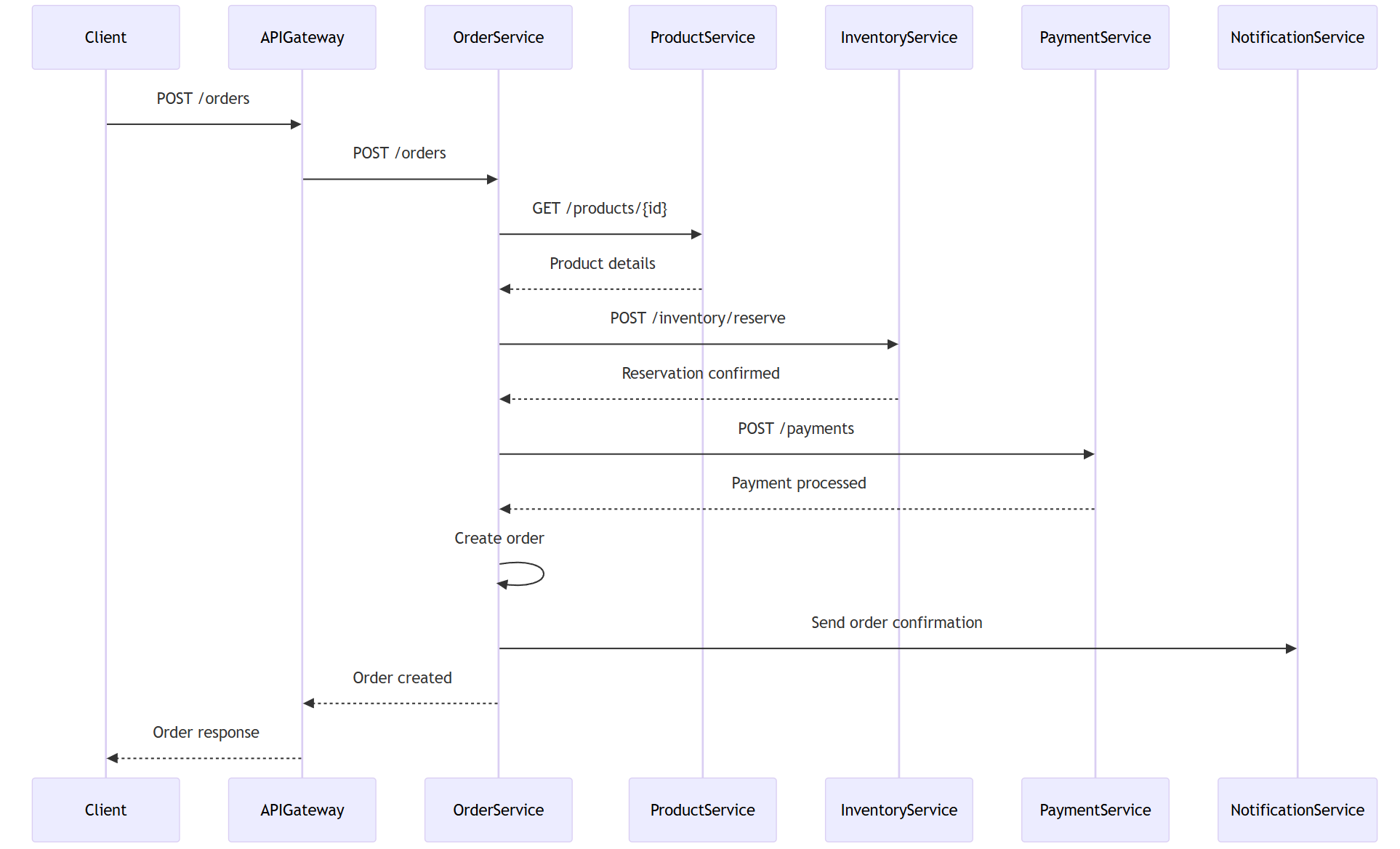
订单服务实现
@Service@Transactionalpublic class OrderService { private final OrderRepository orderRepository; private final ProductServiceClient productClient; private final InventoryServiceClient inventoryClient; private final PaymentServiceClient paymentClient; private final OrderEventPublisher eventPublisher; private final Tracer tracer; public Order createOrder(OrderRequest request) { Span newSpan = tracer.nextSpan().name(\"createOrder\").start(); try (Tracer.SpanInScope ws = tracer.withSpan(newSpan.start())) { // 1. 获取产品信息 Product product = productClient.getProduct(request.getProductId()); newSpan.tag(\"productId\", product.getId().toString()); // 2. 检查库存 InventoryReservation reservation = inventoryClient.reserveInventory( product.getId(), request.getQuantity()); newSpan.tag(\"inventoryReserved\", \"true\"); // 3. 计算总价 Money totalAmount = product.getPrice().multiply(request.getQuantity()); // 4. 处理支付 Payment payment = paymentClient.processPayment( request.getCustomerId(), totalAmount); newSpan.tag(\"paymentProcessed\", \"true\"); // 5. 创建订单 Order order = new Order( request.getCustomerId(), product, request.getQuantity(), totalAmount, payment.getId() ); order = orderRepository.save(order); newSpan.tag(\"orderId\", order.getId().toString()); // 6. 发布事件 eventPublisher.publishOrderCreatedEvent(order); return order; } finally { newSpan.end(); } }}3.3 服务监控与告警
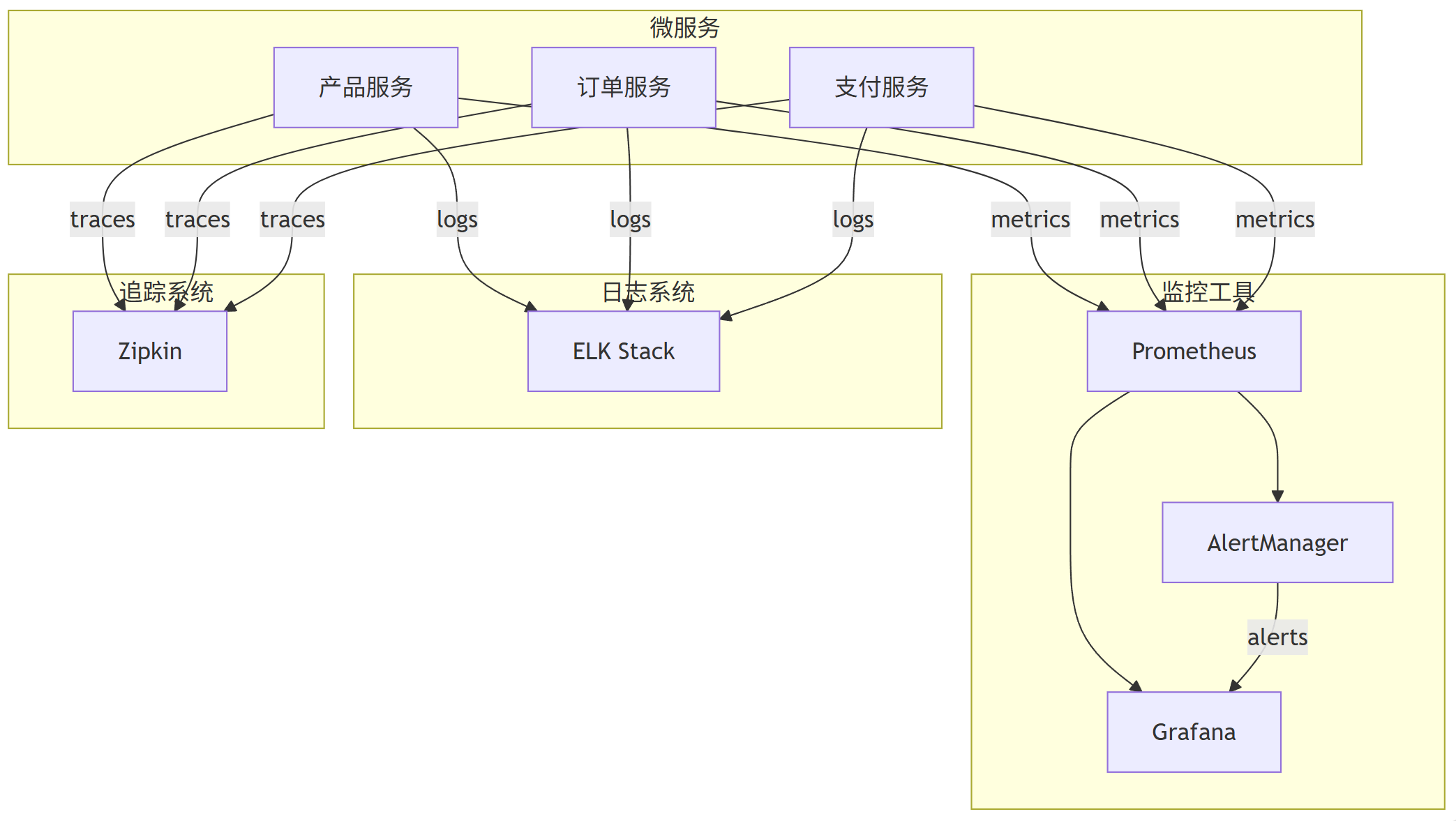
监控架构图
graph TB
subgraph \"微服务\"
A[产品服务]
B[订单服务]
C[支付服务]
end
subgraph \"监控工具\"
D[Prometheus]
E[Grafana]
F[AlertManager]
end
subgraph \"日志系统\"
G[ELK Stack]
end
subgraph \"追踪系统\"
H[Zipkin]
end
A -->|metrics| D
B -->|metrics| D
C -->|metrics| D
A -->|logs| G
B -->|logs| G
C -->|logs| G
A -->|traces| H
B -->|traces| H
C -->|traces| H
D --> E
D --> F
F -->|alerts| E
健康检查实现
@RestControllerpublic class HealthController { private final OrderRepository orderRepository; private final ProductServiceClient productClient; @GetMapping(\"/health\") public ResponseEntity health() { HealthStatus status = new HealthStatus(); // 检查数据库连接 try { orderRepository.count(); status.setDatabase(true); } catch (Exception e) { status.setDatabase(false); } // 检查外部服务 try { productClient.health(); status.setProductService(true); } catch (Exception e) { status.setProductService(false); } // 整体状态 status.setOverall(status.isDatabase() && status.isProductService()); return ResponseEntity.ok(status); }}public class HealthStatus { private boolean overall; private boolean database; private boolean productService; // getters and setters}4. 微服务架构最佳实践
4.1 设计原则
- 单一职责:每个服务专注于单一业务功能
- 去中心化治理:服务可自主选择技术栈
- 去中心化数据管理:每个服务拥有自己的数据存储
- 自动化部署:建立CI/CD流水线
- 容错设计:实现熔断、重试、超时等机制
- 监控可观测性:全面监控、日志和追踪
4.2 部署策略
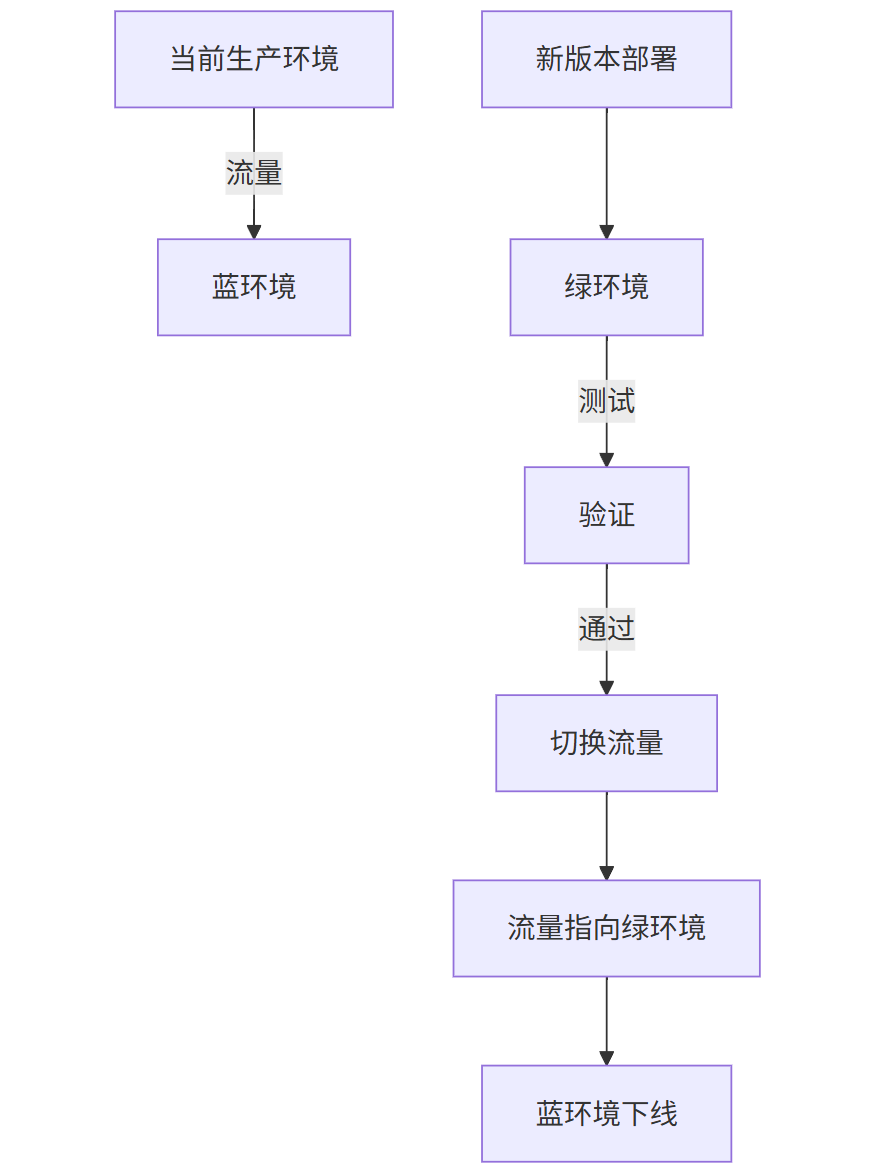
蓝绿部署流程图
graph TD
A[当前生产环境] -->|流量| B[蓝环境]
C[新版本部署] --> D[绿环境]
D -->|测试| E[验证]
E -->|通过| F[切换流量]
F --> G[流量指向绿环境]
G --> H[蓝环境下线]
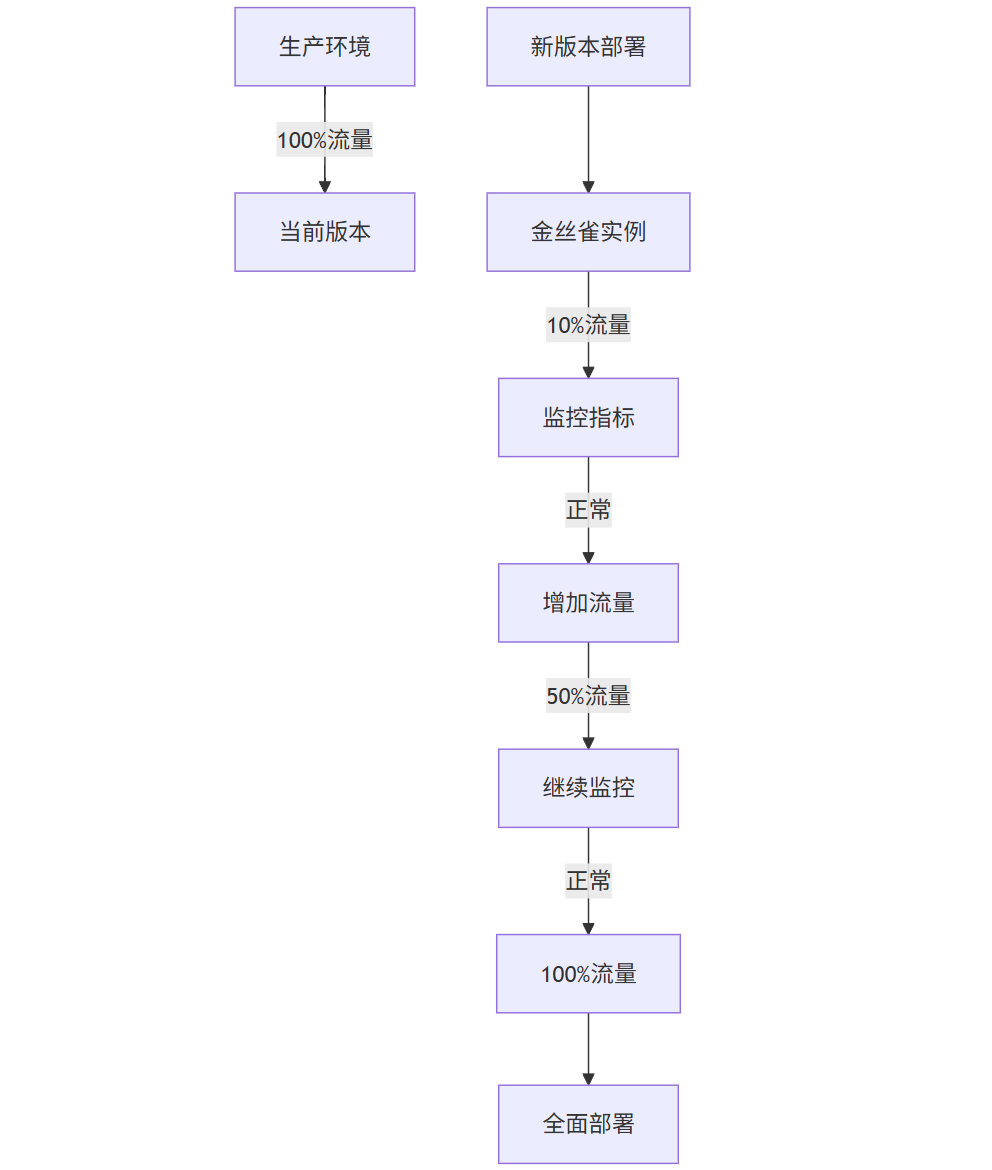
金丝雀发布流程图
graph TD
A[生产环境] -->|100%流量| B[当前版本]
C[新版本部署] --> D[金丝雀实例]
D -->|10%流量| E[监控指标]
E -->|正常| F[增加流量]
F -->|50%流量| G[继续监控]
G -->|正常| H[100%流量]
H --> I[全面部署]
4.3 安全模式
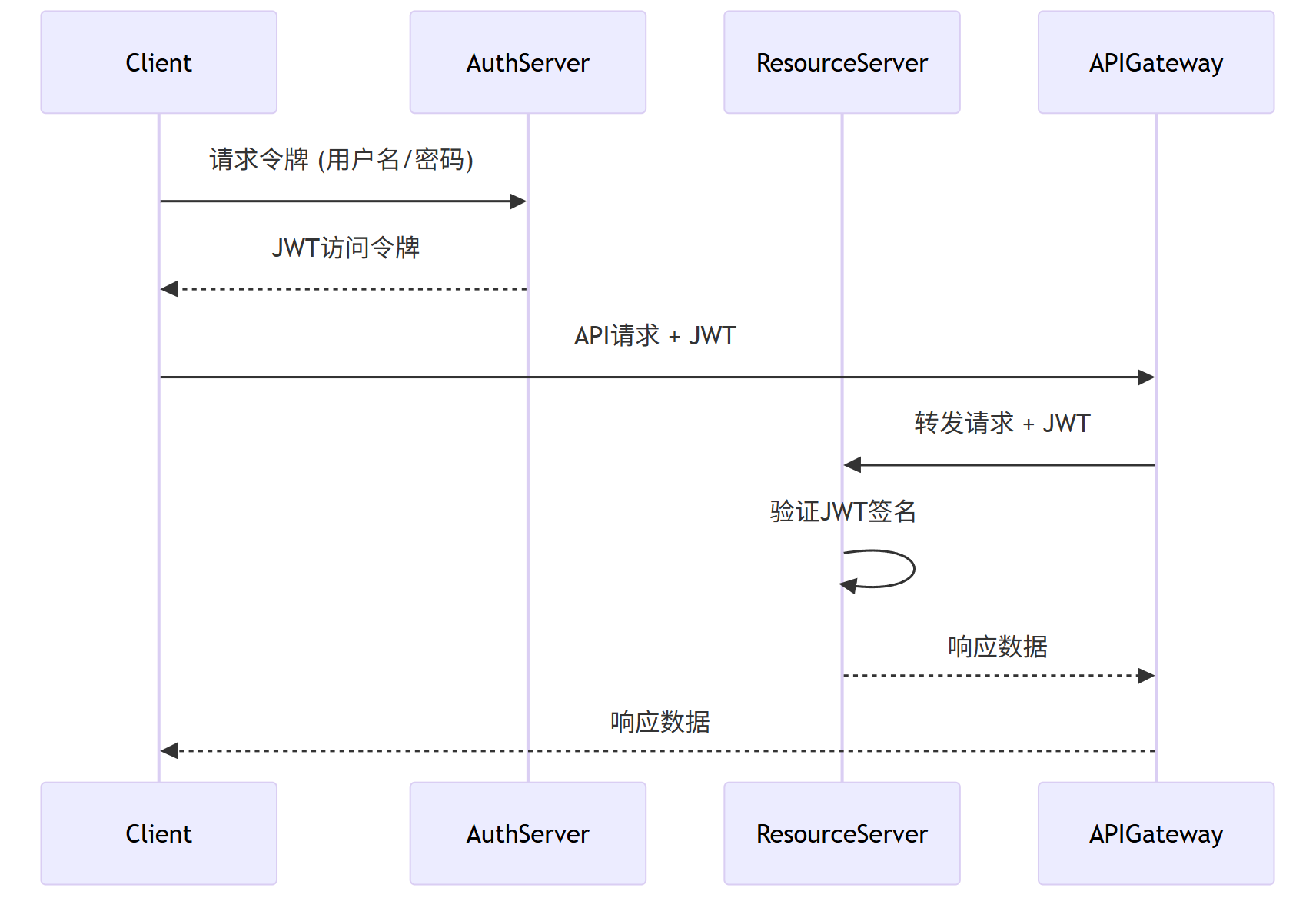
OAuth2 + JWT认证流程
sequenceDiagram
participant Client
participant AuthServer
participant ResourceServer
participant APIGateway
Client->>AuthServer: 请求令牌 (用户名/密码)
AuthServer-->>Client: JWT访问令牌
Client->>APIGateway: API请求 + JWT
APIGateway->>ResourceServer: 转发请求 + JWT
ResourceServer->>ResourceServer: 验证JWT签名
ResourceServer-->>APIGateway: 响应数据
APIGateway-->>Client: 响应数据
API安全实现
@Configuration@EnableWebSecuritypublic class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter { @Override protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception { http .csrf().disable() .authorizeRequests() .antMatchers(\"/actuator/**\").permitAll() .antMatchers(\"/public/**\").permitAll() .anyRequest().authenticated() .and() .oauth2ResourceServer() .jwt() .jwtDecoder(jwtDecoder()); } @Bean public JwtDecoder jwtDecoder() { return NimbusJwtDecoder.withJwkSetUri(jwkSetUri).build(); }}5. 微服务架构演进路线
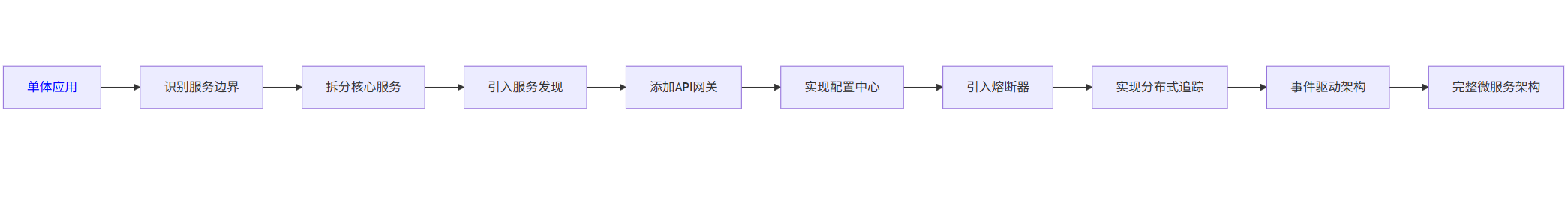
5.1 从单体到微服务的演进
graph LR
A[单体应用] --> B[识别服务边界]
B --> C[拆分核心服务]
C --> D[引入服务发现]
D --> E[添加API网关]
E --> F[实现配置中心]
F --> G[引入熔断器]
G --> H[实现分布式追踪]
H --> I[事件驱动架构]
I --> J[完整微服务架构]
5.2 微服务成熟度模型
6. 微服务架构挑战与解决方案
6.1 分布式事务管理
Saga模式实现
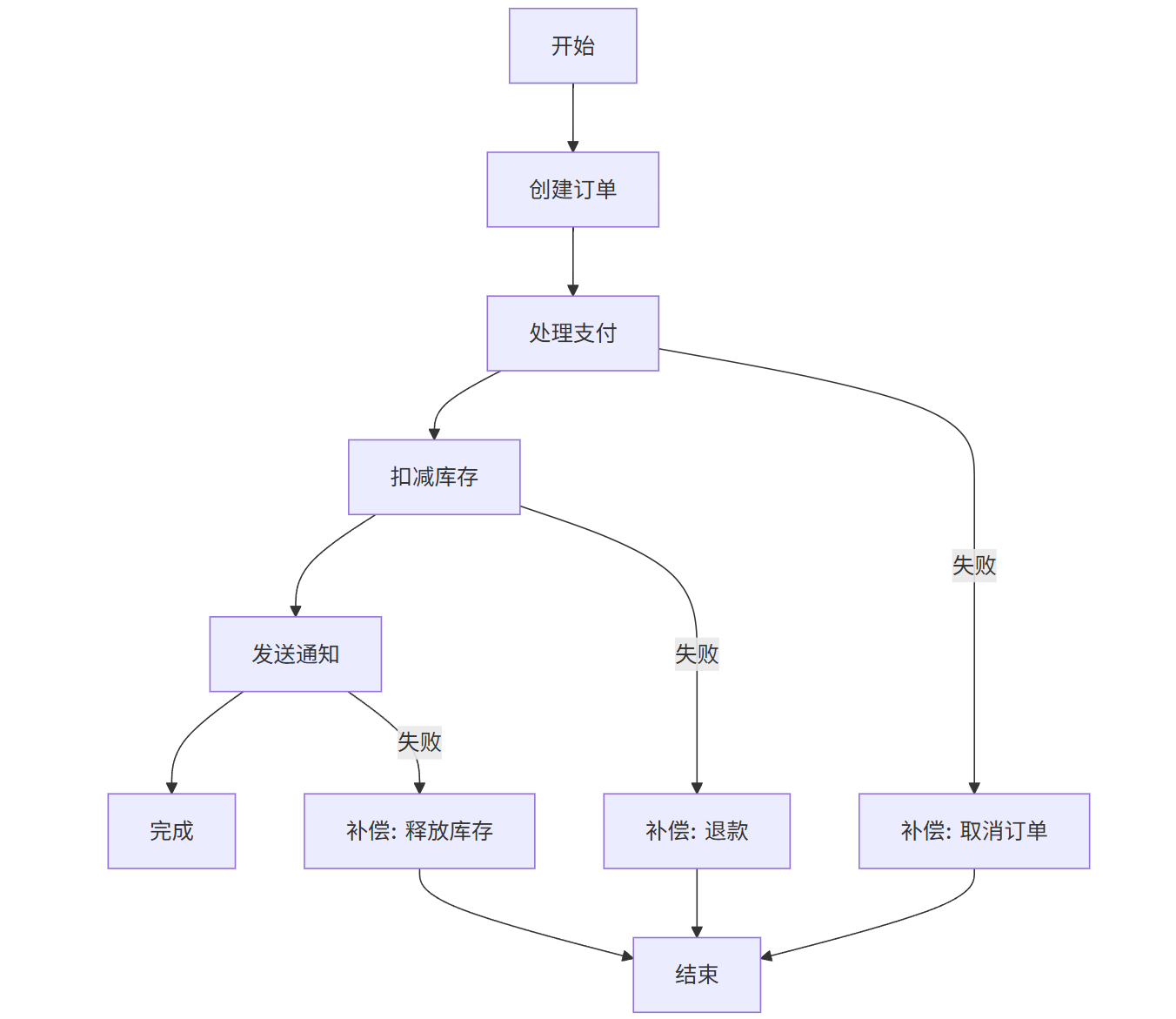
@Servicepublic class OrderSagaOrchestrator { private final OrderService orderService; private final PaymentService paymentService; private final InventoryService inventoryService; private final NotificationService notificationService; @Transactional public Order createOrder(OrderRequest request) { // 1. 创建订单 Order order = orderService.createOrder(request); try { // 2. 处理支付 Payment payment = paymentService.processPayment( order.getId(), order.getTotalAmount()); // 3. 扣减库存 inventoryService.reserveInventory( order.getProductId(), order.getQuantity()); // 4. 发送通知 notificationService.sendOrderConfirmation(order); return order; } catch (Exception e) { // 补偿事务 compensate(order); throw new RuntimeException(\"Order creation failed\", e); } } private void compensate(Order order) { try { paymentService.refundPayment(order.getId()); inventoryService.releaseInventory( order.getProductId(), order.getQuantity()); orderService.cancelOrder(order.getId()); } catch (Exception e) { // 记录补偿失败,需要人工干预 log.error(\"Compensation failed for order {}\", order.getId(), e); } }}Saga模式流程图
graph TD
A[开始] --> B[创建订单]
B --> C[处理支付]
C --> D[扣减库存]
D --> E[发送通知]
E --> F[完成]
C -->|失败| G[补偿: 取消订单]
D -->|失败| H[补偿: 退款]
E -->|失败| I[补偿: 释放库存]
G --> J[结束]
H --> J
I --> J
6.2 服务间通信优化
gRPC实现高效通信
// 定义服务service ProductService { rpc GetProduct(GetProductRequest) returns (Product); rpc ListProducts(ListProductsRequest) returns (ListProductsResponse);}// 服务实现@GrpcServicepublic class ProductGrpcService extends ProductServiceGrpc.ProductServiceImplBase { private final ProductRepository productRepository; @Override public void getProduct(GetProductRequest request, StreamObserver responseObserver) { ProductEntity entity = productRepository.findById(request.getId()) .orElseThrow(() -> new StatusRuntimeException( Status.NOT_FOUND.withDescription(\"Product not found\"))); Product product = Product.newBuilder() .setId(entity.getId()) .setName(entity.getName()) .setPrice(entity.getPrice()) .build(); responseObserver.onNext(product); responseObserver.onCompleted(); }}// 客户端调用@Servicepublic class OrderService { private final ProductServiceGrpc.ProductServiceBlockingStub productClient; public OrderService(ProductServiceGrpc.ProductServiceBlockingStub productClient) { this.productClient = productClient; } public void processOrder(OrderRequest request) { GetProductRequest productRequest = GetProductRequest.newBuilder() .setId(request.getProductId()) .build(); Product product = productClient.getProduct(productRequest); // 处理订单逻辑 }}通信协议对比
7. 微服务架构未来趋势
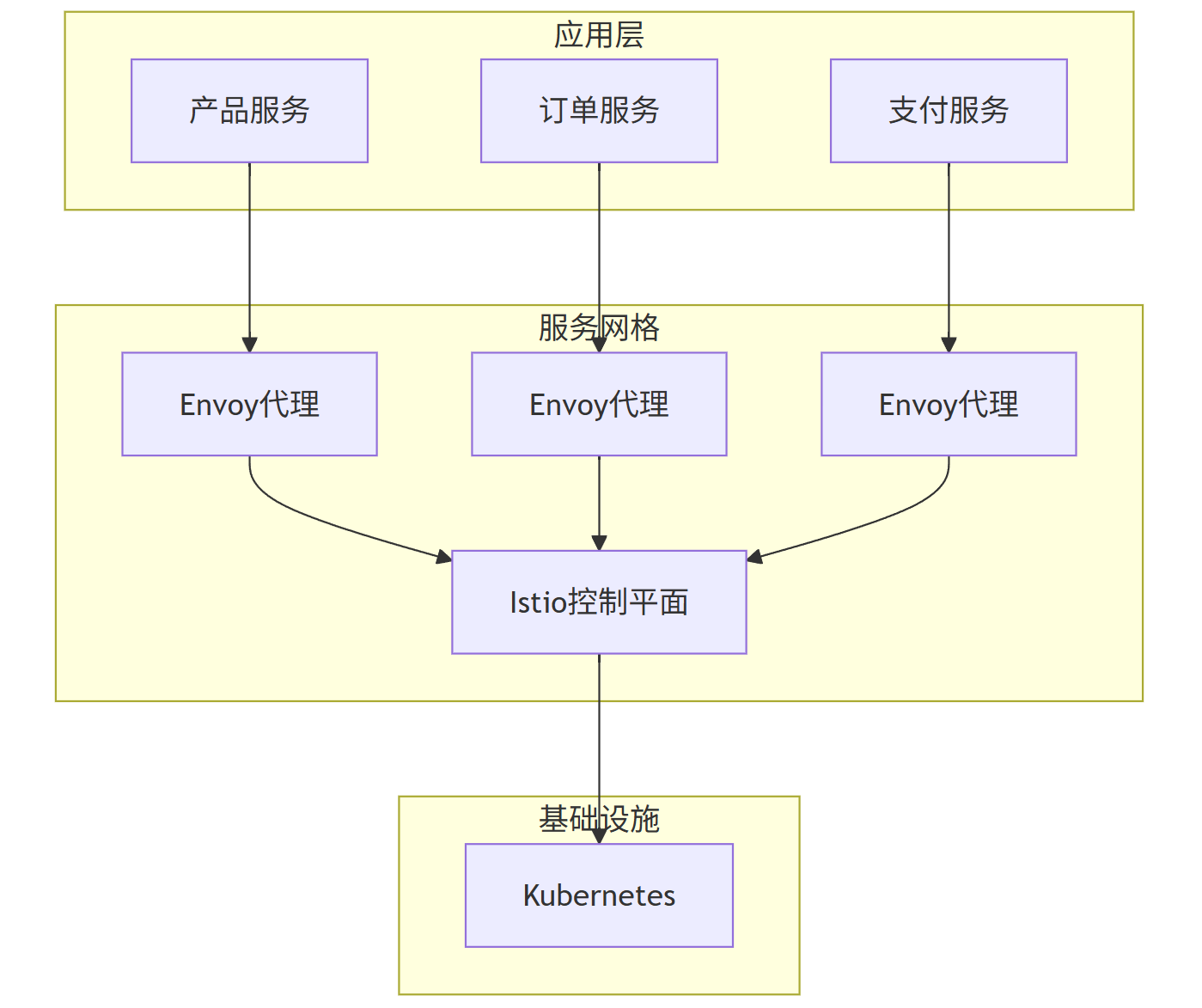
7.1 服务网格(Service Mesh)
graph TB
subgraph \"应用层\"
A[产品服务]
B[订单服务]
C[支付服务]
end
subgraph \"服务网格\"
D[Envoy代理]
E[Envoy代理]
F[Envoy代理]
G[Istio控制平面]
end
subgraph \"基础设施\"
H[Kubernetes]
end
A --> D
B --> E
C --> F
D --> G
E --> G
F --> G
G --> H
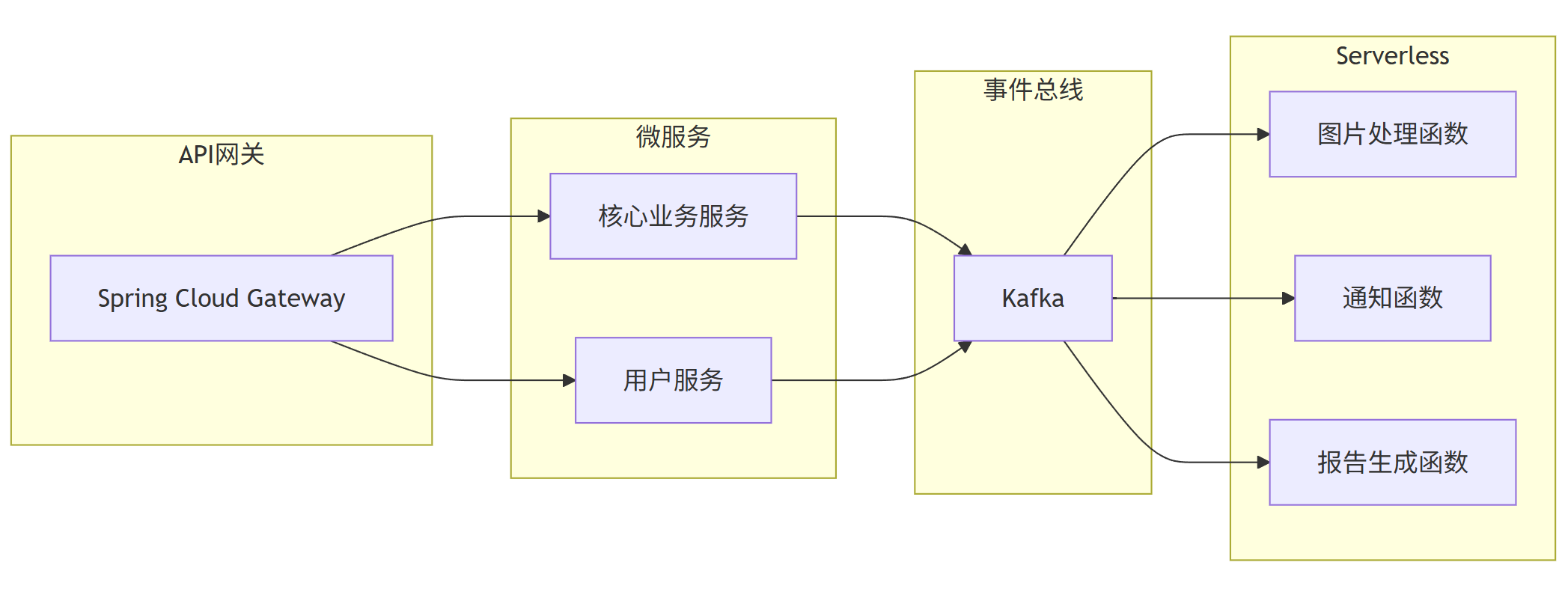
7.2 无服务器(Serverless)与微服务结合
graph LR
subgraph \"API网关\"
A[Spring Cloud Gateway]
end
subgraph \"微服务\"
B[核心业务服务]
C[用户服务]
end
subgraph \"Serverless\"
D[图片处理函数]
E[通知函数]
F[报告生成函数]
end
subgraph \"事件总线\"
G[Kafka]
end
A --> B
A --> C
B --> G
C --> G
G --> D
G --> E
G --> F
8. 结论
Java微服务架构通过一系列设计模式和技术组件,为构建现代化、可扩展的企业级应用提供了强大支持。从服务拆分、服务发现到API网关、配置中心,再到熔断器、分布式追踪和事件驱动架构,每个模式都解决了微服务架构中的特定挑战。
成功实施微服务架构需要:
- 合理的服务边界划分
- 完善的服务治理体系
- 强大的自动化运维能力
- 全面的监控和可观测性
- 持续的架构演进和优化
随着云原生技术的发展,微服务架构将与容器化、服务网格、无服务器计算等趋势深度融合,为企业数字化转型提供更强大的技术支撑。开发者应持续关注这些技术演进,结合业务需求选择合适的架构模式和技术栈,构建具有高弹性、高可用的现代化应用系统。


