Java 流(Stream)、文件(File)和IO_java流的关系图
一、Java 流(Stream)、文件(File)和IO概念和关系
Java 中的流(Stream)、文件(File)和 IO 之间是紧密关联但又各有侧重的概念,它们共同构成了 Java 输入输出系统的核心。可以用\"工具-对象-操作\"的关系来理解:
-
IO 是总称
IO(Input/Output,输入/输出)是所有数据传输操作的统称,涵盖了程序与外部设备(文件、网络、键盘等)之间的数据交换。
流(Stream)和文件(File)都是实现 IO 操作的具体方式或操作对象。 -
File 是操作的实体
java.io.File类代表文件系统中的一个文件或目录,是 IO 操作的具体对象。
但它本身不能直接读写数据,只能描述文件的属性(如路径、大小、是否存在等),并提供创建、删除等文件管理功能。 -
Stream 是操作的工具
流(Stream)是连接程序与外部数据源(包括 File)的数据传输通道,是实现 IO 操作的核心工具。
当需要读写 File 中的内容时,必须通过流来实现:- 读文件:用输入流(如
FileInputStream)从 File 中读取数据到程序 - 写文件:用输出流(如
FileOutputStream)从程序写入数据到 File
- 读文件:用输入流(如
-
三者协作关系
一个典型的文件 IO 操作流程是:创建 File 对象(指定要操作的文件)→通过流连接 File(如 new FileInputStream(file))→通过流进行 IO 操作(读/写数据)
二、读写文件
2.1 操作文件时涉及的字符流和字节流的概念介绍:
字节流
-
基本概念:字节流是以字节(8位二进制数据)作为基本处理单位的流,它能对各种类型的文件进行读写操作,因为计算机中所有的数据在底层都是以字节形式存储和传输的。字节流可以直接操作二进制数据,无论是文本文件还是非文本文件(如图像、音频、视频等)都能处理。
-
字节输入流(InputStream):
用于从文件等数据源读取字节数据到程序中。它是字节流输入操作的抽象基类,提供了如read()等基础方法用于读取字节数据。 -
字节输出流(OutputStream):
负责将程序中的字节数据写入到文件等目标数据源中。它是字节流输出操作的抽象基类,提供了write()等方法用于写入字节数据。
字符流
-
基本概念:字符流以字符(一般是16位的Unicode编码字符)为基本处理单位,更侧重于处理文本文件,它在读写文本时会按照字符编码规范进行转换,能更好地保证文本内容的正确读写,还能方便地按行等文本特性进行操作。
-
字符输入流(Reader):
用于从文件等数据源读取字符数据到程序里,是字符流输入操作的抽象基类,提供了read()等方法来获取字符数据。 -
字符输出流(Writer):
主要用于将程序中的字符数据写入到文件等目标数据源中,是字符流输出操作的抽象基类,具备write()等方法来输出字符数据。
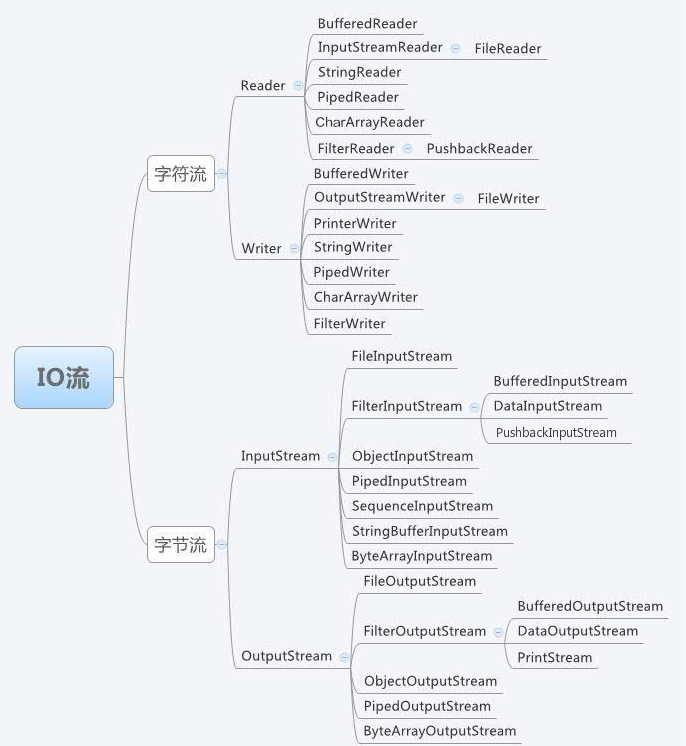
字节流、字符流常用关系图
2.2 字节流常用方法
字节流常用于处理二进制数据,例如文件、图像、时频。
以下是基于表格中各类字节流的读写文件示例,涵盖不同场景的文件操作:
1. FileInputStream/FileOutputStream(基础文件读写)
FileInputStream 和 FileOutputStream 是 Java IO 中用于直接操作文件的字节流,专门负责从文件读取字节数据和向文件写入字节数据,是处理文件字节流的基础类。
import java.io.*;public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { // 写入文件 try { FileOutputStream fileOutputStream =new FileOutputStream(\"file.txt\"); String data=\"Hello byteStream!\"; fileOutputStream.write(data.getBytes()); fileOutputStream.close(); } catch (IOException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } try { FileInputStream fileInputStream =new FileInputStream(\"file.txt\"); int c; while((c=fileInputStream.read())!=-1){ System.out.print((char)c); } } catch (IOException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } }}
2. BufferedInputStream/BufferedOutputStream(缓冲流高效读写)
BufferedInputStream 和 BufferedOutputStream 是 Java IO 中提供缓冲功能的过滤流,它们通过在内存中维护缓冲区来减少物理 I/O 操作次数,从而显著提升读写效率。
import java.io.*;public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { // 写入文件 try { BufferedOutputStream bufferedOutputStream =new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(\"file.txt\")); String data=\"Hello byteStream!\"; bufferedOutputStream.write(data.getBytes()); bufferedOutputStream.close(); } catch (IOException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } try { BufferedInputStream bufferedInputStream =new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(\"file.txt\")); int c; while((c=bufferedInputStream.read())!=-1){ System.out.print((char)c); } } catch (IOException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } }}3. DataInputStream/DataOutputStream(读写基本数据类型)
DataInputStream 和 DataOutputStream 是 Java IO 中用于读写基本数据类型的过滤流,它们可以直接操作 Java 原生数据类型(如 int、double、boolean 等),无需手动处理字节转换,简化了基本类型数据的读写操作。
import java.io.*;public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { // 写入文件 try { DataOutputStream bufferedOutputStream =new DataOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(\"file.bat\")); bufferedOutputStream.writeInt(100); // 写入整数 bufferedOutputStream.writeDouble(3.14); // 写入双精度浮点数 bufferedOutputStream.writeUTF(\"Hello byteStream!\"); bufferedOutputStream.close(); } catch (IOException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } try { DataInputStream bufferedInputStream =new DataInputStream(new FileInputStream(\"file.bat\")); System.out.println(bufferedInputStream.readInt()); System.out.println(bufferedInputStream.readDouble()); System.out.println(bufferedInputStream.readUTF()); } catch (IOException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } }}
4. ObjectInputStream/ObjectOutputStream(对象序列化)
ObjectInputStream 和 ObjectOutputStream 是 Java 中用于对象序列化与反序列化的字节流,主要功能是将内存中的 Java 对象转换为字节序列(序列化)并写入流中,或从流中读取字节序列并恢复为 Java 对象(反序列化)。
import java.io.*;// 需实现Serializable接口才能被序列化class User implements Serializable { private String name; private int age; public User(String name, int age) { this.name = name; this.age = age; } @Override public String toString() { return \"User{name=\'\" + name + \"\', age=\" + age + \"}\"; }}public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { // 序列化对象写入文件 try { ObjectOutputStream objectOutputStream =new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(\"file.obj\")); User user=new User(\"Alice\", 18); objectOutputStream.writeObject(user); objectOutputStream.close(); } catch (IOException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } try { ObjectInputStream objectInputStream=new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(\"file.obj\")); User user=(User) objectInputStream.readObject(); System.out.println(user); } catch (IOException | ClassNotFoundException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } }}
5.ByteArrayOutputStream(内存字节数组读写)
它可以将数据写入内存中的字节数组缓冲区。创建后可以用来收集和操作字节数据,常用于临时存储或处理二进制数据。
public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { ByteArrayOutputStream byteArrayOutputStream =new ByteArrayOutputStream(); byte [] bytes = new byte[1024]; try { bytes[0]=(byte) \'H\'; bytes[1]=(byte) \'e\'; bytes[2]=(byte) \'l\'; bytes[3]=(byte) \'l\'; bytes[4]=(byte) \'o\'; byteArrayOutputStream.write(bytes,0,5); byteArrayOutputStream.close(); } catch (IOException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } ByteArrayInputStream byteArrayInputStream=new ByteArrayInputStream(byteArrayOutputStream.toByteArray()); byte [] bytes1 = new byte[1024]; int c; try{ while ((c=byteArrayInputStream.read(bytes1))!=-1){ System.out.println(new String(bytes1, 0, c)); } }catch (IOException e){ throw new RuntimeException(e); } }}
6. SequenceInputStream(合并多个输入流)
import java.io.*;public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { try { SequenceInputStream sequenceInputStream =new SequenceInputStream(new FileInputStream(\"file.txt\"),new FileInputStream(\"test.txt\")); int c; while((c=sequenceInputStream.read())!=-1){ System.out.print((char)c); } } catch (IOException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); }}}7. FilterInputStream/FilterOutStream
FilterInputStream 和 FilterOutputStream 是 Java IO 中的过滤流基类,属于装饰器模式(Decorator Pattern)的典型实现,用于对现有流进行功能扩展或增强。
import java.io.FilterInputStream;import java.io.FileInputStream;import java.io.InputStream;import java.io.IOException;// 自定义过滤输入流:转换为大写class UpperCaseInputStream extends FilterInputStream { /** * Creates a FilterInputStream * by assigning the argument in * to the field this.in so as * to remember it for later use. * * @param in the underlying input stream, or null if * this instance is to be created without an underlying stream. */ protected UpperCaseInputStream(InputStream in) { super(in); } @Override public int read(byte [] b,int off,int len ) throws IOException { int result = super.read(b, off, len);//读取的字节数 if(result!=-1){ for(int i=off;i<off+result;i++){ b[i]= (byte) Character.toUpperCase((char)b[i]); } } return result; }}public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { try { UpperCaseInputStream upperCaseInputStream =new UpperCaseInputStream(new FileInputStream(\"file.txt\")); int c; byte [] bytes=new byte[1024]; while((c=upperCaseInputStream.read(bytes))!=-1){ System.out.print(new String(bytes,0,c)); } } catch (IOException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } }}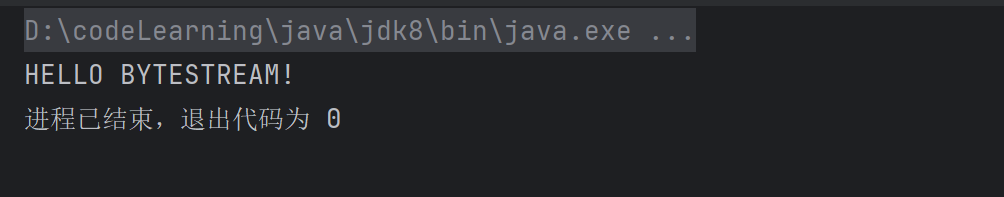
8.pipedOutputStream/pipedInputStream
PipedOutputStream 和 PipedInputStream 是 Java 中用于线程间通信的管道流,二者必须配合使用,形成 “生产者 - 消费者” 模式的数据传输通道。
public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { PipedOutputStream pipedOutputStream =new PipedOutputStream(); PipedInputStream pipedInputStream; try { pipedInputStream =new PipedInputStream(pipedOutputStream); } catch (IOException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { try { pipedOutputStream.write(\"Hello byteStream!\".getBytes()); pipedOutputStream.close(); } catch (IOException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } } }).start(); new Thread(new Runnable(){ @Override public void run() { try { int c; while((c=pipedInputStream.read())!=-1){ System.out.print((char)c); } } catch (IOException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } } }).start(); }}2.3 字符流常用方法
字符流常用于处理文本数据。
以下是字符流各类的读写文件示例,每个示例均包含写入和读取操作:
1. FileReader/FileWriter(文件字符读写)
import java.io.*;public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { // 写入文本到文件 try (FileWriter writer = new FileWriter(\"test.txt\")) { writer.write(\"Hello, FileReader/FileWriter!\\n\"); writer.write(\"这是一行行中文文本\"); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } // 从文件读取文本 try (FileReader reader = new FileReader(\"test.txt\")) { char[] buffer = new char[1024]; int len; while ((len = reader.read(buffer)) != -1) { System.out.print(new String(buffer, 0, len)); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }}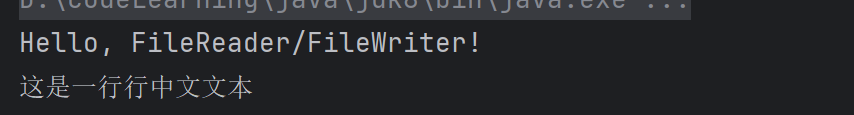
2. BufferedReader/BufferedWriter(缓冲字符流)
public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { // 按行写入文本(指定UTF-8编码) try (BufferedWriter writer = new BufferedWriter( new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream(\"buffered.txt\"), StandardCharsets.UTF_8))) { writer.write(\"第一行内容\"); writer.newLine(); // 跨平台换行 writer.write(\"第二行内容\"); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } // 按行读取文本 try (BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader( new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream(\"buffered.txt\"), StandardCharsets.UTF_8))) { String line; while ((line = reader.readLine()) != null) { // 按行读取 System.out.println(\"读取到:\" + line); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }}3. CharArrayReader/CharArrayWriter(字符数组流)
CharArrayReader 和 CharArrayWriter 是 Java 中以字符数组为操作对象的字符流,所有操作均在内存中基于字符数组完成,无需依赖外部存储。
import java.io.*;public class CharArrayReadWriteExample { public static void main(String[] args) { // CharArrayWriter先写入字符数组(内存中) CharArrayWriter caw = new CharArrayWriter(); try { caw.write(\"先写入内存字符数组,再转存到文件\"); char[] charData = caw.toCharArray(); // 获取字符数组 // 写入文件 try (FileWriter fw = new FileWriter(\"charArray.txt\")) { fw.write(charData); } // CharArrayReader从字符数组读取 CharArrayReader car = new CharArrayReader(charData); char[] buffer = new char[1024]; int len; System.out.println(\"CharArrayReader读取内容:\"); while ((len = car.read(buffer)) != -1) { System.out.print(new String(buffer, 0, len)); } car.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { caw.close(); } }}4. StringReader/StringWriter(字符串流)
StringReader 和 StringWriter 是 Java 中操作内存字符串的字符流,无需依赖外部文件,所有操作均在内存中完成。
import java.io.*;public class StringReadWriteExample { public static void main(String[] args) { // StringWriter写入字符串缓冲区 StringWriter sw = new StringWriter(); try { sw.write(\"字符串流操作示例\\n\"); sw.write(\"数据保存在StringBuffer中\"); String data = sw.toString(); // 获取字符串 // 写入文件 try (FileWriter fw = new FileWriter(\"string.txt\")) { fw.write(data); } // StringReader从字符串读取 StringReader sr = new StringReader(data); char[] buffer = new char[1024]; int len; System.out.println(\"StringReader读取内容:\"); while ((len = sr.read(buffer)) != -1) { System.out.print(new String(buffer, 0, len)); } sr.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { sw.close(); } }}5. PrintWriter(格式化字符输出流)
PrintWriter 是 Java 中功能强大的字符输出流,提供了便捷的文本写入、格式化输出和自动刷新等功能,广泛用于输出文本数据到文件、控制台或其他输出流。
import java.io.*;public class PrintWriterExample { public static void main(String[] args) { // PrintWriter写入(支持格式化和自动刷新) try (PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter(new FileWriter(\"print.txt\"), true)) { // 第二个参数开启自动刷新 pw.println(\"PrintWriter便捷输出\"); pw.printf(\"格式化输出:%d + %d = %d%n\", 2, 3, 5); // 类似printf格式 pw.println(\"自动刷新生效\"); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } // 读取验证 try (BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(\"print.txt\"))) { System.out.println(\"PrintWriter写入内容:\"); String line; while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) { System.out.println(line); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }}6. PipedReader/PipedWriter(管道字符流,线程间通信)
import java.io.*;public class PipedReadWriteExample { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { // 创建管道流对(必须绑定) PipedWriter pw = new PipedWriter(); PipedReader pr = new PipedReader(pw); // 写入线程 Thread writerThread = new Thread(() -> { try { pw.write(\"管道流线程间通信数据\"); pw.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }); // 读取线程(并写入文件) Thread readerThread = new Thread(() -> { try (FileWriter fw = new FileWriter(\"piped.txt\")) { char[] buffer = new char[1024]; int len; while ((len = pr.read(buffer)) != -1) { fw.write(buffer, 0, len); // 写入文件 System.out.println(\"管道读取内容:\" + new String(buffer, 0, len)); } pr.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }); writerThread.start(); readerThread.start(); }}7. LineNumberReader(带行号的字符输入流)
LineNumberReader 是 Java 中带有行号跟踪功能的缓冲字符输入流,继承自 BufferedReader,在提供高效缓冲读取的同时,能自动跟踪当前读取的行号,方便定位文本中的特定行。
import java.io.*;public class LineNumberReaderExample { public static void main(String[] args) { // 先写入多行数据 try (BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(\"linenumber.txt\"))) { bw.write(\"第一行内容\"); bw.newLine(); bw.write(\"第二行内容\"); bw.newLine(); bw.write(\"第三行内容\"); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } // LineNumberReader读取并跟踪行号 try (LineNumberReader lnr = new LineNumberReader(new FileReader(\"linenumber.txt\"))) { lnr.setLineNumber(1); // 设置起始行号(默认从0开始) String line; System.out.println(\"带行号的内容:\"); while ((line = lnr.readLine()) != null) { System.out.printf(\"第%d行:%s%n\", lnr.getLineNumber(), line); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }}8. PushbackReader(可回退字符的输入流)
PushbackReader 是 Java 中的一个字符输入流,继承自 FilterReader,它的特殊之处在于允许将已读取的字符 “推回”(回退)到流中。
import java.io.*;public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { try { PushbackReader reader =new PushbackReader(new FileReader(\"file.txt\")); int c; while((c=reader.read())!=-1){ if(c==\'o\'){ reader.unread(c); break; } System.out.println(\":\"+(char)c ); } } catch (IOException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } }}