揭秘数据结构的魔力:用堆(Heap)打造高效排序

个人主页:一代...
个人专栏:数据结构

1. 定义:
- 堆通常是一个可以被看做一棵树的数组对象,在物理层面上表现为顺序存储结构,但在逻辑层面上是完全二叉树的形态,这意味着除了最后一层外,每一层都被完全填满,且最后一层从左到右填充。
- 堆中某个结点的值总是不大于或不小于其父结点的值,这一性质使得堆成为最高效的优先级队列。
(注意:大堆和小堆的实现都是用数组来实现的,其物理结构是数组 但其逻辑结构是一颗完全二叉树)
用数组实现堆,假设其双亲节点的下标为i,则其左孩子节点的下标为2*i+1,右孩子节点的下标为2*i+2
若孩子节点的坐标为i(这里的孩子节点无论是左孩子还是右孩子),其双亲节点的坐标都为(i-1)/2;
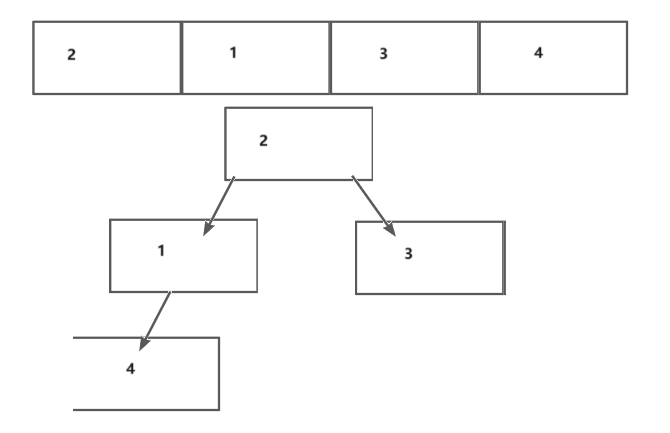
如果想要一个数组变为堆,首先要把其看做完全二叉树的结构
如数组a[4]={2,1,3,4}
将其理解为树的结构就变为:(理解为树的结构后就可以对其进行操作,将其变为大堆或小堆)
2. 堆的分类
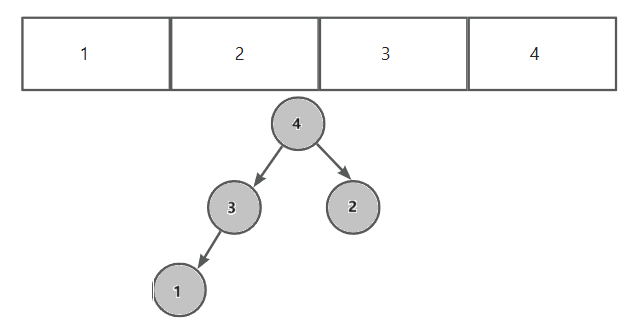
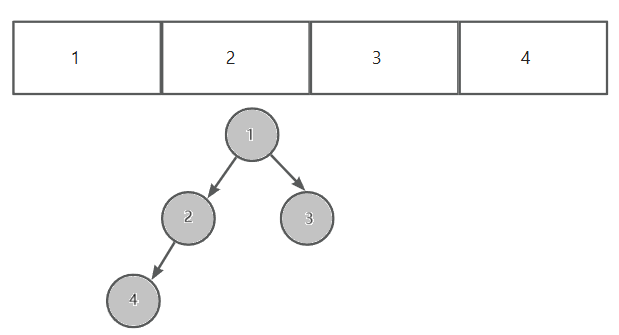
堆分为大堆和小堆
- 大堆:大堆的双亲节点都大于其孩子节点
- 小堆:小堆的双亲节点都小于其孩子节点
3. 堆的实现
a. 堆的结构体定义:
typedef int HPDataType;typedef struct Heap{HPDataType* a;int size;int capacity;}HP;
b. 堆的初始化
void HPInit(HP* php){php->a = NULL;php->capacity = php->size = 0;}
c. 堆的建立
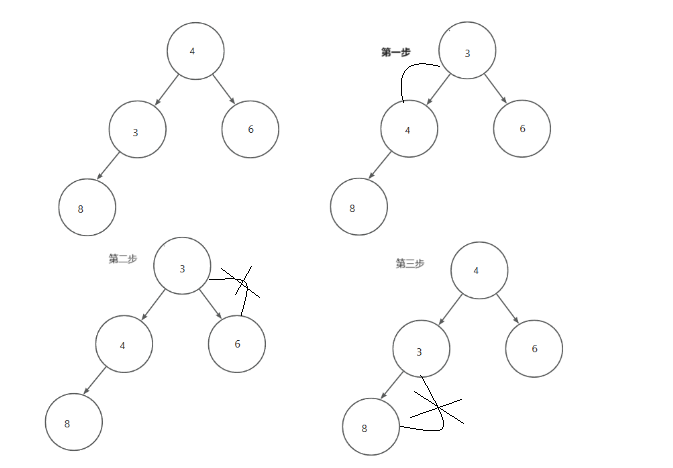
ⅰ. 向上调整法
向上调整法要从第一个元素开始,向上调整法建小堆时,当孩子节点小于双亲节点时,孩子节点的值就和父亲节点的值交换,孩子节点坐标等于双亲节点的坐标,双亲节点的坐标变为(双亲节点的坐标-1)/ 2,当孩子节点==0时循环结束。
void Swap(HPDataType* a, HPDataType* b){HPDataType tmp = *a;*a = *b;*b = tmp;}void AdjustUp(HPDataType* a, int child)//不传结构体,为了后面排序做准备,原因后面会解释{assert(a);int parent = (child - 1) / 2;while (child > 0)//parent>=0可以作为结束条件,但是一个巧合,//因为到最后是依靠当child==0,parent=(child-1)/2=-1/2=0时//a[parent]==a[child]结束的{if (a[child] a[parent]就建大堆{Swap(&a[child], &a[parent]);child = parent;parent = (parent - 1) / 2;}else{break;}}}1. 向上调整法建堆
void Swap(HPDataType* a, HPDataType* b){HPDataType tmp = *a;*a = *b;*b = tmp;}void AdjustUp(HPDataType* a, int child)//不传结构体,为了后面排序做准备,原因后面会解释{assert(a);int parent = (child - 1) / 2;while (child > 0)//parent>=0可以作为结束条件,但是一个巧合,//因为到最后是依靠当child==0,parent=(child-1)/2=-1/2=0时//a[parent]==a[child]结束的{if (a[child] a[parent]就建大堆{Swap(&a[child], &a[parent]);child = parent;parent = (parent - 1) / 2;}else{break;}}}void HPInitArray(HP* php, HPDataType* a, int n){assert(php);php->a = (HPDataType*)malloc(sizeof(HPDataType) * n);if (php->a == NULL){perror(\"malloc fail!\");return;}memcpy(php->a, a, n * sizeof(HPDataType));php->capacity = php->size = n;//向上调整for (int i = 1; i a, i);}}int main(){HPDataType a[] = { 50,100,480,76,31,31,226 };HPSort(a, sizeof(a) / sizeof(a[0]));//之前向上调整和向下调整就是为了这里//直接传a数组,而不是for (int i = 0; i < sizeof(a) / sizeof(a[0]); i++){printf(\"%d \", a[i]);//排升序}HP hp;HPInit(&hp); HPInitArray(&hp,a,sizeof(a)/sizeof(HPDataType)); return 0;}
2. 向上调整法建堆的时间复杂度

所以向上调整建堆的时间复杂度为O(N*logN),向上调整法的时间复杂度为O(logN)(即调整高度次)
ⅱ. 向下调整法
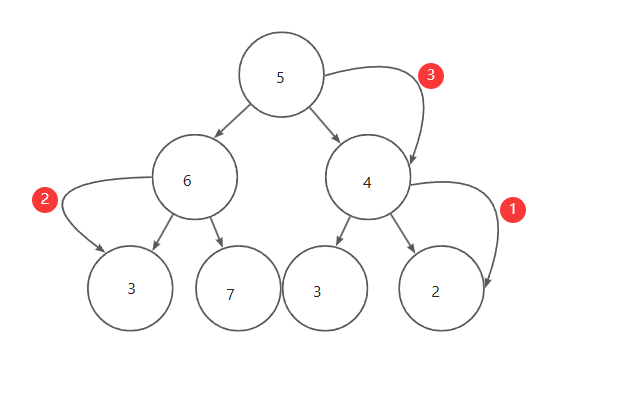
转换之后就变为小堆
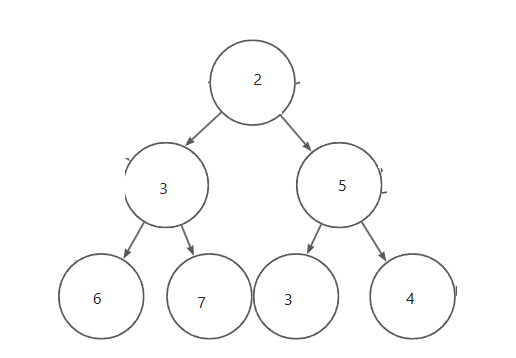
向下调整法时要从最后一个元素的双亲节点开始,在向下调整建小堆的过程中,用假设法选出左右孩子中最小的一个,当孩子节点大于双亲节点时,孩子节点就和双亲节点交换,双亲节点等于孩子节点,孩子节点等于双亲节点*2+1(不可以为双亲节点*2+2,必须为有孩子·,以便后面比较左右孩子的大小),当孩子节点的坐标大于等于总数组的大小时,就跳出循环
void Swap(HPDataType* a, HPDataType* b){HPDataType tmp = *a;*a = *b;*b = tmp;}void AdjustDown(HPDataType* a, int n, int parent)//不传结构体,为了后面排序做准备,原因后面会解释{assert(a);int child = parent * 2 + 1;while (child < n){//假设法if (child + 1 < n && a[child] < a[child + 1]){child++;}if (a[parent] < a[child]){Swap(&a[parent], &a[child]);parent = child;child = parent * 2 + 1;//右孩子,不可以为左孩子,因为上面要比较}else{break;}}}1. 向下调整法建堆
void Swap(HPDataType* a, HPDataType* b){HPDataType tmp = *a;*a = *b;*b = tmp;}void AdjustDown(HPDataType* a, int n, int parent)//不传结构体,为了后面排序做准备,原因后面会解释{assert(a);int child = parent * 2 + 1;while (child < n){//假设法if (child + 1 < n && a[child] < a[child + 1]){child++;}if (a[parent] a = (HPDataType*)malloc(sizeof(HPDataType) * n);if (php->a == NULL){perror(\"malloc fail!\");return;}memcpy(php->a, a, n * sizeof(HPDataType));php->capacity = php->size = n;//向下调整for (int i = (php->size - 1 - 1) / 2; i >= 0; i--)//数组的大小为size,对应下标为size-1,其数组最后一个元素//的双亲为(size-1-1)/2;{AdjustDown(php->a, n, i);}}int main(){HPDataType a[] = { 50,100,480,76,31,31,226 };HPSort(a, sizeof(a) / sizeof(a[0]));//之前向上调整和向下调整就是为了这里//直接传a数组,而不是for (int i = 0; i < sizeof(a) / sizeof(a[0]); i++){printf(\"%d \", a[i]);//排升序}HP hp;HPInit(&hp); HPInitArray(&hp,a,sizeof(a)/sizeof(HPDataType)); return 0;}
2. 向下调整建堆的时间复杂度

所以向下调整法建堆的时间复杂度为O(N),向下调整法的时间复杂度为logN
d. 堆的插入
void HPPush(HP* php, HPDataType x){assert(php);if (php->size == php->capacity){int newcapacity = php->capacity == 0 ? 4 : php->capacity * 2;HPDataType* tmp = (HPDataType*)realloc(php->a,sizeof(HPDataType) * newcapacity);if (tmp == NULL){perror(\"realloc fail!\");return;}php->a = tmp;php->capacity = newcapacity;}php->a[php->size] = x;php->size++;AdjustUp(php->a, php->size - 1);}ⅰ. 时间复杂度
运用了一次向上调整法时间复杂度为O(logN)
e. 堆的删除
堆的删除要交换堆顶元素和最后一个元素,把size--,在用一次向下调整法就可以了,不可以直接删除堆顶元素再建堆,一来这样时间复杂度增大了,二是删除堆顶元素,元素之间关系错乱了,父子变叔侄,兄弟变父子
void HPPop(HP* php){assert(php);assert(php->size > 0);Swap(&php->a[0], &php->a[php->size - 1]);php->size--;AdjustDown(php->a, php->size, 0);}ⅰ. 时间复杂度
运用了一次向下调整法,时间复杂度为O(logN)
f. 堆的判空
bool HPEmpty(HP* php){assert(php);return php->size == 0;}ⅰ. 时间复杂度
时间复杂度为O(1)
g. 取堆元素
HPDataType HPTop(HP* php){assert(php);return php->a[0];}ⅰ. 时间复杂度
时间复杂度为O(1)
h. 堆的摧毁
void HPDestroy(HP* php){assert(php);free(php->a);php->a = NULL;php->size = php->capacity = 0;}
i. 堆的排序(堆的向上调整法和向下调整法不传结构体的原因)
void HPSort(HPDataType* a, int n){//这里不用建大堆选出最大数,建堆的时间复杂度为O(N)// 取出最大数后再N-1个数进行建堆,执行次数为N-1//n个数,执行次数为N+N-1+N-2.....+1;时间复杂度为O(N^2)//,和冒泡排序时间复杂度为一样,没有时间上的优势for(int i=(n-1-1)/2;i>=0;i--){AdjustDown(a, n, i);}//对数组进行升序排列//需要建大堆//收尾交换//把最后一个值不放在堆中,建大堆选出最大数,将其放在最后int end = n-1;while (end > 0){Swap(&a[end], &a[0]);AdjustDown(a, end, 0);end--;}}原因:由于向上调整法和向下调整法传结构体每次都需要建一个堆,太耗费时间,但如果传数组,在用调整法时就不需要写一个堆的结构体,比如堆的排序
ⅰ. 时间复杂度
向下调整法建堆的时间复杂度为O(N),排序的时间复杂度为和向上调整时间一样,计算方式一样,为O(NlogN),总的时间复杂度为O(NlogN)。
习题:在很大的数据个数中找出最大的k个数,借用文件的形式实现
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1#include#include#include#includevoid Swap(int *a,int *b){int tmp = *a;*a = *b;*b = tmp;}void createNData(){ srand((unsigned int)time(NULL));const char* file = \"data.txt\";//要打开的文件FILE* fin = fopen(file, \"w\");if (fin == NULL){perror(\"fopen fail\");return;}for (int i = 1; i <= 20; i++){int x = rand() % 10000 + 1;fprintf(fin, \"%d\\n\", x);}fclose(fin);}void AdjustDown(int* a, int n, int parent){int child = parent * 2 + 1;while (child < n){if (child + 1 a[child + 1]){child++;}if (a[parent] > a[child]){Swap(&a[parent], &a[child]);parent = child;child = parent * 2 + 1;}else{break;}}}void topk(){int k;int x;const char* file = \"data.txt\";//要打开的文件printf(\"要找出的最大数字的个数:>\");scanf(\"%d\", &k);FILE* fout = fopen(\"data.txt\", \"r\");if (fout == NULL){perror(\"fopen fail\");return;}int* minheap = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * k);if (minheap == NULL){perror(\"malloc fail\");return;}for (int i = (k - 1 - 1)/2 ; i >= 0; i--){AdjustDown(minheap, k, i);}while (fscanf(fout, \"%d\", &x) != EOF){if (x > minheap[0]){minheap[0] = x;AdjustDown(minheap, k, 0);}}for (int i = 0; i < k; i++){printf(\"%d\\n\", minheap[i]);}fclose(fout);}int main(){createNData();topk();return 0;}堆的实现全部代码
test.c
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1#include\"Heap.h\"int main(){HPDataType a[] = { 50,100,480,76,31,31,226 };HPSort(a, sizeof(a) / sizeof(a[0]));//之前向上调整和向下调整就是为了这里//直接传a数组,而不是for (int i = 0; i < sizeof(a) / sizeof(a[0]); i++){printf(\"%d \", a[i]);//排升序}HP hp;//HPInitArray(&hp,a,sizeof(a)/sizeof(HPDataType));//HPInit(&hp);//HPInitArray(&hp, a, sizeof(a) / sizeof(HPDataType));//for (int i = 0; i < sizeof(a) / sizeof(a[0]); i++)//{//HPPush(&hp, a[i]);//}//printf(\"%d\", HPTop(&hp));//HPPop(&hp);//for (int i = 0; i a[i]);//}return 0;}Heap.c
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1#include\"Heap.h\"void HPInit(HP* php){php->a = NULL;php->capacity = php->size = 0;}void Swap(HPDataType* a, HPDataType* b){HPDataType tmp = *a;*a = *b;*b = tmp;}void AdjustUp(HPDataType* a, int child)//不传结构体,为了后面排序做准备,原因后面会解释{assert(a);int parent = (child - 1) / 2;while (child>0)//parent>=0可以作为结束条件,但是一个巧合,//因为到最后是依靠当child==0,parent=(child-1)/2=-1/2=0时//a[parent]==a[child]结束的{if (a[child] size == php->capacity){int newcapacity = php->capacity == 0 ? 4 : php->capacity * 2;HPDataType* tmp = (HPDataType*)realloc(php->a,sizeof(HPDataType) * newcapacity);if (tmp == NULL){perror(\"realloc fail!\");return;}php->a = tmp;php->capacity = newcapacity;}php->a[php->size] = x;php->size++;AdjustUp(php->a, php->size - 1);}HPDataType HPTop(HP* php){assert(php);return php->a[0];}void AdjustDown(HPDataType* a, int n, int parent)//不传结构体,为了后面排序做准备,原因后面会解释{assert(a);int child = parent * 2 + 1;while (child < n){//假设法if (child + 1 < n && a[child] < a[child + 1]){child++;}if (a[parent] a = (HPDataType*)malloc(sizeof(HPDataType) * n);if (php->a == NULL){perror(\"malloc fail!\");return;}memcpy(php->a, a, n * sizeof(HPDataType));php->capacity = php->size = n;//向上调整//for (int i = 1; i a, i);// HPPush(php, php->size)//不可以,因为调用函数// 时php->size在函数内还会增加//}//向下调整for (int i = (php->size - 1 - 1) / 2; i >= 0; i--)//数组的大小为size,对应下标为size-1,其数组最后一个元素//的双亲为(size-1-1)/2;{AdjustDown(php->a, n, i);}}//时间复杂度为logNvoid HPPop(HP* php){assert(php);assert(php->size > 0);Swap(&php->a[0], &php->a[php->size - 1]);php->size--;AdjustDown(php->a, php->size, 0);}bool HPEmpty(HP* php){assert(php);return php->size == 0;}void HPDestroy(HP* php){assert(php);free(php->a);php->a = NULL;php->size = php->capacity = 0;}void HPSort(HPDataType* a, int n){//这里不用建大堆选出最大数,建堆的时间复杂度为O(N)// 取出最大数后再N-1个数进行建堆,执行次数为N-1//n个数,执行次数为N+N-1+N-2.....+1;时间复杂度为O(N^2)//,和冒泡排序时间复杂度为一样,没有时间上的优势for(int i=(n-1-1)/2;i>=0;i--){AdjustDown(a, n, i);}//对数组进行升序排列//需要建大堆//收尾交换//把最后一个值不放在堆中,建大堆选出最大数,将其放在最后int end = n-1;while (end > 0){Swap(&a[end], &a[0]);AdjustDown(a, end, 0);end--;}}Heap.h
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1#include#include#include#include#include#includetypedef int HPDataType;typedef struct Heap{HPDataType* a;int size;int capacity;}HP;void HPInit(HP* php);void HPInitArray(HP* php, HPDataType* a, int n);void HPDestroy(HP* php);// 插入后保持数据是堆void HPPush(HP* php, HPDataType x);HPDataType HPTop(HP* php);// 删除堆顶的数据void HPPop(HP* php);void HPSort(HPDataType* a, int n);bool HPEmpty(HP* php);void AdjustUp(HPDataType* a, int child);void AdjustDown(HPDataType* a, int n, int parent);void Swap(HPDataType* px, HPDataType* py);

