SSM框架中关于Spring MVC的技术问题
一、SpringMVC的执行流程
Spring MVC是Spring框架的一个模块,是一个基于Java的实现了MVC设计模式的轻量级Web框架。它通过一套注解和接口,让简单的Java类成为处理请求的控制器,无需实现任何接口,同时支持REST风格的编程。
SpringMVC 的执行流程是其核心工作原理:
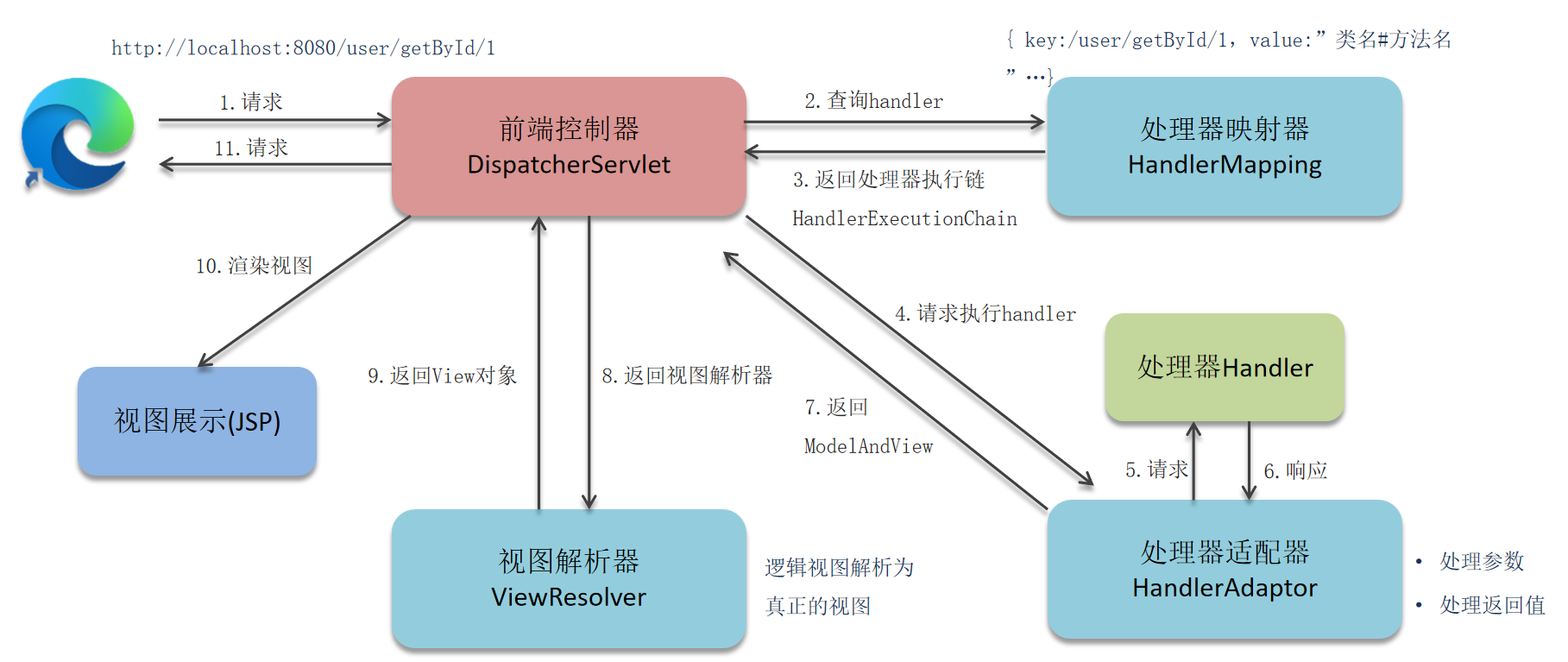
1.视图阶段(JSP)
-
用户发送请求:客户端(浏览器等)发送 HTTP 请求到前端控制器(DispatcherServlet)。
-
前端控制器接收请求:DispatcherServlet 作为 SpringMVC 的核心,接收所有请求并进行统一处理。
-
处理器映射器查找处理器:DispatcherServlet 调用 HandlerMapping(处理器映射器),根据请求 URL 查找对应的 Handler(处理器,如 Controller 中的方法)。
-
返回处理器执行链:HandlerMapping 返回一个 HandlerExecutionChain 对象,包含找到的 Handler 和对应的拦截器(Interceptor)。
-
处理器适配器调用处理器:DispatcherServlet 调用 HandlerAdapter(处理器适配器),由它负责调用具体的 Handler 执行处理逻辑。
-
处理器执行处理逻辑:Handler(通常是 Controller 中的方法)执行具体的业务处理,处理完成后返回一个 ModelAndView 对象(包含模型数据和视图名称)。
-
处理器适配器返回结果:HandlerAdapter 将 Handler 执行后的 ModelAndView 返回给 DispatcherServlet。
-
视图解析器解析视图:DispatcherServlet 调用 ViewResolver(视图解析器),根据 ModelAndView 中的视图名称解析出具体的 View(视图)对象。
-
视图渲染:View 对象结合 Model 中的数据进行渲染,生成最终的响应内容(如 HTML)。
-
返回响应:DispatcherServlet 将渲染后的结果返回给客户端,完成一次请求的处理。
整个流程中,DispatcherServlet 负责协调各个组件的工作,降低了组件之间的耦合度,体现了 SpringMVC 的设计优势。
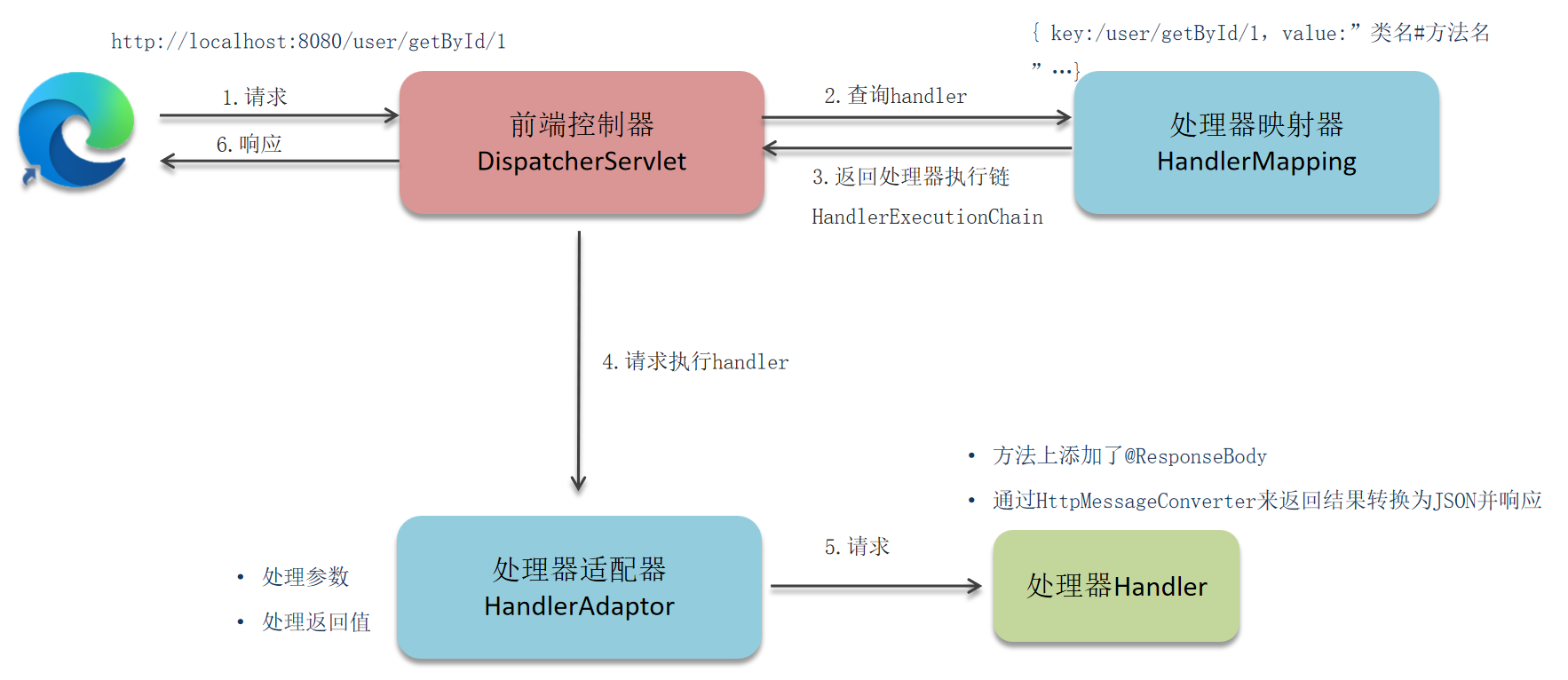
2.前后端分离阶段(接口开发,异步请求)
-
用户发送请求:客户端(浏览器等)发送 HTTP 请求到前端控制器(DispatcherServlet)。
-
前端控制器接收请求:DispatcherServlet 作为 SpringMVC 的核心,接收所有请求并进行统一处理。
-
处理器映射器查找处理器:DispatcherServlet 调用 HandlerMapping(处理器映射器),根据请求 URL 查找对应的 Handler(处理器,如 Controller 中的方法)。
-
返回处理器执行链:HandlerMapping 返回一个 HandlerExecutionChain 对象,包含找到的 Handler 和对应的拦截器(Interceptor)。
-
处理器适配器调用处理器:DispatcherServlet 调用 HandlerAdapter(处理器适配器),由它负责调用具体的 Handler 执行处理逻辑。
-
处理器执行处理逻辑:Handler(通常是 Controller 中的方法)执行具体的业务处理。
-
返回响应:方法上添加了@ResponseBody注解,通过HttpMessageConverter来返回结果转换为JSON并响应。
二、Springboot自动配置原理
Spring Boot 的自动配置是其核心特性之一,它通过约定优于配置的思想,简化了 Spring 应用的搭建和开发过程。
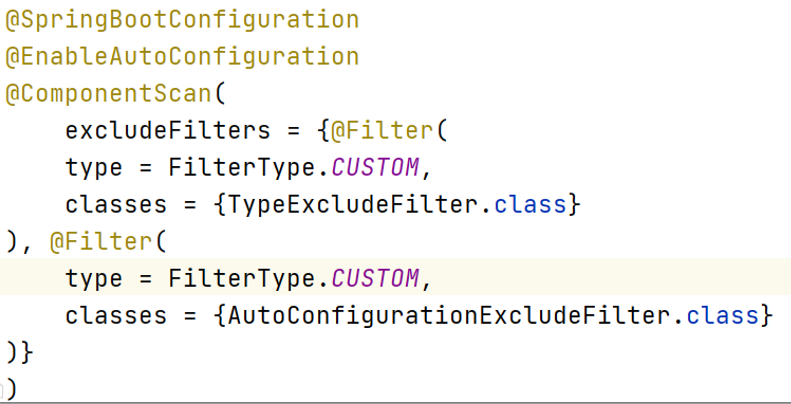
在Spring Boot启动类上有一个@SpringBootApplication注解,包含了以下三个注解的功能:
-
@SpringBootConfiguration:标识该类为一个配置类。 -
@EnableAutoConfiguration:启用自动配置功能。 -
@ComponentScan:扫描并注册组件。
1.@EnableAutoConfiguration 注解
@EnableAutoConfiguration 是自动配置的核心注解,它通过 @Import(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class) 导入了 AutoConfigurationImportSelector 类。这个类负责选择和加载所有符合条件的自动配置类。
@Target({ElementType.TYPE})@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)@Documented@Inherited@AutoConfigurationPackage //作用:将main包下的所有组件注册到容器中@Import({AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class}) //加载自动装配类 xxxAutoconfigurationpublic @interface EnableAutoConfiguration { String ENABLED_OVERRIDE_PROPERTY = \"spring.boot.enableautoconfiguration\"; Class[] exclude() default {}; String[] excludeName() default {};} AutoConfigurationImportSelector 类实现了 ImportSelector接口,也就实现了这个接口中的 selectImports方法,这个方法经过层层调用,最终会读取META-INF 目录下的 后缀名 为imports的文件(springboot2.7以前的版本,读取的是spring.factories文件;2.7~3.0之间的版本读取的是spring.factories或.imports;3.0以后的版本是.import文件)。
protected List getCandidateConfigurations(AnnotationMetadata metadata, AnnotationAttributes attributes) { List configurations = new ArrayList(SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(this.getSpringFactoriesLoaderFactoryClass(), this.getBeanClassLoader())); ImportCandidates.load(AutoConfiguration.class, this.getBeanClassLoader()).forEach(configurations::add); Assert.notEmpty(configurations, \"No auto configuration classes found in META-INF/spring.factories nor in META-INF/spring/org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.AutoConfiguration.imports. If you are using a custom packaging, make sure that file is correct.\"); return configurations; }
读取到全类名了之后,会解析注册条件,也就是@Conditional及其衍生注解,把满足注册条件的Bean对象自动注入到IOC容器中。
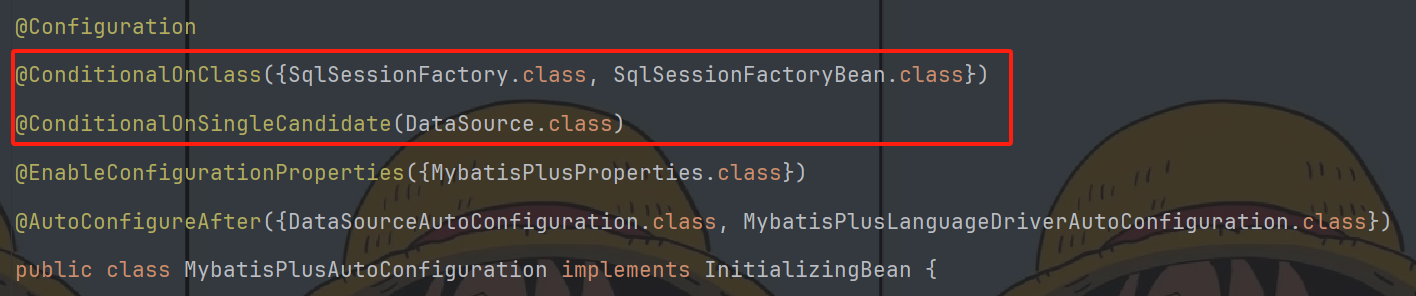
2.自定义start
在实际开发中,经常会定义一些公共组件,提供给各个项目团队使用。而在SpringBoot的项目中,一般会将这些公共组件封装为SpringBoot 的 starter。
实现一个自定义的 Spring Boot Starter,我们需要创建一个能够被 Spring Boot 自动配置的模块。下面将实现一个简单的 \"hello-service\" starter,它提供一个问候服务。
2.1 创建start
创建一个 Maven 项目,结构如下:
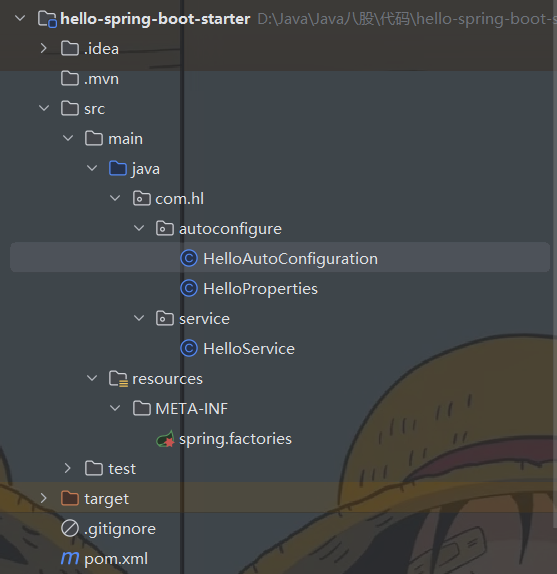
HelloService:
package com.hl.service;/** * 问候服务类,提供基础的问候功能 */public class HelloService { private String prefix; private String suffix; public HelloService(String prefix, String suffix) { this.prefix = prefix; this.suffix = suffix; } /** * 生成问候语 */ public String sayHello(String name) { return prefix + name + suffix; } // getter和setter方法 public String getPrefix() { return prefix; } public void setPrefix(String prefix) { this.prefix = prefix; } public String getSuffix() { return suffix; } public void setSuffix(String suffix) { this.suffix = suffix; }}HelloProperties:
package com.hl.autoconfigure;import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;/** * 配置属性类,用于绑定application.properties中的配置 */@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = \"hello\")public class HelloProperties { // 默认前缀 private String prefix = \"Hello, \"; // 默认后缀 private String suffix = \"!\"; // getter和setter方法 public String getPrefix() { return prefix; } public void setPrefix(String prefix) { this.prefix = prefix; } public String getSuffix() { return suffix; } public void setSuffix(String suffix) { this.suffix = suffix; }}HelloAutoConfiguration:
package com.hl.autoconfigure;import com.hl.service.HelloService;import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionalOnClass;import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionalOnMissingBean;import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.EnableConfigurationProperties;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;/** * 自动配置类,负责创建和配置HelloService实例 */@Configuration@ConditionalOnClass(HelloService.class) // 当类路径下存在HelloService时才生效@EnableConfigurationProperties(HelloProperties.class) // 启用配置属性public class HelloAutoConfiguration { private final HelloProperties helloProperties; // 注入配置属性 public HelloAutoConfiguration(HelloProperties helloProperties) { this.helloProperties = helloProperties; } // 注册HelloService Bean @Bean @ConditionalOnMissingBean // 当容器中没有HelloService Bean时才创建 public HelloService helloService() { return new HelloService( helloProperties.getPrefix(), helloProperties.getSuffix() ); }}在spring.factories中注册自动配置类:
# 注册自动配置类org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=\\com.hl.autoconfigure.HelloAutoConfiguration2.2 使用自定义 Starter
首先将上面的 starter 项目安装到本地 Maven 仓库:
mvn clean install
在需要使用的项目中添加依赖:
com.HL hello-spring-boot-starter 1.0-SNAPSHOT 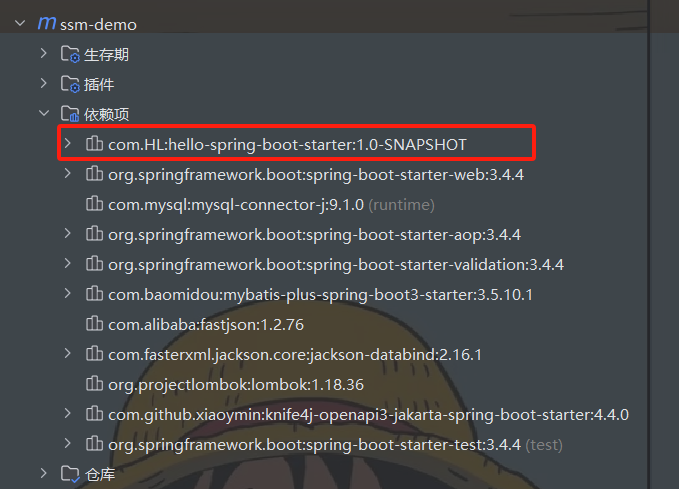
在 application.yml中配置:
hello: prefix: Hi, suffix: Welcome!在代码中使用:
@Tag(name = \"hello接口\")@RestController@RequestMapping(\"/hello\")public class HelloController { @Autowired private HelloService helloService; @Operation(summary = \"hello接口\") @GetMapping(\"/{name}\") public String hello(@PathVariable(\"name\") String name) { return helloService.sayHello(name); }}三、Spring、Spring MVC和Springboot的常见注解
Spring、Spring MVC 和 Spring Boot 提供了丰富的注解简化开发,以下是三类框架中最常用的注解分类总结:
1.Spring 核心注解
主要用于 IoC 容器管理、依赖注入、AOP 等核心功能。
-
IoC 容器相关
@Component:标记类为 Spring 组件,自动扫描并注册到容器(通用组件)。@Controller:特殊的@Component,标记类为 MVC 控制器(归为 Spring MVC 但基于 Spring 核心)。@Service:特殊的@Component,标记类为业务逻辑层服务。@Repository:特殊的@Component,标记类为数据访问层(DAO),自动转换数据库异常。@Scope:指定 Bean 的作用域(如singleton单例、prototype多例等)。@Lazy:延迟初始化 Bean(仅在首次使用时创建)。
-
依赖注入相关
@Autowired:自动注入依赖(默认按类型匹配,结合@Qualifier按名称匹配)。@Qualifier:与@Autowired配合,指定注入 Bean 的名称。@Resource:JDK 注解,按名称注入依赖(默认名称,可指定name或type)。@Value:注入配置文件中的属性值(如@Value(\"${server.port}\"))。
-
AOP 相关
@Aspect:标记类为切面类。@Pointcut:定义切入点(如execution(* com.example.service.*.*(..)))。@Before/@After/@AfterReturning/@AfterThrowing/@Around:定义通知(增强逻辑)。
-
其他核心注解
@Configuration:标记类为配置类(替代 XML 配置)。@Bean:在配置类中定义 Bean(方法返回值作为容器中的 Bean)。@Profile:根据环境激活不同配置(如dev/test/prod环境)。@Conditional:基于条件判断是否注册 Bean(Spring Boot 自动配置的基础)。
2.Spring MVC 注解
主要用于 Web 层请求处理、参数绑定、视图跳转等。
-
请求映射
@RequestMapping:映射 HTTP 请求(支持value路径、method请求方法、params参数等)。@GetMapping:简化@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.GET),处理 GET 请求。@PostMapping:简化处理 POST 请求。@PutMapping/@DeleteMapping:对应 PUT/DELETE 请求方法。
-
参数绑定
@PathVariable:获取 URL 路径中的参数(如/user/{id}中的id)。@RequestParam:获取请求参数(如?name=xxx),可指定是否必传、默认值。@RequestBody:接收请求体中的 JSON/XML 数据(通常用于 POST/PUT 请求)。@RequestHeader:获取请求头信息(如Accept、Cookie)。@CookieValue:获取指定 Cookie 的值。@ModelAttribute:将请求参数绑定到模型对象,或在方法执行前向模型添加属性。
-
响应处理
@ResponseBody:将方法返回值直接作为响应体(不经过视图解析,常用于 JSON 接口)。@RestController:组合@Controller和@ResponseBody,标记类为 REST 接口控制器。@ResponseStatus:指定方法返回的 HTTP 状态码(如HttpStatus.CREATED)。
-
异常处理
@ControllerAdvice:全局异常处理类(结合@ExceptionHandler使用)。@ExceptionHandler:处理指定类型的异常(如@ExceptionHandler(NullPointerException.class))。
3.Spring Boot 注解
基于 Spring 和 Spring MVC 扩展,用于简化配置、自动配置等。
-
启动类相关
@SpringBootApplication:Spring Boot 核心注解,组合以下三个注解:@SpringBootConfiguration:标记类为配置类(继承@Configuration)。@EnableAutoConfiguration:开启自动配置(核心,加载META-INF/spring.factories中的配置类)。@ComponentScan:自动扫描并注册组件(默认扫描当前类所在包及子包)。
-
配置相关
@ConfigurationProperties:将配置文件中的属性绑定到 Java 类(如prefix = \"user\"绑定user.name等)。@EnableConfigurationProperties:启用@ConfigurationProperties注解的类(使其被 Spring 管理)。@PropertySource:加载指定的自定义配置文件(如@PropertySource(\"classpath:custom.properties\"))。
-
条件注解(自动配置核心)
@ConditionalOnClass:类路径存在指定类时生效。@ConditionalOnMissingClass:类路径不存在指定类时生效。@ConditionalOnBean:容器中存在指定 Bean 时生效。@ConditionalOnMissingBean:容器中不存在指定 Bean 时生效(用户自定义 Bean 优先)。@ConditionalOnProperty:配置文件中存在指定属性且值匹配时生效(如@ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = \"server\", name = \"port\", havingValue = \"8080\"))。@ConditionalOnWebApplication/@ConditionalOnNotWebApplication:判断是否为 Web 应用。
四、相关面试问题
1.SpringMVC的执行流程?
SpringMVC的执行流程包含以下步骤:
第一,用户端发送请求给前端处理器
DispatcherServlet,前端处理器接收请求并进行统一处理。第二,
DispatcherServlet调用处理映射器HandleMapping找到具体的处理器,处理映射器返回处理器对象和响应的拦截器。第三,
DispatcherServlet调用处理适配器HandlerAdapter适配并调用相应的处理器Controller,处理器处理完成后返回ModelAndView对象。第四,
DispatcherServlet调用视图解析器ViewResolver解析并返回视图View对象。第五,
DispatcherServlet渲染视图并响应用户。以上是使用JSP视图阶段的执行流程,对于现在常用的前后端分离阶段流程,不同的是在具体处理器处理完成后返回的不是ModelAndView,而是在方法上添加@ResponseBody注解,通过HttpMessageConverter来返回结果转换为JSO并响应。
2.Springboot自动配置原理?
Springboot的自动装配原理依赖于@SpringBootApplication注解,它封装了
@SpringBootConfiguration、@EnableAutoConfiguration和@ComponentScan。其中@EnableAutoConfiguration注解是实现自动装配的核心,该注解又组合了@Import注解,导入了AutoConfigurationImportSelector类,实现了selectImports方法,这个方法经过层层调用,最终会读取META-INF 目录下的后缀名为imports的文件或者spring.factories文件。读取到全类名了之后,会解析注册条件,把满足注册条件的Bean对象自动注入到IOC容器中
3.Spring 的常见注解有哪些?
Spring的常见注解包括:
声明Bean的注解:
@Component、@Service、@Repository、@Controller。依赖注入相关注解:
@Autowired、@Qualifier、@Resource。设置作用域的注解:
@Scope。配置相关注解:
@Configuration、@ComponentScan、@Bean。AOP相关注解:
@Aspect、@Before、@After、@Around、@Pointcut。
4.SpringMVC常见的注解有哪些?
SpringMVC的常见注解有:
@RequestMapping:映射请求路径。
@RequestBody:接收HTTP请求的JSON数据。
@RequestParam:指定请求参数名称。
@PathVariable:从请求路径中获取参数。
@ResponseBody:将Controller方法返回的对象转化为JSON。
@RequestHeader:获取请求头数据。
@PostMapping、@GetMapping等。
5.Springboot常见注解有哪些?
Spring Boot的常见注解包括:
@SpringBootApplication:由@SpringBootConfiguration、@EnableAutoConfiguration和@ComponentScan组成。其他注解如
@RestController、@GetMapping、@PostMapping等,用于简化Spring MVC的配置。


