Spring Boot 整合 Spring MVC:自动配置与扩展实践_springboot xml配置的扩展
Spring MVC 作为 Java Web 开发的核心框架,在传统 SSM 项目中需要大量 XML 配置(如 DispatcherServlet、视图解析器等)。而 Spring Boot 通过 \"自动配置\" 特性,简化了 Spring MVC 的整合过程,同时保留了灵活的扩展能力。本文将从自动配置原理、扩展方式、组件注册等方面,结合实例详解 Spring Boot 与 Spring MVC 的整合实践。
一、Spring Boot 对 Spring MVC 的自动配置
Spring Boot 的核心优势之一是 \"约定大于配置\",对于 Spring MVC 的核心组件,Spring Boot 已完成自动配置,无需手动编写 XML 或 Java 配置。
1.1 核心组件的自动配置
(1)DispatcherServlet(中央转发器)
传统 SSM 中需在web.xml配置 DispatcherServlet:
springmvc org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet 1 springmvc /Spring Boot 通过DispatcherServletAutoConfiguration类自动注册 DispatcherServlet,默认拦截路径为/(不拦截 JSP),且无需web.xml(因为 Spring Boot 以 JAR 包方式运行嵌入式容器)。
(2)控制器(Controller)
只需在类上标注@Controller或@RestController,并确保类在 Spring Boot 的注解扫描范围内(默认扫描主启动类所在包及其子包),Spring Boot 会自动将其注册为 Bean。
(3)视图解析器
传统 SSM 需配置 InternalResourceViewResolver:
public ContentNegotiatingViewResolver viewResolver(BeanFactory beanFactory) { ContentNegotiatingViewResolver resolver = new ContentNegotiatingViewResolver(); resolver.setContentNegotiationManager((ContentNegotiationManager)beanFactory.getBean(ContentNegotiationManager.class)); resolver.setOrder(-2147483648); return resolver;}当我们做文件上传的时候我们也会发现multipartResolver是自动被配置好的
页面
Title Controller
package com.qcby.mavenspringboot.controller;import jakarta.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;import org.springframework.ui.Model;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;import org.springframework.web.multipart.MultipartFile;import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;import java.io.FileOutputStream;import java.io.IOException;import java.nio.file.Files;import java.nio.file.Path;import java.nio.file.Paths;import java.util.UUID;import org.slf4j.Logger;@Controllerpublic class UploadController { private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(UploadController.class); @RequestMapping(value = \"/upload\", method = RequestMethod.GET) public String showUploadForm() { return \"upload\"; } // 2. 处理POST请求:接收文件上传 @RequestMapping(value = \"/upload\", method = RequestMethod.POST) public String upload( @RequestParam(\"pic\") MultipartFile file, HttpServletRequest request, Model model ) { if (file.isEmpty()) { logger.error(\"上传的文件为空\"); return \"upload\"; } String originalFileName = file.getOriginalFilename(); String contentType = file.getContentType(); logger.info(\"原始文件名: {}\", originalFileName); logger.info(\"文件类型: {}\", contentType); String uniqueFileName = generateUniqueFileName(originalFileName); // 本地存储路径(D:/imgup/) Path filePath = Paths.get(\"D:\", \"imgup\"); try { // 上传文件到本地路径 uploadFile(file.getBytes(), filePath, uniqueFileName); String fileAccessUrl = \"/webimg/\" + uniqueFileName; model.addAttribute(\"originalFileName\", originalFileName); model.addAttribute(\"fileUrl\", fileAccessUrl); model.addAttribute(\"fileType\", contentType); } catch (IOException e) { logger.error(\"文件上传失败\", e); return \"error\"; } return \"success\"; } private static void uploadFile(byte[] file, Path filePath, String fileName) throws IOException { // 若目录不存在则创建 if (!Files.exists(filePath)) { Files.createDirectories(filePath); } Path targetPath = filePath.resolve(fileName); // 写入文件(try-with-resources自动关闭流) try (FileOutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(targetPath.toFile())) { out.write(file); } } // 生成唯一文件名(UUID+原文件后缀) private static String generateUniqueFileName(String originalFileName) { String extension = \"\"; int dotIndex = originalFileName.lastIndexOf(\'.\'); if (dotIndex > 0) { extension = originalFileName.substring(dotIndex); } return UUID.randomUUID().toString() + extension; }}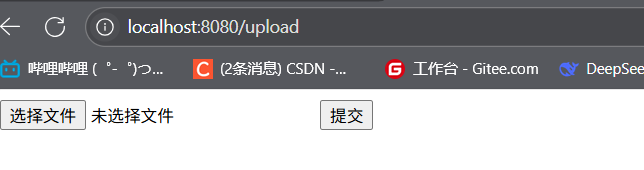
上传文件展示代码:
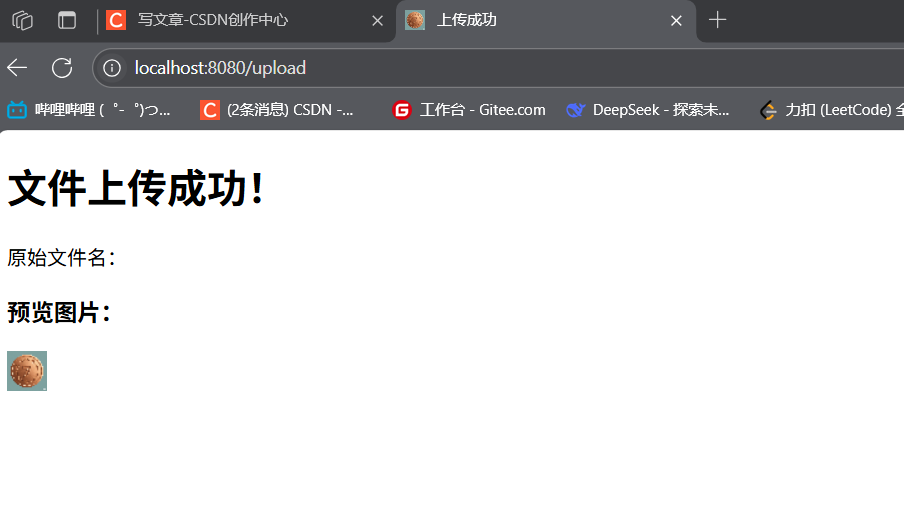
上传成功 文件上传成功!
原始文件名:
预览图片:
![]() <!---->
<!---->
Spring Boot 自动注册ContentNegotiatingViewResolver(组合所有视图解析器)和BeanNameViewResolver。ContentNegotiatingViewResolver会根据请求头(如Accept)动态选择合适的视图解析器,无需手动配置前缀 / 后缀(如需自定义,可通过扩展方式实现)。
(4)文件上传(MultipartResolver)
Spring Boot 自动配置StandardServletMultipartResolver,支持文件上传。前端表单需指定enctype=\"multipart/form-data\",后端通过@RequestParam(\"file\") MultipartFile file接收文件。
默认上传大小限制为 10MB,可在application.properties中修改:
spring.servlet.multipart.max-file-size=100MB # 单个文件大小spring.servlet.multipart.max-request-size=500MB # 总请求大小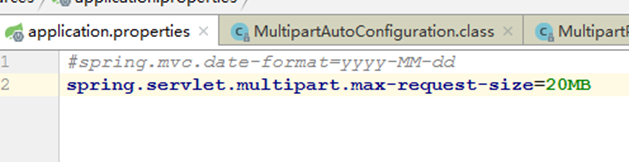
(5)静态资源访问
Spring Boot 默认将classpath:/static/、classpath:/public/、classpath:/resources/、classpath:/META-INF/resources/目录下的资源视为静态资源,可直接通过 URL 访问(如http://localhost:8080/xxx.js)。
(6)消息转换器与格式化
- 消息转换器:自动配置
HttpMessageConverter,支持 JSON(默认 Jackson)、XML 等数据格式的序列化 / 反序列化。 - 格式化:默认支持日期、数字等类型的格式化,可通过
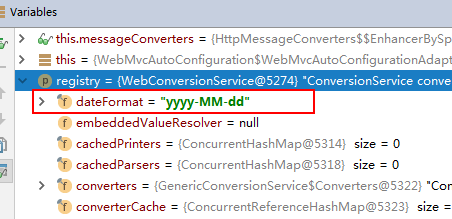
application.properties配置全局日期格式:spring.mvc.format.date=yyyy-MM-dd
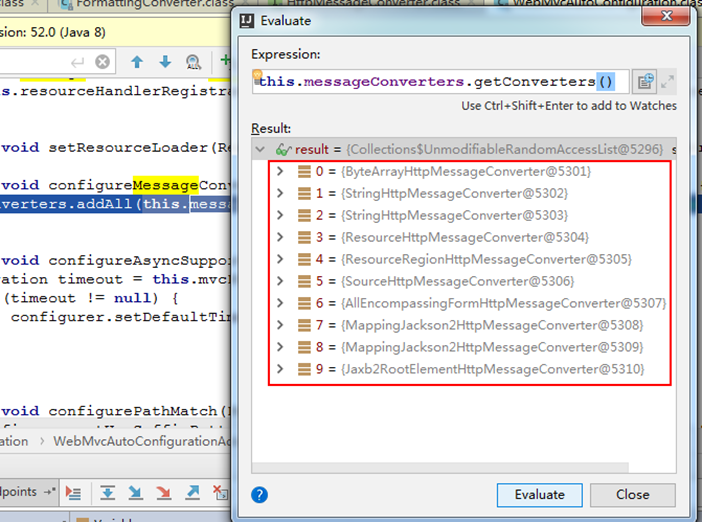
格式化转换器的自动注册
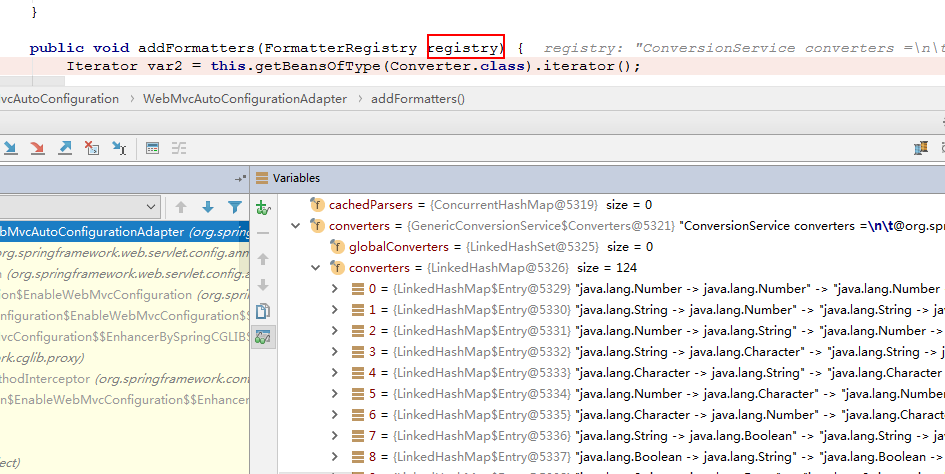
时间类型我们可以在这里修改
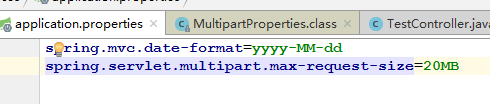
在配置文件中指定好时间的模式我们就可以输入了
(7)欢迎页
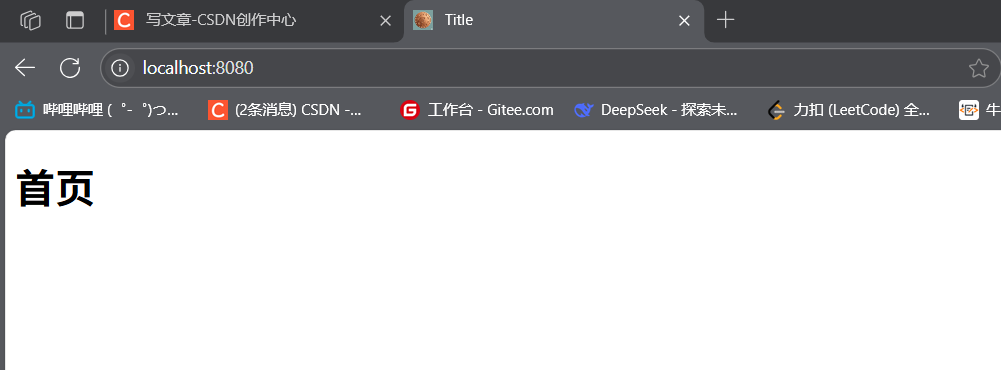
默认将classpath:/static/index.html或classpath:/templates/index.html(Thymeleaf)作为欢迎页,访问http://localhost:8080/时自动跳转。
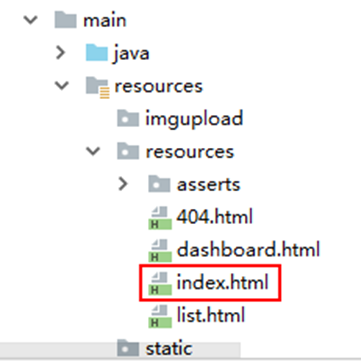
Title 首页
二、扩展 Spring MVC:通过 WebMvcConfigurer
Spring Boot 的自动配置并非 \"一刀切\",实际开发中常需自定义配置(如拦截器、消息转换器)。通过实现WebMvcConfigurer接口(推荐),可在不覆盖自动配置的前提下扩展 Spring MVC。
2.1 核心扩展场景与示例
创建配置类MyMVCCofnig实现WebMvcConfigurer,并重写对应方法:
@Configurationpublic class MyMVCCofnig implements WebMvcConfigurer { // 扩展方法...}(1)视图控制器(请求转发)
通过addViewControllers实现 URL 与视图的直接映射(无需编写 Controller):
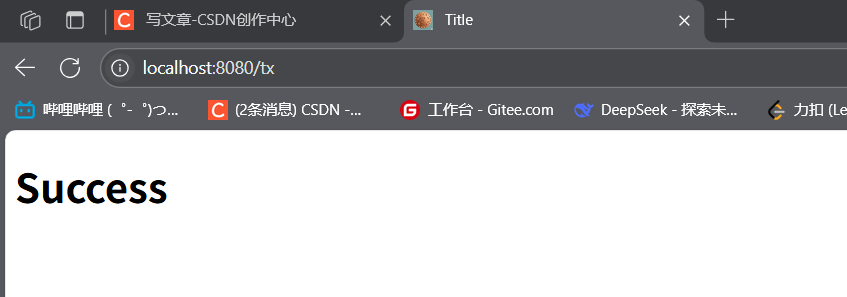
@Overridepublic void addViewControllers(ViewControllerRegistry registry) { // 访问http://localhost:8080/tx时,转发到success.html registry.addViewController(\"/tx\").setViewName(\"success\");}success页面:
Title Success
(2)自定义格式化器
通过addFormatters注册自定义格式化器(如日期解析):
@Overridepublic void addFormatters(FormatterRegistry registry) { // 自定义日期格式化(将\"yyyy-MM-dd\"字符串转为Date) registry.addFormatter(new Formatter() { @Override public String print(Date date, Locale locale) { return null; // 响应时格式化(按需实现) } @Override public Date parse(String s, Locale locale) throws ParseException { return new SimpleDateFormat(\"yyyy-MM-dd\").parse(s); } });}测试:控制器接口接收 Date 参数:
@GetMapping(\"/testDate\")public String testDateFormatter(@RequestParam(\"date\") Date date) { return \"日期:\" + date.toLocaleString();}// 访问:http://localhost:8080/testDate?date=2023-10-01 可正常解析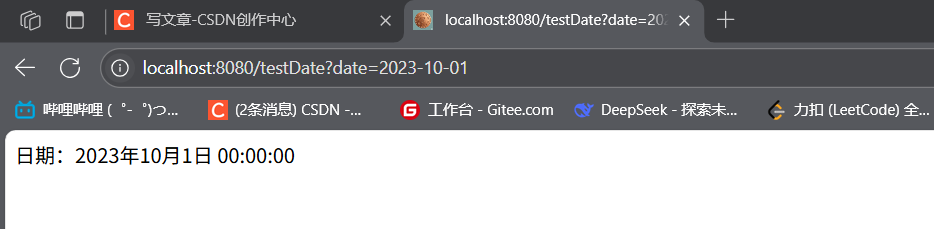
(3)整合 FastJSON 消息转换器
默认 Jackson 可能无法满足需求(如 JSON 格式化),可替换为 FastJSON:
- 引入依赖:
com.alibaba fastjson 1.2.47- 注册 FastJSON 转换器:
@Overridepublic void configureMessageConverters(List<HttpMessageConverter> converters) { FastJsonHttpMessageConverter converter = new FastJsonHttpMessageConverter(); FastJsonConfig config = new FastJsonConfig(); // 配置JSON格式化(如PrettyFormat) config.setSerializerFeatures(SerializerFeature.PrettyFormat); converter.setFastJsonConfig(config); converters.add(converter);}- 实体类自定义字段格式:
public class User { @JSONField(format = \"yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss\") // 序列化日期格式 private Date date; // 其他字段...}测试:接口返回 User 对象时,日期将按指定格式序列化:
@GetMapping(\"/user\")public User getUser() { User user = new User(\"张三\", \"123\", 20, 90.5, 1); user.setDate(new Date()); return user;} 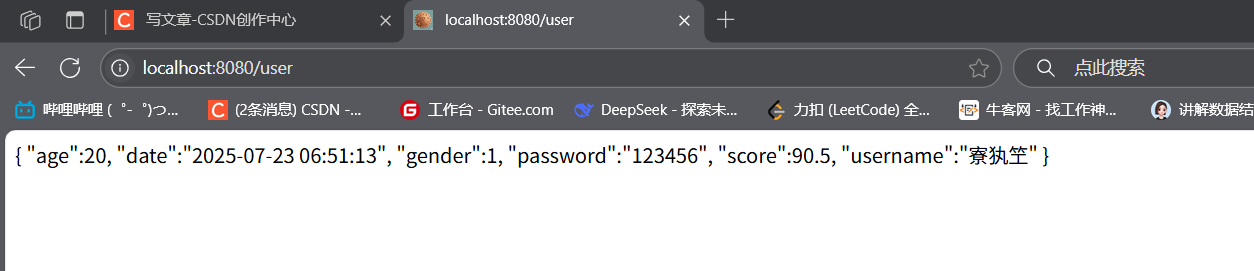
(4)注册拦截器
拦截器可用于登录验证、日志记录等场景,需两步:
- 创建自定义拦截器:
public class MyInterceptor implements HandlerInterceptor { @Override public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) { System.out.println(\"前置拦截(请求处理前)\"); return true; // true放行,false拦截 } @Override public void postHandle(...) { System.out.println(\"后置拦截(视图渲染前)\"); } @Override public void afterCompletion(...) { System.out.println(\"最终拦截(请求完成后)\"); }}- 通过
addInterceptors注册拦截器:
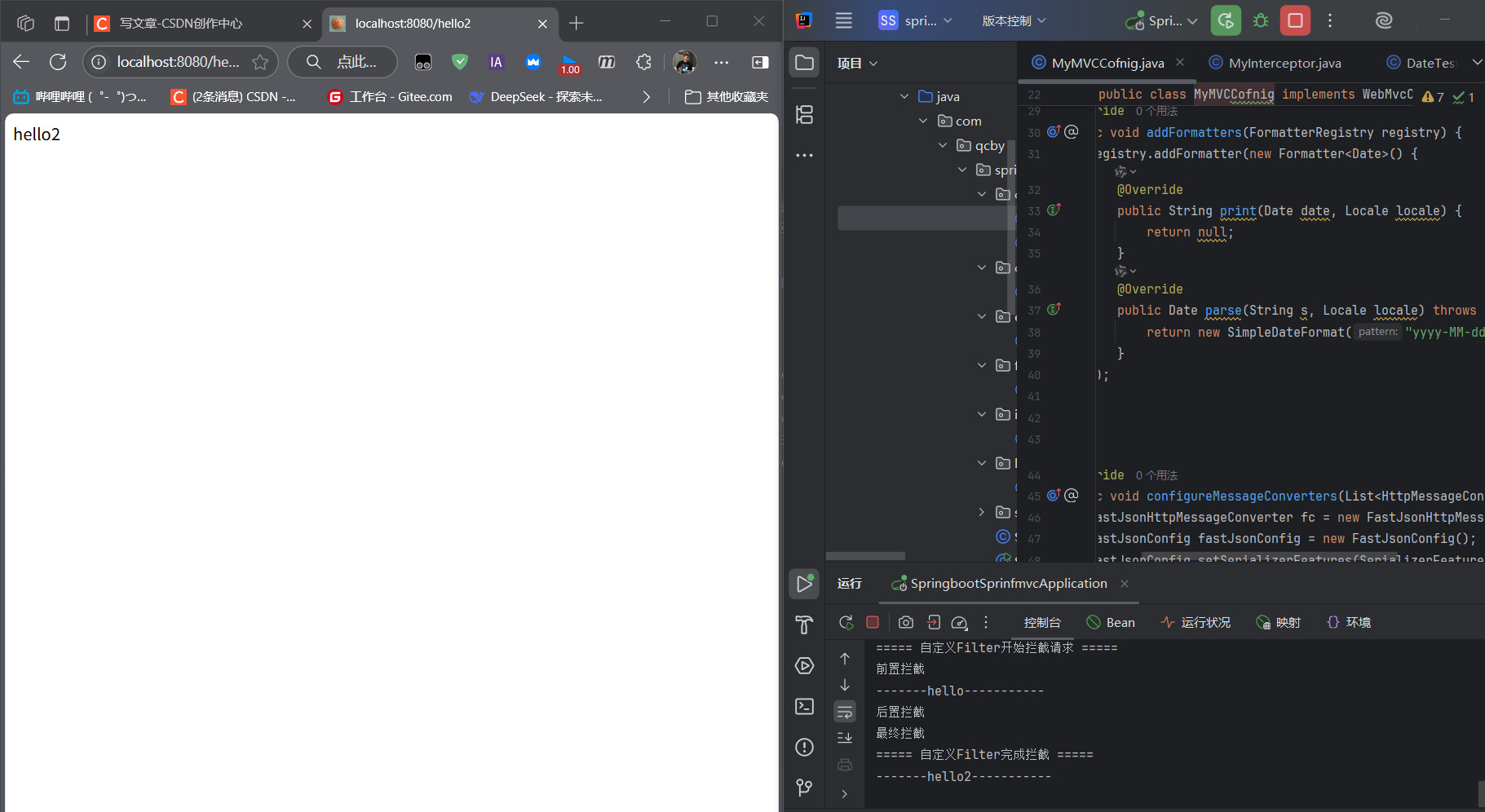
@Overridepublic void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) { registry.addInterceptor(new MyInterceptor()) .addPathPatterns(\"/**\") // 拦截所有请求 .excludePathPatterns(\"/hello2\"); // 排除/hello2请求}测试:访问/hello会被拦截,访问/hello2不会:
@GetMapping(\"/hello\")public String hello() { System.out.println(\"执行/hello业务逻辑\"); return \"hello\";}@GetMapping(\"/hello2\")public String hello2() { return \"hello2\";}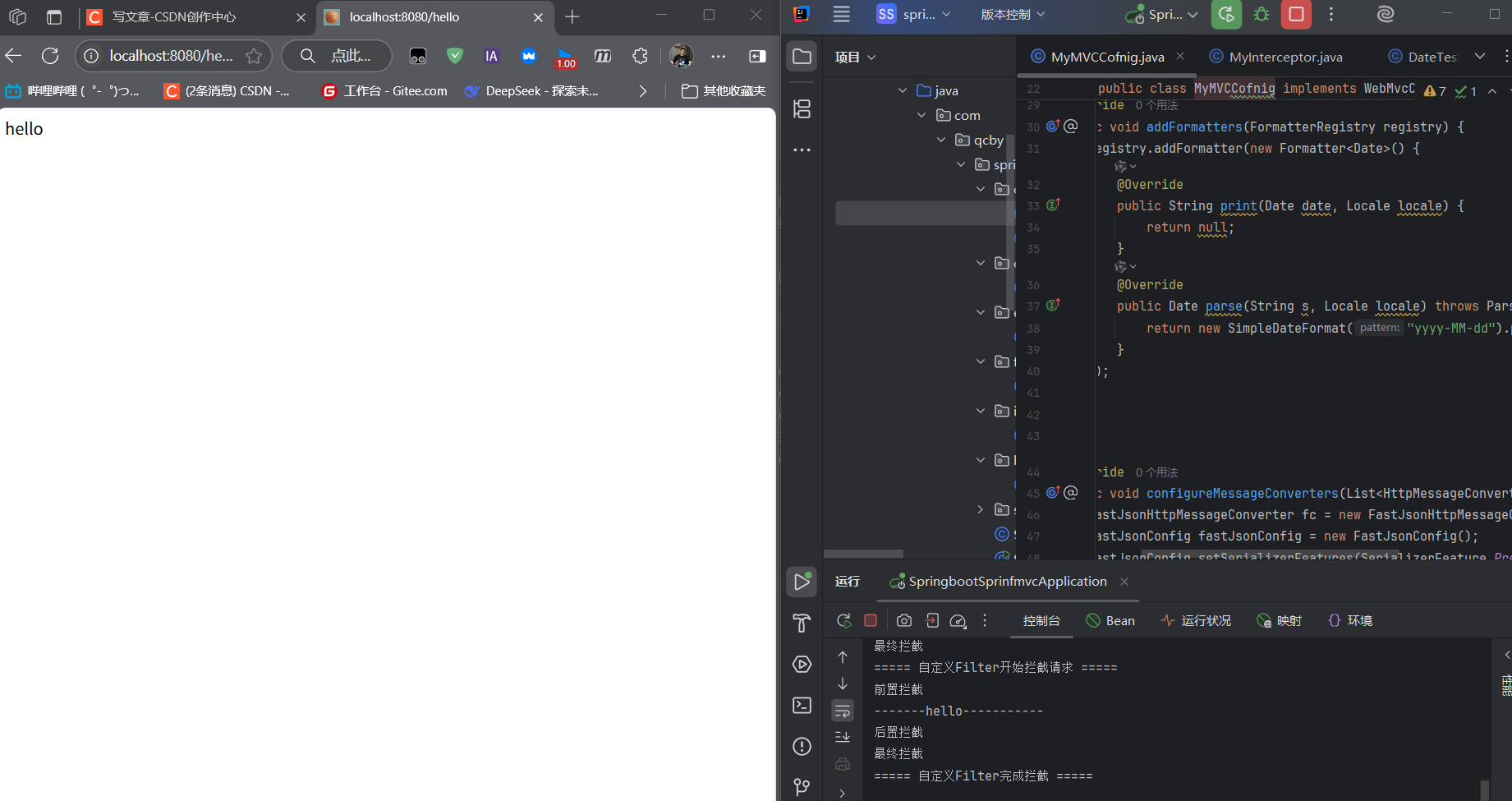
三、注册 Servlet 三大组件(Servlet、Filter、Listener)
传统 Web 项目通过web.xml注册 Servlet、Filter、Listener,而 Spring Boot 需通过@Bean手动注册(因无 web.xml)。
3.1 注册示例(配置类 ServletConfig)
@Configurationpublic class ServletConfig { // 1. 注册Servlet @Bean public ServletRegistrationBean myServlet() { // 参数1:自定义Servlet实例;参数2:访问路径 ServletRegistrationBean registrationBean = new ServletRegistrationBean(new MyServlet(), \"/myServlet\"); registrationBean.setLoadOnStartup(1); // 启动时加载(优先级) return registrationBean; } // 2. 注册Filter @Bean public FilterRegistrationBean myFilter() { FilterRegistrationBean registrationBean = new FilterRegistrationBean(); registrationBean.setFilter(new MyFilter()); // 自定义Filter registrationBean.setUrlPatterns(Arrays.asList(\"/hello\", \"/myServlet\")); // 拦截路径 return registrationBean; } // 3. 注册Listener @Bean public ServletListenerRegistrationBean myListener() { ServletListenerRegistrationBean registrationBean = new ServletListenerRegistrationBean(new MyListener()); return registrationBean; }}3.2 自定义组件实现
(1)自定义 Servlet
public class MyServlet extends HttpServlet { @Override protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws IOException { resp.getWriter().write(\"Hello MyServlet\"); }}访问http://localhost:8080/myServlet会执行该 Servlet。
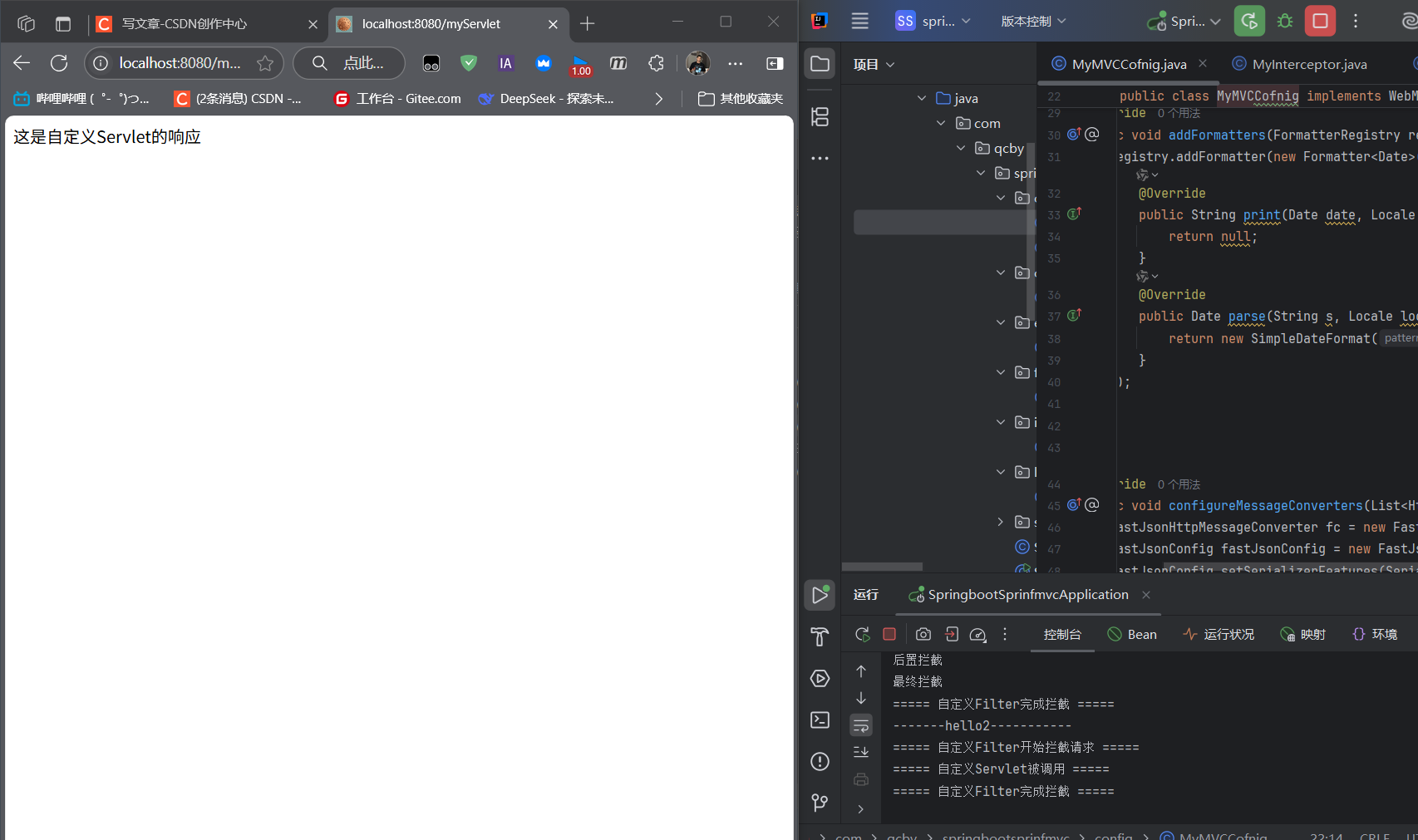
(2)自定义 Filter
public class MyFilter implements Filter { @Override public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, FilterChain chain) throws IOException, ServletException { System.out.println(\"Filter拦截请求\"); chain.doFilter(request, response); // 放行 System.out.println(\"Filter处理完成\"); }}(3)自定义 Listener
public class MyListener implements ServletContextListener { @Override public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent sce) { System.out.println(\"Listener:应用启动初始化\"); } @Override public void contextDestroyed(ServletContextEvent sce) { System.out.println(\"Listener:应用关闭销毁\"); }}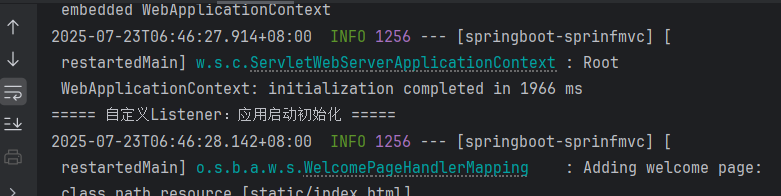
四、项目依赖与配置
4.1 核心依赖(pom.xml)
org.springframework.boot spring-boot-starter-web com.alibaba fastjson 1.2.47 org.springframework.boot spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf org.springframework.boot spring-boot-devtools true 

