Flink-1.19.0源码详解8-ExecutionGraph生成-前篇
Flink是Apache软件基金会下开源的分布式流批一体计算框架,具备实时流计算和高吞吐批处理计算的大数据计算能力。本专栏内容为Flink源码解析的记录与分享。
本文解析的Kafka源码版本为:flink-1.19.0
1.ExecutionGraph生成功能概述
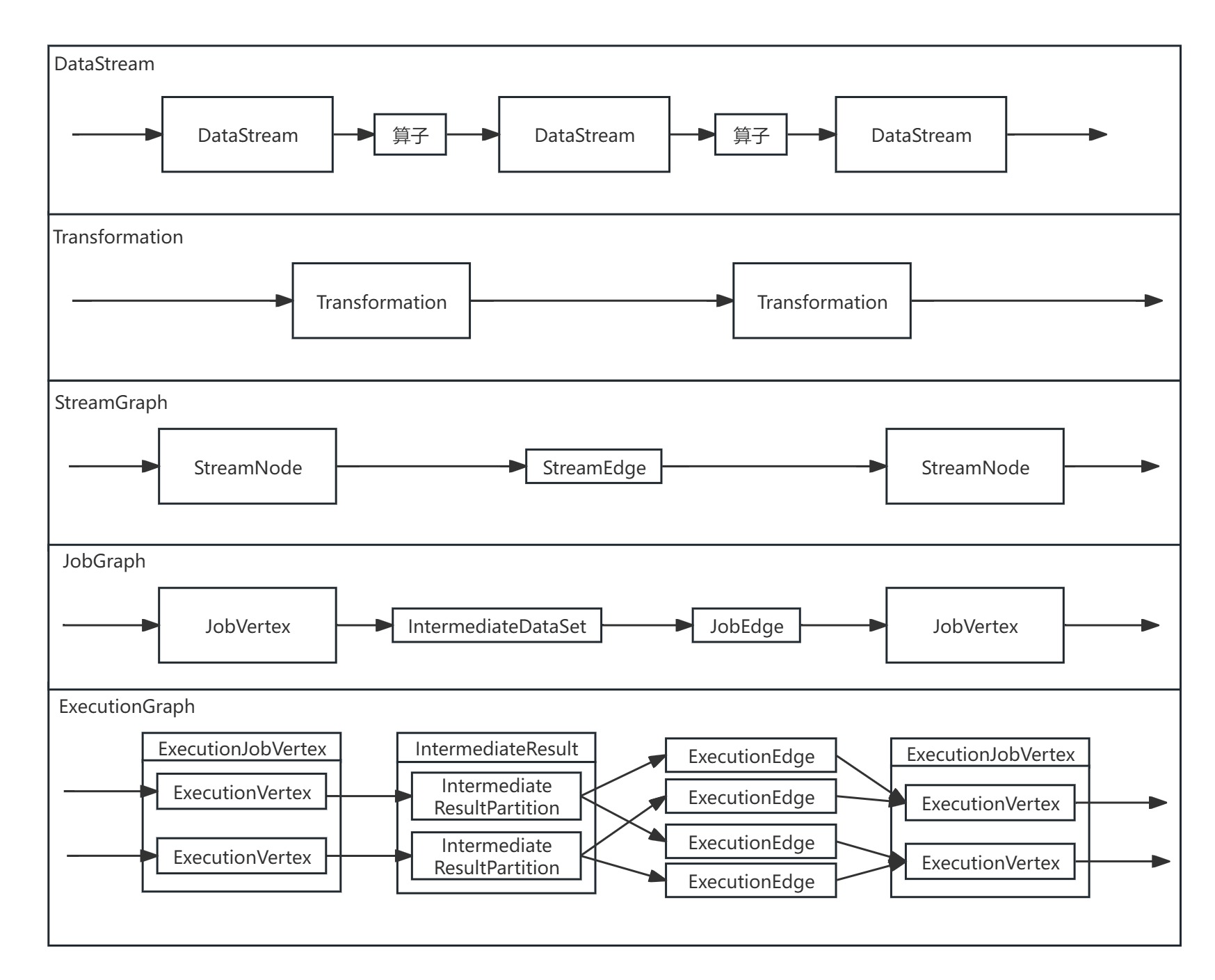
在前文《Flink-1.19.0源码详解5-JobGraph生成-前篇》和《Flink-1.19.0源码详解6-JobGraph生成-后篇》中,已介绍了Flink JobGraph生成的源码,解析Flink遍历StreamGraph的每个StreamNode节点,逐步生成JobVertex节点、JobEdge边和IntermediateDataSet数据集,构建JobGraph图的过程。在完成 JobGraph的生成后,Flink Client会向Yarn中的Flink集群提交调度请求与JobGraph图,完成把调度从客户端进行到集群端的转变。
本文从Flink集群端调度开始解析ExecutionGraph生成源码(内容为下流程图的红色部分),解析了Flink JobMaster对JobVertex节点进行遍历,依次生成ExecutionJobVertex节点、ExecutionVertex节点、IntermediateResult数据集、IntermediateResultPartition数据集分区和其连接关系,解析了构建ExecutionGraph图的完整源码。

ExecutionGraph生成的本质是在原本逻辑数据处理流图JobGraph的基础上,按并行度做分布式展开,生成分布式数据处理流图ExecutionGraph。
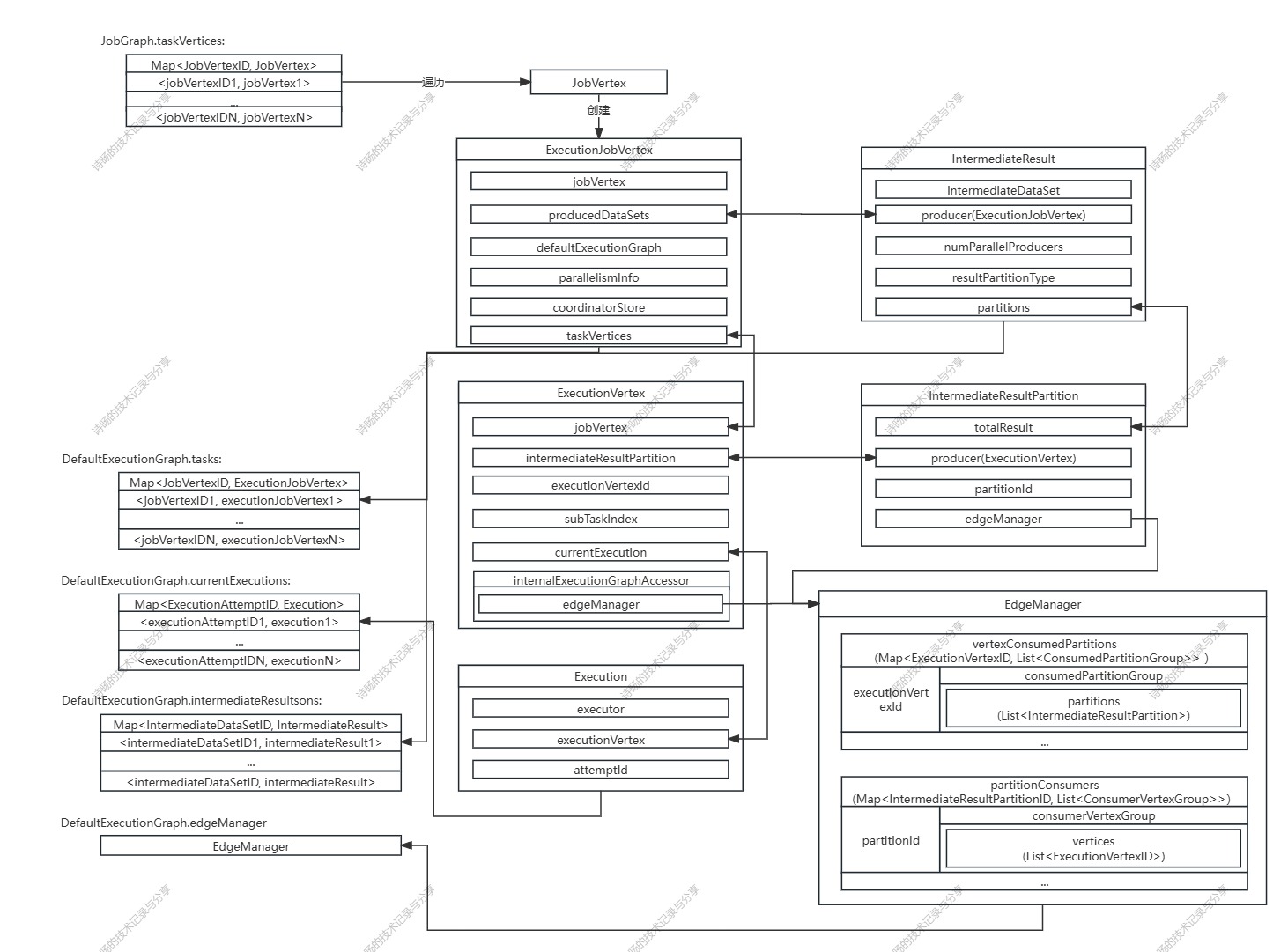
Flink的ExecutionGraph生成主要是通过遍历JobGraph中每个JobVertex节点,生成其对应的ExecutionJobVertex节点,并为每个JobVertex节点的IntermediateDataSet数据集生成IntermediateResult数据集。ExecutionGraph进一步把原有的JobGraph进行分布式并行化展开,把ExecutionJobVertex节点按并行度创建ExecutionVertex节点和封装其执行信息的Execution,把IntermediateResult数据集按并行度创建IntermediateResultPartition数据集分区,并创建边连接上下游IntermediateResultPartition数据集分区与ExecutionVertex节点。
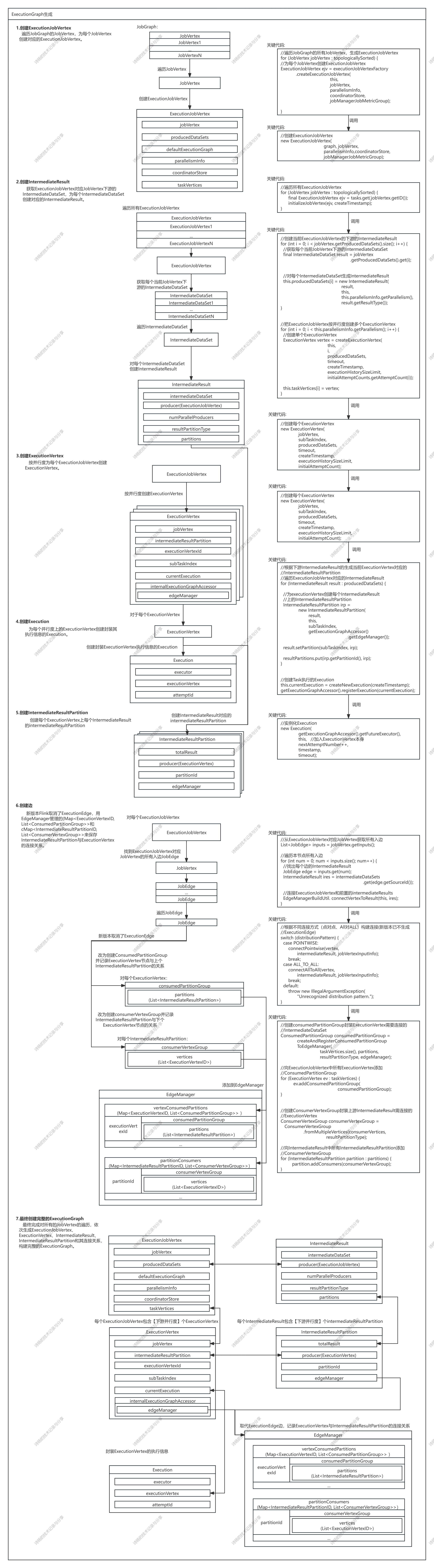
ExecutionGraph生成的具体步骤如下:
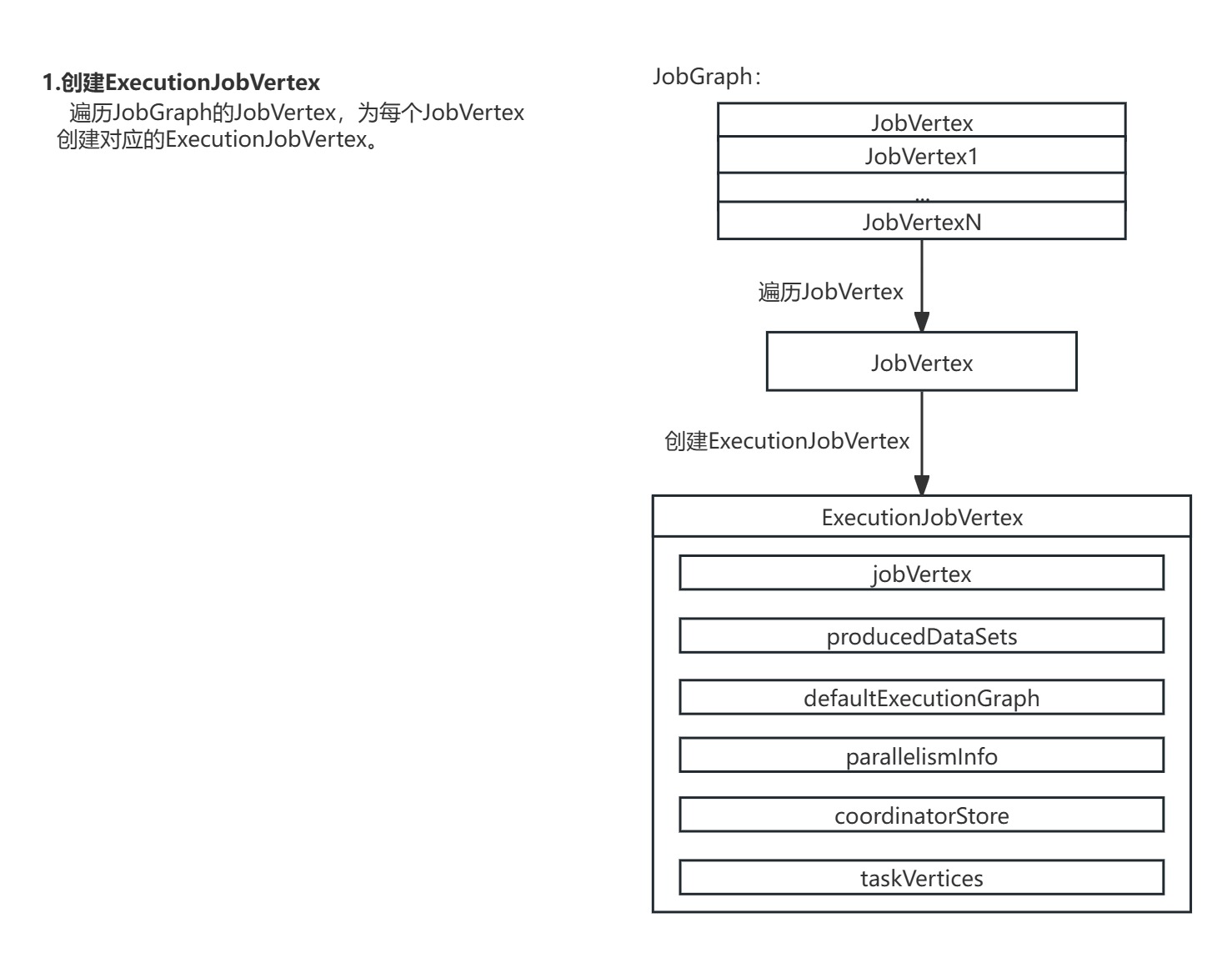
1.创建ExecutionJobVertex:遍历JobGraph的JobVertex,为每个JobVertex创建对应的ExecutionJobVertex。
2.创建IntermediateResul:获取ExecutionJobVertex对应JobVertex下游的IntermediateDataSet,为每个IntermediateDataSet创建对应的IntermediateResult。
3.创建ExecutionVertex:按并行度为每个ExecutionJobVertex创建ExecutionVertex。
4.创建Execution:为每个并行度上的ExecutionVertex创建封装其执行信息的Execution。
5.创建IntermediateResultPartition:创建每个ExecutionVertex上每个IntermediateResult的IntermediateResultPartition。
6.创建边:Flink在新版本(1.13后)取消了ExecutionEdge,用EdgeManager管理的(Map<ExecutionVertexID, List>和Map<IntermediateResultPartitionID, List>来保存IntermediateResultPartition与ExecutionVertex的连接关系。
7.最终创建完整的ExecutionGraph:最终完成对所有的JobVertex的遍历,依次生成ExecutionJobVertex、ExecutionVertex、IntermediateResult、IntermediateResultPartition和其连接关系,构建完整的ExecutionGraph图。
ExecutionGraph生成源码图解:
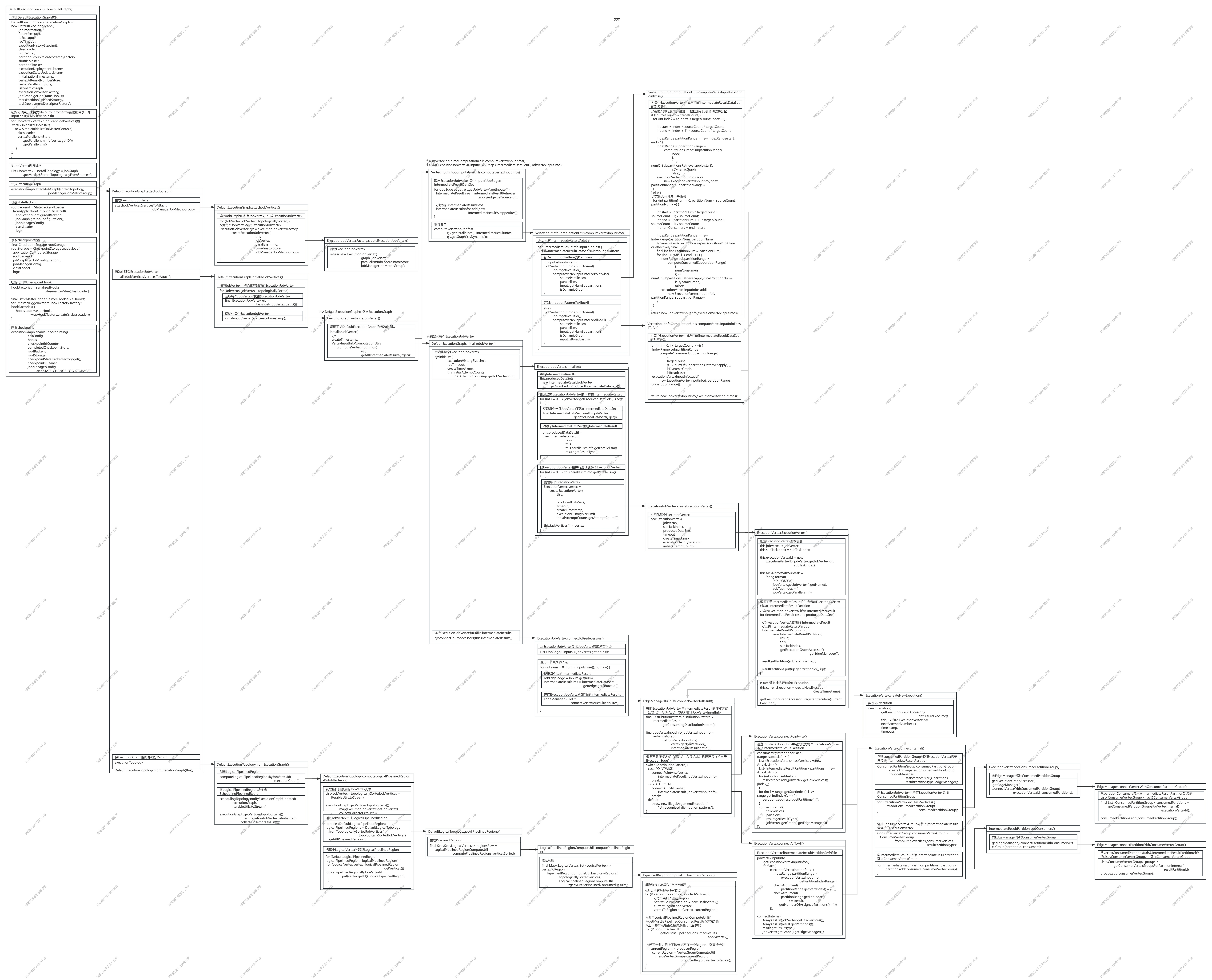
完整代码解析:
2.进入ExecutionGraph调度
在创建JobMaster时,JobMaster会在创建SchedulerNG实例时,调用DefaultExecutionGraphBuilder的buildGraph()方法,开始进行ExecutionGraph的生成。
源码图解:

DefaultExecutionGraphBuilder.buildGraph()方法创建了ExecutionGraph实例、初始化了JobVertex节点并对其进行了排序,配置了StateBackend和Checkpoint。其中关键是调用ExecutionGraph的attachJobGraph()方法,开始了ExecutionGraph图节点与边的生成。
DefaultExecutionGraphBuilder.buildGraph()方法源码:
public static DefaultExecutionGraph buildGraph( JobGraph jobGraph, Configuration jobManagerConfig, ScheduledExecutorService futureExecutor, Executor ioExecutor, ClassLoader classLoader, CompletedCheckpointStore completedCheckpointStore, CheckpointsCleaner checkpointsCleaner, CheckpointIDCounter checkpointIdCounter, Time rpcTimeout, BlobWriter blobWriter, Logger log, ShuffleMaster shuffleMaster, JobMasterPartitionTracker partitionTracker, TaskDeploymentDescriptorFactory.PartitionLocationConstraint partitionLocationConstraint, ExecutionDeploymentListener executionDeploymentListener, ExecutionStateUpdateListener executionStateUpdateListener, long initializationTimestamp, VertexAttemptNumberStore vertexAttemptNumberStore, VertexParallelismStore vertexParallelismStore, Supplier checkpointStatsTrackerFactory, boolean isDynamicGraph, ExecutionJobVertex.Factory executionJobVertexFactory, MarkPartitionFinishedStrategy markPartitionFinishedStrategy, boolean nonFinishedHybridPartitionShouldBeUnknown, JobManagerJobMetricGroup jobManagerJobMetricGroup) throws JobExecutionException, JobException { checkNotNull(jobGraph, \"job graph cannot be null\"); final String jobName = jobGraph.getName(); final JobID jobId = jobGraph.getJobID(); final JobInformation jobInformation = new JobInformation( jobId, jobName, jobGraph.getSerializedExecutionConfig(), jobGraph.getJobConfiguration(), jobGraph.getUserJarBlobKeys(), jobGraph.getClasspaths()); final int executionHistorySizeLimit = jobManagerConfig.get(JobManagerOptions.MAX_ATTEMPTS_HISTORY_SIZE); final PartitionGroupReleaseStrategy.Factory partitionGroupReleaseStrategyFactory = PartitionGroupReleaseStrategyFactoryLoader.loadPartitionGroupReleaseStrategyFactory( jobManagerConfig); final int offloadShuffleDescriptorsThreshold = jobManagerConfig.get( TaskDeploymentDescriptorFactory.OFFLOAD_SHUFFLE_DESCRIPTORS_THRESHOLD); final TaskDeploymentDescriptorFactory taskDeploymentDescriptorFactory; try { taskDeploymentDescriptorFactory = new TaskDeploymentDescriptorFactory( BlobWriter.serializeAndTryOffload(jobInformation, jobId, blobWriter), jobId, partitionLocationConstraint, blobWriter, nonFinishedHybridPartitionShouldBeUnknown, offloadShuffleDescriptorsThreshold); } catch (IOException e) { throw new JobException(\"Could not create the TaskDeploymentDescriptorFactory.\", e); } //创建DefaultExecutionGraph实例 // create a new execution graph, if none exists so far final DefaultExecutionGraph executionGraph = new DefaultExecutionGraph( jobInformation, futureExecutor, ioExecutor, rpcTimeout, executionHistorySizeLimit, classLoader, blobWriter, partitionGroupReleaseStrategyFactory, shuffleMaster, partitionTracker, executionDeploymentListener, executionStateUpdateListener, initializationTimestamp, vertexAttemptNumberStore, vertexParallelismStore, isDynamicGraph, executionJobVertexFactory, jobGraph.getJobStatusHooks(), markPartitionFinishedStrategy, taskDeploymentDescriptorFactory); // set the basic properties try { executionGraph.setJsonPlan(JsonPlanGenerator.generatePlan(jobGraph)); } catch (Throwable t) { log.warn(\"Cannot create JSON plan for job\", t); // give the graph an empty plan executionGraph.setJsonPlan(\"{}\"); } // initialize the vertices that have a master initialization hook // file output formats create directories here, input formats create splits final long initMasterStart = System.nanoTime(); log.info(\"Running initialization on master for job {} ({}).\", jobName, jobId); //初始化顶点,主要为file output fomart准备输出目录;为input splits创建对应的splits等 for (JobVertex vertex : jobGraph.getVertices()) { String executableClass = vertex.getInvokableClassName(); if (executableClass == null || executableClass.isEmpty()) { throw new JobSubmissionException( jobId, \"The vertex \" + vertex.getID() + \" (\" + vertex.getName() + \") has no invokable class.\"); } try { vertex.initializeOnMaster( new SimpleInitializeOnMasterContext( classLoader, vertexParallelismStore .getParallelismInfo(vertex.getID()) .getParallelism())); } catch (Throwable t) { throw new JobExecutionException( jobId, \"Cannot initialize task \'\" + vertex.getName() + \"\': \" + t.getMessage(), t); } } log.info( \"Successfully ran initialization on master in {} ms.\", (System.nanoTime() - initMasterStart) / 1_000_000); //对JobVertex进行排序 // topologically sort the job vertices and attach the graph to the existing one List sortedTopology = jobGraph.getVerticesSortedTopologicallyFromSources(); if (log.isDebugEnabled()) { log.debug( \"Adding {} vertices from job graph {} ({}).\", sortedTopology.size(), jobName, jobId); } //生成ExecutionGraph executionGraph.attachJobGraph(sortedTopology, jobManagerJobMetricGroup); if (log.isDebugEnabled()) { log.debug( \"Successfully created execution graph from job graph {} ({}).\", jobName, jobId); } // configure the state checkpointing if (isDynamicGraph) { // dynamic graph does not support checkpointing so we skip it log.warn(\"Skip setting up checkpointing for a job with dynamic graph.\"); } else if (isCheckpointingEnabled(jobGraph)) { JobCheckpointingSettings snapshotSettings = jobGraph.getCheckpointingSettings(); // load the state backend from the application settings final StateBackend applicationConfiguredBackend; final SerializedValue serializedAppConfigured = snapshotSettings.getDefaultStateBackend(); if (serializedAppConfigured == null) { applicationConfiguredBackend = null; } else { try { applicationConfiguredBackend = serializedAppConfigured.deserializeValue(classLoader); } catch (IOException | ClassNotFoundException e) { throw new JobExecutionException( jobId, \"Could not deserialize application-defined state backend.\", e); } } //创建StateBackend final StateBackend rootBackend; try { rootBackend = StateBackendLoader.fromApplicationOrConfigOrDefault( applicationConfiguredBackend, jobGraph.getJobConfiguration(), jobManagerConfig, classLoader, log); } catch (IllegalConfigurationException | IOException | DynamicCodeLoadingException e) { throw new JobExecutionException( jobId, \"Could not instantiate configured state backend\", e); } // load the checkpoint storage from the application settings final CheckpointStorage applicationConfiguredStorage; final SerializedValue serializedAppConfiguredStorage = snapshotSettings.getDefaultCheckpointStorage(); if (serializedAppConfiguredStorage == null) { applicationConfiguredStorage = null; } else { try { applicationConfiguredStorage = serializedAppConfiguredStorage.deserializeValue(classLoader); } catch (IOException | ClassNotFoundException e) { throw new JobExecutionException( jobId, \"Could not deserialize application-defined checkpoint storage.\", e); } } //读取checkpoint配置 final CheckpointStorage rootStorage; try { rootStorage = CheckpointStorageLoader.load( applicationConfiguredStorage, rootBackend, jobGraph.getJobConfiguration(), jobManagerConfig, classLoader, log); } catch (IllegalConfigurationException | DynamicCodeLoadingException e) { throw new JobExecutionException( jobId, \"Could not instantiate configured checkpoint storage\", e); } // instantiate the user-defined checkpoint hooks final SerializedValue serializedHooks = snapshotSettings.getMasterHooks(); final List<MasterTriggerRestoreHook> hooks; //初始化用户checkpoint hook if (serializedHooks == null) { hooks = Collections.emptyList(); } else { final MasterTriggerRestoreHook.Factory[] hookFactories; try { hookFactories = serializedHooks.deserializeValue(classLoader); } catch (IOException | ClassNotFoundException e) { throw new JobExecutionException( jobId, \"Could not instantiate user-defined checkpoint hooks\", e); } final Thread thread = Thread.currentThread(); final ClassLoader originalClassLoader = thread.getContextClassLoader(); thread.setContextClassLoader(classLoader); try { hooks = new ArrayList(hookFactories.length); for (MasterTriggerRestoreHook.Factory factory : hookFactories) { hooks.add(MasterHooks.wrapHook(factory.create(), classLoader)); } } finally { thread.setContextClassLoader(originalClassLoader); } } final CheckpointCoordinatorConfiguration chkConfig = snapshotSettings.getCheckpointCoordinatorConfiguration(); //配置Checkpoint executionGraph.enableCheckpointing( chkConfig, hooks, checkpointIdCounter, completedCheckpointStore, rootBackend, rootStorage, checkpointStatsTrackerFactory.get(), checkpointsCleaner, jobManagerConfig.get(STATE_CHANGE_LOG_STORAGE)); } return executionGraph;}在DefaultExecutionGraph的attachJobGraph()方法中,进行了ExecutionJobVertex节点的生成与初始化,并把ExecutionGraph划分了SchedulingPipelinedRegion。
DefaultExecutionGraph.attachJobGraph()方法源码:
public void attachJobGraph( List verticesToAttach, JobManagerJobMetricGroup jobManagerJobMetricGroup) throws JobException { assertRunningInJobMasterMainThread(); LOG.debug( \"Attaching {} topologically sorted vertices to existing job graph with {} \" + \"vertices and {} intermediate results.\", verticesToAttach.size(), tasks.size(), intermediateResults.size()); //生成ExecutionJobVertex attachJobVertices(verticesToAttach, jobManagerJobMetricGroup); if (!isDynamic) { //初始化所有ExecutionJobVertex initializeJobVertices(verticesToAttach); } //将ExecutionGraph的拓扑划分Region // the topology assigning should happen before notifying new vertices to failoverStrategy executionTopology = DefaultExecutionTopology.fromExecutionGraph(this); partitionGroupReleaseStrategy = partitionGroupReleaseStrategyFactory.createInstance(getSchedulingTopology());}3.创建ExecutionJobVertex
在DefaultExecutionGraph的attachJobGraph()方法中,调用了DefaultExecutionGraph的attachJobVertices()方法进行ExecutionJobVertex节点的生成。
源码图解:
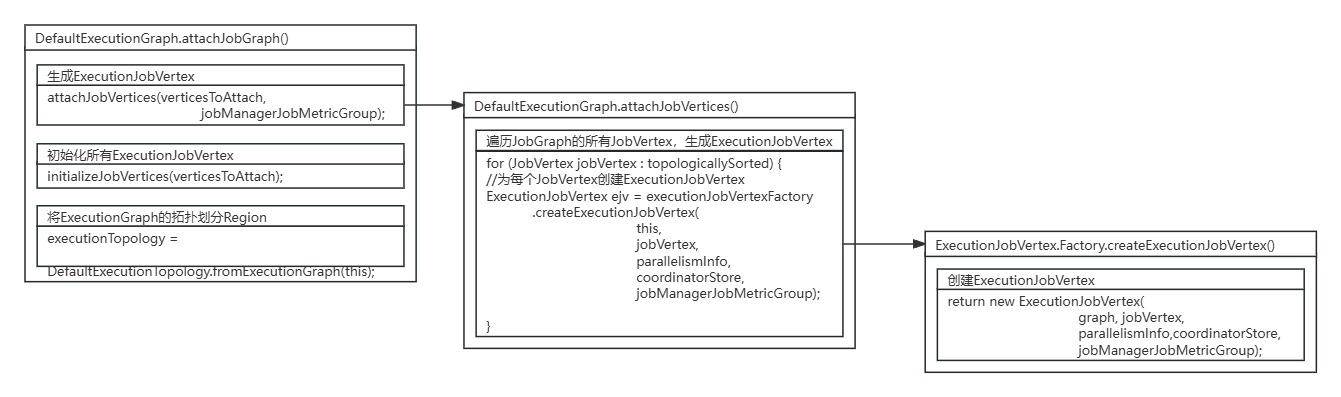
DefaultExecutionGraph的attachJobVertices()方法遍历了JobGraph中所有的JobVertex节点,为每个JobVertex节点生成对应的ExecutionJobVertex节点。
DefaultExecutionGraph.attachJobVertices()方法源码:
private void attachJobVertices( List topologicallySorted, JobManagerJobMetricGroup jobManagerJobMetricGroup) throws JobException { //遍历所有JobVertex for (JobVertex jobVertex : topologicallySorted) { //... //遍历JobGraph的所有JobVertex,生成ExecutionJobVertex // create the execution job vertex and attach it to the graph ExecutionJobVertex ejv = executionJobVertexFactory.createExecutionJobVertex( this, jobVertex, parallelismInfo, coordinatorStore, jobManagerJobMetricGroup); //... }}其中调用的ExecutionJobVertex.Factory.createExecutionJobVertex()方法具体创建了ExecutionJobVertex实例。
ExecutionJobVertex.Factory.createExecutionJobVertex()方法源码:
public static class Factory { ExecutionJobVertex createExecutionJobVertex( InternalExecutionGraphAccessor graph, JobVertex jobVertex, VertexParallelismInformation parallelismInfo, CoordinatorStore coordinatorStore, JobManagerJobMetricGroup jobManagerJobMetricGroup) throws JobException { //创建ExecutionJobVertex实例 return new ExecutionJobVertex( graph, jobVertex, parallelismInfo, coordinatorStore, jobManagerJobMetricGroup);}4.进入ExecutionJobVertex初始化
完成了ExecutionJobVertex节点创建后,还需要对ExecutionJobVertex节点对应的ExecutionVertex节点与IntermediateResult数据集进行创建。
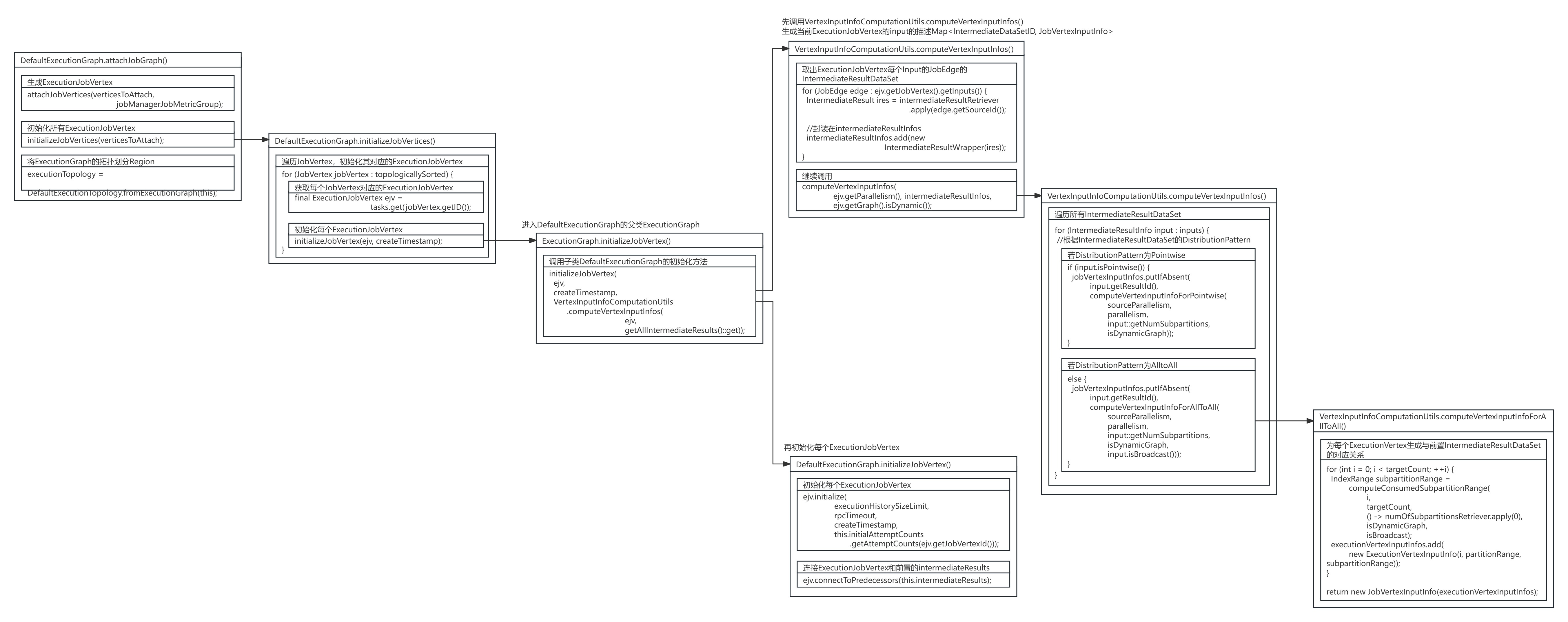
在DefaultExecutionGraph的attachJobGraph()方法中,在执行完DefaultExecutionGraph的attachJobVertices()方法创建完ExecutionJobVertex节点后,会继续执行DefaultExecutionGraph的initializeJobVertices()方法开始初始化ExecutionJobVertex节点。
源码图解:
DefaultExecutionGraph.attachJobGraph()方法源码:
public void attachJobGraph( List verticesToAttach, JobManagerJobMetricGroup jobManagerJobMetricGroup) throws JobException { assertRunningInJobMasterMainThread(); LOG.debug( \"Attaching {} topologically sorted vertices to existing job graph with {} \" + \"vertices and {} intermediate results.\", verticesToAttach.size(), tasks.size(), intermediateResults.size()); //生成ExecutionJobVertex attachJobVertices(verticesToAttach, jobManagerJobMetricGroup); if (!isDynamic) { //初始化所有ExecutionJobVertex initializeJobVertices(verticesToAttach); } //将ExecutionGraph的拓扑划分Region // the topology assigning should happen before notifying new vertices to failoverStrategy executionTopology = DefaultExecutionTopology.fromExecutionGraph(this); partitionGroupReleaseStrategy = partitionGroupReleaseStrategyFactory.createInstance(getSchedulingTopology());}DefaultExecutionGraph.initializeJobVertices()方法遍历了JobGraph中所有JobVertex节点,找到每个JobVertex节点对应的ExecutionJobVertex节点,并对其进行初始化。
DefaultExecutionGraph.initializeJobVertices()方法源码:
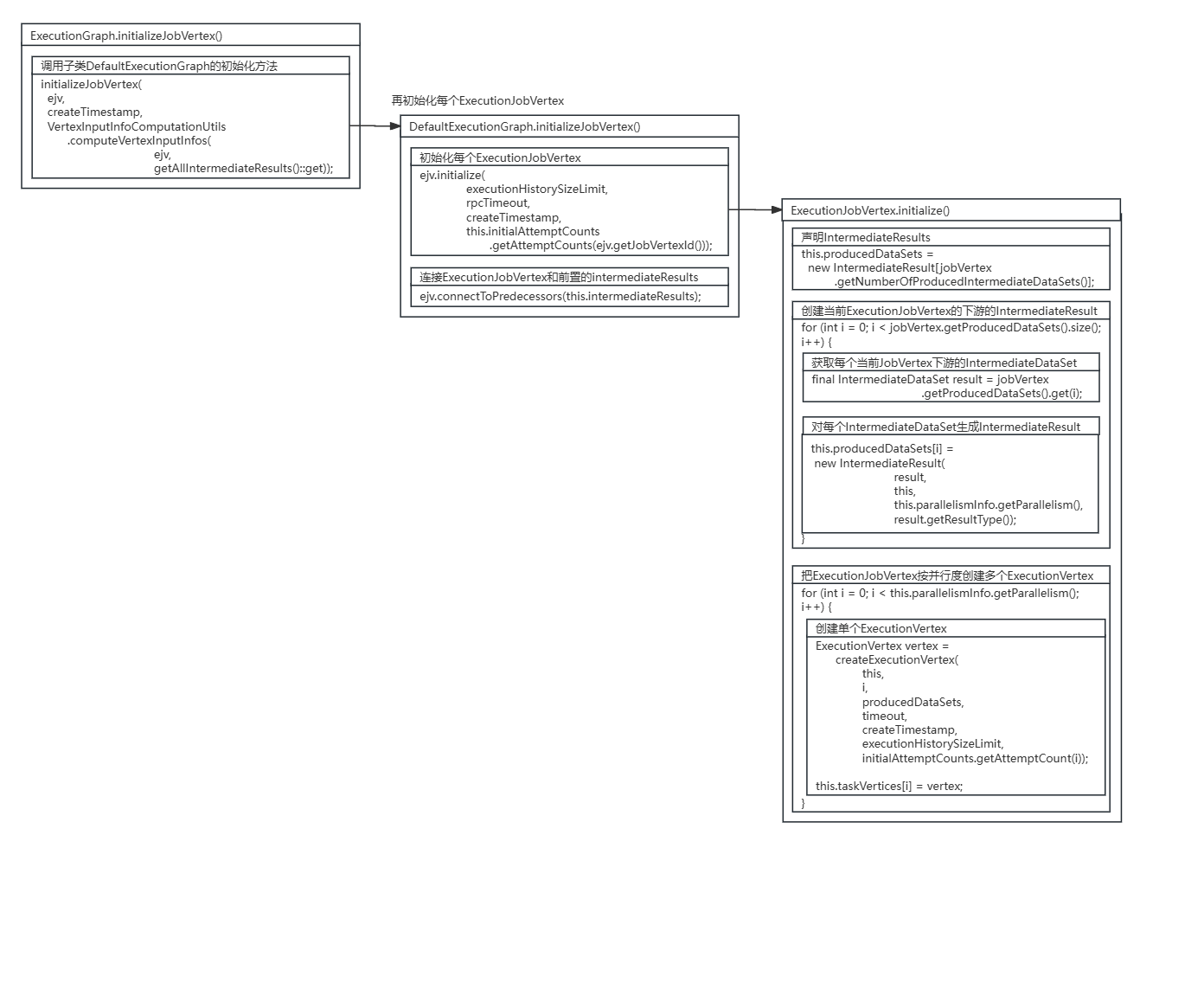
private void initializeJobVertices(List topologicallySorted) throws JobException { final long createTimestamp = System.currentTimeMillis(); //遍历JobVertex,初始化其对应的ExecutionJobVertex for (JobVertex jobVertex : topologicallySorted) { //获取每个JobVertex对应的ExecutionJobVertex final ExecutionJobVertex ejv = tasks.get(jobVertex.getID()); //初始化每个ExecutionJobVertex initializeJobVertex(ejv, createTimestamp); }}DefaultExecutionGraph的initializeJobVertex()方法继承自其父类ExecutionGraph,在ExecutionGraph.initializeJobVertex()方法中,先调用VertexInputInfoComputationUtils的computeVertexInputInfos()方法生成当前ExecutionJobVertex节点的每个输入描述Map,再初始化每个ExecutionJobVertex节点。
ExecutionGraph.initializeJobVertex()方法源码:
default void initializeJobVertex(ExecutionJobVertex ejv, long createTimestamp) throws JobException { //2.再初始化每个ExecutionJobVertex initializeJobVertex( ejv, createTimestamp, //1.先调用VertexInputInfoComputationUtils.computeVertexInputInfos()生成当前ExecutionJobVertex的input的描述Map VertexInputInfoComputationUtils.computeVertexInputInfos( ejv, getAllIntermediateResults()::get));}VertexInputInfoComputationUtils的computeVertexInputInfos()方法取出ExecutionJobVertex节点每个输入JobEdge的IntermediateResultDataSet数据集,并继续调用VertexInputInfoComputationUtils的computeVertexInputInfos()方法。
VertexInputInfoComputationUtils.computeVertexInputInfos()方法源码:
public static Map computeVertexInputInfos( ExecutionJobVertex ejv, Function intermediateResultRetriever) throws JobException { checkState(ejv.isParallelismDecided()); final List intermediateResultInfos = new ArrayList(); //取出ExecutionJobVertex每个Input的JobEdge的IntermediateResultDataSet for (JobEdge edge : ejv.getJobVertex().getInputs()) { IntermediateResult ires = intermediateResultRetriever.apply(edge.getSourceId()); if (ires == null) { throw new JobException( \"Cannot connect this job graph to the previous graph. No previous intermediate result found for ID \" + edge.getSourceId()); } intermediateResultInfos.add(new IntermediateResultWrapper(ires)); } //继续调用computeVertexInputInfos()方法 return computeVertexInputInfos( ejv.getParallelism(), intermediateResultInfos, ejv.getGraph().isDynamic());}VertexInputInfoComputationUtils的computeVertexInputInfos()方法遍历ExecutionJobVertex节点上游JobEdge中的每个IntermediateResultDataSet,根据DistributionPattern为Pointwise或AlltoAll生成不同的节点输入描述JobVertexInputInfo。
VertexInputInfoComputationUtils.computeVertexInputInfos()方法源码:
public static Map computeVertexInputInfos( int parallelism, List inputs, boolean isDynamicGraph) { checkArgument(parallelism > 0); final Map jobVertexInputInfos = new LinkedHashMap(); //遍历所有IntermediateResultDataSet for (IntermediateResultInfo input : inputs) { //根据IntermediateResultDataSet的DistributionPattern int sourceParallelism = input.getNumPartitions(); 若DistributionPattern为Pointwise if (input.isPointwise()) { jobVertexInputInfos.putIfAbsent( input.getResultId(), computeVertexInputInfoForPointwise( sourceParallelism, parallelism, input::getNumSubpartitions, isDynamicGraph)); } else { //若DistributionPattern为AlltoAll jobVertexInputInfos.putIfAbsent( input.getResultId(), computeVertexInputInfoForAllToAll( sourceParallelism, parallelism, input::getNumSubpartitions, isDynamicGraph, input.isBroadcast())); } } return jobVertexInputInfos;}为每个ExecutionVerte节点生成对应的输入描述JobVertexInputInfo,需根据不同的DistributionPattern连接类型生成,若DistributionPattern为Pointwise,根据索引比例滑动选择分区为每个ExecutionJobVertex安排JobVertexInputInfo,若DistributionPattern为AlltoAll,则为每ExecutionJobVertex的每个上游生成对应的索引JobVertexInputInfo。
若DistributionPattern为Pointwise:
VertexInputInfoComputationUtils.computeVertexInputInfoForPointwise()方法源码:
static JobVertexInputInfo computeVertexInputInfoForPointwise( int sourceCount, int targetCount, Function numOfSubpartitionsRetriever, boolean isDynamicGraph) { final List executionVertexInputInfos = new ArrayList(); //若输入并行度大于输出 if (sourceCount >= targetCount) { for (int index = 0; index numOfSubpartitionsRetriever.apply(start), isDynamicGraph, false); executionVertexInputInfos.add( new ExecutionVertexInputInfo(index, partitionRange, subpartitionRange)); } } else { //若输入并行度小于输出 for (int partitionNum = 0; partitionNum < sourceCount; partitionNum++) { //根据索引比例滑动选择分区 int start = (partitionNum * targetCount + sourceCount - 1) / sourceCount; int end = ((partitionNum + 1) * targetCount + sourceCount - 1) / sourceCount; int numConsumers = end - start; IndexRange partitionRange = new IndexRange(partitionNum, partitionNum); // Variable used in lambda expression should be final or effectively final final int finalPartitionNum = partitionNum; for (int i = start; i numOfSubpartitionsRetriever.apply(finalPartitionNum), isDynamicGraph, false); executionVertexInputInfos.add( new ExecutionVertexInputInfo(i, partitionRange, subpartitionRange)); } } } return new JobVertexInputInfo(executionVertexInputInfos);}若DistributionPattern为AlltoAll:
VertexInputInfoComputationUtils.computeVertexInputInfoForAllToAll()方法源码:
static JobVertexInputInfo computeVertexInputInfoForAllToAll( int sourceCount, int targetCount, Function numOfSubpartitionsRetriever, boolean isDynamicGraph, boolean isBroadcast) { final List executionVertexInputInfos = new ArrayList(); IndexRange partitionRange = new IndexRange(0, sourceCount - 1); //为每个ExecutionVertex生成与前置IntermediateResultDataSet的对应关系 for (int i = 0; i numOfSubpartitionsRetriever.apply(0), isDynamicGraph, isBroadcast); executionVertexInputInfos.add( new ExecutionVertexInputInfo(i, partitionRange, subpartitionRange)); } return new JobVertexInputInfo(executionVertexInputInfos);}在ExecutionGraph.initializeJobVertex()方法中,调用VertexInputInfoComputationUtils的computeVertexInputInfos()方法生成当前ExecutionJobVertex节点的每个输入描述Map,为后续生成每个ExecutionJobVertex节点与IntermediateResult数据集的连接做了分配。
执行完VertexInputInfoComputationUtils.computeVertexInputInfos()方法后,DefaultExecutionGraph开始调用其initializeJobVertex()方法,开始初始化每个ExecutionJobVertex节点。
ExecutionGraph.initializeJobVertex()方法源码:
default void initializeJobVertex(ExecutionJobVertex ejv, long createTimestamp) throws JobException { //2.再初始化每个ExecutionJobVertex initializeJobVertex( ejv, createTimestamp, //1.先调用VertexInputInfoComputationUtils.computeVertexInputInfos()生成当前ExecutionJobVertex的input的描述Map VertexInputInfoComputationUtils.computeVertexInputInfos( ejv, getAllIntermediateResults()::get));}DefaultExecutionGraph的initializeJobVertex()方法初始化了每个ExecutionJobVertex节点,并连接了ExecutionJobVertex节点和前置的intermediateResults数据集。
DefaultExecutionGraph.initializeJobVertex()方法源码:
public void initializeJobVertex( ExecutionJobVertex ejv, long createTimestamp, Map jobVertexInputInfos) throws JobException { //... //初始化每个ExecutionJobVertex ejv.initialize( executionHistorySizeLimit, rpcTimeout, createTimestamp, this.initialAttemptCounts.getAttemptCounts(ejv.getJobVertexId())); //连接ExecutionJobVertex和前置的intermediateResults ejv.connectToPredecessors(this.intermediateResults); //... }ExecutionJobVertex.initialize()方法创建了ExecutionJobVertex节点对应的ExecutionVertex节点与IntermediateResult数据集。
5.创建ExecutionVertex节点与IntermediateResult数据集
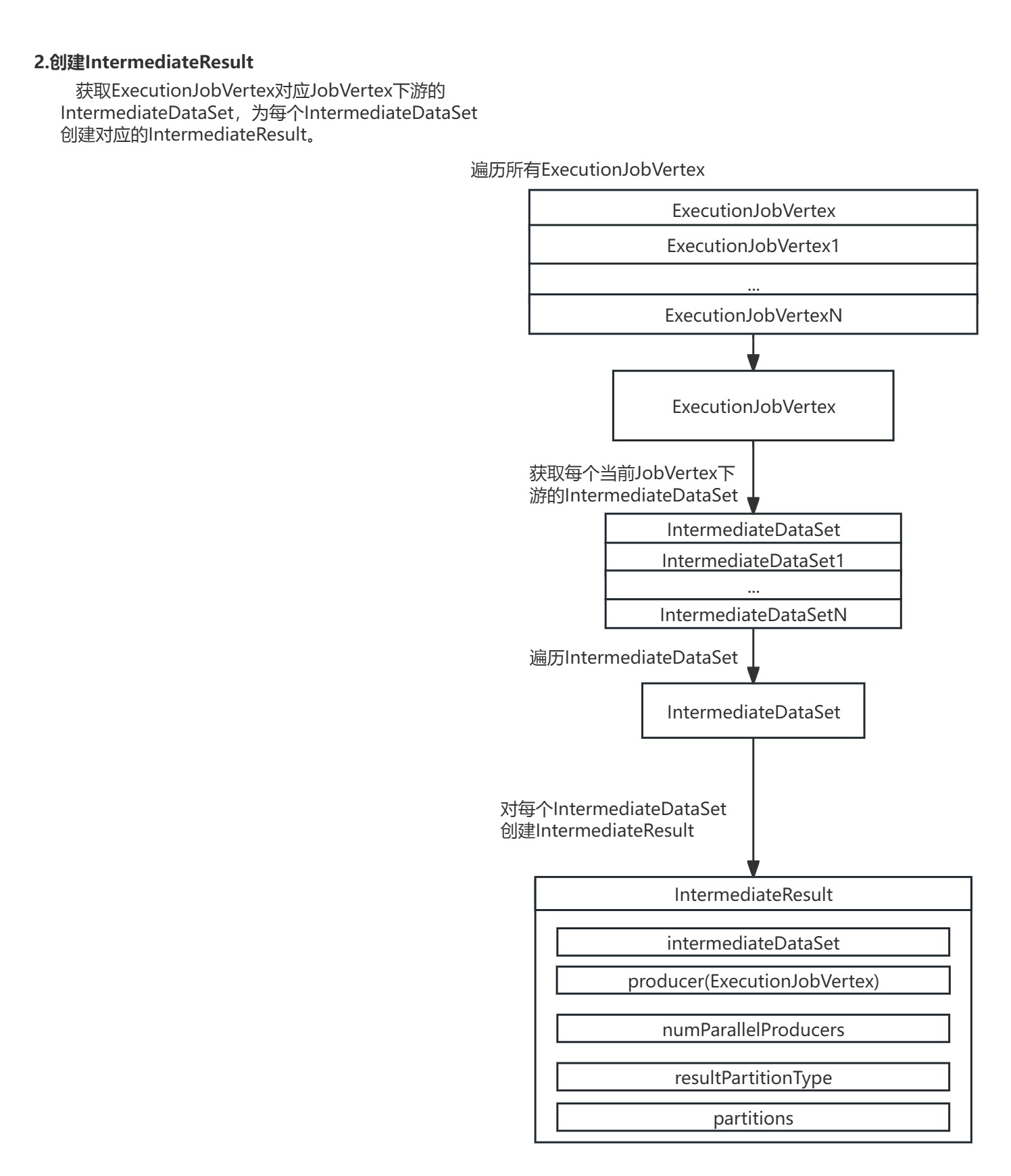
进入ExecutionJobVertex的initialize()方法,方法会为ExecutionJobVertex节点下游每个IntermediateDataSet数据集创建对应的IntermediateResult数据集,并按并行度为每个ExecutionJobVertex节点创建ExecutionVertex节点。
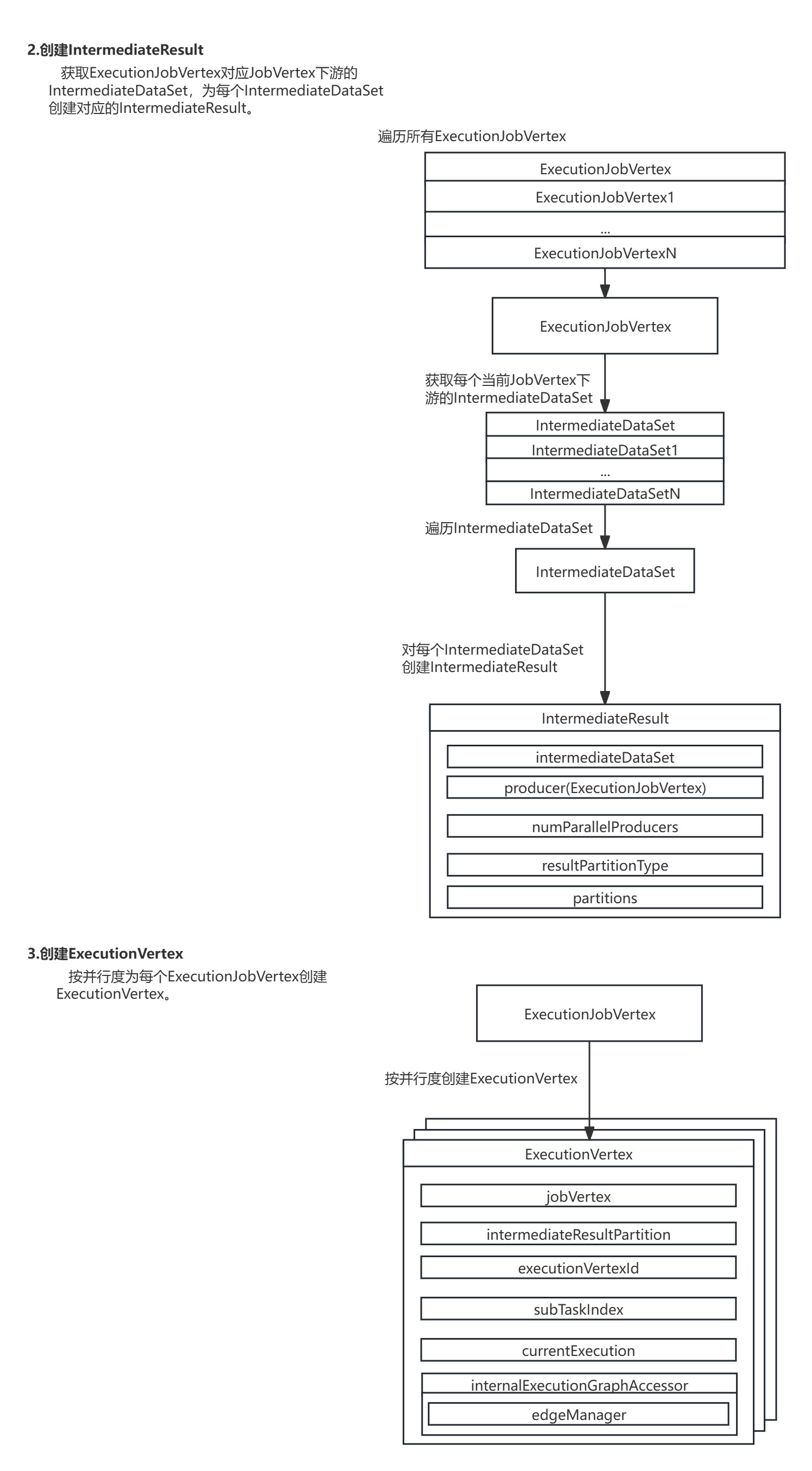
源码图解:
在ExecutionJobVertex的initialize()方法中,对ExecutionJobVertex节点每个下游IntermediateDataSet数据集生成对应的IntermediateResult数据集,并按并行度创建了每个ExecutionVertex。
ExecutionJobVertex.initialize()方法源码:
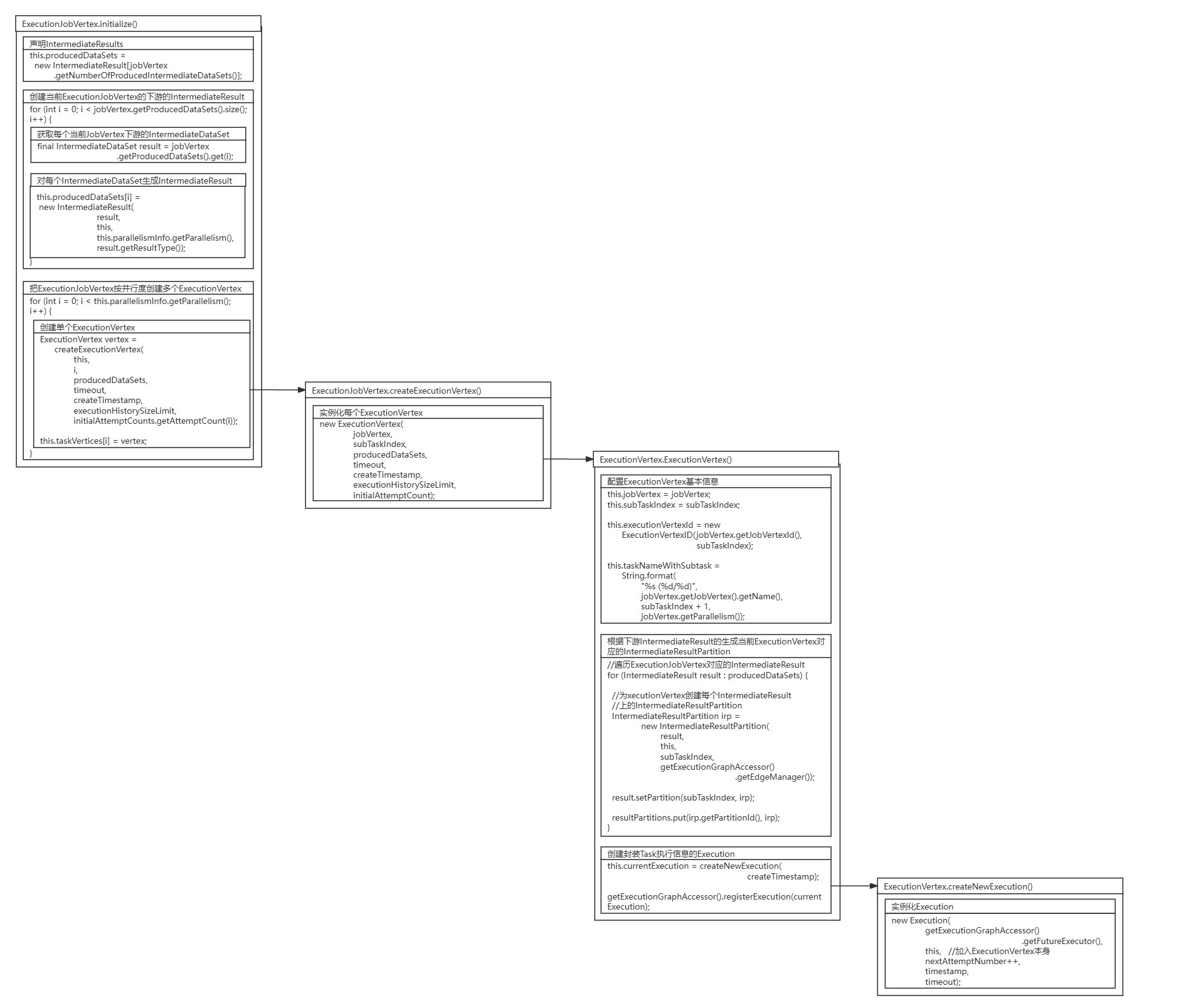
protected void initialize( int executionHistorySizeLimit, Time timeout, long createTimestamp, SubtaskAttemptNumberStore initialAttemptCounts) throws JobException { checkState(parallelismInfo.getParallelism() > 0); checkState(!isInitialized()); this.taskVertices = new ExecutionVertex[parallelismInfo.getParallelism()]; this.inputs = new ArrayList(jobVertex.getInputs().size()); //声明IntermediateResults // create the intermediate results this.producedDataSets = new IntermediateResult[jobVertex.getNumberOfProducedIntermediateDataSets()]; //创建当前ExecutionJobVertex的下游的IntermediateResult for (int i = 0; i < jobVertex.getProducedDataSets().size(); i++) { //获取每个当前JobVertex下游的IntermediateDataSet final IntermediateDataSet result = jobVertex.getProducedDataSets().get(i); //对每个IntermediateDataSet生成IntermediateResult this.producedDataSets[i] = new IntermediateResult( result, this, this.parallelismInfo.getParallelism(), result.getResultType()); } //把ExecutionJobVertex按并行度创建多个ExecutionVertex // create all task vertices for (int i = 0; i < this.parallelismInfo.getParallelism(); i++) { //创建每个ExecutionVertex ExecutionVertex vertex = createExecutionVertex( this, i, producedDataSets, timeout, createTimestamp, executionHistorySizeLimit, initialAttemptCounts.getAttemptCount(i)); this.taskVertices[i] = vertex; } // sanity check for the double referencing between intermediate result partitions and // execution vertices for (IntermediateResult ir : this.producedDataSets) { if (ir.getNumberOfAssignedPartitions() != this.parallelismInfo.getParallelism()) { throw new RuntimeException( \"The intermediate result\'s partitions were not correctly assigned.\"); } } // set up the input splits, if the vertex has any try { @SuppressWarnings(\"unchecked\") InputSplitSource splitSource = (InputSplitSource) jobVertex.getInputSplitSource(); if (splitSource != null) { Thread currentThread = Thread.currentThread(); ClassLoader oldContextClassLoader = currentThread.getContextClassLoader(); currentThread.setContextClassLoader(graph.getUserClassLoader()); try { inputSplits = splitSource.createInputSplits(this.parallelismInfo.getParallelism()); if (inputSplits != null) { splitAssigner = splitSource.getInputSplitAssigner(inputSplits); } } finally { currentThread.setContextClassLoader(oldContextClassLoader); } } else { inputSplits = null; } } catch (Throwable t) { throw new JobException( \"Creating the input splits caused an error: \" + t.getMessage(), t); }}其中ExecutionVertex节点的创建是通过调用ExecutionJobVertex的createExecutionVertex()方法,进行了对ExecutionVertex节点的实例化。
ExecutionJobVertex.createExecutionVertex()方法源码:
protected ExecutionVertex createExecutionVertex( ExecutionJobVertex jobVertex, int subTaskIndex, IntermediateResult[] producedDataSets, Time timeout, long createTimestamp, int executionHistorySizeLimit, int initialAttemptCount) { //实例化每个ExecutionVertex return new ExecutionVertex( jobVertex, subTaskIndex, producedDataSets, timeout, createTimestamp, executionHistorySizeLimit, initialAttemptCount);}6.创建每个ExecutionVertex节点对应的Execution与IntermediateResultPartition数据集分区
在ExecutionVertex的构造方法中,首先配置了ExecutionVertex节点的基本信息,然后根据下游IntermediateResult数据集的生成当前ExecutionVertex节点对应的IntermediateResultPartition数据集分区,最后创建封装Task执行信息的Execution。
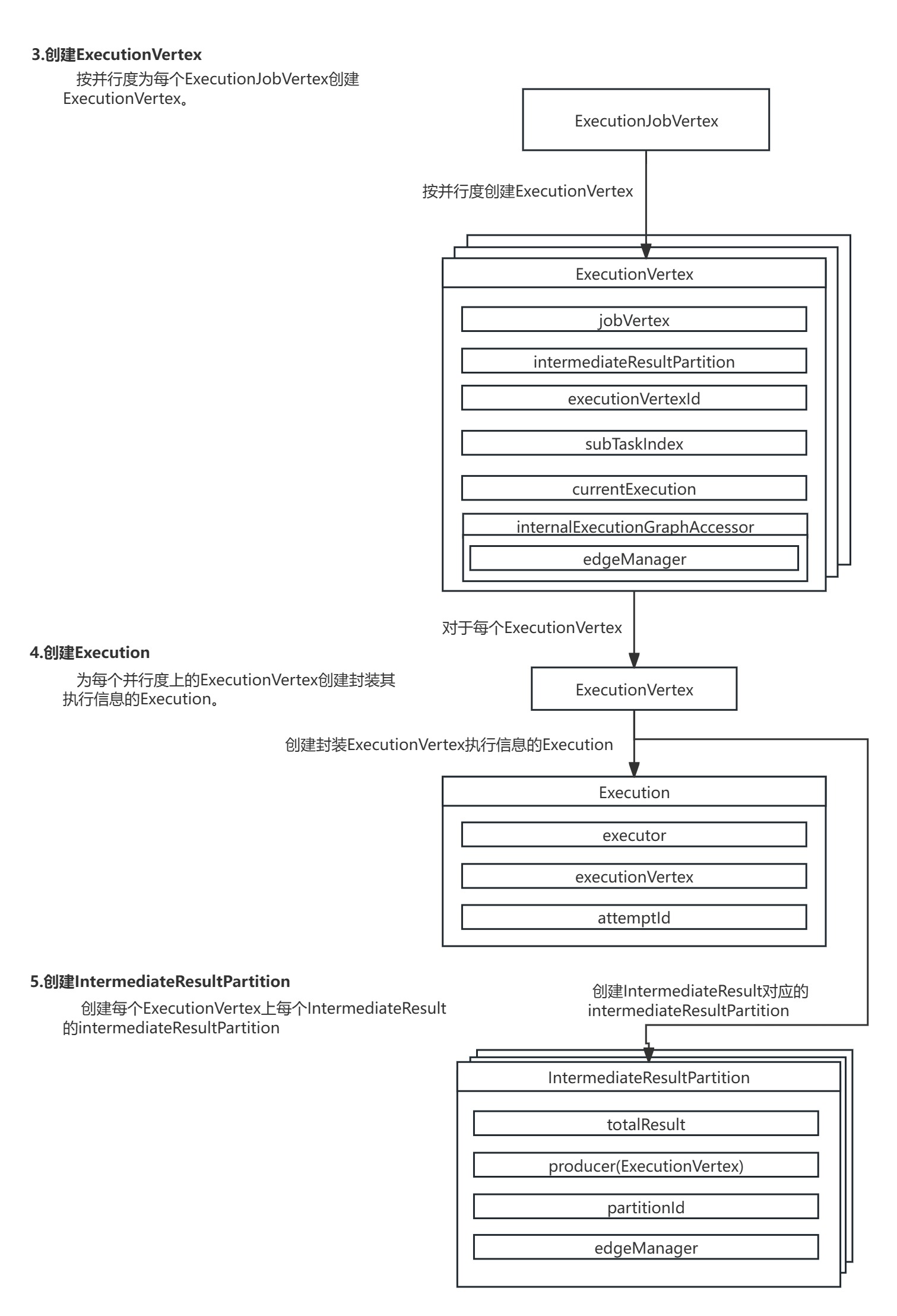
源码图解:
ExecutionVertex.ExecutionVertex()方法源码:
public ExecutionVertex( ExecutionJobVertex jobVertex, int subTaskIndex, IntermediateResult[] producedDataSets, Time timeout, long createTimestamp, int executionHistorySizeLimit, int initialAttemptCount) { //配置ExecutionVertex基本信息 this.jobVertex = jobVertex; this.subTaskIndex = subTaskIndex; this.executionVertexId = new ExecutionVertexID(jobVertex.getJobVertexId(), subTaskIndex); this.taskNameWithSubtask = String.format( \"%s (%d/%d)\", jobVertex.getJobVertex().getName(), subTaskIndex + 1, jobVertex.getParallelism()); //根据下游IntermediateResult的生成当前ExecutionVertex对应的IntermediateResultPartition this.resultPartitions = new LinkedHashMap(producedDataSets.length, 1); for (IntermediateResult result : producedDataSets) { IntermediateResultPartition irp = new IntermediateResultPartition( result, this, subTaskIndex, getExecutionGraphAccessor().getEdgeManager()); result.setPartition(subTaskIndex, irp); resultPartitions.put(irp.getPartitionId(), irp);} this.executionHistory = new ExecutionHistory(executionHistorySizeLimit); this.nextAttemptNumber = initialAttemptCount; this.inputBytes = NUM_BYTES_UNKNOWN; this.timeout = timeout; this.inputSplits = new ArrayList(); //创建封装Task执行信息的Execution this.currentExecution = createNewExecution(createTimestamp); getExecutionGraphAccessor().registerExecution(currentExecution);}在创建封装Task执行信息的Execution时,调用了ExecutionVertex.createNewExecution()方法进行了Execution的实例化。
ExecutionVertex.createNewExecution()方法源码:
Execution createNewExecution(final long timestamp) { //实例化Execution return new Execution( getExecutionGraphAccessor().getFutureExecutor(), this, nextAttemptNumber++, timestamp, timeout);}7.结语
至此,ExecutionGraph的ExecutionJobVertex节点、ExecutionVertex节点、IntermediateResult数据集、IntermediateResultPartition数据集分区与封装Task执行信息的Execution都已创建完毕。因篇幅关系,ExecutionGraph生成的后续源码解析将继续在本专栏的下篇博文展开。


