【SpringBoot】07 容器功能 - SpringBoot底层注解的应用与实战 - @ConfigurationProperties配置绑定
一、@Component + @ConfigurationProperties配置绑定
首先新建一个Car类(组件)。
添加
package com.hello.bean;public class Car { private String brand; // 品牌 private Integer price; // 价格 public String getBrand() { return brand; } public void setBrand(String brand) { this.brand = brand; } public Integer getPrice() { return price; } public void setPrice(Integer price) { this.price = price; } @Override public String toString() { return \"Car{\" + \"brand=\'\" + brand + \'\\\'\' + \", price=\" + price + \'}\'; }}
接着在配置文件中yml对汽车的品牌和价格进行配置。
mycar.brand: BYDmycar.price: 100000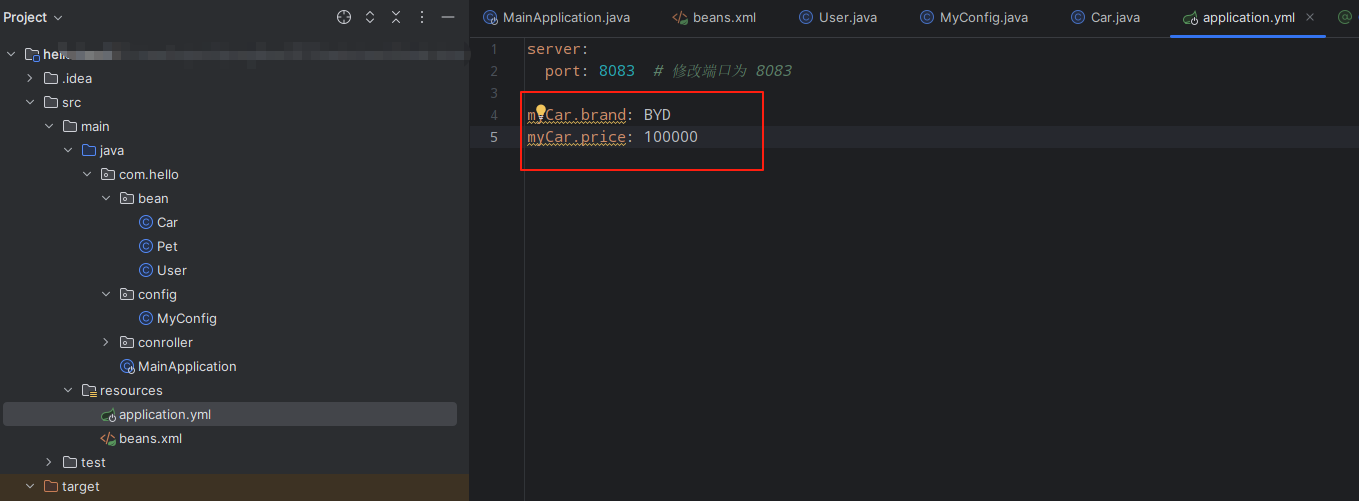
以前要将这个属性加到类中,要有很多代码要写,现在使用注解进行配置。
/** * 只有在容器中的组件,才能使用 @ConfigurationProperties 注解进行批量注入,所以要加@Component */@Component@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = \"mycar\")public class Car {测试
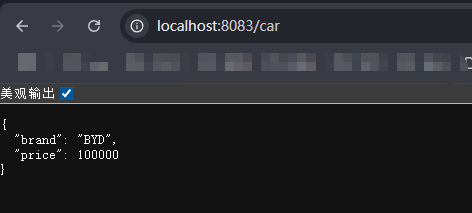
在容器中进行调用测试。
@Autowired Car car; // 组件扫描,自动装配(加入到容器后,直接使用) @RequestMapping(\"/car\") public Car car(){ return car; }package com.hello.conroller;import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;import com.hello.bean.Car;//@ResponseBody // 类上加,表示该类下所有方法返回值作为响应体返回给浏览器//@Controller // 类上加,表示该类下所有方法都是控制器方法@RestController // 是@ResponseBody与@Controller的合并体public class HelloController { // @ResponseBody 单个方法的返回值作为响应体返回给浏览器 @RequestMapping(\"hello\") public String handle01(){ int a = 23; int b = 100; int c = a + b; return \"Hello, Spring Boot2 !\" + \"🎉 **返回信息成功!** (ノ◕ヮ◕)ノ*:\" + c; } @Autowired Car car; // 组件扫描,自动装配(加入到容器后,直接使用) @RequestMapping(\"/car\") public Car car(){ return car; }}运行项目,然后在浏览器输入/car进行验证。
可以看到通过@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = “mycar”)注解,已经将配置文件中的值给到了car对象进行了与对象属性的绑定。
二、@EnableAutoConfiguration + @ConfigurationProperties配置绑定
注意@EnableAutoConfiguration只能在配置类中添加。
@EnableConfigurationProperties(Car.class)// 1、开启配置自动绑定// 2、将组件自动加入到容器中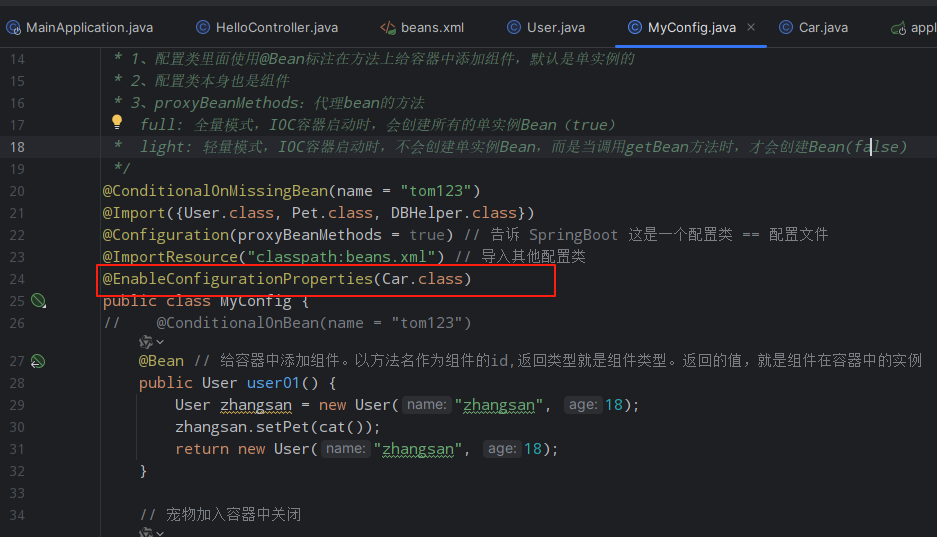
然后我们注解掉controller类中的@Component注解
然后我们重新运行项目,依然可以实现配置的值与属性的绑定。
三、完整代码
application.yml
server: port: 8083 # 修改端口为 8083mycar.brand: toyotamycar.price: 100000MainApplication
package com.hello;import ch.qos.logback.core.db.DBHelper;import com.hello.bean.Pet;import com.hello.bean.User;import com.hello.config.MyConfig;import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;import org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext;import javax.security.auth.login.Configuration;/** * 主程序类 * @SpringBootApplication 这是一个SpringBoot应用 */@SpringBootApplicationpublic class MainApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { // 1、返回我们IOC容器 ConfigurableApplicationContext run = SpringApplication.run(MainApplication.class, args); // 2、查看容器里面的所有组件 String[] names = run.getBeanDefinitionNames(); for (String name : names){ System.out.println(name); }// // 3、从容器中获取组件// Pet tom1 = run.getBean(\"tom123\", Pet.class);// Pet tom2 = run.getBean(\"tom123\", Pet.class);//// System.out.println(\"两个组件是否相同\" + (tom1 == tom2));//// MyConfig bean = run.getBean(MyConfig.class);// System.out.println(bean);////// // 4、获取Import组件// String[] beanNamesForType = run.getBeanNamesForType(User.class);// System.out.println(\"=====\");// for (String name : beanNamesForType){// System.out.println(name);// }//// DBHelper bean1= run.getBean(DBHelper.class);// System.out.println(bean1); boolean tom222 = run.containsBean(\"tom222\"); System.out.println(\"tom123是否存在:\" + tom222); // 判断用户组件是否加入到容器中 boolean user01 = run.containsBean(\"user01\"); System.out.println(\"user01是否存在:\" + user01); boolean haha = run.containsBean(\"haha\"); System.out.println(\"haha是否存在:\" + haha); boolean hehe = run.containsBean(\"hehe\"); System.out.println(\"hehe是否存在:\" + hehe); // 拼接最终启动成功信息 String successMessage = \"🎉 **启动成功!** (ノ◕ヮ◕)ノ*:・゚✧\\n\" + \"✨ *服务已就绪,端口 8083* ✨\\n\" + \"💻 访问地址:`http://localhost:8083`\\n\" + \"💪 **Go! Go! Go!** (ง •_•)ง\"; System.out.println(successMessage); }}car
package com.hello.bean;import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;/** * 只有在容器中的组件,才能使用 @ConfigurationProperties 注解进行批量注入,所以要加@Component *///@Component@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = \"mycar\")public class Car { private String brand; // 品牌 private Integer price; // 价格 public String getBrand() { return brand; } public void setBrand(String brand) { this.brand = brand; } public Integer getPrice() { return price; } public void setPrice(Integer price) { this.price = price; } @Override public String toString() { return \"Car{\" + \"brand=\'\" + brand + \'\\\'\' + \", price=\" + price + \'}\'; }}HelloController
package com.hello.conroller;import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;import com.hello.bean.Car;//@ResponseBody // 类上加,表示该类下所有方法返回值作为响应体返回给浏览器//@Controller // 类上加,表示该类下所有方法都是控制器方法@RestController // 是@ResponseBody与@Controller的合并体public class HelloController { // @ResponseBody 单个方法的返回值作为响应体返回给浏览器 @RequestMapping(\"hello\") public String handle01(){ int a = 23; int b = 100; int c = a + b; return \"Hello, Spring Boot2 !\" + \"🎉 **返回信息成功!** (ノ◕ヮ◕)ノ*:\" + c; } @Autowired Car car; // 组件扫描,自动装配(加入到容器后,直接使用) @RequestMapping(\"/car\") public Car car(){ return car; }}总结
Spring Boot 配置属性绑定的两种核心方式总结
Spring Boot 提供了灵活的配置属性绑定机制,能够将外部配置(如 YAML/Properties 文件)中的值自动映射到 Java 对象的属性中,极大简化了配置管理。核心方式分为两种:@Component + @ConfigurationProperties 和 @EnableConfigurationProperties + @ConfigurationProperties,两者均通过类型安全的方式实现批量属性注入,避免了传统 @Value 注解的冗余代码。
1. @Component + @ConfigurationProperties 组合
此方式需将目标类(如 Car)标记为 Spring 组件(@Component),使其纳入容器管理,再通过 @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = \"mycar\") 指定配置前缀。Spring Boot 会自动扫描容器中的此类,并将配置文件中 mycar.brand、mycar.price 等属性绑定到对应字段。优点是简单直接,适合常规组件;缺点是需确保类被组件扫描到(如位于主类同级或子包下)。
2. @EnableConfigurationProperties + @ConfigurationProperties 组合
在配置类(如 @SpringBootApplication 主类)上使用 @EnableConfigurationProperties(Car.class),可显式启用指定类的配置绑定功能,并自动将其注册为 Bean。此时即使 Car 类未标注 @Component,也能完成属性注入。优点是解耦组件扫描与配置绑定,适合第三方库或需要集中管理的配置类;缺点是需额外配置注解。
验证与扩展
通过控制器(HelloController)的 /car 接口可验证绑定结果,浏览器返回的 JSON 数据会显示配置值已正确注入。两种方式本质相同,均依赖 Spring Boot 的自动配置机制,开发者可根据场景选择:简单项目推荐 @Component 方式,复杂或多模块项目推荐 @EnableConfigurationProperties 方式。此外,需确保字段名与配置键名匹配(或通过 @JsonProperty 等注解指定),并添加 spring-boot-configuration-processor 依赖以获得配置提示支持。


