Spring Boot 整合 MyBatis 与 Druid 数据源全流程
引言:为什么选择 Spring Boot+MyBatis+Druid?
在现代 Java 开发中,Spring Boot 以其 \"约定大于配置\" 的理念简化了项目搭建,MyBatis 作为轻量级 ORM 框架灵活处理数据库交互,而 Druid 作为高性能数据源提供了完善的监控和连接池管理能力。三者结合既能享受 Spring Boot 的自动配置便利,又能通过 MyBatis 灵活操作数据库,同时借助 Druid 保障数据访问的稳定性与可监控性。
一、项目初始化与依赖配置
1.1 项目结构设计
首先明确项目目录结构,遵循 Spring Boot 与 MyBatis 的最佳实践:
src/├── main/│ ├── java/com/qcby/springbootmybatis/│ │ ├── config/ # 配置类(Druid、MyBatis等)│ │ ├── entity/ # 实体类(与数据库表映射)│ │ ├── mapper/ # MyBatis映射接口│ │ └── SpringbootMybatisApplication.java # 启动类│ ├── resources/│ │ ├── application.yaml # 主配置文件│ │ ├── mybatis/│ │ │ ├── sqlMapConfig.xml # MyBatis核心配置│ │ │ └── mapper/ # MyBatis映射文件目录│ │ └── static/ # 静态资源(可选)└── test/# 单元测试目录1.2 核心依赖配置(pom.xml)
Spring Boot 项目的依赖管理通过pom.xml实现,需引入以下关键依赖:
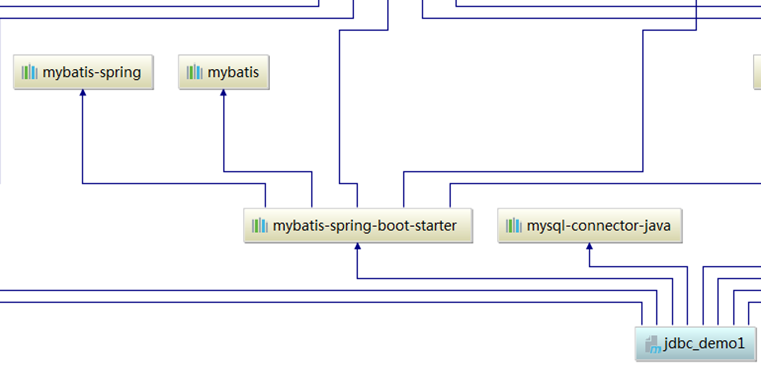
org.springframework.boot spring-boot-starter-parent 2.7.18 org.springframework.boot spring-boot-starter-web org.mybatis.spring.boot mybatis-spring-boot-starter 1.3.1 com.alibaba druid 1.2.20 mysql mysql-connector-java runtime org.springframework.boot spring-boot-starter-test test 依赖说明:
spring-boot-starter-web:提供 Spring MVC 与 Web 容器支持;mybatis-spring-boot-starter:实现 MyBatis 与 Spring Boot 的自动整合;druid:阿里巴巴开源数据源,支持连接池、监控等高级功能;mysql-connector-java:MySQL 数据库驱动,注意与数据库版本匹配(8.x 需用com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver)。
二、数据源配置:Druid 深度整合
2.1 Druid 数据源配置类
Druid 需要手动配置才能启用其监控、连接池等功能,创建DruidConfig.java:
package com.qcby.springbootmybatis.config;import com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource;import com.alibaba.druid.support.http.StatViewServlet;import com.alibaba.druid.support.http.WebStatFilter;import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;import org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.FilterRegistrationBean;import org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.ServletRegistrationBean;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;import javax.sql.DataSource;import java.util.HashMap;import java.util.Map;@Configurationpublic class DruidConfig { // 绑定配置文件中的数据源属性 @Bean @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = \"spring.datasource\") public DataSource dataSource() { return new DruidDataSource(); } // 配置Druid监控Servlet @Bean public ServletRegistrationBean statViewServlet() { ServletRegistrationBean bean = new ServletRegistrationBean(new StatViewServlet(), \"/druid/*\"); // 监控页登录配置 Map initParams = new HashMap(); initParams.put(\"loginUsername\", \"root\"); // 监控页登录账号 initParams.put(\"loginPassword\", \"root\"); // 监控页登录密码 initParams.put(\"allow\", \"\"); // 允许所有IP访问(生产环境需限制IP) initParams.put(\"deny\", \"192.168.43.195\"); // 禁止该IP访问 bean.setInitParameters(initParams); return bean; } // 配置Druid监控过滤器 @Bean public FilterRegistrationBean webStatFilter() { FilterRegistrationBean bean = new FilterRegistrationBean(new WebStatFilter()); // 过滤规则:排除静态资源与监控页 Map initParams = new HashMap(); initParams.put(\"exclusions\", \"*.js,*.css,/druid/*\"); bean.setInitParameters(initParams); bean.setUrlPatterns(Arrays.asList(\"/*\")); // 监控所有请求 return bean; }}核心功能:
- 通过
@ConfigurationProperties绑定配置文件中的 Druid 属性; - 注册
StatViewServlet:提供/druid路径的监控页面,支持登录验证、IP 黑白名单; - 注册
WebStatFilter:监控所有请求,排除静态资源与监控页自身请求。
把 DruidDataSource 实例注册成 Spring 应用上下文中的一个 Bean,这样一来,其他组件就能够通过依赖注入的方式获取这个数据源,进而进行数据库操作。
依赖注入:
传统的方式是在对象内部创建依赖对象,而依赖注入则是将依赖对象的创建和管理交给外部容器,由容器将依赖对象注入到需要的对象中。常用的依赖注入的方式有构造函数的方法和通过setter方法注入,这里明显使用的是构造函数的方法注入依赖。
在配置类这里配置更灵活(在yml文件里配了为什么还要在配置类配置)。
2.2 数据源配置文件(application.yaml)
在application.yaml中配置 Druid 数据源参数与 MyBatis 路径:
不同的数据库有不同的驱动程序,每个驱动程序都有对应的类名,而 driver-class-name 就是用来指定使用哪个数据库驱动类的。
如果Hikari可用, Springboot将使用它。
如果Commons DBCP2可用, 我们将使用它。
三种数据库,dbcp,hikari(默认的),druid,任选其一即可。
我们可以自己指定数据源配置,通过type来选取使用哪种数据源(数据库连接池)
spring: datasource: username: root # 数据库用户名 password: root # 数据库密码 # MySQL连接地址(适配8.x版本,指定时区) url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/boot_demo?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver # 8.x驱动类 type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource # 指定Druid数据源 # Druid连接池参数 initialSize: 5 # 初始化连接数 minIdle: 5 # 最小空闲连接数 maxActive: 20 # 最大活跃连接数 maxWait: 60000 # 获取连接的最大等待时间(毫秒) timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis: 60000 # 连接检测间隔(毫秒) minEvictableIdleTimeMillis: 300000 # 连接最小空闲时间(毫秒) validationQuery: SELECT 1 FROM DUAL # 连接校验SQL testWhileIdle: true # 空闲时检测连接有效性 testOnBorrow: false # 借出连接时不检测(提升性能) testOnReturn: false # 归还连接时不检测(提升性能) # Druid监控参数 filters: stat,wall,slf4j # 启用监控、防火墙、日志 connectionProperties: druid.stat.mergeSql=true;druid.stat.slowSqlMillis=500 # 慢SQL阈值(500ms)# MyBatis配置mybatis: config-location: classpath:mybatis/sqlMapConfig.xml # 核心配置文件路径 mapper-locations: classpath:mybatis/mapper/*.xml # 映射文件路径 type-aliases-package: com.qcby.springbootmybatis.entity # 实体类别名包关键配置说明:
driver-class-name:MySQL 8.x 需使用com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver,并指定serverTimezone;filters: stat,wall:启用 SQL 监控(stat)和防火墙(wall),防止 SQL 注入;slowSqlMillis=500:慢 SQL 阈值,超过 500ms 的 SQL 会被标记为慢查询。- initialSize: 5: 该配置指定了连接池在初始化时创建的连接数量。设置为 5 意味着在应用启动时,Druid 连接池会创建 5 个数据库连接并放入连接池中。
- minIdle: 5:它表示连接池保持的最小空闲连接数。即使在没有数据库操作时,连接池也会确保至少有 5 个连接处于空闲状态,这样可以避免在有新的数据库请求时频繁创建连接,提高响应速度。
- maxActive: 20:此配置定义了连接池允许的最大活动连接数。当有数据库请求时,连接池最多可以同时提供 20 个连接给应用程序使用。如果达到这个上限,新的请求将等待,直到有连接被释放。
- maxWait: 60000:单位为毫秒,指的是当连接池中的连接都被占用时,新的请求等待获取连接的最大时间。这里设置为 60000 毫秒(即 60 秒),如果在 60 秒内没有可用连接,请求将抛出异常。
- timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis: 60000:单位为毫秒,它表示连接池进行空闲连接检查的时间间隔。每隔 60000 毫秒(即 60 秒),连接池会执行一次空闲连接的检查操作。
- minEvictableIdleTimeMillis: 300000:单位为毫秒,该配置规定了连接在连接池中保持空闲状态的最小时间,超过这个时间的空闲连接可能会被移除。这里设置为 300000 毫秒(即 5 分钟),意味着空闲时间超过 5 分钟的连接可能会被清理。
- validationQuery: SELECT 1 FROM DUAL:这是一个用于验证连接是否有效的 SQL 查询语句。对于不同的数据库,该语句可能不同,例如在 MySQL 中可以使用 SELECT 1。连接池会执行这个查询来检查连接是否正常。
- testWhileIdle: true:当设置为 true 时,连接池在进行空闲连接检查时,会使用 validationQuery 来验证连接的有效性。如果连接无效,会将其从连接池中移除。
- testOnBorrow: false:若设置为 true,在从连接池获取连接时,会先使用 validationQuery 验证连接的有效性,确保获取到的连接是可用的。这里设置为 false,表示不进行此验证。
- testOnReturn: false:当设置为 true 时,在将连接归还到连接池时,会使用 validationQuery 验证连接的有效性。这里设置为 false,表示不进行此验证。
- poolPreparedStatements: true:当设置为 true 时,连接池会开启预编译语句缓存功能,这样可以提高预编译语句的执行效率,避免重复编译相同的 SQL 语句。
- maxPoolPreparedStatementPerConnectionSize: 20:该配置指定了每个连接最多可以缓存的预编译语句数量。这里设置为 20,表示每个连接最多可以缓存 20 条预编译语句。
- filters: stat,wall,log4j:此配置指定了连接池使用的过滤器。stat 过滤器用于统计 SQL 执行的性能信息,wall 过滤器用于防止 SQL 注入攻击,log4j 过滤器用于将相关信息记录到日志中。
- useGlobalDataSourceStat: true:当设置为 true 时,会使用全局的数据源统计信息,方便对整个应用的数据库连接和 SQL 执行情况进行统一监控。
- connectionProperties: druid.stat.mergeSql=true;druid.stat.slowSqlMillis=500:druid.stat.mergeSql=true 表示合并相同的 SQL 语句进行统计,这样可以减少统计数据的数量,提高统计效率。
- druid.stat.slowSqlMillis=500 表示将执行时间超过 500 毫秒的 SQL 语句标记为慢 SQL,并记录相关信息,方便后续进行性能优化。
在默认情况下, 数据库连接可以使用DataSource池进行自动配置
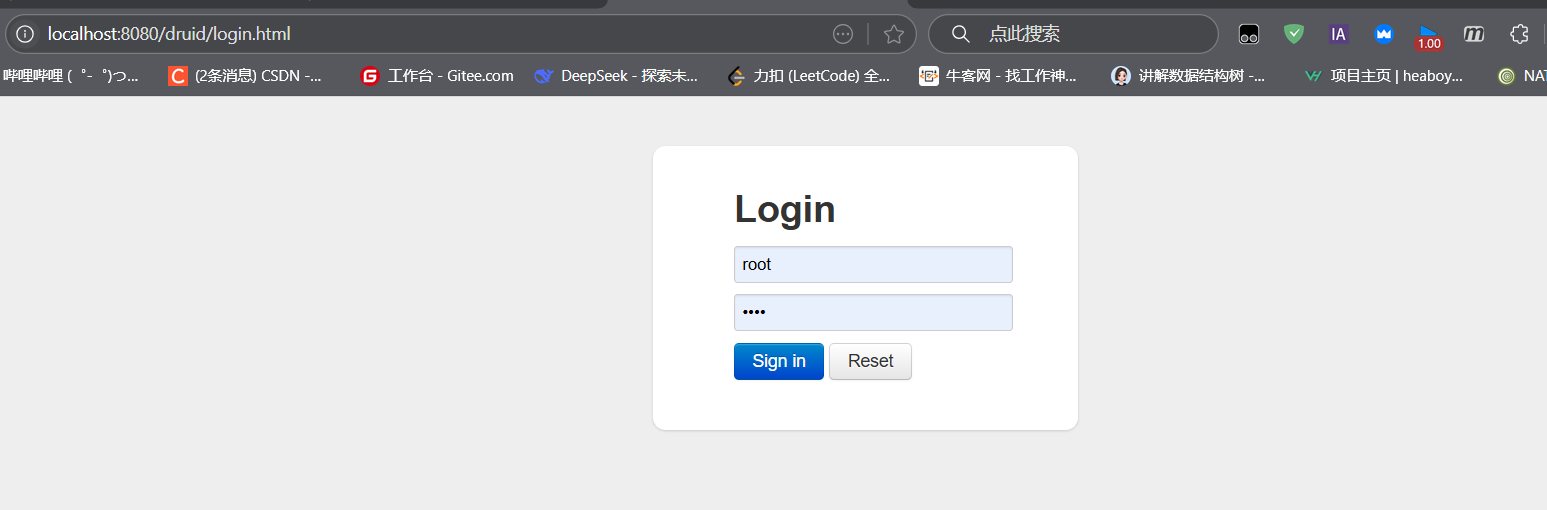
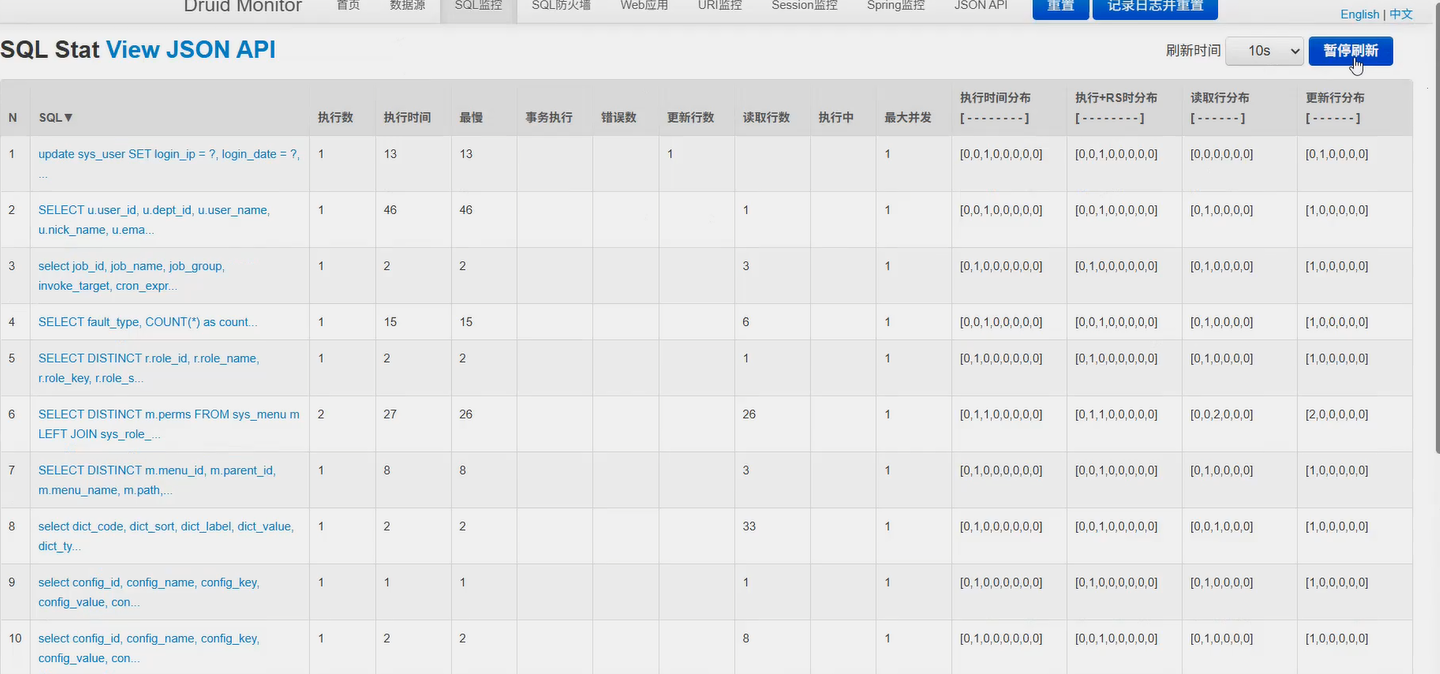
打开监控页面
http://localhost:8080/druid
三、 SpringBoot整合jdbcTemplate
什么是 JdbcTemplate
JdbcTemplate 是 Spring 框架提供的一个核心类,它对 JDBC 进行了封装,简化了 Java 代码与数据库的交互过程。作为 Spring 生态的一部分,JdbcTemplate 与 Spring Boot 有着天然的整合优势,能够帮助开发者快速实现数据库操作。
JdbcTemplate 的特点
-
速度快:相对于 ORM 框架,基于 JDBC 的方式性能更优,减少了对象映射的开销
-
配置简单:Spring 封装的模板类,除了数据库连接之外,几乎没有额外的配置
-
使用方便:类似 DBUtils 工具类,只需注入 JdbcTemplate 对象即可快速使用
-
功能强大:提供了丰富、实用的方法,主要分为以下几类:
- execute 方法:可执行任何 SQL 语句,一般用于执行 DDL 语句
- update、batchUpdate 方法:用于执行新增、修改与删除等语句
- query 和 queryForXXX 方法:用于执行查询相关的语句
- call 方法:用于执行数据库存储过程和函数相关的语句
总的来说,新增、删除与修改操作主要使用 update 和 batchUpdate 方法;查询功能主要通过 query 和 queryForObject 方法完成;execute 方法可执行任意 SQL;call 方法用于调用存储过程。
Spring Boot 整合 JdbcTemplate 实战
3.1 数据库表设计
首先在数据库中创建所需的数据表,这里以tx_user表为例:
SET FOREIGN_KEY_CHECKS=0;-- ------------------------------ Table structure for tx_user-- ----------------------------DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `tx_user`;CREATE TABLE `tx_user` ( `username` varchar(10) DEFAULT NULL, `userId` int(10) NOT NULL, `password` varchar(10) DEFAULT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`userId`)) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;可以插入一些测试数据:
INSERT INTO `tx_user` VALUES (\'张三\', 1, \'123456\');INSERT INTO `tx_user` VALUES (\'李四\', 2, \'654321\');3.2 项目依赖配置
在 Spring Boot 项目的pom.xml中添加必要的依赖:
org.springframework.boot spring-boot-starter-parent 3.2.8 org.springframework.boot spring-boot-starter-web org.springframework.boot spring-boot-starter-jdbc com.mysql mysql-connector-j runtime org.springframework.boot spring-boot-starter-test test
3.3 数据源配置
在application.yaml(或application.properties)中配置数据库连接信息:
spring: datasource: driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/your_database_name?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai username: root password: your_password3.4 创建 Controller 实现数据库操作
创建一个 Controller 类,注入 JdbcTemplate 并实现基本的查询功能:
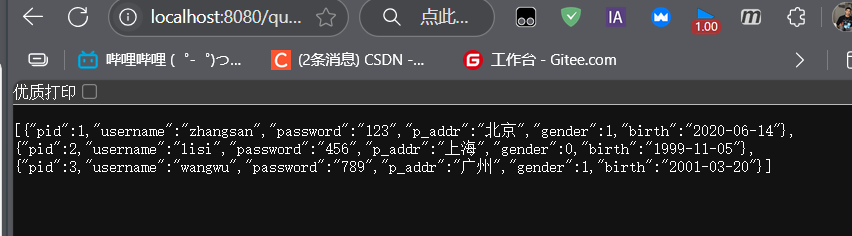
package com.qcby.springbootmybatis.controller;import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;import java.util.List;import java.util.Map;@Controllerpublic class TestController { @Autowired JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate; @ResponseBody @RequestMapping(\"/query\") public List<Map> query(){ List<Map> maps = jdbcTemplate.queryForList(\"SELECT * FROM tx_user\"); return maps; }}启动springboot访问
http://localhost:8080/query
四、MyBatis 整合MyBatis配置文件
4.1 MyBatis 核心配置
创建 MyBatis 全局配置文件mybatis/sqlMapConfig.xml(可扩展插件、别名等):
4.2 映射文件与接口
MyBatis 支持注解与 XML 两种映射方式,本文采用 \"注解 + XML\" 混合模式:
(1)实体类(TxPerson.java)
package com.qcby.springbootmybatis.entity;import java.util.Date;public class TxPerson { private Integer pid; // 主键(自增) private String pname; // 姓名 private String addr; // 地址 private Integer gender; // 性别(0-女,1-男) private Date birth; // 生日 // Getter、Setter与toString public Integer getPid() { return pid; } public void setPid(Integer pid) { this.pid = pid; } public String getPname() { return pname; } public void setPname(String pname) { this.pname = pname; } public String getAddr() { return addr; } public void setAddr(String addr) { this.addr = addr; } public Integer getGender() { return gender; } public void setGender(Integer gender) { this.gender = gender; } public Date getBirth() { return birth; } public void setBirth(Date birth) { this.birth = birth; } @Override public String toString() { return \"TxPerson{\" + \"pid=\" + pid + \", pname=\'\" + pname + \'\\\'\' + \", addr=\'\" + addr + \'\\\'\' + \", gender=\" + gender + \", birth=\" + birth + \'}\'; }}(2)Mapper 接口(TxPersonMapper.java)
package com.qcby.springbootmybatis.mapper;import com.qcby.springbootmybatis.entity.TxPerson;import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.*;import java.util.List;@Mapper // 标记为MyBatis映射接口public interface TxPersonMapper { // 注解方式:查询单条记录 @Select(\"select * from tx_person where pid = #{id}\") TxPerson getPersonById(Integer id); // XML方式:查询所有记录(映射文件中实现) List getPersons(); // 注解方式:插入记录(自增主键) @Options(useGeneratedKeys = true, keyProperty = \"pid\") // 自动生成主键并回写 @Insert(\"insert into tx_person(pname, addr, gender, birth) values(#{pname}, #{addr}, #{gender}, #{birth})\") void insert(TxPerson person); // 注解方式:删除记录(注意方法名与SQL语义一致,此处update为笔误,实际是delete) @Delete(\"delete from tx_person where pid = #{id}\") void delete(Integer id);}(3)XML 映射文件(MyBatis/Mapper/TxPersonMapper.xml)
select * from tx_person 4.3 MyBatis 配置类(解决驼峰映射)
数据库表字段若为下划线命名(如p_name),实体类为驼峰命名(pname),需配置驼峰映射:
package com.qcby.springbootmybatis.config;import org.mybatis.spring.boot.autoconfigure.ConfigurationCustomizer;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;@Configurationpublic class MyBatisConfig { // 开启MyBatis驼峰命名映射(下划线转驼峰) @Bean public ConfigurationCustomizer configurationCustomizer() { return configuration -> configuration.setMapUnderscoreToCamelCase(true); }}五、单元测试验证
5.1 测试类编写
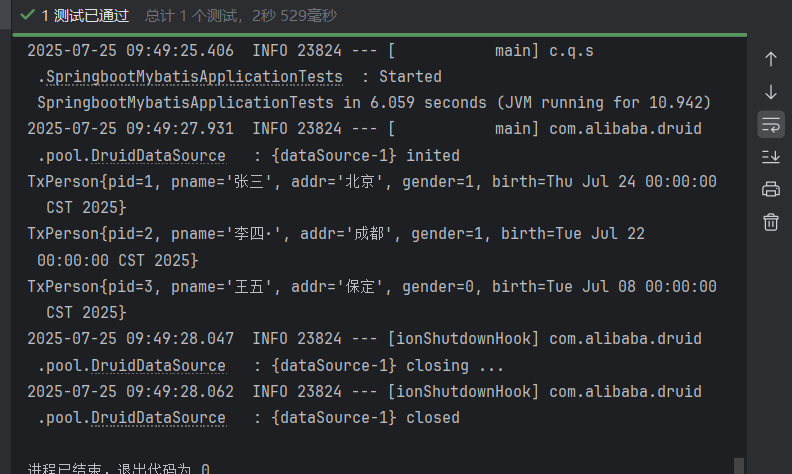
创建SpringbootMybatisApplicationTests.java,验证数据源与 MyBatis 功能:
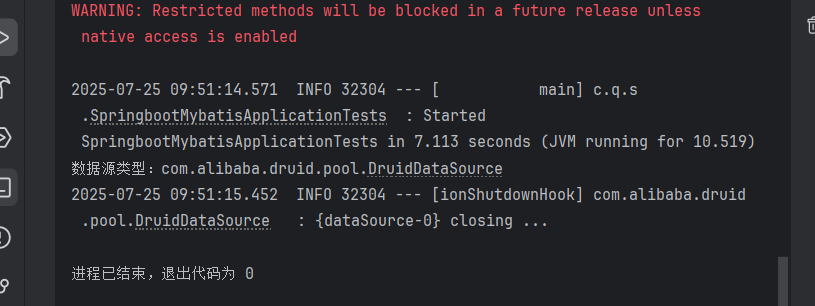
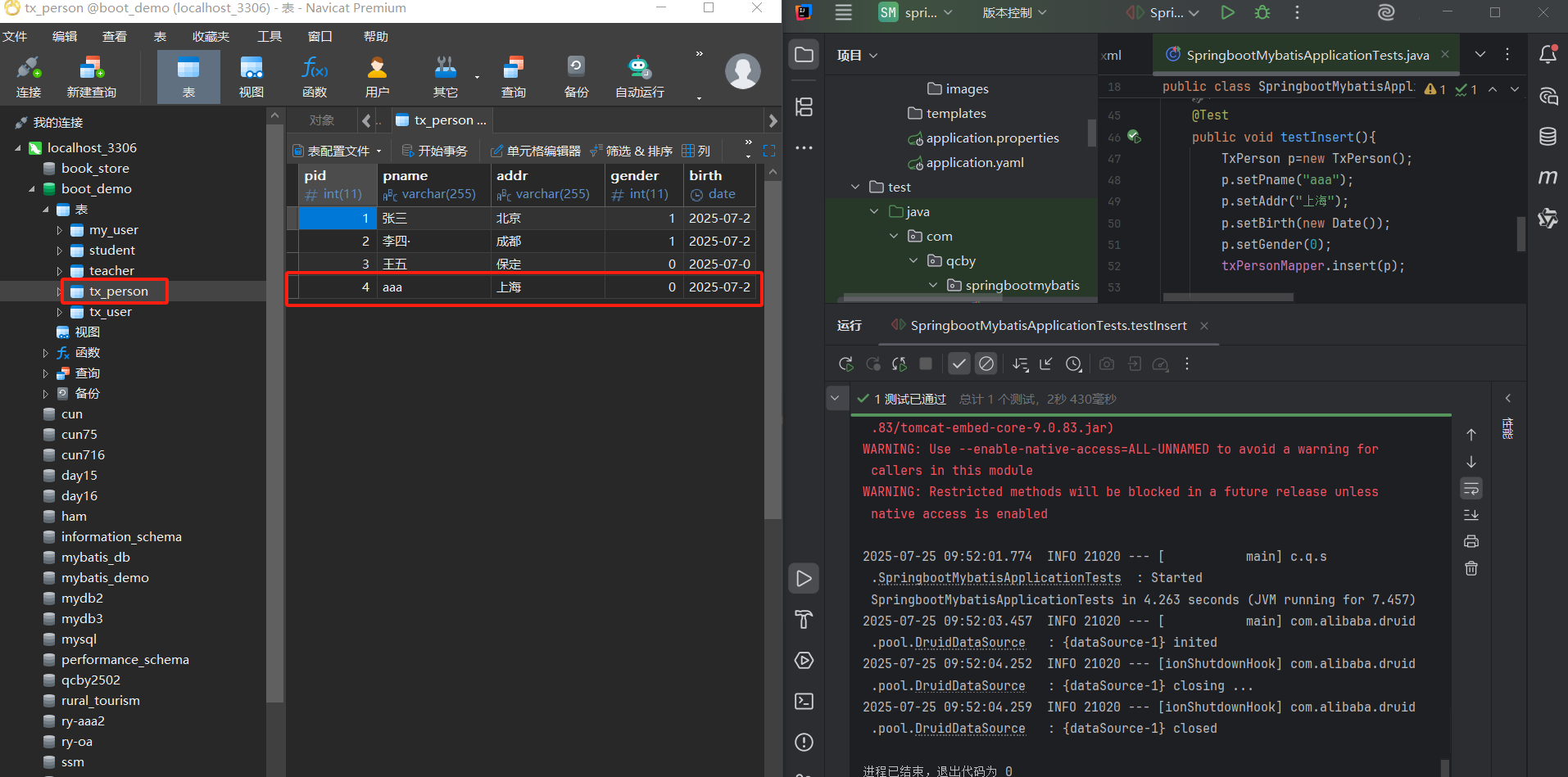
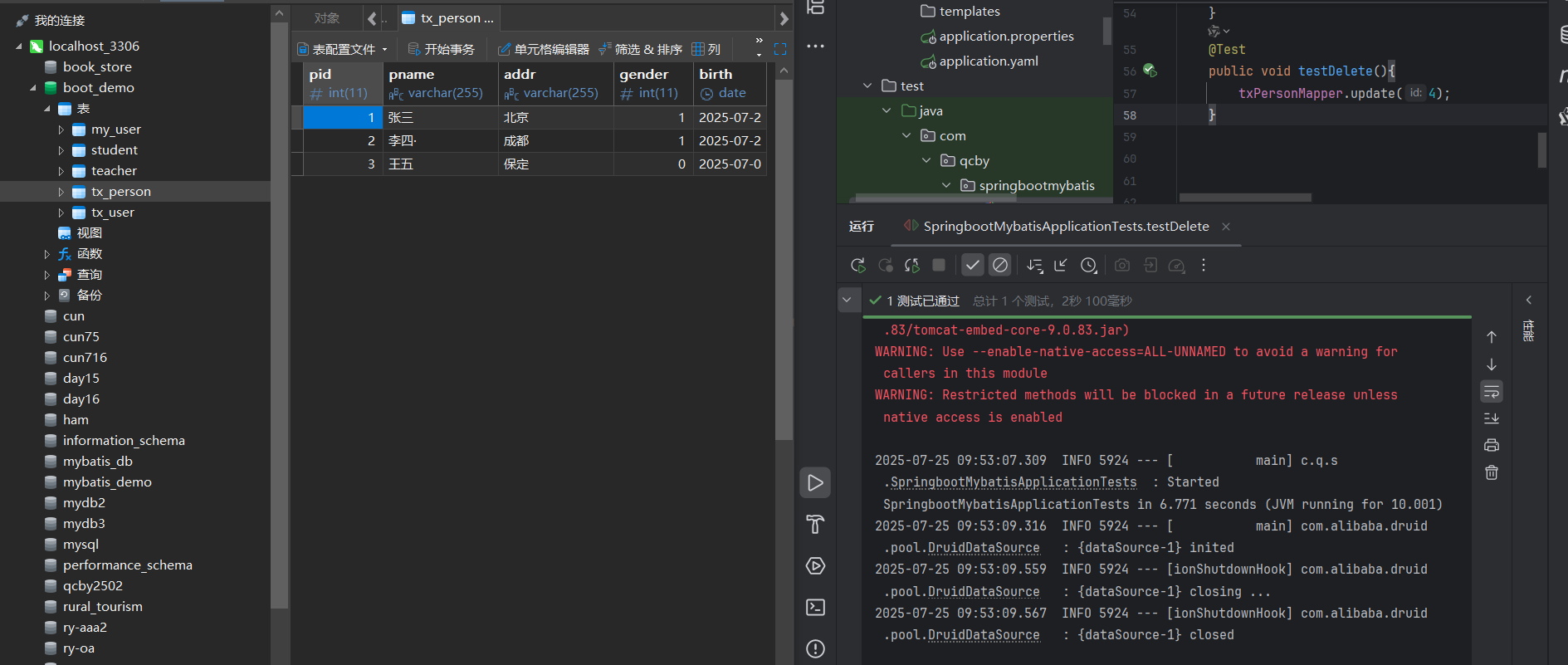
package com.qcby.springbootmybatis;import com.qcby.springbootmybatis.entity.TxPerson;import com.qcby.springbootmybatis.mapper.TxPersonMapper;import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;import javax.sql.DataSource;import java.sql.SQLException;import java.util.Date;import java.util.List;@SpringBootTestpublic class SpringbootMybatisApplicationTests { @Autowired private TxPersonMapper txPersonMapper; @Autowired private DataSource dataSource; // 验证数据源是否正确初始化 @Test public void testDataSource() throws SQLException { System.out.println(\"数据源类型:\" + dataSource.getClass().getName()); // 应输出com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource } // 测试查询单条记录 @Test public void testGetPersonById() { TxPerson person = txPersonMapper.getPersonById(1); // 假设存在ID=1的记录 System.out.println(\"查询结果:\" + person); } // 测试查询所有记录 @Test public void testGetAllPersons() { List persons = txPersonMapper.getPersons(); System.out.println(\"总记录数:\" + persons.size()); persons.forEach(System.out::println); } // 测试插入记录 @Test public void testInsert() { TxPerson person = new TxPerson(); person.setPname(\"测试用户\"); person.setAddr(\"北京\"); person.setGender(1); person.setBirth(new Date()); txPersonMapper.insert(person); System.out.println(\"插入成功,自增ID:\" + person.getPid()); // 验证主键回写 } // 测试删除记录 @Test public void testDelete() { txPersonMapper.delete(5); // 假设存在ID=5的记录 System.out.println(\"删除成功\"); }}5.2 测试结果分析
- 数据源测试:输出
com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource,证明 Druid 已生效; - 查询测试:成功打印数据库中的
TxPerson记录,说明 MyBatis 映射正确; - 插入测试:通过
useGeneratedKeys自动生成主键并回写,验证自增功能; - 删除测试:执行后数据库中对应 ID 的记录被删除,SQL 执行正常。
六、 Springboot整合Mybatis注解版
org.mybatis.spring.boot mybatis-spring-boot-starter 1.3.16.1 配置数据源相关属性
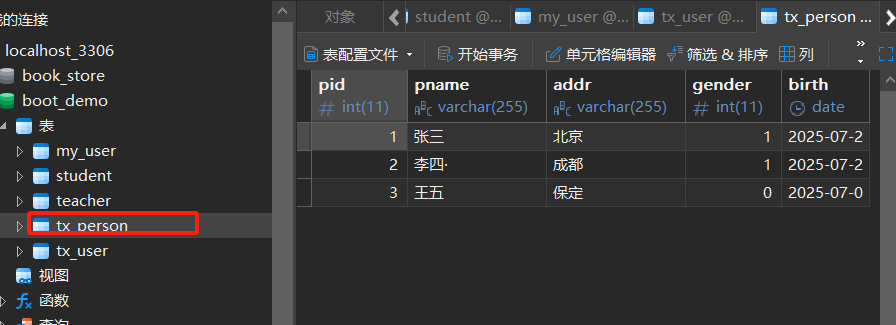
6.2 给数据库建表
6.3 创建javabean
package com.qcby.entity;import java.util.Date; public class TxPerson { private int pid; private String pname; private String addr; private int gender; private Date birth; public TxPerson() { } public TxPerson(int pid, String pname, String addr, int gender, Date birth) { this.pid = pid; this.pname = pname; this.addr = addr; this.gender = gender; this.birth = birth; } @Override public String toString() { return \"TxPerson{\" + \"pid=\" + pid + \", pname=\'\" + pname + \'\\\'\' + \", addr=\'\" + addr + \'\\\'\' + \", gender=\" + gender + \", birth=\" + birth + \'}\'; } public int getPid() { return pid; } public void setPid(int pid) { this.pid = pid; } public String getPname() { return pname; } public void setPname(String pname) { this.pname = pname; } public String getAddr() { return addr; } public void setAddr(String addr) { this.addr = addr; } public int getGender() { return gender; } public void setGender(int gender) { this.gender = gender; } public Date getBirth() { return birth; } public void setBirth(Date birth) { this.birth = birth; }}6.4 创建Mapper
package com.qcby.mapper; import com.qcby.entity.TxPerson;import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.*;import java.util.List; @Mapperpublic interface TxPersonMapper { @Select(\"select * from tx_person\") public List getPersons(); @Select(\"select * from tx_person t where t.pid = #{id}\") public TxPerson getPersonById(int id); @Options(useGeneratedKeys =true, keyProperty = \"pid\") @Insert(\"insert into tx_person(pid, pname, addr,gender, birth)\" + \" values(#{pid}, #{pname}, #{addr},#{gender}, #{birth})\") public void insert(TxPerson person); @Delete(\"delete from tx_person where pid = #{id}\") public void update(int id);}- 当 useGeneratedKeys 设为 true 时,MyBatis 会在执行插入操作之后,获取数据库自动生成的主键值。
- keyProperty = \"pid\" MyBatis 获取到数据库自动生成的主键值后,会把这个值赋给 Java 对象的 pid 属性。
6.5 测试
package com.qcby.springbootmybatis;import com.qcby.springbootmybatis.entity.TxPerson;import com.qcby.springbootmybatis.mapper.TxPersonMapper;import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration;import javax.sql.DataSource;import java.sql.SQLException;import java.util.Date;import java.util.List;@ContextConfiguration(classes = SpringbootMybatisApplication.class)@SpringBootTestpublic class SpringbootMybatisApplicationTests { @Autowired private TxPersonMapper txPersonMapper; @Autowired private DataSource dataSource; @Test public void testDataSource() throws SQLException { System.out.println(\"数据源类型:\" + dataSource.getClass().getName()); // 应输出com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource } @Test public void testGetPerson() { TxPerson person = txPersonMapper.getPersonById(1); // 假设存在 id 为 1 的记录 // 进行断言 if (person != null) { System.out.println(person); } } @Test public void testGetperson(){ List persons = txPersonMapper.getPersons(); for(TxPerson p: persons){ System.out.println( p); } } @Test public void testInsert(){ TxPerson p=new TxPerson(); p.setPname(\"aaa\"); p.setAddr(\"上海\"); p.setBirth(new Date()); p.setGender(0); txPersonMapper.insert(p); } @Test public void testDelete(){ txPersonMapper.update(4); }}七、常见问题与解决方案
-
数据库连接失败
- 检查
url中的数据库名、端口是否正确; - 确认 MySQL 服务已启动,用户名密码无误;
- MySQL 8.x 需指定
serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai。
- 检查
-
MyBatis 映射错误
- 检查
mapper-locations路径是否正确(需与 XML 文件位置匹配); - 确保
type-aliases-package指向实体类包,否则resultType=\"TxPerson\"会报错。
- 检查
-
Druid 监控页面无法访问
- 检查
filters是否包含stat,并确保StatViewServlet配置正确; - 访问路径为
http://localhost:8080/druid,使用配置的loginUsername和loginPassword登录。
- 检查
-
驼峰命名映射失败
- 确认
MyBatisConfig中已开启setMapUnderscoreToCamelCase(true); - 数据库字段
p_name需对应实体类pname,而非pName(严格驼峰规则)。
- 确认