Java 反射_java反射
目录
什么是反射?
获取 Class 对象
反射的使用
反射相关的类
使用反射创建对象
反射构造方法
反射属性
反射方法
反射的优缺点
什么是反射?
反射(reflection)是 Java 中的一项特性,它允许程序 在运行时 查询和操作类的信息。即,在运行状态中,对于任意一个类,都能够知道这个类的所有属性和方法;对于任意一个对象,都能调用它的任意方法和属性。获取到方法和属性后,就可以对其进行修改。这种动态获取信息以及动态调用对象方法的功能也就是Java的反射机制
Java文件被编译后,生成了 .class 文件,此时,JVM 就需要解读 .class 文件,.class 文件被 JVM 解析成一个对象,这个对象就是 java.lang.Class。因此,程序在运行时,每个Java文件最终都变成了 Class 类对象的一个实例
通过Java的反射机制,就可以获取甚至修改这个类的属性和动作,使这个类成为一个动态的类
获取 Class 对象
要使用反射机制,我们首先要拿到需要使用反射的类的 Class 对象,然后使用 Class 对象的方法,从而达到反射的目的
需要反射的类:
public class Student { // 私有属性 id private int id = 1; // 公有属性 name public String name = \"张三\"; public Student(){} private Student(int id, String name) { this.id = id; this.name = name; } // 公有方法 public void method1() { System.out.println(\"method1... \"); } // 私有方法 private int method2(int a, int b) { System.out.println(\"method2...\"); return a + b; } @Override public String toString() { return \"Student{\" + \"id=\" + id + \", name=\'\" + name + \'\\\'\' + \'}\'; }}(1)可以使用静态方法 Class.forName() 来获取 Class 对象
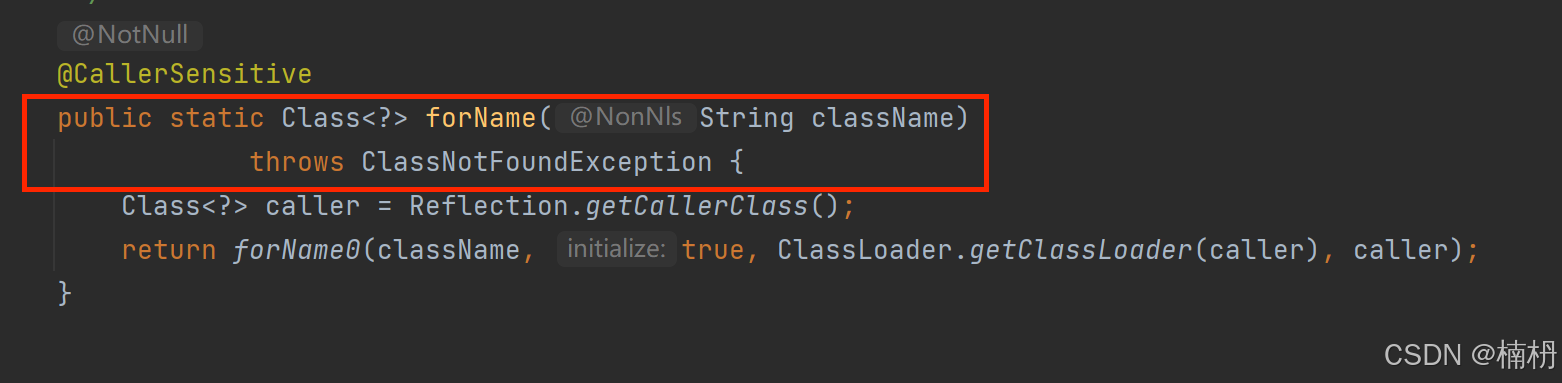
传递的参数 className 为类的全路径名,因此这种方式适用于已经确定了全路径名的类, ClassNotFoundException 为受查异常,需要进行处理
public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { // 1. Class.forName() try { Class studentClass = Class.forName(\"Student\"); System.out.println(studentClass); } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } }}(2) 通过 类名.class 获取 Class 对象
public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { // 2. 类名.class Class studentClass2 = Student.class; System.out.println(studentClass2); }}若在编译之前就已经明确了要操作的类,就可以使用 类名.class 的方式获取 Class 对象
(3)使用类对象的 getClass() 方法
public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { // 3. 对象.getClass() Student student = new Student(); Class studentClass3 = student.getClass(); System.out.println(studentClass3); }}要使用类对象的 getClass() 方法获取 Class 对象,需要先创建类对象
那么,每次获取的 Class 对象是同一个吗?
我们来测试一下:
public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { // 1. Class.forName() Class studentClass = null; try { studentClass = Class.forName(\"Student\"); System.out.println(studentClass); } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } // 2. 类名.class Class studentClass2 = Student.class; System.out.println(studentClass2); // 3. 对象.getClass() Student student = new Student(); Class studentClass3 = student.getClass(); System.out.println(studentClass3); System.out.println(studentClass.equals(studentClass2)); System.out.println(studentClass.equals(studentClass3)); System.out.println(studentClass2.equals(studentClass3)); }}运行结果:
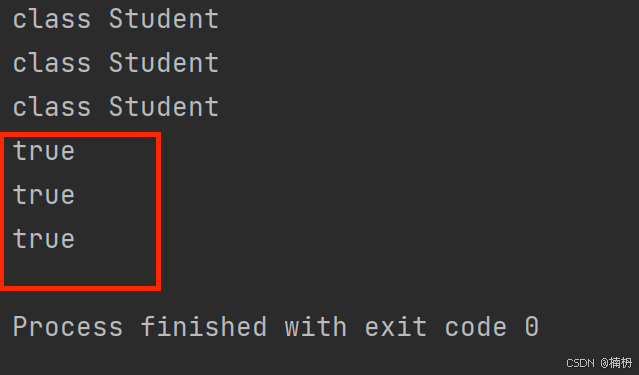
一个类在 JVM 中只会有一个 Class 实例,因此,获取的 Class 对象是同一个
获取到 Class 对象后,我们就来对类中的方法和属性进行调用和修改
反射的使用
要使用反射,我们首先来了解与反射相关的类
反射相关的类
Class 位于 java.lang 包下,而 Field、Method、Constructor 都位于 java.lang.reflect 包下
使用反射创建对象
Class 类中获取类相关的方法:`
ClassLoader getClassLoader()
Class[] getDeclaredClasses()
static Class forName(String className)
T newInstance()
String getName()
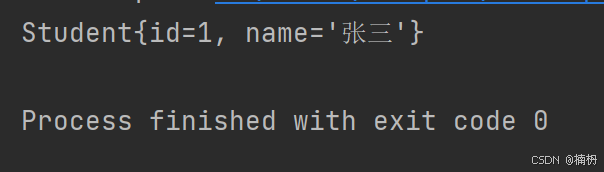
使用 newInstance() 方法来创建 Student 类的实例:
public static void reflectNewInstance() { Class studentClass = null; try { studentClass = Class.forName(\"Student\"); Student student = (Student) studentClass.newInstance(); System.out.println(student); } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } catch (InstantiationException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } catch (IllegalAccessException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } } public static void main(String[] args) { reflectNewInstance(); }运行结果:
反射构造方法
Class 类中获得构造器相关方法:
Constructor getConstructor(Class... parameterTypes)
Constructor[] getConstructors()
Constructor getDeclaredConstructor(Class... parameterTypes)
Constructor[] getDeclaredConstructors()
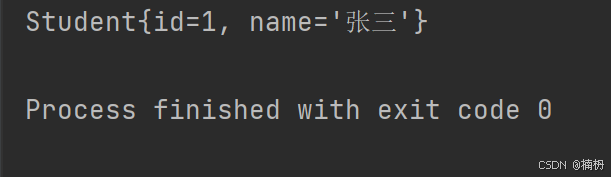
通过 getConstructor 获取公有的无参构造方法:
// 反射公有构造方法 public static void reflectPublicConstructor() { Class studentClass = null; try { studentClass = Class.forName(\"Student\"); // 公有构造方法 Constructor constructor = studentClass.getConstructor(); // 创建对象 Student student = (Student) constructor.newInstance(); System.out.println(student); } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } catch (NoSuchMethodException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } catch (InvocationTargetException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } catch (InstantiationException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } catch (IllegalAccessException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } } public static void main(String[] args) { reflectPublicConstructor(); }运行结果:
接下来,我们反射私有的构造方法:
使用 getDeclaredConstructor 可以获得该类中与参数类型匹配的构造方法(包括私有的)
私有的构造方法中带有两个参数 id 和 name,在获取时,需要传递参数类型
// 反射私有构造方法 public static void reflectPrivateConstructor() { Class studentClass = null; try { studentClass = Class.forName(\"Student\"); // 私有构造方法 Constructor constructor = studentClass.getDeclaredConstructor(int.class, String.class); // 创建对象 Student student = (Student) constructor.newInstance(2, \"李四\"); System.out.println(student); } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } catch (NoSuchMethodException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } catch (InvocationTargetException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } catch (InstantiationException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } catch (IllegalAccessException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } } public static void main(String[] args) { reflectPrivateConstructor(); }运行结果:
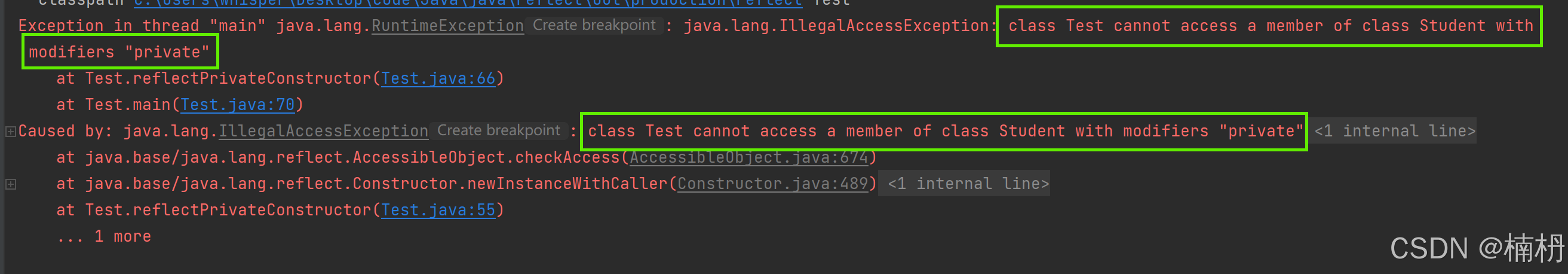
此时程序抛出了 IllegalAccessException 异常,为什么呢?
这是因为,在默认情况下,Java的访问控制机制会阻止对私有成员的直接访问,若想要访问私有字段和方法,需要使用 setAccessible(true) 进行设置 ,确认允许在运行时修改和访问私有成员
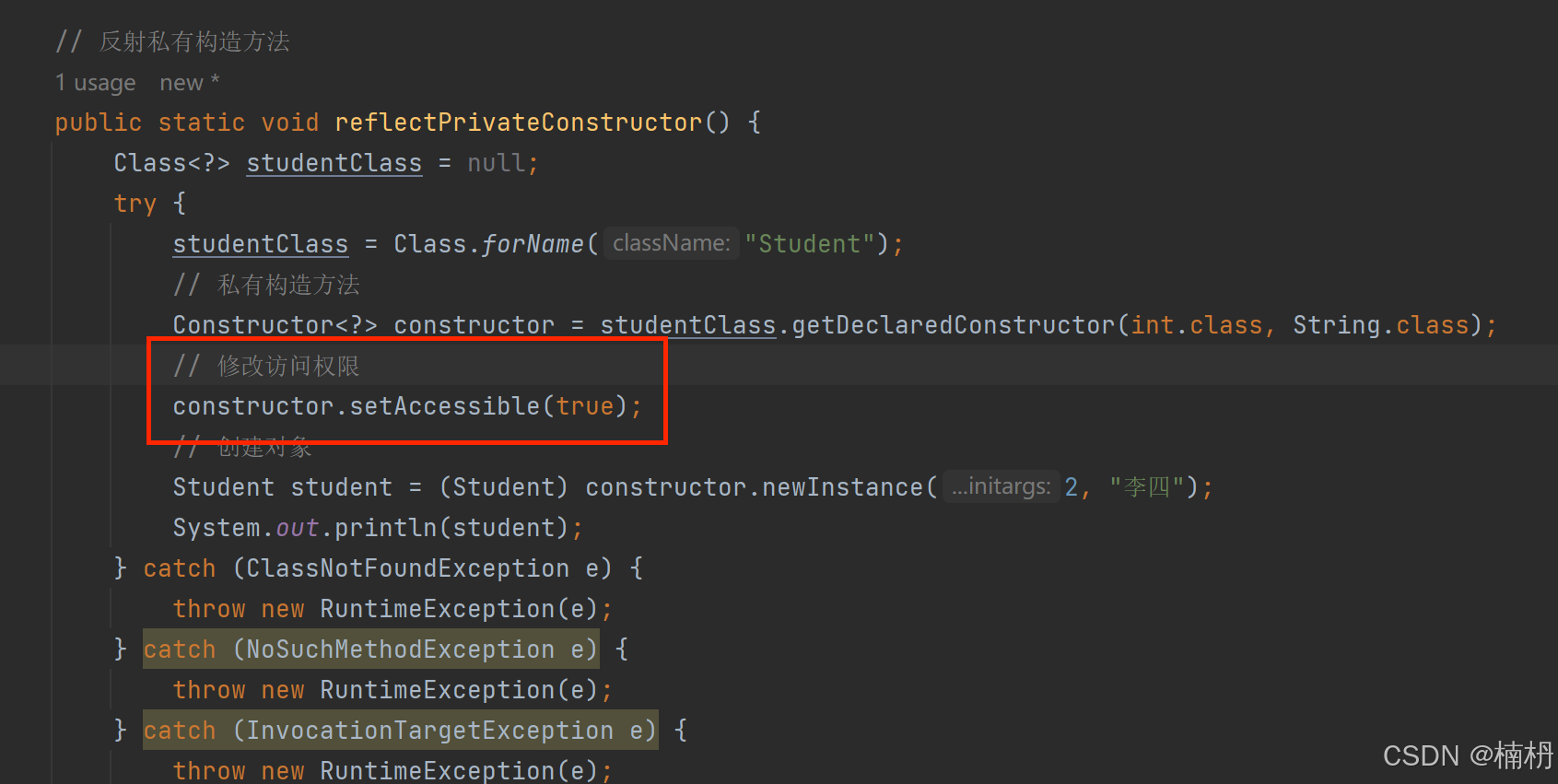
再次运行:
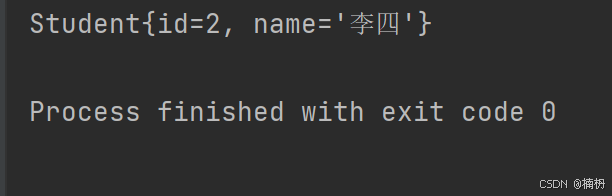
成功使用私有构造方法创建出 Student 对象
反射属性
Class 类中获取类属性相关方法:
Field getField(String name)
Field[] getFields()
Field getDeclaredField(String name)
Field[] getDeclaredFields()
使用 getField(String name) 方法可以获得对象的公有属性对象,而使用 getDeclaredField(String name) 可以获得对象任意权限的属性对象(包括私有的)
我们使用 getDeclaredField(String name) 来获取 Student 的私有属性 id 并使用 Field 类中的 set 方法对其进行修改:
// 反射属性 public static void reflectField() { Class studentClass = null; try { studentClass = Class.forName(\"Student\"); // 获取私有属性 Field field = studentClass.getDeclaredField(\"id\"); // 修改访问权限 field.setAccessible(true); Student student = new Student(); // 修改对象的私有属性值 System.out.println(student); field.set(student, 5); System.out.println(student); } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } catch (NoSuchFieldException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } catch (IllegalAccessException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } } public static void main(String[] args) { reflectField(); }同样的,由于要修改私有的属性,因此需要使用 setAccessible(true) 确认允许在运行时修改和访问私有属性
反射方法
Class 类中获取类方法相关方法:
Method getMethod(String name, Class... parameterTypes)
Method[] getMethods()
Method getDeclaredMethod(String name, Class... parameterTypes)
Method[] getDeclaredMethods()
在获取类的方法时,需要传入方法的名称 以及 方法的参数类型
使用 getDeclaredMethod 方法获取私有方法,并使用 Mehod 类中的 invoke 方法调用私有方法:
// 反射方法 public static void reflectMethod() { Class studentClass = null; try { studentClass = Class.forName(\"Student\"); // 获取私有方法 Method method = studentClass.getDeclaredMethod(\"method2\", int.class, int.class); // 修改访问权限 method.setAccessible(true); Student student = new Student(); // 调用私有方法 System.out.println(method.invoke(student, 2, 3)); } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } catch (NoSuchMethodException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } catch (InvocationTargetException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } catch (IllegalAccessException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } } public static void main(String[] args) { reflectMethod(); }运行结果:
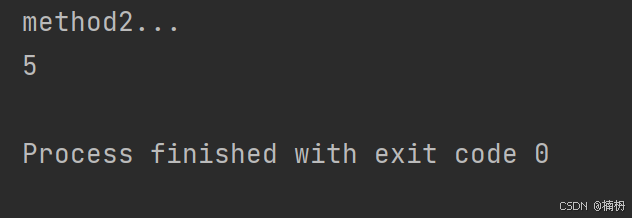
反射的优缺点
优点:
(1)对于任意一个类,都能够知道这个类的所有属性和方法;对于任意一个对象,都能调用它的所有方法和属性
(2)增加了程序的灵活性和扩展性,降低了耦合性,提高自适应能力
(3)许多Java框架(如Spring、Hibernate)利用反射来实现依赖注入、对象关系映射等功能
缺点:
(1)反射操作相比于直接的方法调用和字段访问,速度较慢,因为它涉及到动态查找
(2)反射可以访问和修改私有成员,可能会导致安全隐患,破坏封装性
(3)使用反射的代码通常不如直接代码易读,增加了理解和维护的难度
(4)反射绕过了编译时类型检查,可能导致运行时错误,降低了程序的安全性


