【深入理解 Linux 网络】收包原理与内核实现(上) 从网卡到协议层
本系列文章
- 【深入理解 Linux 网络】关键术语
- 【深入理解 Linux 网络】内核初始化流程
- 【深入理解 Linux 网络】收包原理与内核实现(上) 从网卡到协议层
- 【深入理解 Linux 网络】收包原理与内核实现(中)TCP 传输层处理
- 【深入理解 Linux 网络】收包原理与内核实现(下)应用层读取与 epoll 实现
- 【深入理解 Linux 网络】数据发送处理流程与内核实现
- 【深入理解 Linux 网络】配置调优与性能优化
整体流程
Linux 收包的整体流程如下:
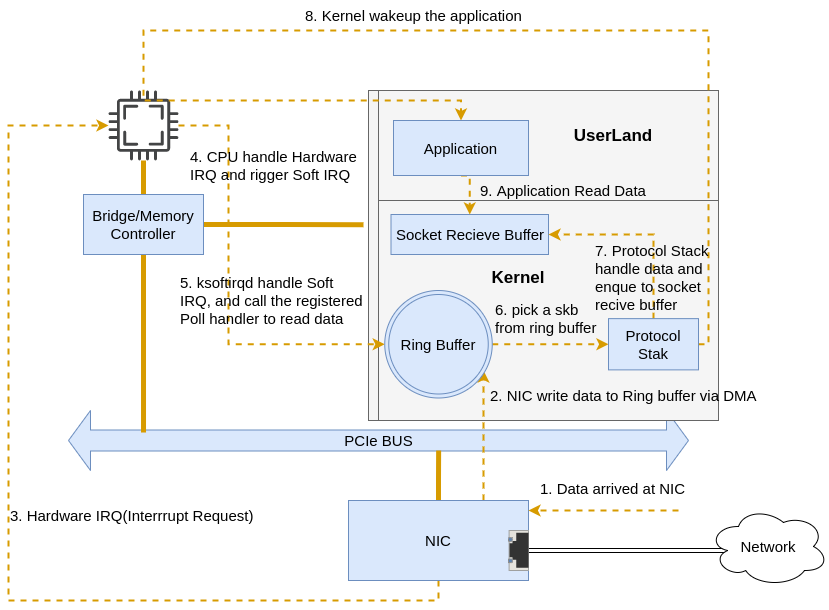
图片来自 Linux Networking Stack tutorial: Receiving Data
0. 系统初始化:比如创建软中断进程,注册网络协议栈、网卡驱动等。
1. 网卡: 接收包。
2. 网卡: 通过 DMA 将数据包复制到系统内核的 RingBuffer。
3. 网卡: 产生硬中断(Hardware interrupt),通知内核有新数据到达。
4. 内核: 响应硬中断,做简要处理后发出软中断。
5. 内核: 唤醒 ksoftirqd 线程,执行软中断处理,调用 NAPI(New API)Poll 函数来处理数据。
6. 内核: NAPI 从 RingBuffer 中取出数据,转为 skb(Socket Buffer)的形式向上传递给协议栈。skb 是 Linux 处理网络数据包的核心数据结构,接收和发送数据包都使用该数据结构表示。
7. 内核: skb 交给内核协议栈进行处理。这里包含 L2、L3、L4 各个协议层的处理。
8. 内核: 协议栈处理完成后,会将数据包传递到 socket 接收缓冲区。
9. 应用: 应用程序利用系统调用从 socket 接收缓冲区读取数据。
1.网卡接收包
初始化过程结束,系统、网卡正常启动后,服务器就可以接收数据包了,这里主要涉及 L1/L2 硬件层的内容,不做深究。
2.DMA 复制数据包
这里到第 2 步,数据达到网卡后,网卡使用 DMA(Direct Memory Access)技术将接收到的数据包直接复制到 RingBuffer 内存中,这样可以不消耗 CPU 资源。
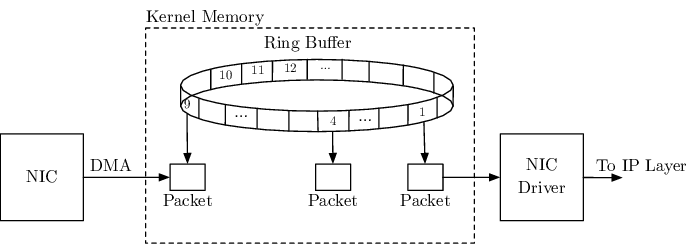
关于 DMA 的细节可以参考内核文档 DMA API HOWTO: Dynamic DMA mapping Guide。
3.触发硬中断
网卡通过 DMA 将数据存入 RingBuffer 后就需要通知 CPU 来处理数据了,这一步是通过硬件中断(IRQ)实现的。
传统的中断触发机制是通过引起 CPU 的中断请求引脚(IRQ)进行电平或边沿触发来实现的。现代操作系统引入了 MSI/MSIX(Message Signaled Interrupts) 机制,通过在特定的内存地址记录消息,从而支持更多的中断类型(MSIX 支持每个设备分配 2048 个中断),后续触发通过内存读写的方式实现,大致流程如下:
- 网卡到达数据包,基于 RSS 哈希决定要使用的 RX 队列。
- 基于初始化时确定的队列-向量-CPU 映射关系,通过对固定内存地址记录消息,触发硬中断
- 根据 CPU 亲和性,会通知相应的 CPU 调用 irq 处理函数,执行硬中断处理。
4.硬中断处理,触发软中断
当 CPU 收到网卡的硬中断请求后,会执行对应的中断处理程序 ISR,i40e 驱动的 ISR 是 i40e_msix_clean_rings()函数,代码如下:
// https://elixir.bootlin.com/linux/v5.15.139/source/drivers/net/ethernet/intel/i40e/i40e_main.c#L4039/** * i40e_msix_clean_rings - MSIX mode Interrupt Handler * @irq: interrupt number * @data: pointer to a q_vector **/static irqreturn_t i40e_msix_clean_rings(int irq, void *data){struct i40e_q_vector *q_vector = data;if (!q_vector->tx.ring && !q_vector->rx.ring)return IRQ_HANDLED;napi_schedule_irqoff(&q_vector->napi);return IRQ_HANDLED;}可以看到这一步的处理非常简单:
- 检查发送或接收队列是否有数据,如果都没有则直接返回。
- 如果有则调用
napi_schedule_irqoff()进行后续处理。
napi_schedule_irqoff > ____napi_schedule
napi_schedule_irqoff 调用栈如下:
- napi_schedule_irqoff└── __napi_schedule_irqoff └── __napi_schedule└── ____napi_schedule核心处理逻辑是在 ____napi_schedule() 函数执行的,代码如下:
// https://elixir.bootlin.com/linux/v5.15.139/source/net/core/dev.c#L4346/* Called with irq disabled */static inline void ____napi_schedule(struct softnet_data *sd, struct napi_struct *napi){struct task_struct *thread; ...list_add_tail(&napi->poll_list, &sd->poll_list);// 触发 NET_RX_SOFTIRQ 软中断__raise_softirq_irqoff(NET_RX_SOFTIRQ);}可以看到该函数主要有两个任务:
-
将驱动程序 napi_struct 中的 poll_list 添加到 softnet_data 中的 poll_list 中。
-
触发
NET_RX_SOFTIRQ类型的软中断。
5.ksoftirqd 软中断处理,调用 NAPI
NET_RX_SOFTIRQ 软中断被触发后,现在到了第 5 步。ksoftirqd 会开启循环等待软中断的发生,当有软中断触发时,最终会调用到 _do_softirq 函数处理,代码如下:
asmlinkage __visible void __softirq_entry __do_softirq(void){// 时间片占用的最大时间,一般为 2ms,防止长时间占用 CPUunsigned long end = jiffies + MAX_SOFTIRQ_TIME;unsigned long old_flags = current->flags;// 最大重启次数,通常是 10 次,防止软中断处理过于频繁int max_restart = MAX_SOFTIRQ_RESTART;// 软中断处理函数的指针struct softirq_action *h;bool in_hardirq;// 软中断的位图,代表是哪种软中断类型__u32 pending; // 当前要处理的软中断位int softirq_bit;/* * Mask out PF_MEMALLOC as the current task context is borrowed for the * softirq. A softirq handled, such as network RX, might set PF_MEMALLOC * again if the socket is related to swapping. */current->flags &= ~PF_MEMALLOC; // 获取待处理的软中断pending = local_softirq_pending();softirq_handle_begin();in_hardirq = lockdep_softirq_start();account_softirq_enter(current);restart:/* Reset the pending bitmask before enabling irqs */set_softirq_pending(0);local_irq_enable();h = softirq_vec; // 循环处理所有软中断while ((softirq_bit = ffs(pending))) {unsigned int vec_nr;int prev_count; // 基于 bit 获取对应的处理函数h += softirq_bit - 1;vec_nr = h - softirq_vec;prev_count = preempt_count();kstat_incr_softirqs_this_cpu(vec_nr);trace_softirq_entry(vec_nr);// 执行具体的软中断处理函数,对于网络收包,其接收函数是 net_rx_action()h->action(h);trace_softirq_exit(vec_nr);if (unlikely(prev_count != preempt_count())) {pr_err(\"huh, entered softirq %u %s %p with preempt_count %08x, exited with %08x?\\n\", vec_nr, softirq_to_name[vec_nr], h->action, prev_count, preempt_count());preempt_count_set(prev_count);}// 移动到下个软中断,继续处理h++;pending >>= softirq_bit;}// 后续处理if (!IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_PREEMPT_RT) && __this_cpu_read(ksoftirqd) == current)rcu_softirq_qs();local_irq_disable();pending = local_softirq_pending();if (pending) {if (time_before(jiffies, end) && !need_resched() && --max_restart)goto restart;wakeup_softirqd();}account_softirq_exit(current);lockdep_softirq_end(in_hardirq);softirq_handle_end();current_restore_flags(old_flags, PF_MEMALLOC);}可以看到核心逻辑就是:
- 获取到待处理的软中断类型。
- 根据类型获取到 softirq_vec 中注册好的处理函数(action)。
- 执行 action 函数
对于 NET_RX_SOFTIRQ 网络收包软中断,其处理函数是 net_rx_action(),我们来看下这个函数的实现。
net_rx_action() 软中断处理
net_rx_action() 源码如下:
// https://elixir.bootlin.com/linux/v5.15.139/source/net/core/dev.c#L7163static __latent_entropy void net_rx_action(struct softirq_action *h){// 获取当前 CPU 的 softnet_datastruct softnet_data *sd = this_cpu_ptr(&softnet_data);// 计算本次软中断处理的时间限制,默认为 2msunsigned long time_limit = jiffies +usecs_to_jiffies(READ_ONCE(netdev_budget_usecs));// 网络设备的总预算,代表可处理的数据包限制,默认为 300int budget = READ_ONCE(netdev_budget);LIST_HEAD(list);LIST_HEAD(repoll); // 禁用硬中断,防止处理过程被打断local_irq_disable();// 将 sd->poll_list 中的所有元素移动到 list 中list_splice_init(&sd->poll_list, &list);// 重新启用硬中断local_irq_enable();/* 主循环:处理所有待轮询的网络设备 */for (;;) {struct napi_struct *n;if (list_empty(&list)) {if (!sd_has_rps_ipi_waiting(sd) && list_empty(&repoll))return;break;} // 获取第一个待处理的 NAPI 设备n = list_first_entry(&list, struct napi_struct, poll_list);// 核心处理步骤// 执行网卡驱动注册的 poll() 方法,返回的是实际处理的包的数量// 该函数执行完成后,数据包从 RingBuffer 取出,传到了上层协议栈。budget -= napi_poll(n, &repoll);/* If softirq window is exhausted then punt. * Allow this to run for 2 jiffies since which will allow * an average latency of 1.5/HZ. */if (unlikely(budget <= 0 || time_after_eq(jiffies, time_limit))) {sd->time_squeeze++;break;}}local_irq_disable();list_splice_tail_init(&sd->poll_list, &list);list_splice_tail(&repoll, &list);list_splice(&list, &sd->poll_list);if (!list_empty(&sd->poll_list))__raise_softirq_irqoff(NET_RX_SOFTIRQ);net_rps_action_and_irq_enable(sd);}核心逻辑
这里的核心逻辑就是开启 for(;;) 循环,不断调用 napi_poll 函数来处理网络数据包。有三种情况会导致循环退出:
-
poll list 为空:说明没有可用的 NAPI poll 函数,也就是没有需要处理的网络设备。
-
网卡收包预算耗尽:处理的包数量超过了预算限制,退出循环。
-
软中断时间预算耗尽:处理时间超过了预设的时间限制, 退出循环。
预算计算
软中断处理有两种预算限制:
- 收包预算 budget:最多处理的包的数量。
- 时间预算 time_limit:最多处理的时间。
这两个预算由 CPU 上所有的 NAPI 共享,两者的默认是在代码中定义好的:
// https://elixir.bootlin.com/linux/v5.15.139/source/net/core/dev.c#L4336// 300 个包int netdev_budget __read_mostly = 300;// 2 毫秒/* Must be at least 2 jiffes to guarantee 1 jiffy timeout */unsigned int __read_mostly netdev_budget_usecs = 2 * USEC_PER_SEC / HZ;不过这两个值都是 sysctl 配置项,因此可以按需进行调优设置,像我的云服务器将时间运算由 2000us 改为了 8000us,即 8ms。
$ sudo sysctl -a | grep netdev_budgetnet.core.netdev_budget = 300net.core.netdev_budget_usecs = 8000 // 单位 us,总和为 8ms6.NAPI 处理: RingBuffer 到协议栈
现在我们到了第 6 步,网卡驱动的 poll 函数从 RingBuffer 取包并发送到协议栈。
napi_poll() -> i40e_napi_poll()
i40e 驱动的 napi_poll 函数是 i40e_napi_poll,处理 RingBuffer 数据的逻辑从这里开始。
https://elixir.bootlin.com/linux/v5.15.139/source/drivers/net/ethernet/intel/i40e/i40e_txrx.c#L2675/** * i40e_napi_poll - NAPI polling Rx/Tx cleanup routine * @napi: napi struct with our devices info in it * @budget: amount of work driver is allowed to do this pass, in packets * * This function will clean all queues associated with a q_vector. * * Returns the amount of work done **/int i40e_napi_poll(struct napi_struct *napi, int budget){ // 1. 初始化并检查相关状态struct i40e_q_vector *q_vector = container_of(napi, struct i40e_q_vector, napi);struct i40e_vsi *vsi = q_vector->vsi;struct i40e_ring *ring;bool clean_complete = true;bool arm_wb = false;int budget_per_ring;int work_done = 0;if (test_bit(__I40E_VSI_DOWN, vsi->state)) {napi_complete(napi);return 0;} // 2. 处理 Tx 数据发送队列i40e_for_each_ring(ring, q_vector->tx) {bool wd = ring->xsk_pool ? i40e_clean_xdp_tx_irq(vsi, ring) : // XDP发送清理 i40e_clean_tx_irq(vsi, ring, budget); // 普通发送清理if (!wd) {clean_complete = false;continue;}arm_wb |= ring->arm_wb;ring->arm_wb = false;} // ... 代码省略 // 3. 处理 Rx 数据接收队列i40e_for_each_ring(ring, q_vector->rx) {int cleaned = ring->xsk_pool ? // 零拷贝处理 i40e_clean_rx_irq_zc(ring, budget_per_ring) : // 普通处理 i40e_clean_rx_irq(ring, budget_per_ring); work_done += cleaned;/* if we clean as many as budgeted, we must not be done */if (cleaned >= budget_per_ring)clean_complete = false;}// 4. 检查是否清理完成,决定是否继续清理还是结束循环等待下次硬中断再次触发调度。if (!clean_complete) {int cpu_id = smp_processor_id();/* It is possible that the interrupt affinity has changed but, * if the cpu is pegged at 100%, polling will never exit while * traffic continues and the interrupt will be stuck on this * cpu. We check to make sure affinity is correct before we * continue to poll, otherwise we must stop polling so the * interrupt can move to the correct cpu. */if (!cpumask_test_cpu(cpu_id, &q_vector->affinity_mask)) {/* Tell napi that we are done polling */napi_complete_done(napi, work_done);/* Force an interrupt */i40e_force_wb(vsi, q_vector);/* Return budget-1 so that polling stops */return budget - 1;}tx_only:if (arm_wb) {q_vector->tx.ring[0].tx_stats.tx_force_wb++;i40e_enable_wb_on_itr(vsi, q_vector);}return budget;}if (q_vector->tx.ring[0].flags & I40E_TXR_FLAGS_WB_ON_ITR)q_vector->arm_wb_state = false;/* Exit the polling mode, but don\'t re-enable interrupts if stack might * poll us due to busy-polling */if (likely(napi_complete_done(napi, work_done)))i40e_update_enable_itr(vsi, q_vector);return min(work_done, budget - 1);}可以看到该函数会接收一个 budget 参数,这里表示的是网卡一次执行 poll() 是允许处理的最大数据包数量,这是个硬编码的值,为 64。
// https://elixir.bootlin.com/linux/v5.15.139/source/drivers/net/ethernet/intel/i40e/i40e_main.c#L11958netif_napi_add(vsi->netdev, &q_vector->napi, i40e_napi_poll, NAPI_POLL_WEIGHT);// https://elixir.bootlin.com/linux/v5.15.139/source/include/linux/netdevice.h#L2488/* Default NAPI poll() weight * Device drivers are strongly advised to not use bigger value */#define NAPI_POLL_WEIGHT 64不过可以通过 sysctl 修改,但一般不建议,否则会导致收包软中断占用 CPU 时间过长,影响其他处理。
$ sudo sysctl -a | grep dev_weightnet.core.dev_weight = 64net.core.dev_weight_rx_bias = 1net.core.dev_weight_tx_bias = 1i40e 网卡的 TX/RX 队列是一起的,因此会在 poll() 函数会依次处理,分别执行:
- XDP TX 发送
- 普通 TX 发送
- 零拷贝 RX
- 普通 RX
我们这里只关注普通 RX 队列的处理。
i40e_napi_poll() -> i40e_clean_rx_irq()
普通 RX 队列处理的主要逻辑在 i40e_clean_rx_irq() 函数,i40e 驱动在该函数中将 RingBuffer 中的数据转为 skb(socket buffer) 结构体,并交给上层协议栈处理。我们来详细分析下该函数的处理过程。
static int i40e_clean_rx_irq(struct i40e_ring *rx_ring, int budget){// 接收的总字节数、总包数、帧大小unsigned int total_rx_bytes = 0, total_rx_packets = 0, frame_sz = 0;u16 cleaned_count = I40E_DESC_UNUSED(rx_ring);unsigned int offset = rx_ring->rx_offset;struct sk_buff *skb = rx_ring->skb;unsigned int xdp_xmit = 0;bool failure = false;struct xdp_buff xdp;int xdp_res = 0;#if (PAGE_SIZE < 8192)frame_sz = i40e_rx_frame_truesize(rx_ring, 0);#endifxdp_init_buff(&xdp, frame_sz, &rx_ring->xdp_rxq); /* 主处理循环:在预算范围内处理尽可能多的数据包 */while (likely(total_rx_packets < (unsigned int)budget)) {struct i40e_rx_buffer *rx_buffer;union i40e_rx_desc *rx_desc;int rx_buffer_pgcnt;unsigned int size;u64 qword;/* return some buffers to hardware, one at a time is too slow */if (cleaned_count >= I40E_RX_BUFFER_WRITE) {failure = failure || i40e_alloc_rx_buffers(rx_ring, cleaned_count);cleaned_count = 0;}rx_desc = I40E_RX_DESC(rx_ring, rx_ring->next_to_clean);/* status_error_len will always be zero for unused descriptors * because it\'s cleared in cleanup, and overlaps with hdr_addr * which is always zero because packet split isn\'t used, if the * hardware wrote DD then the length will be non-zero */qword = le64_to_cpu(rx_desc->wb.qword1.status_error_len);/* This memory barrier is needed to keep us from reading * any other fields out of the rx_desc until we have * verified the descriptor has been written back. */dma_rmb();if (i40e_rx_is_programming_status(qword)) {i40e_clean_programming_status(rx_ring, rx_desc->raw.qword[0], qword);rx_buffer = i40e_rx_bi(rx_ring, rx_ring->next_to_clean);i40e_inc_ntc(rx_ring);i40e_reuse_rx_page(rx_ring, rx_buffer);cleaned_count++;continue;}size = (qword & I40E_RXD_QW1_LENGTH_PBUF_MASK) >> I40E_RXD_QW1_LENGTH_PBUF_SHIFT;if (!size)break;i40e_trace(clean_rx_irq, rx_ring, rx_desc, skb);rx_buffer = i40e_get_rx_buffer(rx_ring, size, &rx_buffer_pgcnt);/* retrieve a buffer from the ring */if (!skb) {unsigned char *hard_start;hard_start = page_address(rx_buffer->page) + rx_buffer->page_offset - offset;xdp_prepare_buff(&xdp, hard_start, offset, size, true);#if (PAGE_SIZE > 4096)/* At larger PAGE_SIZE, frame_sz depend on len size */xdp.frame_sz = i40e_rx_frame_truesize(rx_ring, size);#endifxdp_res = i40e_run_xdp(rx_ring, &xdp);} // 处理 XDP 返回结果if (xdp_res) {if (xdp_res & (I40E_XDP_TX | I40E_XDP_REDIR)) {xdp_xmit |= xdp_res;i40e_rx_buffer_flip(rx_ring, rx_buffer, size);} else {rx_buffer->pagecnt_bias++;}total_rx_bytes += size;total_rx_packets++;} else if (skb) {// 如果已有SKB(多描述符数据包),添加接收片段 i40e_add_rx_frag(rx_ring, rx_buffer, skb, size);} else if (ring_uses_build_skb(rx_ring)) {// 直接在现有缓冲区上构建 skb,避免拷贝skb = i40e_build_skb(rx_ring, rx_buffer, &xdp);} else {// 传统方式构建 skbskb = i40e_construct_skb(rx_ring, rx_buffer, &xdp);}/* exit if we failed to retrieve a buffer */if (!xdp_res && !skb) {rx_ring->rx_stats.alloc_buff_failed++;rx_buffer->pagecnt_bias++;break;}i40e_put_rx_buffer(rx_ring, rx_buffer, rx_buffer_pgcnt);cleaned_count++;i40e_inc_ntc(rx_ring);if (i40e_is_non_eop(rx_ring, rx_desc))continue;if (xdp_res || i40e_cleanup_headers(rx_ring, skb, rx_desc)) {skb = NULL;continue;}/* probably a little skewed due to removing CRC */total_rx_bytes += skb->len;/* populate checksum, VLAN, and protocol */i40e_process_skb_fields(rx_ring, rx_desc, skb);i40e_trace(clean_rx_irq_rx, rx_ring, rx_desc, skb);napi_gro_receive(&rx_ring->q_vector->napi, skb);skb = NULL;/* update budget accounting */total_rx_packets++;}i40e_finalize_xdp_rx(rx_ring, xdp_xmit);rx_ring->skb = skb;i40e_update_rx_stats(rx_ring, total_rx_bytes, total_rx_packets);/* guarantee a trip back through this routine if there was a failure */return failure ? budget : (int)total_rx_packets;}i40e_construct_skb() vs i40e_build_skb()
可以看到有i40e_construct_skb() 和 i40e_build_skb() 两个函数用来构建 skb,但它们的处理方式有所不同。
这里我们主要关注普通的i40e_construct_skb() 函数中处理的,代码如下:
static struct sk_buff *i40e_construct_skb(struct i40e_ring *rx_ring, struct i40e_rx_buffer *rx_buffer, struct xdp_buff *xdp){unsigned int size = xdp->data_end - xdp->data;#if (PAGE_SIZE < 8192)unsigned int truesize = i40e_rx_pg_size(rx_ring) / 2;#elseunsigned int truesize = SKB_DATA_ALIGN(size);#endifunsigned int headlen;struct sk_buff *skb;/* prefetch first cache line of first page */net_prefetch(xdp->data); ... /* allocate a skb to store the frags */// 分配 skb 存储空间skb = __napi_alloc_skb(&rx_ring->q_vector->napi, I40E_RX_HDR_SIZE, GFP_ATOMIC | __GFP_NOWARN);if (unlikely(!skb))return NULL;/* Determine available headroom for copy */headlen = size;if (headlen > I40E_RX_HDR_SIZE)headlen = eth_get_headlen(skb->dev, xdp->data, I40E_RX_HDR_SIZE);// 数据拷贝,注意只拷贝 headlen 长度的数据。memcpy(__skb_put(skb, headlen), xdp->data, ALIGN(headlen, sizeof(long)));/* update all of the pointers */// 对多余的数据,直接引用原始界面size -= headlen;if (size) {skb_add_rx_frag(skb, 0, rx_buffer->page,rx_buffer->page_offset + headlen,size, truesize);/* buffer is used by skb, update page_offset */#if (PAGE_SIZE < 8192)rx_buffer->page_offset ^= truesize;#elserx_buffer->page_offset += truesize;#endif} else {/* buffer is unused, reset bias back to rx_buffer */rx_buffer->pagecnt_bias++;}return skb;}这里的核心是 skb 的构建过程,过程为:
__napi_alloc_skb()分配 skb 存储空间memcpy()将长度不超过 256 bytes 的头部数据拷贝至 skb,这样可以保证 L2/L3/L4 三层协议的协议头都被拷贝进来。- 如果数据包总大小超过 256 字节,对于剩余数据则引用其 DMA 页面,不会执行真正的拷贝。
这种方式仅拷贝 256 字节的头部数据,而 i40e_build_skb() 函数的执行更为激进,它直接在 DMA 空间构建 skb,最后将指针赋值给 skb,从而实现真正的零拷贝,这对于小包处理性能提升尤为明显,是高性能网络处理的关键优化之一。
可以看到无论采用哪种方式构建 skb,i40e 驱动都不会拷贝所有数据,这和传统网卡的处理不同。传统网卡的收包处理往往需要两次数据拷贝:
- 第一次拷贝:网卡通过 DMA 将数据拷贝进内存
- 第二次拷贝:内核将数据从内存拷贝到 skb 中
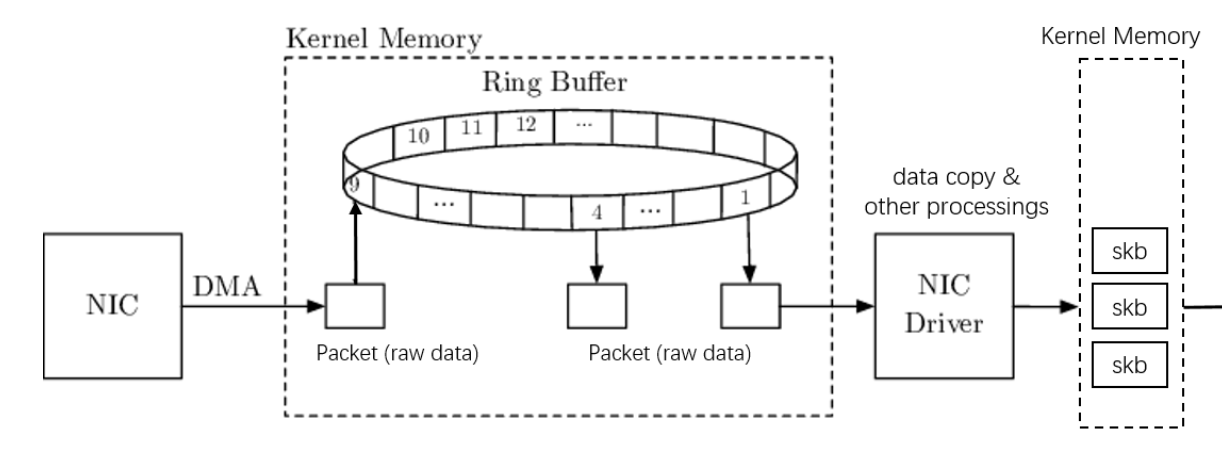
图片来自 Linux 网络栈接收数据(RX):原理及内核实现(2022)
最终,经过漫长的系统初始化、硬中断、软中断、NAPI 处理后,终于生成了我们内核协议栈中的数据包: skb。有了 skb,像邻居子系统、路由、TC、netfilter/iptables、BPF 等模块就有用武之地。
i40e_process_skb_fields():初始化 L2 header、IPSec、时间戳、vlan header 等
skb 结构初始化完成后,后续会进行一系列梳理,完善 skb 的各个字段。
/** * i40e_process_skb_fields - Populate skb header fields from Rx descriptor * * This function checks the ring, descriptor, and packet information in * order to populate the hash, checksum, VLAN, protocol, and * other fields within the skb. **/void i40e_process_skb_fields(struct i40e_ring *rx_ring, union i40e_rx_desc *rx_desc, struct sk_buff *skb){u64 qword = le64_to_cpu(rx_desc->wb.qword1.status_error_len);u32 rx_status = (qword & I40E_RXD_QW1_STATUS_MASK) >>I40E_RXD_QW1_STATUS_SHIFT;u32 tsynvalid = rx_status & I40E_RXD_QW1_STATUS_TSYNVALID_MASK;u32 tsyn = (rx_status & I40E_RXD_QW1_STATUS_TSYNINDX_MASK) >> I40E_RXD_QW1_STATUS_TSYNINDX_SHIFT;u8 rx_ptype = (qword & I40E_RXD_QW1_PTYPE_MASK) >> I40E_RXD_QW1_PTYPE_SHIFT;if (unlikely(tsynvalid))i40e_ptp_rx_hwtstamp(rx_ring->vsi->back, skb, tsyn);// 处理RSS(Receive Side Scaling)哈希值i40e_rx_hash(rx_ring, rx_desc, skb, rx_ptype);// 处理IPSeci40e_rx_ipsec(rx_ring->vsi, skb, rx_desc);i40e_rx_checksum(rx_ring->vsi, skb, rx_desc);skb_record_rx_queue(skb, rx_ring->queue_index); // vlan 标签处理if (qword & BIT(I40E_RX_DESC_STATUS_L2TAG1P_SHIFT)) {__le16 vlan_tag = rx_desc->wb.qword0.lo_dword.l2tag1;__vlan_hwaccel_put_tag(skb, htons(ETH_P_8021Q), le16_to_cpu(vlan_tag));}/* modifies the skb - consumes the enet header */// skb->protocol = eth_type_trans(skb, rx_ring->netdev);}napi_gro_receive()
上述步骤处理完成后,最终由 napi_gro_receive() 函数负责将 skb 数据送到协议栈。
GRO(Generic Receive Offloading)
GRO 的功能是将 把多个小包合并成大包再交给协议栈处理,从而减少 CPU 处理负担,提高网络性能。其前身是 LRO(Large Receive Offload),LRO 是一个硬件特性,GRO 是其软件实现,对于包的合并处理更加的灵活。
与 GRO 类型的功能还有 TSO(TCP Segmentation Offload)和 GSO(Generic Segmentation Offload),都是执行类似的合并包和拆包操作。
一般内核会默认开启上述特性,我们可以通过 ethtool 命令查看和设置:
- 查看特性开关
$ sudo ethtool -k eth0 | grep -E \"generic-segmentation-offload|generic-receive-offload|tcp-segmentation-offload\"tcp-segmentation-offload: ongeneric-segmentation-offload: ongeneric-receive-offload: on - 设置开关
$ sudo ethtool -K eth0 gro off$ sudo ethtool -K eth0 gso off$ sudo ethtool -K eth0 tso off有时候我们通过 tcpdump 抓包时会抓到实际大小远超 MTU 的巨帧(Jumbo Frames),就是由于 GRO 特性导致的,因为 tcpdump 的处理是在更往后的步骤处理的。
GRO 处理流程
这里我们更关注流程的跳转,不去分析具体 GRO 处理的细节。napi_gro_receive() 源码如下:
https://elixir.bootlin.com/linux/v5.15.139/source/net/core/dev.c#L6214static gro_result_t napi_gro_receive(struct napi_struct *napi, struct sk_buff *skb){gro_result_t ret;skb_mark_napi_id(skb, napi);trace_napi_gro_receive_entry(skb);skb_gro_reset_offset(skb, 0);ret = napi_skb_finish(napi, skb, dev_gro_receive(napi, skb));trace_napi_gro_receive_exit(ret);return ret;}主要处理任务在 dev_gro_receive()以及 napi_gro_complete()完成,处理结束后会将 skb 发送到协议栈,完整调用栈如下:
| napi_gro_receive()└── napi_skb_finish()└── gro_normal_one()└── gro_normal_list()最后由 gro_normal_list 函数调用 netif_receive_skb_list_internal() 函数,到这一步网络包最终进入协议栈处理。
/* Pass the currently batched GRO_NORMAL SKBs up to the stack. */static void gro_normal_list(struct napi_struct *napi){// 如果没有接收的 skb,直接返回if (!napi->rx_count)return;// 将接收的 skb 列表传递给上层协议栈netif_receive_skb_list_internal(&napi->rx_list);// INIT_LIST_HEAD(&napi->rx_list);// 重置接收计数器napi->rx_count = 0;}7.1 L2 层协议栈处理
终于到了图中的第 7 步:内核协议栈处理。细分的话还可以分为 L2、L3、L4 三层的处理逻辑,本篇我们主要关注 L2 和 L3 层的处理,L4 层 TCP 协议的处理比较复杂,放到下一篇中做单独分析。
协议栈的处理从 netif_receive_skb_list_internal() 函数开始进行一系列的处理,主要调用栈如下
└── netif_receive_skb_list_internal()└── __netif_receive_skb_list()└── __netif_receive_skb_list_core()└── __netif_receive_skb_core() __netif_receive_skb_core()
这里经过一系列的调用最终是由 __netif_receive_skb_core() 函数处理完成后交给 IP 协议层处理,函数代码如下:
// https://elixir.bootlin.com/linux/v5.15.139/source/net/core/dev.c#L5339static int __netif_receive_skb_core(struct sk_buff **pskb, bool pfmemalloc, struct packet_type **ppt_prev){struct packet_type *ptype, *pt_prev;rx_handler_func_t *rx_handler;struct sk_buff *skb = *pskb;struct net_device *orig_dev;bool deliver_exact = false;int ret = NET_RX_DROP;__be16 type;net_timestamp_check(!READ_ONCE(netdev_tstamp_prequeue), skb);trace_netif_receive_skb(skb);orig_dev = skb->dev;skb_reset_network_header(skb);if (!skb_transport_header_was_set(skb))skb_reset_transport_header(skb);skb_reset_mac_len(skb);pt_prev = NULL;another_round:skb->skb_iif = skb->dev->ifindex;__this_cpu_inc(softnet_data.processed);if (static_branch_unlikely(&generic_xdp_needed_key)) {int ret2;migrate_disable();ret2 = do_xdp_generic(rcu_dereference(skb->dev->xdp_prog), skb);migrate_enable();if (ret2 != XDP_PASS) {ret = NET_RX_DROP;goto out;}}if (eth_type_vlan(skb->protocol)) {skb = skb_vlan_untag(skb);if (unlikely(!skb))goto out;}if (skb_skip_tc_classify(skb))goto skip_classify;if (pfmemalloc)goto skip_taps;list_for_each_entry_rcu(ptype, &ptype_all, list) {if (pt_prev)ret = deliver_skb(skb, pt_prev, orig_dev);pt_prev = ptype;}list_for_each_entry_rcu(ptype, &skb->dev->ptype_all, list) {if (pt_prev)ret = deliver_skb(skb, pt_prev, orig_dev);pt_prev = ptype;}skip_taps:#ifdef CONFIG_NET_INGRESSif (static_branch_unlikely(&ingress_needed_key)) {bool another = false;skb = sch_handle_ingress(skb, &pt_prev, &ret, orig_dev, &another);if (another)goto another_round;if (!skb)goto out;if (nf_ingress(skb, &pt_prev, &ret, orig_dev) < 0)goto out;}#endifskb_reset_redirect(skb);skip_classify:if (pfmemalloc && !skb_pfmemalloc_protocol(skb))goto drop;if (skb_vlan_tag_present(skb)) {if (pt_prev) {ret = deliver_skb(skb, pt_prev, orig_dev);pt_prev = NULL;}if (vlan_do_receive(&skb))goto another_round;else if (unlikely(!skb))goto out;}rx_handler = rcu_dereference(skb->dev->rx_handler);if (rx_handler) {if (pt_prev) {ret = deliver_skb(skb, pt_prev, orig_dev);pt_prev = NULL;}switch (rx_handler(&skb)) {case RX_HANDLER_CONSUMED:ret = NET_RX_SUCCESS;goto out;case RX_HANDLER_ANOTHER:goto another_round;case RX_HANDLER_EXACT:deliver_exact = true;break;case RX_HANDLER_PASS:break;default:BUG();}}if (unlikely(skb_vlan_tag_present(skb)) && !netdev_uses_dsa(skb->dev)) {check_vlan_id:if (skb_vlan_tag_get_id(skb)) {/* Vlan id is non 0 and vlan_do_receive() above couldn\'t * find vlan device. */skb->pkt_type = PACKET_OTHERHOST;} else if (eth_type_vlan(skb->protocol)) {/* Outer header is 802.1P with vlan 0, inner header is * 802.1Q or 802.1AD and vlan_do_receive() above could * not find vlan dev for vlan id 0. */__vlan_hwaccel_clear_tag(skb);skb = skb_vlan_untag(skb);if (unlikely(!skb))goto out;if (vlan_do_receive(&skb))/* After stripping off 802.1P header with vlan 0 * vlan dev is found for inner header. */goto another_round;else if (unlikely(!skb))goto out;else/* We have stripped outer 802.1P vlan 0 header. * But could not find vlan dev. * check again for vlan id to set OTHERHOST. */goto check_vlan_id;}/* Note: we might in the future use prio bits * and set skb->priority like in vlan_do_receive() * For the time being, just ignore Priority Code Point */__vlan_hwaccel_clear_tag(skb);}type = skb->protocol;/* deliver only exact match when indicated */if (likely(!deliver_exact)) {deliver_ptype_list_skb(skb, &pt_prev, orig_dev, type, &ptype_base[ntohs(type) & PTYPE_HASH_MASK]);}deliver_ptype_list_skb(skb, &pt_prev, orig_dev, type, &orig_dev->ptype_specific);if (unlikely(skb->dev != orig_dev)) {deliver_ptype_list_skb(skb, &pt_prev, orig_dev, type, &skb->dev->ptype_specific);}if (pt_prev) {if (unlikely(skb_orphan_frags_rx(skb, GFP_ATOMIC)))goto drop;*ppt_prev = pt_prev;} else {drop:if (!deliver_exact)atomic_long_inc(&skb->dev->rx_dropped);elseatomic_long_inc(&skb->dev->rx_nohandler);kfree_skb(skb);/* Jamal, now you will not able to escape explaining * me how you were going to use this. :-) */ret = NET_RX_DROP;}out:/* The invariant here is that if *ppt_prev is not NULL * then skb should also be non-NULL. * * Apparently *ppt_prev assignment above holds this invariant due to * skb dereferencing near it. */*pskb = skb;return ret;}函数还是比较冗长的,按顺序主要做了下面一些任务:
- 处理 skb 时间戳和协议头
- 软件执行 XDP(eXpress Data Path)
- 处理 VLAN header
- TAP 处理:tcpdump 在这里生效
- 入口处理:TC ingress 以及 TC BPF 处理
- 入口处理:Netfilter Ingress hook 处理
这里我们简要看下。
XDP 处理
XDP 本来属于硬件的功能,但如果硬件不支持,则推迟到这里来执行。但和硬件实现相比,这里的软件实现本身并不能提升性能,主要用来测试功能。
Tap 处理
这里主要是检查是否插入了 tap(探测点),如果有就会将 skb 发送给探测程序进行处理。libpcap/tcpdump 抓包就是在这里起作用,具体实现细节可以参考 af_packet.c#packet_rcv()。
// https://elixir.bootlin.com/linux/v5.15.139/source/net/core/dev.c#L5326static int __netif_receive_skb_core() { ... // 遍历list_for_each_entry_rcu(ptype, &ptype_all, list) {if (pt_prev)ret = deliver_skb(skb, pt_prev, orig_dev);pt_prev = ptype;}list_for_each_entry_rcu(ptype, &skb->dev->ptype_all, list) {if (pt_prev)ret = deliver_skb(skb, pt_prev, orig_dev);pt_prev = ptype;}...}// https://elixir.bootlin.com/linux/v5.15.139/source/net/core/dev.c#L2227static inline int deliver_skb(struct sk_buff *skb, struct packet_type *pt_prev, struct net_device *orig_dev){if (unlikely(skb_orphan_frags_rx(skb, GFP_ATOMIC)))return -ENOMEM;refcount_inc(&skb->users);return pt_prev->func(skb, skb->dev, pt_prev, orig_dev);}TC 处理
TC(traffic control)是 Linux 的流量控制模块,可以用来对流程进行分类、限速等操作。
除此之外,引入 TC BPF 后,还能通过 BPF 编程来做流量的透明拦截和处理,例如实现 K8s 的 Service 负载均衡。
这里通过 sch_handle_ingress() 函数进入 tc ingress 的处理,设置的入口规则会在这里生效。
Netfilter ingress 处理
Ingress 是在内核 4.2 引入的新 hook,区别于传统的 5 个在 IP 层工作的 hook,Ingress hook 主要用于处理进入网络设备的流量。可以通过 nfttable 进行设置,从而在 prerouting 之前就对流量进行处理。这里通过 nf_ingress 进入其处理逻辑。
// https://elixir.bootlin.com/linux/v5.15.139/source/net/core/dev.c#L5339skip_taps:#ifdef CONFIG_NET_INGRESSif (static_branch_unlikely(&ingress_needed_key)) {bool another = false;// 进入 tc ingress 处理skb = sch_handle_ingress(skb, &pt_prev, &ret, orig_dev, &another);if (another)goto another_round;if (!skb)goto out;// 进入 netfilter ingress 处理if (nf_ingress(skb, &pt_prev, &ret, orig_dev) < 0)goto out;}#endif发送到 L3 协议层
__netif_receive_skb_core() 函数最终会调用 deliver_skb(skb, pt_prev, orig_dev); 函数将 skb 向上层传递,逻辑如下:
static inline int deliver_skb(struct sk_buff *skb, struct packet_type *pt_prev, struct net_device *orig_dev){if (unlikely(skb_orphan_frags_rx(skb, GFP_ATOMIC)))return -ENOMEM;refcount_inc(&skb->users);// return pt_prev->func(skb, skb->dev, pt_prev, orig_dev);}这里的 pt_prev 就是 协议的注册信息,最终会调用其 .func 函数进行后续的处理,以 IP 协议为例其注册信息如下,后续我们以 IP 协议为例进行分析。
static struct packet_type ip_packet_type __read_mostly = {.type = cpu_to_be16(ETH_P_IP),.func = ip_rcv,.list_func = ip_list_rcv,};7.2 L3 层协议栈处理
在调用 ip_rcv() 函数后,网络包终于到了我们熟悉的 IP 协议层。该函数代码如下:
// https://elixir.bootlin.com/linux/v5.15.139/source/net/ipv4/ip_input.c#L557/* * IP receive entry point */int ip_rcv(struct sk_buff *skb, struct net_device *dev, struct packet_type *pt, struct net_device *orig_dev){struct net *net = dev_net(dev);skb = ip_rcv_core(skb, net);if (skb == NULL)return NET_RX_DROP;return NF_HOOK(NFPROTO_IPV4, NF_INET_PRE_ROUTING, net, NULL, skb, dev, NULL, ip_rcv_finish);}可以看到核心逻辑非常简单,主要就是对接收到的 skb 进行了一系列的合法性校验、统计计数更新等操作,然后会通过 NF_HOOK 宏将 skb 传递给下一个处理函数 ip_rcv_finish。
上述调用 NF_HOOK 的 各个参数含义如下:
- NFPROTO_IPV4:协议族:IPv4,
- NF_INET_PRE_ROUTING:Hook 点:PRE_ROUTING
- net:网络命名空间
- NULL:socket 为空(还没关联到具体 socket)
- skb:当前收到的 socket buffer (网络包)
- dev:输入网卡设备
- NULL:输出设备(此时还不知道走哪)
- ip_rcv_finish:okfn:如果通过钩子,继续执行的函数
进入 netfilter 处理
NF_HOOK 是一个宏,用于在 netfilter 中注册钩子函数,代码如下:
static inline intNF_HOOK(uint8_t pf, unsigned int hook, struct net *net, struct sock *sk, struct sk_buff *skb,struct net_device *in, struct net_device *out,int (*okfn)(struct net *, struct sock *, struct sk_buff *)){int ret = nf_hook(pf, hook, net, sk, skb, in, out, okfn);if (ret == 1)ret = okfn(net, sk, skb);return ret;}可以看到 NF_HOOK 宏的实现非常简单,它首先调用 nf_hook 函数进行钩子处理,如果我们通过 iptables 或者其他方式设置了回调,这里就会执行处理。如果结束完成后包没有被丢弃,就会执行 okfn 函数,这里就是我们传入的 ip_rcv_finish 函数。
ip_rcv_finish -> ip_rcv_finish_core:输入路由查找
这一步的核心处理是在 ip_rcv_finish_core 函数中执行的,其主要任务是决定接收包还是转发包。
// https://elixir.bootlin.com/linux/v5.15.139/source/net/ipv4/ip_input.c#L433static int ip_rcv_finish(struct net *net, struct sock *sk, struct sk_buff *skb){struct net_device *dev = skb->dev;int ret;/* if ingress device is enslaved to an L3 master device pass the * skb to its handler for processing */skb = l3mdev_ip_rcv(skb);if (!skb)return NET_RX_SUCCESS;ret = ip_rcv_finish_core(net, sk, skb, dev, NULL);if (ret != NET_RX_DROP)ret = dst_input(skb);return ret;}// https://elixir.bootlin.com/linux/v5.15.139/source/net/ipv4/ip_input.c#L315static int ip_rcv_finish_core(struct net *net, struct sock *sk, struct sk_buff *skb, struct net_device *dev, const struct sk_buff *hint){const struct iphdr *iph = ip_hdr(skb);int err, drop_reason;struct rtable *rt;drop_reason = SKB_DROP_REASON_NOT_SPECIFIED;// 路由提示优化if (ip_can_use_hint(skb, iph, hint)) {err = ip_route_use_hint(skb, iph->daddr, iph->saddr, iph->tos,dev, hint);if (unlikely(err))goto drop_error;} // 早期解复用(Early Demux)优化if (READ_ONCE(net->ipv4.sysctl_ip_early_demux) && !skb_dst(skb) && !skb->sk && !ip_is_fragment(iph)) {switch (iph->protocol) {case IPPROTO_TCP:if (READ_ONCE(net->ipv4.sysctl_tcp_early_demux)) {tcp_v4_early_demux(skb);/* must reload iph, skb->head might have changed */iph = ip_hdr(skb);}break;case IPPROTO_UDP:if (READ_ONCE(net->ipv4.sysctl_udp_early_demux)) {err = udp_v4_early_demux(skb);if (unlikely(err))goto drop_error;/* must reload iph, skb->head might have changed */iph = ip_hdr(skb);}break;}}/* *Initialise the virtual path cache for the packet. It describes *how the packet travels inside Linux networking. */if (!skb_valid_dst(skb)) {// 输入路由查找err = ip_route_input_noref(skb, iph->daddr, iph->saddr, iph->tos, dev);if (unlikely(err))goto drop_error;} else {struct in_device *in_dev = __in_dev_get_rcu(dev);if (in_dev && IN_DEV_ORCONF(in_dev, NOPOLICY))IPCB(skb)->flags |= IPSKB_NOPOLICY;}#ifdef CONFIG_IP_ROUTE_CLASSIDif (unlikely(skb_dst(skb)->tclassid)) {struct ip_rt_acct *st = this_cpu_ptr(ip_rt_acct);u32 idx = skb_dst(skb)->tclassid;st[idx&0xFF].o_packets++;st[idx&0xFF].o_bytes += skb->len;st[(idx>>16)&0xFF].i_packets++;st[(idx>>16)&0xFF].i_bytes += skb->len;}#endifif (iph->ihl > 5 && ip_rcv_options(skb, dev))goto drop; // 基于路由结果做处理rt = skb_rtable(skb);if (rt->rt_type == RTN_MULTICAST) {__IP_UPD_PO_STATS(net, IPSTATS_MIB_INMCAST, skb->len);} else if (rt->rt_type == RTN_BROADCAST) {__IP_UPD_PO_STATS(net, IPSTATS_MIB_INBCAST, skb->len);} else if (skb->pkt_type == PACKET_BROADCAST || skb->pkt_type == PACKET_MULTICAST) {struct in_device *in_dev = __in_dev_get_rcu(dev);/* RFC 1122 3.3.6: * * When a host sends a datagram to a link-layer broadcast * address, the IP destination address MUST be a legal IP * broadcast or IP multicast address. * * A host SHOULD silently discard a datagram that is received * via a link-layer broadcast (see Section 2.4) but does not * specify an IP multicast or broadcast destination address. * * This doesn\'t explicitly say L2 *broadcast*, but broadcast is * in a way a form of multicast and the most common use case for * this is 802.11 protecting against cross-station spoofing (the * so-called \"hole-196\" attack) so do it for both. */if (in_dev && IN_DEV_ORCONF(in_dev, DROP_UNICAST_IN_L2_MULTICAST)) {drop_reason = SKB_DROP_REASON_UNICAST_IN_L2_MULTICAST;goto drop;}}return NET_RX_SUCCESS;drop:kfree_skb_reason(skb, drop_reason);return NET_RX_DROP;drop_error:if (err == -EXDEV) {drop_reason = SKB_DROP_REASON_IP_RPFILTER;__NET_INC_STATS(net, LINUX_MIB_IPRPFILTER);}goto drop;}核心代码是下面两行:
// ... 代码省略if (!skb_valid_dst(skb)) {// 输入路由查找err = ip_route_input_noref(skb, iph->daddr, iph->saddr, iph->tos, dev);if (unlikely(err))goto drop_error;}// 基于路由结果做处理rt = skb_rtable(skb);if (rt->rt_type == RTN_MULTICAST) {// ..处理多播数据包} else if (rt->rt_type == RTN_BROADCAST) {// 处理广播数据包} else if (skb->pkt_type == PACKET_BROADCAST ||// ..}return NET_RX_SUCCESS;上述处理会获取路由查找的结果类型,主要有如下类型:
- RTN_LOCAL: 数据包的目标是本机,应该传递给上层协议栈。
- RTN_FORWARD: 数据包需要转发到其他主机。
- RTN_MULTICAST: 多播数据包。
- RTN_BROADCAST: 广播数据包。
- RTN_BLACKHOLE: 数据包应该被丢弃。
全部类型以枚举的形式定义,参考 rtm_type
这里有两个优化:
- ip_route_use_hint:路由提示优化,基于历史路由信息来优化路由查找过程。
- 早期解复用(Early Demux)优化:主要是针对 TCP/UDP 包,检查相应的信息是否缓存在 socket 上。这里是一个优化项,控制参数如下:
$ sysctl -a |grep early demuxnet.ipv4.ip_early_demux = 1 net.ipv4.tcp_early_demux = 1net.ipv4.udp_early_demux = 1上述处理流程最终会获取到一个 dst_entry 结构体,包含了路由查找的结果信息和处理方式。
ip_local_deliver:本地收包处理
ip_rcv_finish_core 获取到路由目标后,会调用 dst_input 进行后续处理。
/* Input packet from network to transport. */static inline int dst_input(struct sk_buff *skb){return INDIRECT_CALL_INET(skb_dst(skb)->input, ip6_input, ip_local_deliver, skb);}上述代码的意思是如果 skb_dst(skb)->input 是 ip6_input 或 ip_local_deliver 函数,则直接调用,否则就会调用 input 函数,常用的 input 函数有:
-
dst->input = ip_local_deliver:本地收包 -
dst->input = ip_forward:IPv4 转发 -
dst->input = ip6_input:IPv6 处理 -
dst->input = dst_discard:丢弃包
对于本地收包是调用 ip_local_deliver 函数进行处理。
/* * Deliver IP Packets to the higher protocol layers. */int ip_local_deliver(struct sk_buff *skb){/* *Reassemble IP fragments. */struct net *net = dev_net(skb->dev);if (ip_is_fragment(ip_hdr(skb))) {if (ip_defrag(net, skb, IP_DEFRAG_LOCAL_DELIVER))return 0;}return NF_HOOK(NFPROTO_IPV4, NF_INET_LOCAL_IN, net, NULL, skb, skb->dev, NULL, ip_local_deliver_finish);可以看到其核心逻辑如下:
- 如果需要重组,则对 IP 分片进行重组处理。
- 调用 NF_HOOK 交给 netfilter 处理,这里的 hook 为
NF_INET_LOCAL_IN,表示本地输入数据包。 - netfilter 处理结果后,调用 ip_local_deliver_finish(),将包交给上层协议栈处理。
ip_local_deliver_finish():发送包给传输层
这里的完整调用栈是:
| ip_local_deliver_finish()|__ ip_protocol_deliver_rcu()|__ transport_protocol.callback()代码如下:
// https://elixir.bootlin.com/linux/v5.15.139/source/net/ipv4/ip_input.c#L226static int ip_local_deliver_finish(struct net *net, struct sock *sk, struct sk_buff *skb){__skb_pull(skb, skb_network_header_len(skb));rcu_read_lock();ip_protocol_deliver_rcu(net, skb, ip_hdr(skb)->protocol);rcu_read_unlock(); // 永远返回成功return 0;}// https://elixir.bootlin.com/linux/v5.15.139/source/net/ipv4/ip_input.c#L187// 返回值为空,所有错误在内部处理void ip_protocol_deliver_rcu(struct net *net, struct sk_buff *skb, int protocol){const struct net_protocol *ipprot;int raw, ret;resubmit:raw = raw_local_deliver(skb, protocol);ipprot = rcu_dereference(inet_protos[protocol]);if (ipprot) {if (!ipprot->no_policy) {if (!xfrm4_policy_check(NULL, XFRM_POLICY_IN, skb)) {kfree_skb(skb);return;}nf_reset_ct(skb);}ret = INDIRECT_CALL_2(ipprot->handler, tcp_v4_rcv, udp_rcv, skb);if (ret < 0) {protocol = -ret;goto resubmit;}__IP_INC_STATS(net, IPSTATS_MIB_INDELIVERS);} else {if (!raw) {if (xfrm4_policy_check(NULL, XFRM_POLICY_IN, skb)) {__IP_INC_STATS(net, IPSTATS_MIB_INUNKNOWNPROTOS);icmp_send(skb, ICMP_DEST_UNREACH, ICMP_PROT_UNREACH, 0);}kfree_skb(skb);} else {__IP_INC_STATS(net, IPSTATS_MIB_INDELIVERS);consume_skb(skb);}}}该函数会解析 skb 数据包中的 struct net_protocol 协议信息,并在 INDIRECT_CALL_2(ipprot->handler, tcp_v4_rcv, udp_rcv, skb); 调用协议栈初始化时注册的 handler 回调函数发送给传输层处理,传输层各协议对应的 handler 如下:
- TCP:tcp_v4_rcv。
- UDP:udp_rcv。
- ICMP:icmp_rcv。
小结
至此,Linux 内核完成了 IP 层数据包的接收处理,并将其交给相应的传输层协议进行处理。我们会在下一篇文章中探讨分析 TCP 传输层的处理流程。


