【文献阅读】使用多FPGA进行验证_芯片仿真中用的emulation是什么?
Farooq, U., Mehrez, H. Pre-Silicon Verification Using Multi-FPGA Platforms: A Review. J Electron Test 37, 7–24 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10836-021-05929-1
文献链接:
Pre-Silicon Verification Using Multi-FPGA Platforms: A Review | Journal of Electronic Testing
(半自我理解表述,欢迎交流)
楔子:
全文先介绍了四种主流验证方式,然后针对复杂系统单一FPGA不够的问题,进行多FPGA验证介绍。
四种方式有基于软件的解决方案,也有使用硬件或硬件/软件集成技术进行流片前验证。
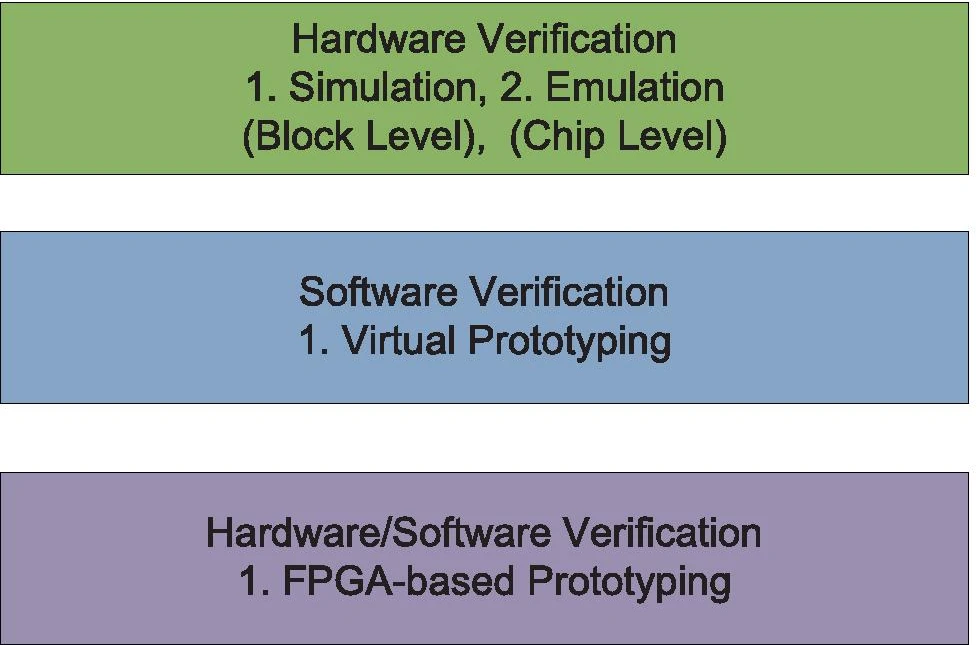
(文献原图)
先解释以下simulation和emulation的区别,模拟(simulation)是对设计方案结果的替代,仿真(emulation)是对设计方案全部的替代。就像图中说的一个是模块级,一个是芯片级。
(我暂时以模拟代表simulation,仿真代表emulation,可能没那么准确)
具体可参考这篇文章,我觉得写的挺明白的:
分不清simulation和emulation?快来围观此文 - small5的日志 - EETOP 创芯网论坛 (原名:电子顶级开发网) -
4种验证方式
模拟(simulation)
跑在PC机上,软件仿真(上图写hardware是指验证硬件设计的功能,不是用硬件去验证),模块化验证,启动时间短(我觉得是相对于连接硬件进行数据传输,毕竟纯软件工具会优化吧),扩展性强(改起来方便?最早的验证?),比较便宜(这还挺重要的),对代码进行功能和事务验证。
工具有ModelSim,VCS等。速度慢慢的。
仿真(emulation)
(我觉得原文很好)
In simulation, the digital systems are modeled in a virtual environment through variables and configurations. However, in emulation, the digital systems are completely imitated where an emulator tries to mimic all the hardware features of the design under test. Emulation is just done in the virtual environment rather than real world. Contrary to simulators where the design is verified in isolation, emulators are used to perform full chip verification.
这一段其实就是simulation和emulation的区别,看上边的科普链接就行。
搜了一下,emulator 总结 - 知乎这篇文章提到了一些,我作为补充吧:
Emulator是软件仿真的硬件化,但还不是真实的硬件,是个虚拟的世界。 它通过厂商定制化的流程,将rtl映射到各自的硬件仿真平台上,可以像软件仿真一样dump全部的波形,dump的波形是fsdb格式直接可以用verdi打开查看。 由于是映射到专门的硬件上,所以速度比软件仿真快很多。
Emulartor是介于软件仿真和FPGA原型验证之间的,具有二者的有点,速度快,方便调试;
Emulator本质上是通过处理器集群来加速验证任务,并不是实际的电路,在于外设协调时,需要用速度适配器来进行转换,这也是为什么FPGA上的问题emulator有时候不能复现。
回到文献:
与simulation相比用emulation做验证的优势:
- 与只能模块化验证的模拟器相反,仿真器用于执行完整的芯片验证。
- 执行速度更高(高达 5 MHz)
缺点:贵
(具体的平台我没接触过,就不展开了)
虚拟原型(Virtual Prototyping)
简单来说,就相当于,我开发了一款app,同时团队在设计新的硬件系统,我的app要支持新的硬件平台,一般来说要等团队开发完,但是我等不及了,于是先搞了个虚拟机(相当于硬件系统的目标),在虚拟机上先验证app的移植性。
虚拟原型验证技术允许硬件和软件的共同开发和验证,用于验证 SoC 和 ASIC 的全功能模型以及虚拟化 I/O 和接口,加快最终产品的推出时间。
基于FPGA的原型(FPGA-Based Prototyping)
直接运行在FPGA上,电路实现和设计的不同,但功能一样,且走的是硬件流。可以使用真实的外部接口执行速度远远优于第一第二种。和emulator比,面积更小。FPGA 使用真实接口几乎实时运行SoC设计。
缺点:可见性差(毕竟走的硬件,内部逻辑已经封装起来了),不那么贵但也不便宜。
基于 FPGA 的原型设计需要硬件和软件方面的专业知识,以便将 RTL 实现到 FPGA。
这方面工具不仅要FPGA板,还要有转化的解决方案(会依赖于FPGA板型号)
总体对比
Technique
Setup time
Cost
Execution Speed
Footprint
(面积)
Simulation
Very small
A few thousand dollars
Up to a few KHz
No
Emulation
Moderate
Up to a few million dollars
Up to a few MHz
Medium to large
Virtual Prototyping
Small
Up to a few thousand dollars
Up to a few KHz
Small
FPGA-based prototyping
Moderate to long
Up to a few thousand dollars
Up to a dozen MHz
Small
(文献原表)
多FPGA平台
因为单PFGA无法满足现代SoC设计的逻辑要求,于是采用多FPGA平台。
主要是以下三种(系统翻译,我也不太确定,所以附上英文)
1) 硬连线现成多FPGA平台(Hardwired off-the-shelf multi-FPGA platform)
2) 硬连线定制多 FPGA 平台(Hardwired custom multi-FPGA platform)
3) 布线多 FPGA 平台(Cabling multi-FPGA platform)
是什么我这里就不展开了,感觉就是字面意思,第三个cabling就是通过电缆和连接器将FPGA板相互连接,从硬件角度再深我也没懂【狗头】。
Platform Type
Availability
Data Rate
Track Distribution
Flexibility
Price
Performance
Hardwired off-the-shelf
Immediate
High
Generic
Medium
Low
Low
Hardwired custom
6-8 months
High
Custom
Low
High
High
Cabling
2-4 months
High
Custom
High
Meidum
Medium
(文献原表)
多FPGA的后端流程(Back End)
关键都是综合(Synthesis)、分区(Partitioning)、FPGA 间路由( inter-FPGA routing)、FPGA 内部布局和布线(Intra-FPGA Placement and Routing)
综合将设计的 RTL 描述被转换为 netlist(使用特定工具,商业的针对自家产品,自研的效果没那么好)
分区,根据每个FPGA能力来划分设计,找到最优分区是一个NP难问题。文献里介绍了3种前人的方法,具体的不在这展开了(我看的晕乎乎的,给人一种分布式操作系统的考量),有商用工具,但这方面好像还比较欠缺。这一部分很重要也很具有挑战性。
Reference
Provider
Nature
Remarks
[29] HAPS
Synopsys
Platform dependent
It is a commercial tool that gives complete back end flow. Partitioning is only a part of the flow that works for HAPS specific platform.
[6] AUSPY
Mentor Graphics
Generic
It is a commercial tool. It is generic in nature and can be used for any FPGA board.
[24] WASGA
Mentor Graphics
Generic
It is a commercial tool (previously a start-up, now part of Mentor Graphics). It is generic in nature and can be used for any FPGA board.
[12] Protium
Cadence
Platform dependent
It is a commercial tool that gives complete back end flow. Partitioning is only a part of the flow that works for Protium specific platform.
[14] CERTIFY
Syopsys
Generic
It was a commercial tool provided by Synopsys. It was generic. However, it was discontinued in 2017.
[50] Zied et al.
Academic Tool
Generic
An academic tool used for hierarchical FPGAs. Can handle only homogeneous blocks. Not used for multiple FPGAs.
[71] Turki et al.
Academic Work
N/A
This work compares only existing commercial tools. They do not provide a solution of their own.
(文献原表,分区工具对比)
分区步骤之后是FPGA间布线。如上所述,partitioning 步骤尝试最小化遍历不同 partitions 的 cut-net 的数量。然而,这些 cut-nets 比多 FPGA 板上 FPGAs 的可用 I/O 要多得多。因此,这些切割网络必须使用互斥的时分复用(TDM)技术在 FPGA 间轨道上布线。如果直接连线不适用于一组 cut-nets,则cut-nets可能会通过中间 FPGAs进行找路(route)。每个中间FPGA在inter-FPGA routing中称为一个跃点。hops的使用也会影响 design 的执行速度。inter-FPGA routing 工具的主要目标是最小化mux ratio(复用率)以及routing hops的数量。
Reference
Provider
Nature
Remarks
[29] HAPS
Synopsys
Platform dependent
It is a commercial tool that gives complete back end flow. Inter-FPGA routing is only a part of the flow that works for HAPS specific platform.
[12] Protium
Cadence
Platform dependent
It is a commercial tool that gives complete back end flow. Inter-FPGA routing is only a part of the flow that works for Protium specific platform.
[19] Farooq et al.
Academic Solution
Generic
Uses hybrid routing approach to explore the effect of combination of two point and multi point tracks on the routing results.
[68] Qingshan et al.
Academic Solution
Generic
Uses Patfinder [52] algorithm to find conflict free solution for inter-FPGA routing. Applicable to FPGA boards with both two and multi point tracks.
[37] Takashima et al.
Academic Solution
Generic
Uses integer linear programming to give solution for simple routing problems.
[32] Hauck et al.
Academic Solution
Generic
Uses congestion avoidance approach to find conflict-free solution for inter-FPGA routing.
[70] Turki et al.
Academic Solution
Generic
Uses Patfinder [52] algorithm to find conflict free solution for inter-FPGA routing. Applicable to FPGA boards with two point tracks only.
(文献原表,不展开了)
FPGA 内部布局和布线,终于见到熟悉的vivado,谁懂这种救赎感。
三种平台,从左至右:现成、定制、连线
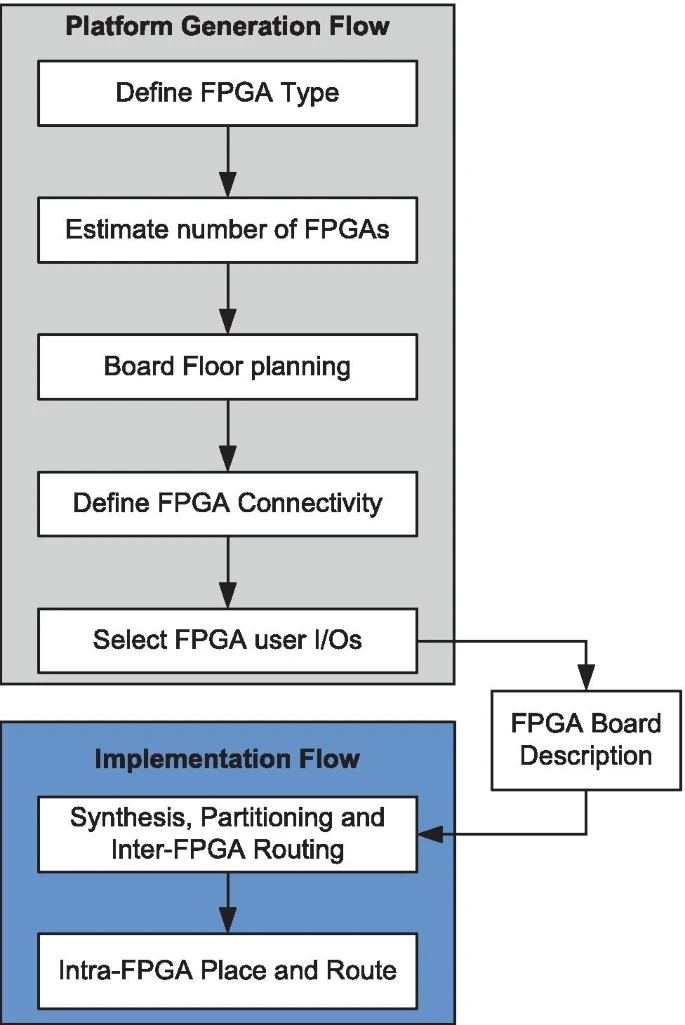
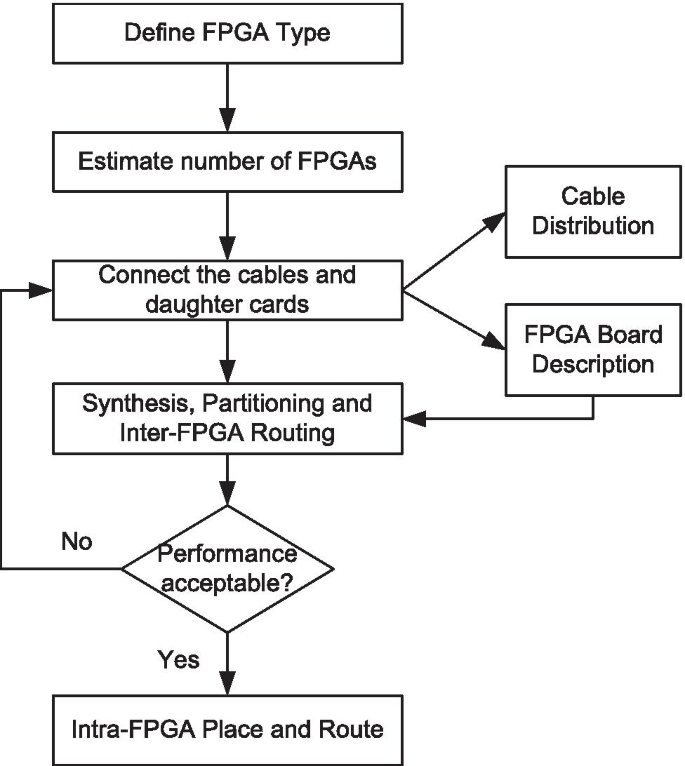
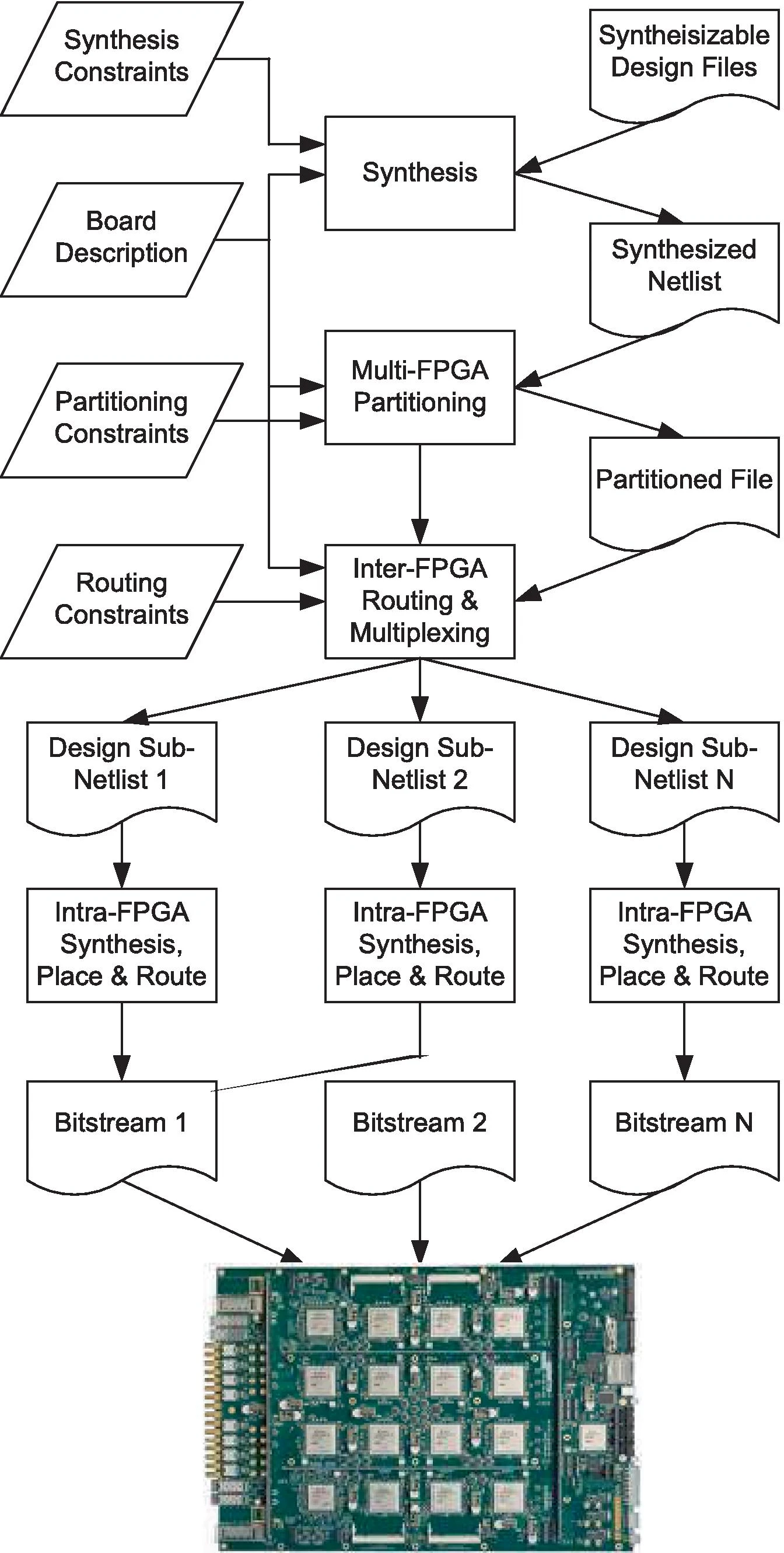
(文献原图)
总结
回顾三种多FPGA平台,现成的平台容易获得,但是,与定制和布线多FPGA平台相比,它的性能较差。定制多FPGA平台具有非常好的性能,但是,自动设计流程的不可用阻碍了它们在上市时间较短的情况下的使用。就布线平台而言,它是相对较新的,如果我们从可用性和性能的角度来看,它介于现成和定制的多 FPGA 平台之间。与现成平台相比,布线平台性能更好但可用性差,与定制平台相比,它的可用性更好但性能较差。除了多 FPGA 平台的各种优势外,它们还面临着许多挑战,例如非标准化设计流程、增加逻辑与 I/O 比率、缺乏标准基准和比较指标等。(原文翻译)


