Java 链表 + 面试题
文章目录
- 顺序表的优缺点
- 链表模拟实现
- 面试题
- 双向链表
-
- 模拟实现
-
- 头插
- 尾插
- 在指定位置插入节点
- 删除值为key的指定节点
- 删除所有值为key的节点
- 清空
- LinedList的遍历
- 面试题
顺序表的优缺点
缺点:
- 对于插入和删除最坏情况下,在0下标要移动N个数据,时间复杂度是O(N)
- 如果进行扩容,可能会浪费空间,比如扩容后只使用1个空间
优点: - 对于给定下标的查找是O(1)的复杂度
顺序表比较适合给定下标的查找
链表模拟实现
单向 双向
带头 不带头
循环 非循环
- 我们要学的是单向不带头非循环和双向不带头非循环
- 链表逻辑上连续,物理上不一定连续
构造链表节点
// 节点的内部类 static class ListNode{ public int val; public ListNode next; // next默认不知道下一个节点的地址,默认为 null // 构造方法没有返回值 public ListNode(int val){ this.val = val; } } public ListNode head;创建链表
public ListNode createList(){ ListNode node1 = new ListNode(12); ListNode node2 = new ListNode(13); ListNode node3 = new ListNode(14); ListNode node4 = new ListNode(15); ListNode node5 = new ListNode(16); node1.next = node2; node2.next = node3; node3.next = node4; node4.next = node5; head = node1; return head; }遍历链表

public void display() { ListNode cur = this.head; while(cur != null){ System.out.print(cur.val + \" \"); cur = cur.next; } System.out.println(); }计算链表长度
public int size() { int count = 0; ListNode cur = this.head; while(cur != null) { cur = cur.next; count++; } return count; }链表中是否包含key值的节点
public boolean contains(int key) { ListNode cur = head; while(cur != null){ if(cur.val == key){ return true; } cur = cur.next; } return false; }头插法
链表不为空:
- 实例化一个节点
- 让新节点指向旧的头节点(改变插入节点的next)
- 让头结点更新为现在新的节点(改变head)
链表为空:
- 实例化一个节点
- 让head指向新的节点
public void addFirst(int data) { ListNode node = new ListNode(data); if(this.head == null){ this.head = node; }else{ node.next = this.head; this.head = node; } }时间复杂度:O(1)
尾插法
- 分为链表不为空和链表为空
- 如果是要找到链表的最后一个节点,cur.next != null
- 如果是要遍历整个链表,cur != null
public void addLast(int data) { ListNode node = new ListNode(data); ListNode cur = head; if(this.head == null){ this.head = node; } else{ while(cur.next != null){ cur = cur.next; } cur.next = node; } }时间复杂度:O(N)
在Index位置插入节点
@Override public void addIndex(int index, int data) { ListNode node = new ListNode(data); if(index < 0 || index > size()){ // throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(\"下标出现异常\" + \" Index:\" + index); return ; } if(index == 0){ addFirst(data); } else if(index == size()){ addLast(data); } else{ // 找到index - 1位置的节点 ListNode cur = searchPrev(index); node.next = cur.next; cur.next = node; } } public ListNode searchPrev(int index){ ListNode cur = this.head; int count = 0; while(count != index - 1){ cur = cur.next; count++; } return cur; }删除值为key的节点
- 找到值为key的前驱节点
- 判断返回值是否为空(为空没有这个节点)
- 删除
public void remove(int key) { // 一个节点都没有,无法删除! if(this.head == null){ System.out.println(\"一个节点都没有\"); return; } // 头结点为要删除的节点 if(this.head.val == key){ ListNode cur = this.head.next; this.head = cur; return; } ListNode prev = findPrev(key); if(prev == null){ // 没有值为key的节点 System.out.println(\"没有值为key的节点\"); return; } else{ ListNode del = prev.next; prev.next = del.next; } } /* 找到值为key的前驱节点 */ public ListNode findPrev(int key){ ListNode cur = this.head; while(cur.next != null){ if(cur.next.val == key){ return cur; } cur = cur.next; } return null; }链表模拟代码
删除所有值为key的节点
- 先把除头结点之外所有为key的节点删除,如果头结点是key,再把头节点删除
- 如果链表为空不能删除
/* 删除所有值为 key 的节点 */ @Override public void removeAllKey(int key) { if(this.head == null){ // 没有节点可以删除 return; } ListNode cur = this.head.next; ListNode prev = this.head; // 除头结点外是val的节点要删除 while(cur != null){ if(cur.val == key){ prev.next = cur.next; cur = cur.next; } else{ prev = cur; cur = cur.next; } } // 如果头结点是val要删除 if(this.head.val == key){ this.head = this.head.next; } }清空所有节点
- 一个节点一个节点地释放
public void clear() { if(this.head == null){ return; } ListNode cur = this.head; while(cur != null){ ListNode ccur = cur.next; cur.next = null; // cur.val = 0; cur = ccur; } // 记得释放头节点 head = null; }面试题
移除链表元素
反转链表
链表的中间节点
删除链表的倒数第n个节点
合并两个有序链表
链表的回文结构
链表分割
相交链表
环形链表
环形链表II
双向链表
- 无头双向链表
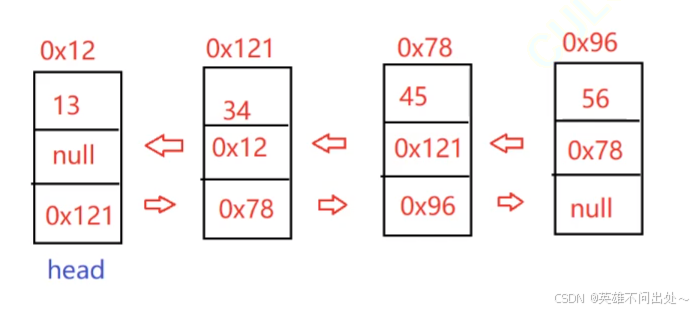
模拟实现
- 打印,求链表大小,求链表是否包含这个节点的值的代码都是一样的
头插
- 注意新插入节点的头节点也要有指向
- 时间复杂度:O(1)
public void addLast(int data) { ListNode node = new ListNode(data); ListNode cur = head; // 空链表 if(cur == null){ head = node; last = node; return; } // 非空链表 while(cur.next != null){ cur = cur.next; } // 找到尾结点cur node.prev = cur; cur.next = node; last = node; }尾插
- 时间复杂度:O(1)
public void addLast(int data) { ListNode node = new ListNode(data); ListNode cur = head; // 空链表 if(cur == null){ head = node; last = node; return; } // 非空链表 node.prev = last; last.next = node; last = node; }在指定位置插入节点
- 找到cur节点,让cur走index步
- 注意有尾插和头插
- 先处理next,再处理prev
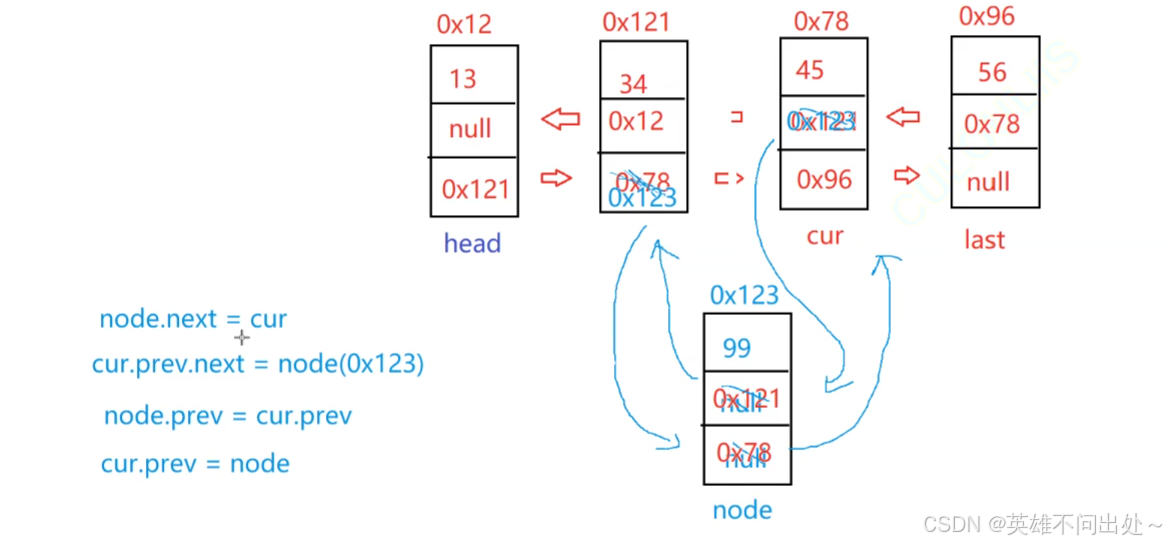
public void addIndex(int index, int data) { if(index < 0 || index > size()){ throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(\"下标异常,index为:\" + index); } // 头插 if(index == 0){ addFirst(data); return; } // 尾插 if(index == size()){ addLast(data); return; } // 中间插入节点,要找到index下标节点 ListNode node = new ListNode(data); ListNode cur = findIndex(index); node.next = cur; cur.prev.next = node; node.prev = cur.prev; cur.prev = node; } private ListNode findIndex(int index){ ListNode cur = head; while(index != 0){ cur = cur.next; index--; } return cur; }删除值为key的指定节点
- 分情况要分删除头,删除尾,删除中间节点的情况
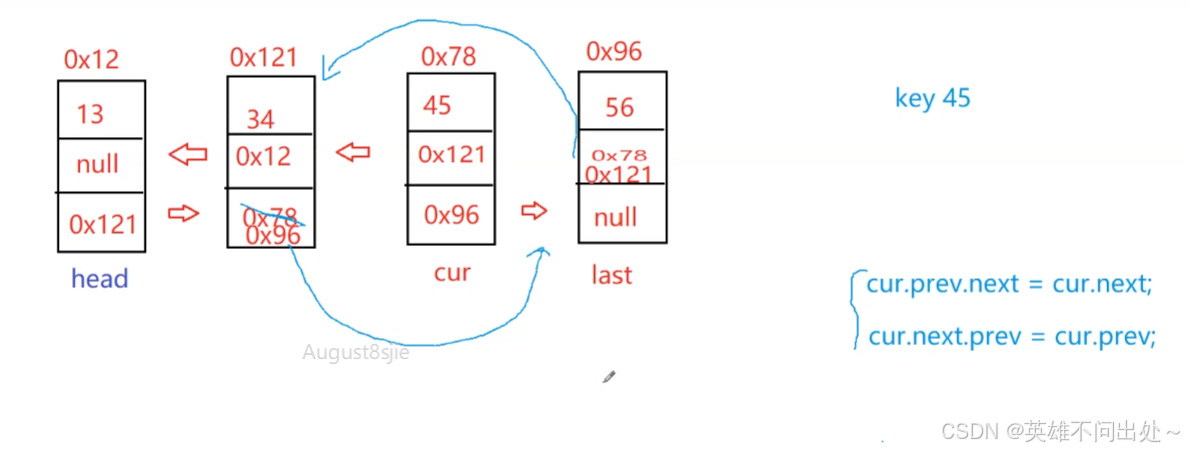
// 删除指定值的节点 @Override public void remove(int key) { ListNode cur = head; while(cur != null){ if(cur.val == key){ // 头删 if(cur == head){ head = head.next; // 如果head为空 if(head != null){ head.prev = null; }else{ // 只有一个节点 last = null; } }else{ cur.prev.next = cur.next; if(cur.next == null){// 尾删last = last.prev; } else{ cur.next.prev = cur.prev; } } // 删除一个节点就返回 return; }else{ cur = cur.next; } } }删除所有值为key的节点
- 在上一个方法的基础上不加return就行
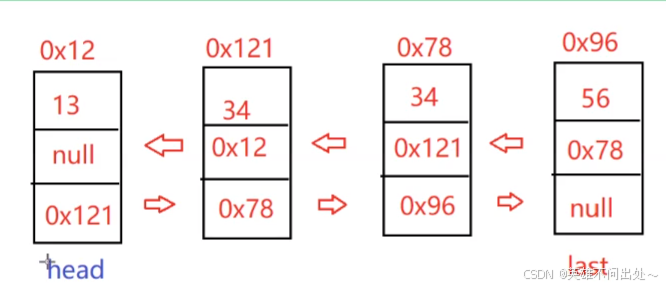
public void removeAllKey(int key) { ListNode cur = head; while(cur != null){ if(cur.val == key){ // 头删 if(cur == head){ head = head.next; // 如果head为空 if(head != null){ head.prev = null; }else{ // 只有一个节点 last = null; } }else { cur.prev.next = cur.next; if (cur.next == null) { // 尾删 last = last.prev; } else { cur.next.prev = cur.prev; } } } cur = cur.next; } }清空
- 把head和last置为空是会被JS回收的,但是更稳妥的方法是需要我们手动把所有节点置为空
- 没有形成环的引用是可以被回收的
public void clear() { ListNode cur = head; while(cur != null){ ListNode tmp = cur.next; // cur.val = null; cur.next = null; cur.prev = null; cur = tmp; }head = null; last = null; }LinedList的遍历
public static void main(String[] args) { LinkedList<Integer> list = new LinkedList<>(); list.add(1); list.add(2); list.add(3); list.add(4); list.add(5); // 继承了toString方法 System.out.println(list); // 通过for each 遍历 for(Integer x : list){ System.out.print(x + \" \"); } System.out.println(); // for循环 for(int i = 0;i < list.size();i++){ System.out.print(list.get(i) + \" \"); } System.out.println(); // 迭代器 ListIterator<Integer> it = list.listIterator(); // 当它有下一个的时候打印下一个元素,并且走到下一个元素的位置 while(it.hasNext()){ System.out.print(it.next() + \" \"); } System.out.println(); ListIterator<Integer> it2 = list.listIterator(list.size()); // 当它有前一个的时候打印前一个元素,并且走到前一个元素的位置 while(it2.hasPrevious()){ System.out.print(it2.previous() + \" \"); } System.out.println(); }面试题
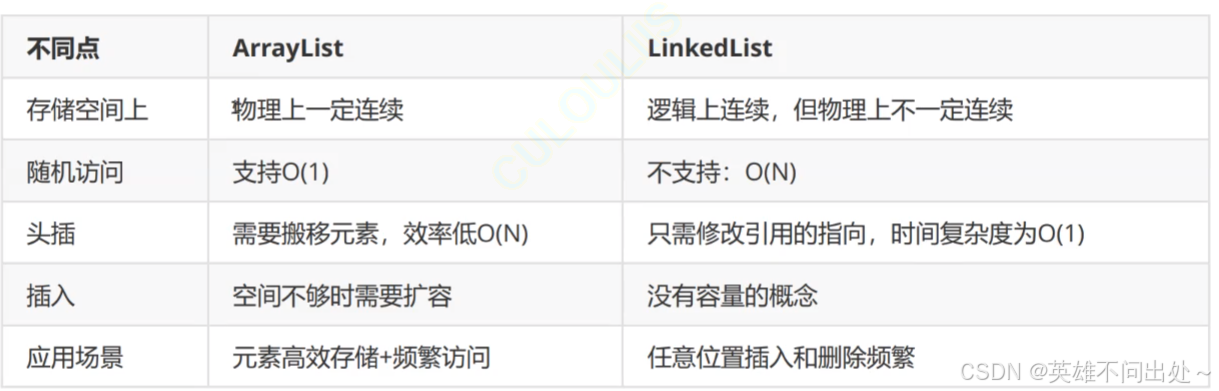
- ArrayList(顺序表)和LinkedList(双向链表)的区别是什么?
- 顺序表和链表的区别?
- 数组和链表的区别?
如果经常进行下标的查找可以使用ArrayList
如果经常进行插入和删除的可以使用LinkedList