数据结构3-单双链表的泛型实现及ArrayList与LinkedList的区别
文章目录
- ★引言:
- 一. 单向链表
-
- (一)属性
- (二)方法实现
-
- (1)addFirst(T data)
-
- 测试:
- (2)addLast(T data)
-
- 测试:
- (3)dispaly()
- (4)size()
-
- 测试:
- (5)IllegalIndexExc
- (6)addIndex(int index, T data)
-
- 测试:
- (7)contains(Object key)
-
- 测试:
- (8)remove(Object key)
-
- 测试:
- (9)removeAllKey(Object key)
-
- 测试:
- (10)clear()
-
- 测试:
- 二. 双向链表
-
- (一)属性
- (二)方法实现
-
- (1)addFirst(E data)
-
- 测试:
- (2)addLast(E data)
-
- 测试:
- (3)display()
- (4)size()
-
- 测试:
- (5)addIndex(int index, E data)
-
- 测试:
- (6)contains(Object key)
-
- 测试:
- (7)remove(Object key)
-
- 测试:
- (8)removeAllKey(Object key)
-
- 测试:
- (9)clear()
-
- 测试:
- 三. ArrayList与LinkedList的区别
★引言:
本篇博客依旧是基于泛型实现的简易单双链表,最后都会测试其中的方法,如果这篇博客对你有所帮助,可以给个三连,小编都会回关的!
一. 单向链表
(一)属性
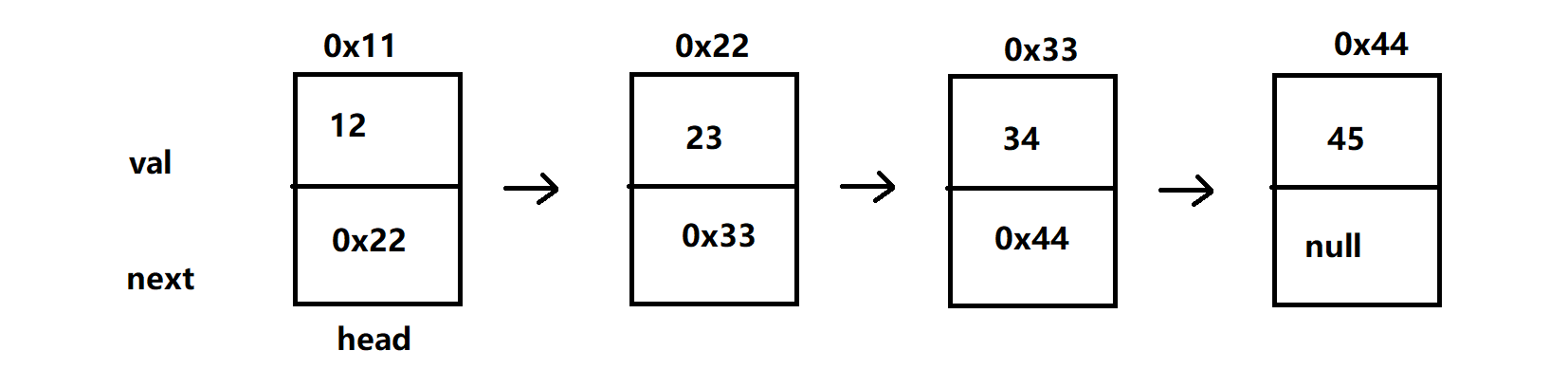
- 单链表中每个节点 Node 有两个域,值域 val,连接下一节点的域 next
- 将一个个节点定义为静态内部类,同时单链表让头结点 head 指向第一个节点
public class MySingleLinkedList<T> { public Node head; static class Node { public Object val; public Node next; public Node(Object val, Node next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; } public Node() { } public Node(Object val) { this.val = val; } }}(二)方法实现
(1)addFirst(T data)
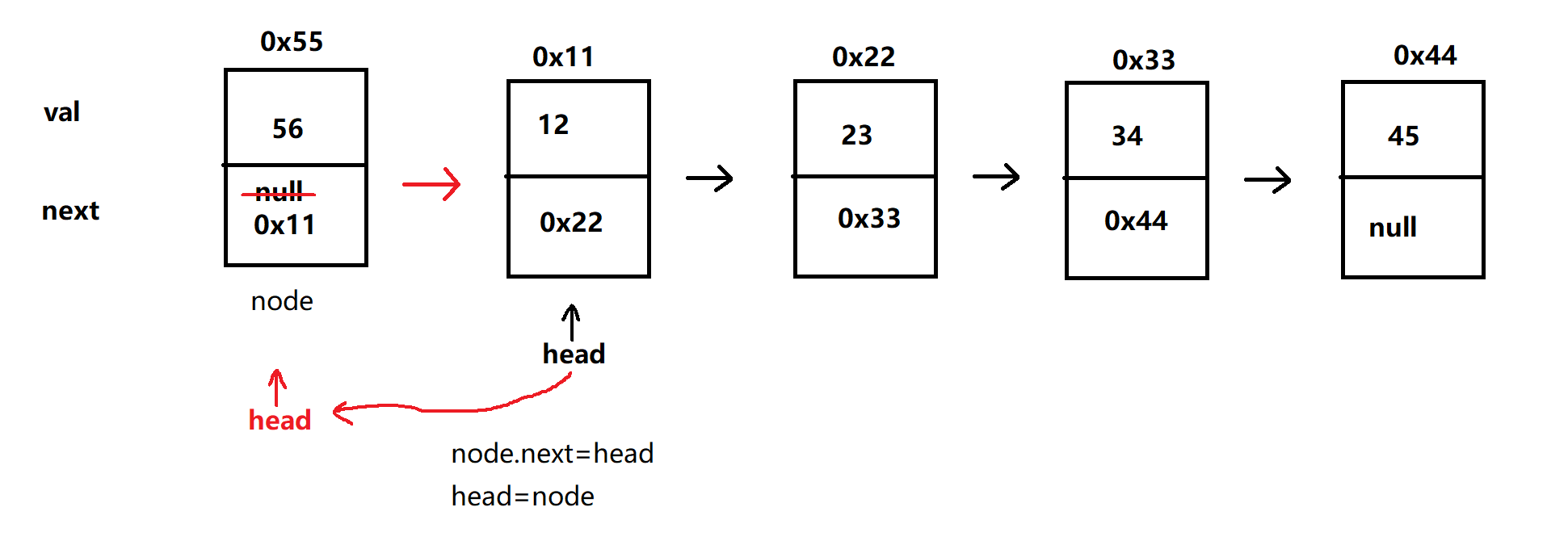
- 头插法
- 有两种情况:
① 头节点为 null,将头节点 head 直接指向 node
② 头节点不为 null,将该节点 node 与链表连接起来,head 节点指向 node
//头插法 public void addFirst(T data) { Node node = new Node(data); if (head == null) { head = node; }else { node.next = head; head = node; } }测试:
public static void main(String[] args) { MySingleLinkedList<Integer> list = new MySingleLinkedList<>(); list.addFirst(12); list.addFirst(23); list.addFirst(34); list.addFirst(45); list.display(); MySingleLinkedList<String> list1 = new MySingleLinkedList<>(); list1.addFirst(\"hello\"); list1.addFirst(\"my\"); list1.addFirst(\"name\"); list1.addFirst(\"is\"); list1.addFirst(\"Ran\"); list1.display(); }
(2)addLast(T data)
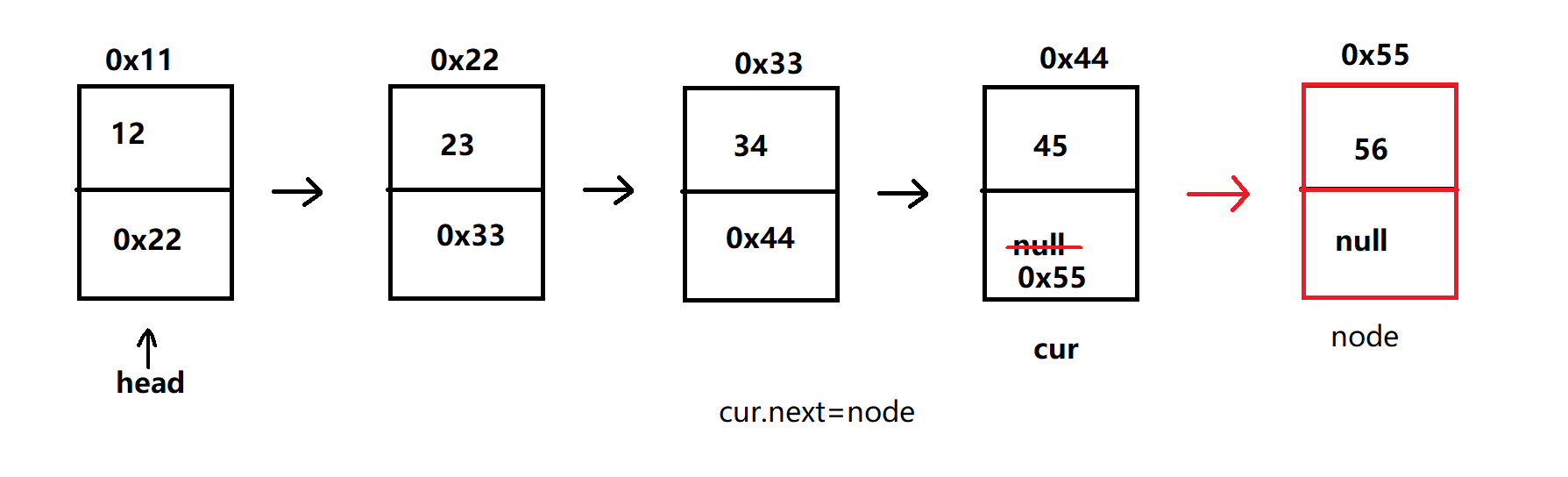
- 尾插法
- 有两种情况:
① 头节点为 null,将头节点 head 直接指向 node
② 头节点不为 null,找到最后一个节点 cur,将该节点 cur 与 node 连接起来
//尾插法 public void addLast(T data) { Node node = new Node(data); if (head == null) { head = node; return; } Node cur = head; while (cur.next != null) { cur = cur.next; } cur.next = node; }测试:
public static void main(String[] args) { MySingleLinkedList<Integer> list = new MySingleLinkedList<>(); list.addLast(12); list.addLast(23); list.addLast(34); list.addLast(45); list.display(); MySingleLinkedList<String> list1 = new MySingleLinkedList<>(); list1.addLast(\"hello\"); list1.addLast(\"my\"); list1.addLast(\"name\"); list1.addLast(\"is\"); list1.addLast(\"Ran\"); list1.display(); }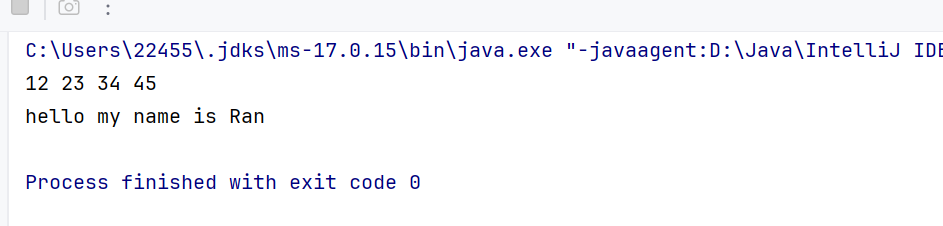
(3)dispaly()
- 打印链表元素
- 从头结点 head遍历完所有系欸但,打印其中元素
public void display() { Node cur = head; while (cur != null) { System.out.print(cur.val + \" \"); cur = cur.next; } System.out.println(); }(4)size()
- 得到单链表的⻓度
- 变量单链表,来求长度
//得到单链表的⻓度 public int size() { int count = 0; Node cur = head; while (cur != null) { count++; cur = cur.next; } return count; }测试:
public static void main(String[] args) { MySingleLinkedList<Integer> list = new MySingleLinkedList<>(); list.addLast(12); list.addLast(23); list.addLast(34); list.addLast(45); list.display(); System.out.println(\"链表长度:\" + list.size()); }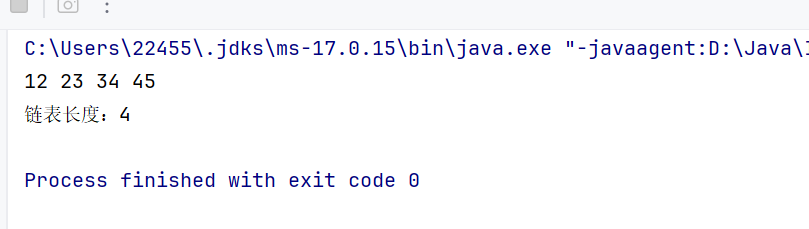
(5)IllegalIndexExc
下标不合法异常
public class IllegalIndexExc extends RuntimeException{ public IllegalIndexExc() { } public IllegalIndexExc(String message) { super(message); }}(6)addIndex(int index, T data)
- 任意位置插⼊,第⼀个数据节点为0号下标
- 先判断下标是否合法,合法后可以插入,不合法抛异常
//任意位置插⼊,第⼀个数据节点为0号下标 public void addIndex(int index, T data) { int size = size(); if (index < 0 || index > size) { throw new IllegalIndexExc(\"index 不合法!!!\"); } if (index == 0) { addFirst(data); return; } if (index == size) { addLast(data); return; } Node<T> node = new Node<T>(data); Node<T> cur = head; while (index - 1 > 0) { cur = cur.next; index--; } node.next = cur.next; cur.next = node; }测试:
public static void main(String[] args) { MySingleLinkedList<Integer> list = new MySingleLinkedList<>(); list.addLast(12); list.addLast(23); list.addLast(34); list.addLast(45); System.out.print(\"插入前:\"); list.display(); System.out.println(\"链表长度:\" + list.size()); list.addIndex(2,56); System.out.print(\"插入后:\"); list.display(); System.out.println(\"链表长度:\" + list.size()); }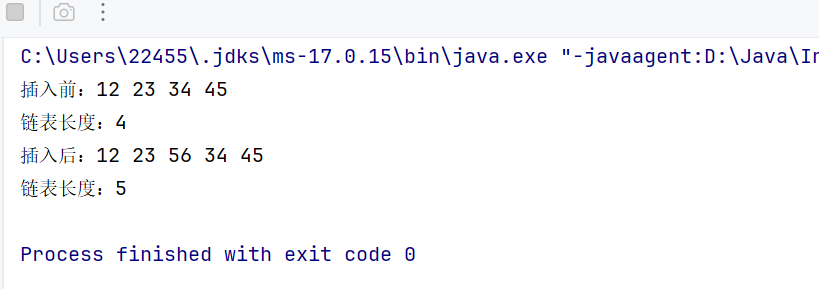
(7)contains(Object key)
- 查找是否包含关键字key是否在单链表当中
- 遍历链表查找
//查找是否包含关键字key是否在单链表当中 public boolean contains(Object key) { Node<T> cur = head; while (cur != null) { if (cur.val.equals(key)) { return true; } cur = cur.next; } return false; }测试:
public static void main(String[] args) { MySingleLinkedList<Integer> list = new MySingleLinkedList<>(); list.addLast(12); list.addLast(23); list.addLast(34); list.addLast(45); System.out.print(\"插入前:\"); list.display(); System.out.println(\"链表长度:\" + list.size()); list.addIndex(2,56); System.out.print(\"插入后:\"); list.display(); System.out.println(\"链表长度:\" + list.size()); System.out.println(\"是否存在:\" + list.contains(56)); System.out.println(\"是否存在:\" + list.contains(66)); }
(8)remove(Object key)
- 删除第⼀次出现关键字为key的节点
- 先判断是否存在这个值
- 遍历找到第一个跳出循环 找出节点 cur,两种情况:
① 该节点是 head,头节点向右移,同时 head 节点置为 null
② 不是头节点,要设立前驱节点prev与目标节点cur
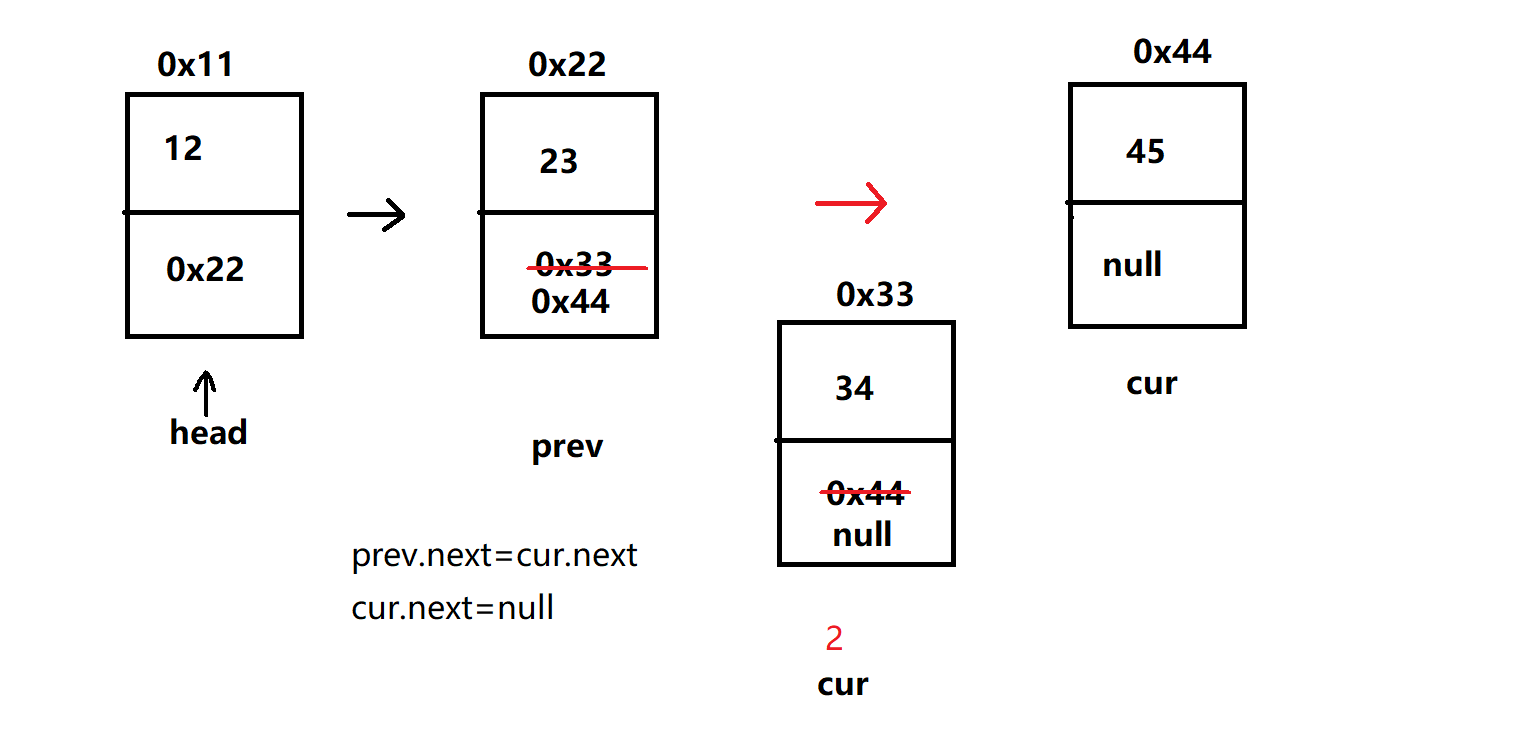
//删除第⼀次出现关键字为key的节点 public void remove(Object key) { if (!contains(key)) { System.out.println(\"不存在该节点!!!\"); return; } Node<T> cur = head; Node<T> prev = head; while (cur != null) { if (cur.val.equals(key)) { break; } prev = cur; cur = cur.next; } if (cur == head) { head = head.next; return; } prev.next = cur.next; cur.next = null; }测试:
public static void main(String[] args) { MySingleLinkedList<Integer> list = new MySingleLinkedList<>(); list.addLast(12); list.addLast(22); list.display(); System.out.println(\"链表长度:\" + list.size()); list.remove(22); list.display(); System.out.println(\"链表长度:\" + list.size()); }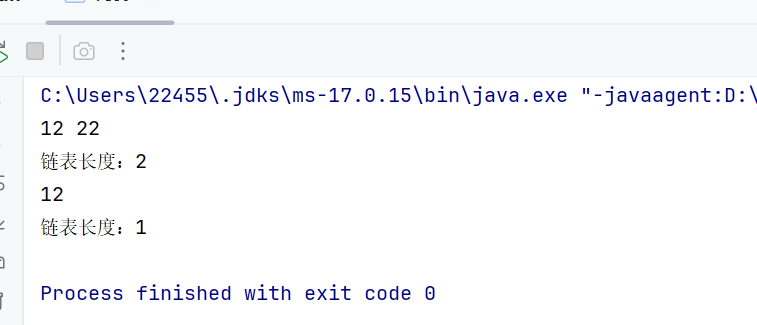
(9)removeAllKey(Object key)
- 删除所有值为key的节点
- 需要前驱 prev 与目标节点 cur,让 prev 与 cur 连接,最后判断 head 节点是否是目标值
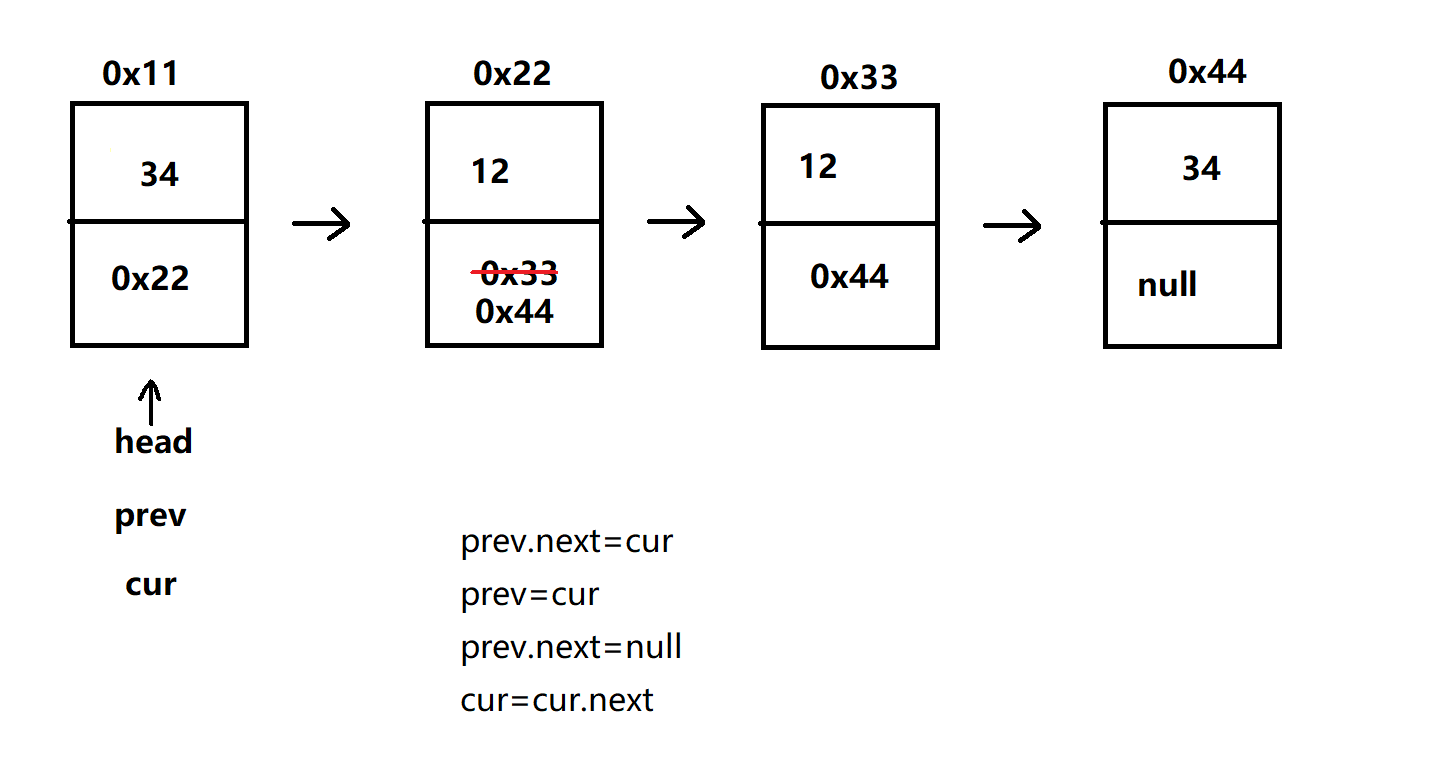
//删除所有值为key的节点 public void removeAllKey(Object key) { if (!contains(key)) { System.out.println(\"没有你要删除的节点!!!\"); return; } Node<T> cur = head; Node<T> prev = head; while (cur != null) { if (cur.val.equals(key)) { prev.next = cur; prev = cur; prev.next = null; } cur = cur.next; } if (head.val.equals(key)) { head = head.next; } }测试:
public static void main(String[] args) { MySingleLinkedList<Integer> list = new MySingleLinkedList<>(); list.addLast(12); list.addLast(12); list.display(); System.out.println(\"删除前链表长度:\" + list.size()); list.removeAllKey(12); list.display(); System.out.println(\"删除后链表长度:\" + list.size()); }
(10)clear()
删除所有值
public void clear() { Node<T> cur = head; head = null; while (cur != null) { Node<T> curN = cur.next; cur.next = null; cur = curN; } }测试:
public static void main(String[] args) { MySingleLinkedList<Integer> list = new MySingleLinkedList<>(); list.addLast(12); list.addLast(23); list.addLast(34); list.addLast(45); list.display(); System.out.println(\"删除前链表长度:\" + list.size()); list.clear(); list.display(); System.out.println(\"删除后链表长度:\" + list.size()); }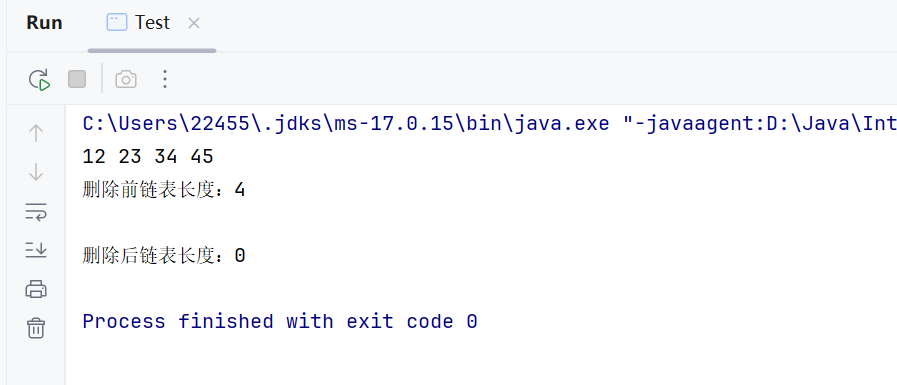
二. 双向链表
(一)属性
- 双向链表中每个节点 Node 有三个域,值域 key,连接下一节点的域 next,连接上一节点的域 prev
- 将一个个节点定义为静态内部类,同时双向链表让头结点 head 指向第一个节点 ,尾节点 last 指向最后一个节点
import java.util.Objects;public class MyLinkedList<E> { static class Node<E> { public E key; public Node<E> prev; public Node<E> next; public Node() { } public Node(E key) { this.key = key; } @Override public boolean equals(Object o) { if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false; Node<?> node = (Node<?>) o; return Objects.equals(key, node.key) && Objects.equals(prev, node.prev) && Objects.equals(next, node.next); } }}(二)方法实现
(1)addFirst(E data)
- 头插法
- 两种情况:
① head = last = null,那么让头与尾都指向 node
② 头尾不为空,改变 head 的前驱 prev 与 node 的后置 next
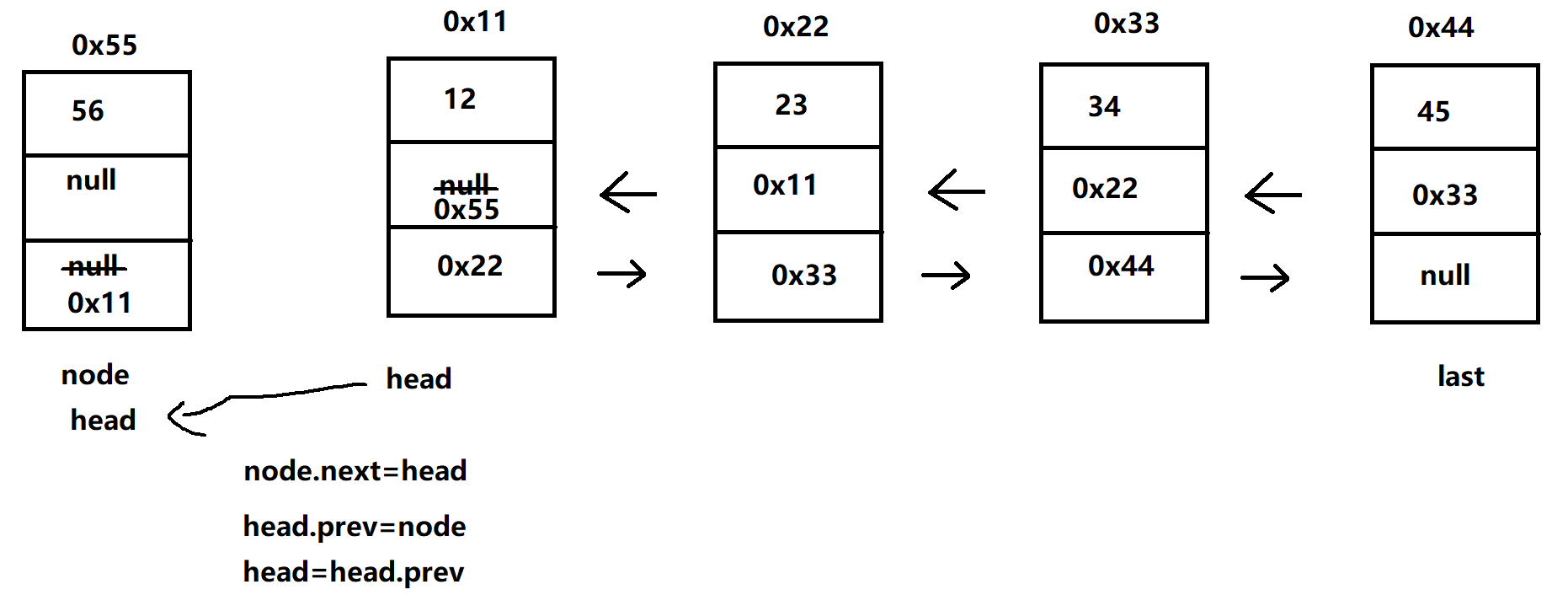
//头插法 public void addFirst(E data) { Node<E> node = new Node<>(data); if (head == null && last == null) { head = last = node; return; } node.next = head; head.prev = node; head = head.prev; }测试:
public static void main(String[] args) { MyLinkedList<Integer> list = new MyLinkedList<>(); list.addFirst(12); list.addFirst(23); list.addFirst(34); list.addFirst(45); System.out.print(\"头插法:\"); list.display(); }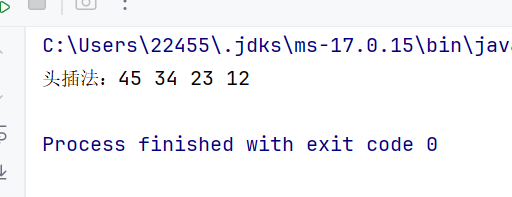
(2)addLast(E data)
- 尾插法
- 两种情况:
① head = last = null,那么让头与尾都指向 node
② 头尾不为空,改变 last 的后驱 next 与 node 的前驱 prev
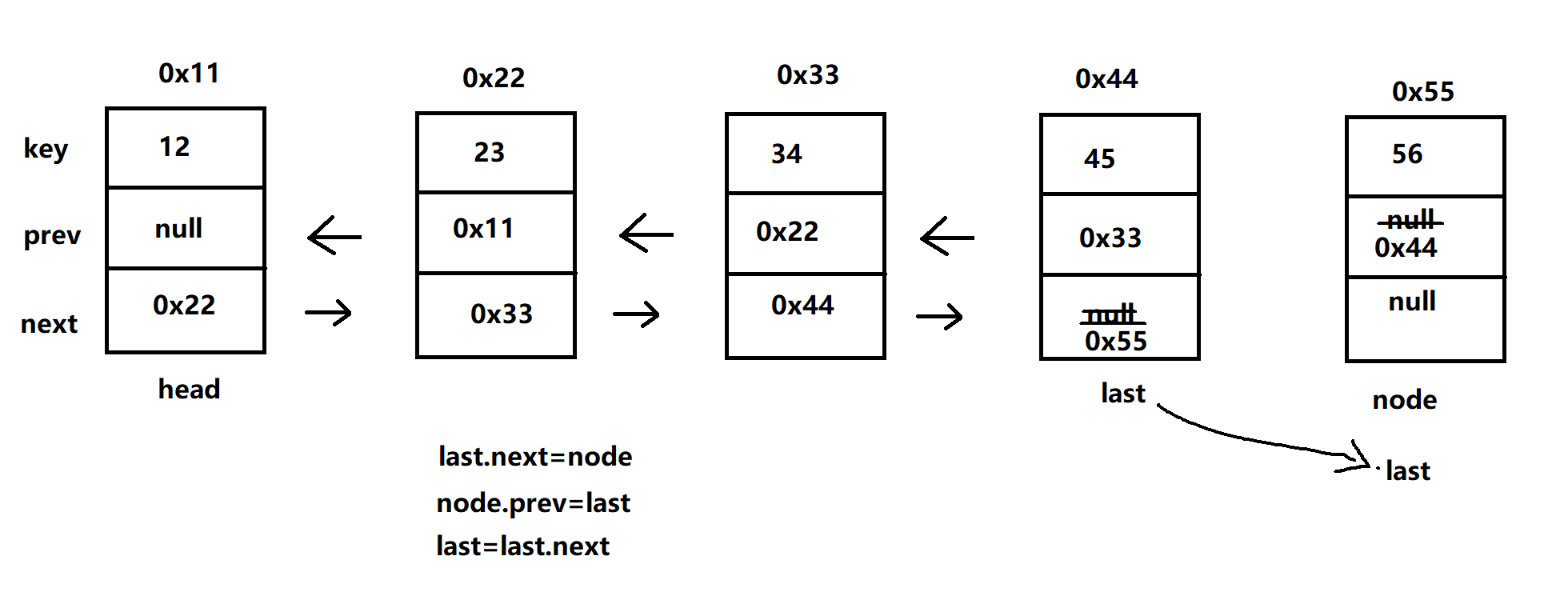
//尾插法 public void addLast(E data) { Node<E> node = new Node<>(data); if (head == null && last == null) { head = last = node; return; } last.next = node; node.prev = last; last = last.next; }测试:
public static void main(String[] args) { MyLinkedList<Integer> list = new MyLinkedList<>(); list.addLast(12); list.addLast(23); list.addLast(34); list.addLast(45); System.out.print(\"尾插法:\"); list.display(); }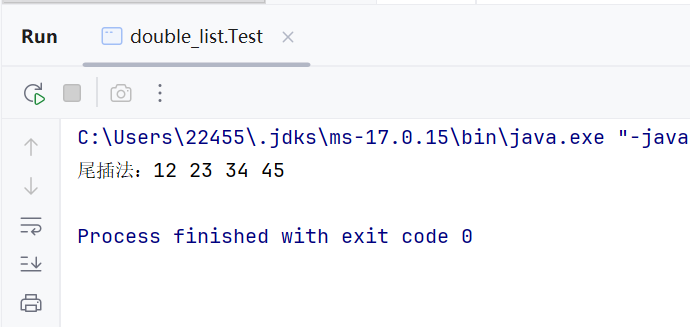
(3)display()
遍历链表,打印所有元素
public void display() { Node<E> cur = head; while (cur != null) { System.out.print(cur.key + \" \"); cur = cur.next; } System.out.println(); }(4)size()
求链表长度
//得到单链表的⻓度 public int size() { int count = 0; Node<E> cur = head; while (cur != null) { cur = cur.next; count++; } return count; }测试:
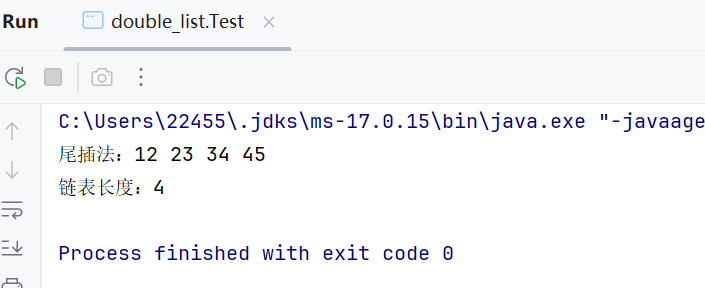
public static void main(String[] args) { MyLinkedList<Integer> list = new MyLinkedList<>(); list.addLast(12); list.addLast(23); list.addLast(34); list.addLast(45); System.out.print(\"尾插法:\"); list.display(); System.out.println(\"链表长度:\" + list.size()); }(5)addIndex(int index, E data)
- 任意位置插⼊,第⼀个数据节点为0号下标
- 判断下标是否合法
- 分为头插,尾插,中间插
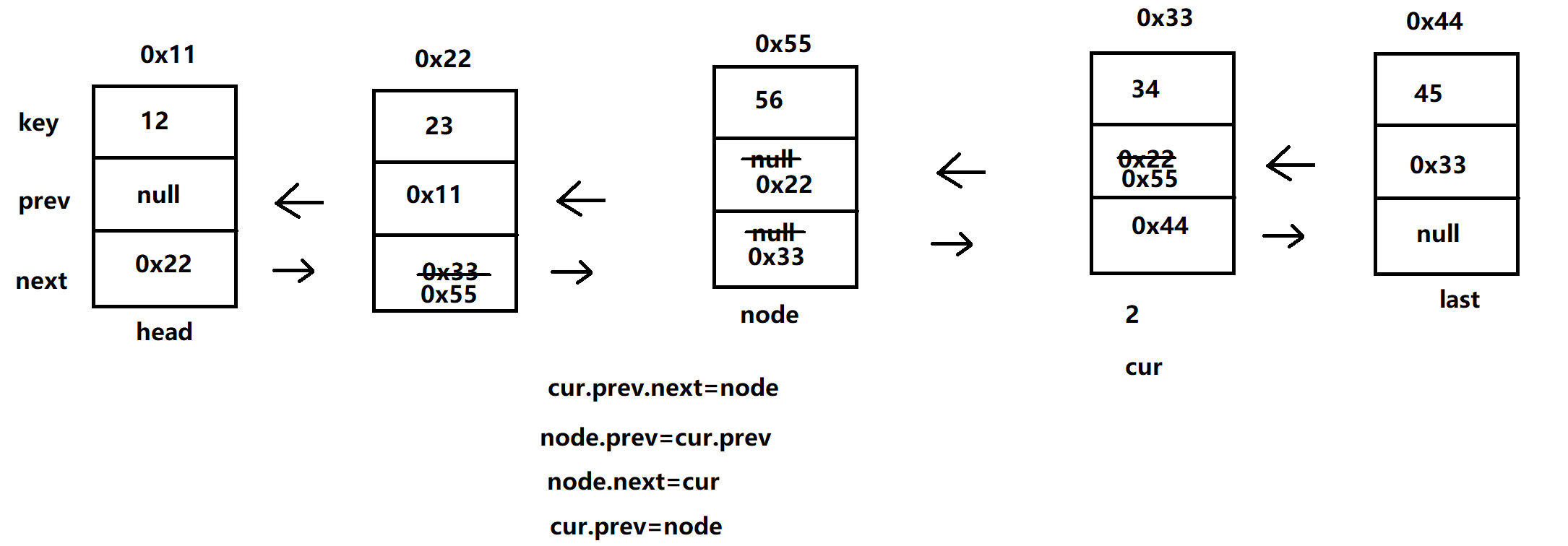
//任意位置插⼊,第⼀个数据节点为0号下标 public void addIndex(int index, E data) { int size = size(); if (index < 0 || index > size) { throw new IllegalIndexExc(\"index 不合法!!!\"); } if (index == 0) { addFirst(data); return; } if (index == size) { addLast(data); return; } Node<E> node = new Node<>(data); Node<E> cur = head; while (index > 0) { cur = cur.next; index--; } cur.prev.next = node; node.prev = cur.prev; node.next = cur; cur.prev = node; }测试:
public static void main(String[] args) { MyLinkedList<Integer> list = new MyLinkedList<>(); list.addLast(12); list.addLast(23); list.addLast(34); list.addLast(45); System.out.print(\"插入前:\"); list.display(); System.out.println(\"链表长度:\" + list.size()); list.addIndex(2,56); System.out.print(\"插入后:\"); list.display(); System.out.println(\"链表长度:\" + list.size()); }(6)contains(Object key)
链表中是否含有该值,遍历链表
//查找是否包含关键字key是否在单链表当中 public boolean contains(Object key) { Node<E> cur = head; while (cur != null) { if (cur.key.equals(key)) { return true; } cur = cur.next; } return false; }测试:
public static void main(String[] args) { MyLinkedList<Integer> list = new MyLinkedList<>(); list.addLast(12); list.addLast(23); list.addLast(34); list.addLast(45); list.addIndex(2,56); System.out.println(\"45 是否存在:\" + list.contains(45)); System.out.println(\"66 是否存在:\" + list.contains(66)); }(7)remove(Object key)
- 删除第⼀次出现关键字为key的节点
- 四种情况:
① 目标节点 cur 既是 head 也是 last
② 目标节点 cur 是 head 但不是 last
③ 目标节点 cur 不是 head 是 last
④ 目标节点 cur 既不是 head 也不是 last
四种情况都要讨论
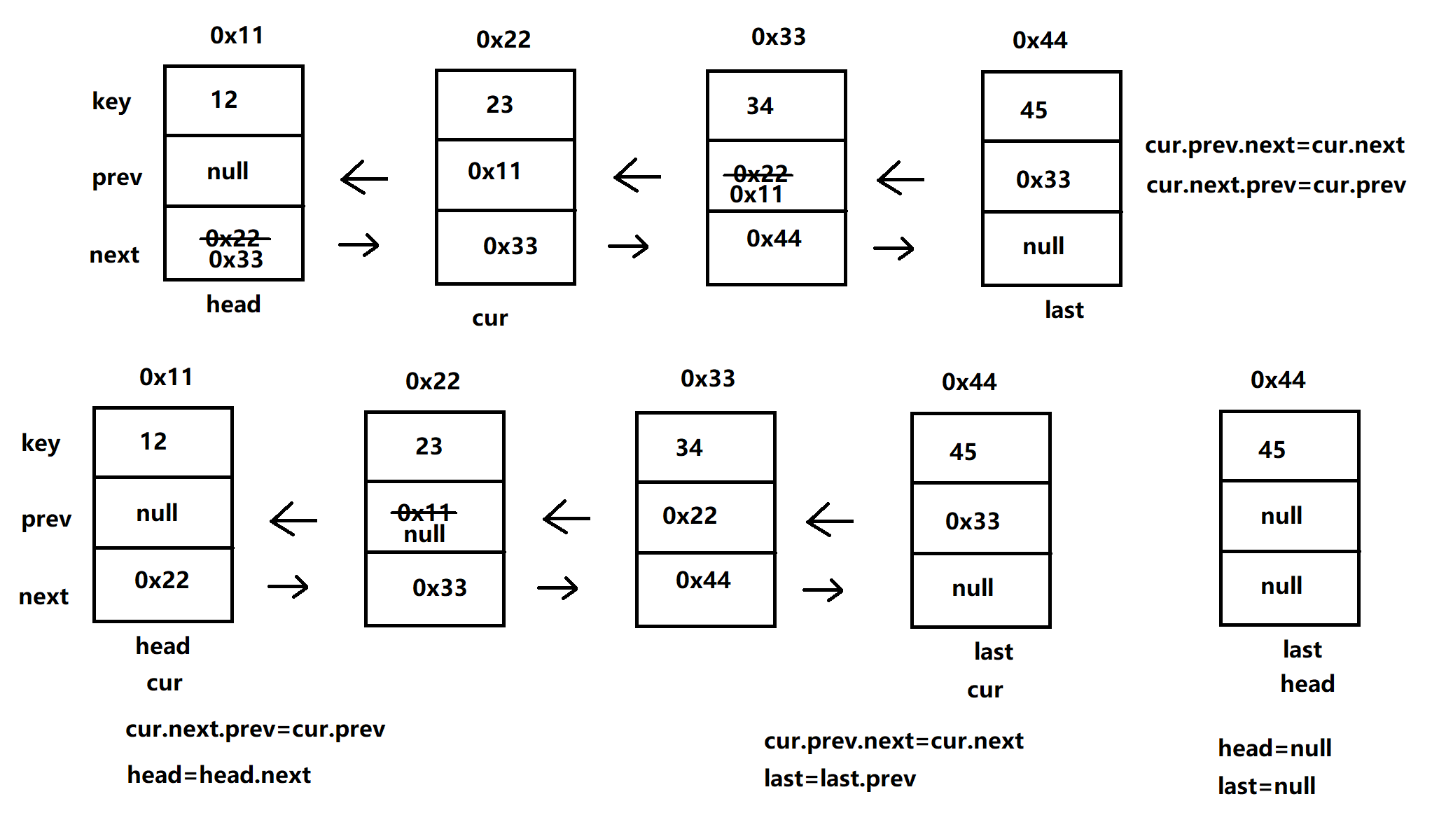
//删除第⼀次出现关键字为key的节点 public void remove(Object key) { if (!contains(key)) { System.out.println(\"没有该值你不能删除!!!\"); return; } Node<E> cur = head; while (cur != null) { if (cur.key.equals(key)) { if (cur == head && cur == last) { head = last = null; }else if (cur == head) { cur.next.prev = cur.prev; head = head.next; }else if (cur == last) { cur.prev.next = cur.next; last = last.prev; }else { cur.prev.next = cur.next; cur.next.prev = cur.prev; } return; } cur = cur.next; } }测试:
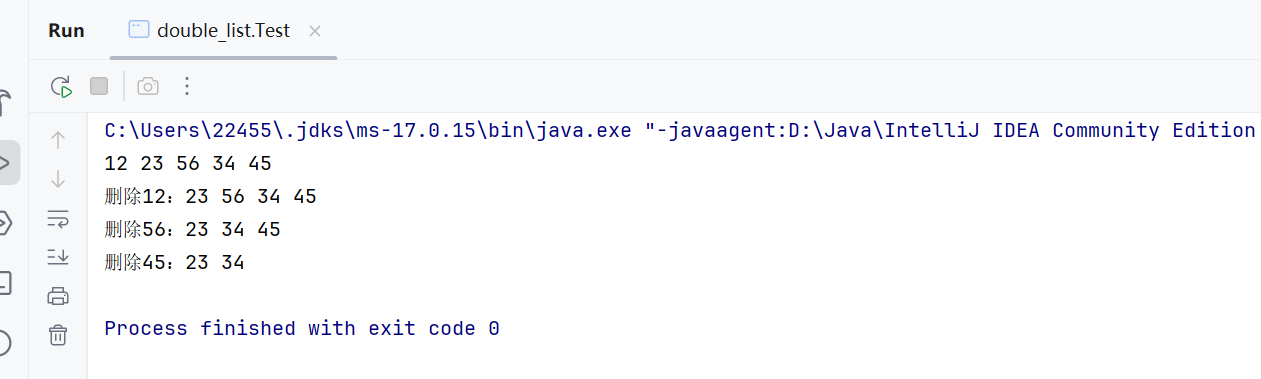
public static void main(String[] args) { MyLinkedList<Integer> list = new MyLinkedList<>(); list.addLast(12); list.addLast(23); list.addLast(34); list.addLast(45); list.addIndex(2,56); list.display(); System.out.print(\"删除12:\"); list.remove(12); list.display(); System.out.print(\"删除56:\"); list.remove(56); list.display(); System.out.print(\"删除45:\"); list.remove(45); list.display(); }(8)removeAllKey(Object key)
- 删除所有值为key的节点
- 同分四种情况,跟上面的remove方法一致,这里不过多赘述,直接将return删去,就是该方法
//删除所有值为key的节点 public void removeAllKey(Object key) { if (!contains(key)) { System.out.println(\"没有该值你不能删除!!!\"); return; } Node<E> cur = head; while (cur != null) { if (cur.key.equals(key)) { if (cur == head && cur == last) { head = last = null; }else if (cur == head) { cur.next.prev = cur.prev; head = head.next; }else if (cur == last) { cur.prev.next = cur.next; last = last.prev; }else { cur.prev.next = cur.next; cur.next.prev = cur.prev; } } cur = cur.next; } }测试:
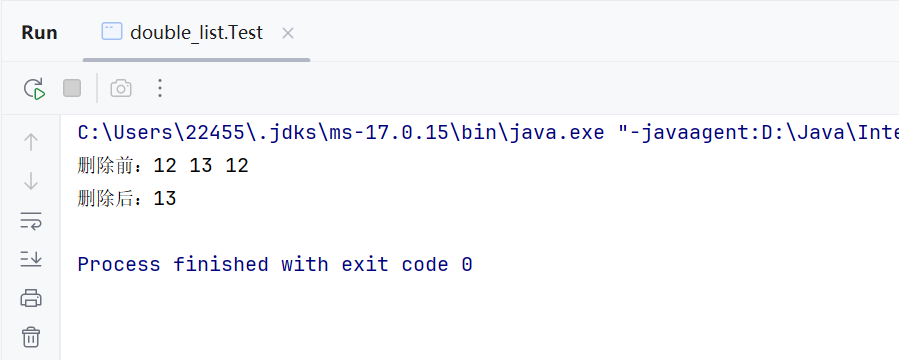
public static void main(String[] args) { MyLinkedList<Integer> list = new MyLinkedList<>(); list.addLast(12); list.addLast(13); list.addLast(12); System.out.print(\"删除前:\"); list.display(); list.removeAllKey(12); System.out.print(\"删除后:\"); list.display(); }(9)clear()
清除链表
public void clear() { Node<E> cur = head; while (cur != null) { Node<E> curN = cur.next; cur.next = null; cur.prev = null; cur = curN; } head = null; last = null; }测试:
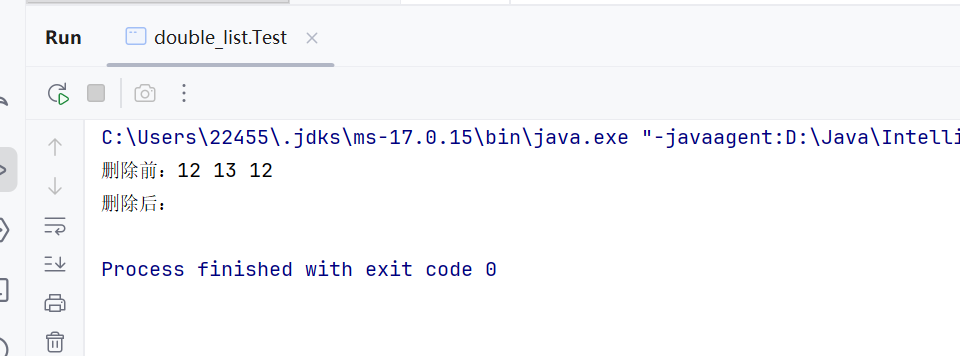
public static void main(String[] args) { MyLinkedList<Integer> list = new MyLinkedList<>(); list.addLast(12); list.addLast(13); list.addLast(12); System.out.print(\"删除前:\"); list.display(); list.clear(); System.out.print(\"删除后:\"); list.display(); }

