HarmonyOS Next应用分层架构下组件封装开发实践_harmonyos next项目框架封装
基于鸿蒙应用分层架构的ArkUI组件封装实践
在鸿蒙应用开发中,合理利用 ArkUI 组件进行封装,可以实现代码复用,提升开发效率。本文将结合鸿蒙应用分层架构的特点,详细探讨几个典型的 ArkUI 组件封装场景及其实现方案。
华为鸿蒙应用分层架构概览
鸿蒙应用架构分层:将应用划分为产品定制层、基础特性层和公共能力层,可以降低层间的依赖性,从而提升代码的可维护性。通过分层架构设计进一步明确了每层的职责和层间的交互机制,为开发者呈现了一个清晰且结构化的开发框架,通过封装可复用的组件,为上层业务逻辑提供支持。
一、公用组件封装
在应用开发中,不同业务场景常需要相同功能和样式的 ArkUI 组件,例如统一的登录按钮或弹窗按钮。以 Button 组件为例,封装统一的样式和逻辑后,可提供给不同业务团队使用。
封装方案探讨
传统方法是通过自定义组件,并将通用逻辑抽取封装。但此方法存在一些问题,如使用方式与系统组件不一致、自定义组件入参过大、不利于后期维护。
为解决这些问题,ArkTS 提供了 attributeModifier 属性方法。通过自定义 Class 类实现 AttributeModifier 接口,可对系统组件属性进行扩展。
实现方案对比
方案一:适用于组合多个系统组件的场景。提供方创建自定义组件并导出,同时接受外部传入的 AttributeModifier 类实例。
方案二:适用于单一类型组件的场景。提供方直接创建 AttributeModifier 接口实现类,并导出供使用方调用。
二、分层架构介绍和实现
产品定制层
产品定制层的各个子目录会被编译成一个Entry类型的HAP,作为应用的主入口。该层面向多种设备,集成相应功能和特性。产品定制层划分为多个功能模块,每个模块针对特定设备或使用场景设计,并根据产品需求进行功能和交互的定制开发。在产品定制层,开发者可以从不同设备对应的应用UX设计和功能两个维度,结合具体的业务场景,选择一次编译生成相同或者不同的HAP(或其组合)。通过使用定制多目标构建产物的定制功能,可以将应用所对应的HAP编译成各自的.app文件,用于上架到应用市场。
基础特性层
在基础特性层中,功能模块根据部署需求被分为两类。对于需要通过Ability承载的功能,可以设计为Feature类型的HAP,而对于不需要通过Ability承载的功能,根据是否需要实现按需加载,可以选择设计为HAR模块或者HSP模块,编译后对应HAR包或者HSP包。
公共能力层
公共能力层的各子目录将编译成HAR包,仅产品定制层和基础特性层可依赖,不允许反向依赖。该层提取模块化公共基础能力,为上层提供标准接口和协议,提高复用率和开发效率。
应用分层架构实现

此次我们的组件封装就是在common文件中的compontHAR静态共享包中,需要将自定义组件在HAR的index.ets中导出组件,在使用方的oh-package.json5文件中引入
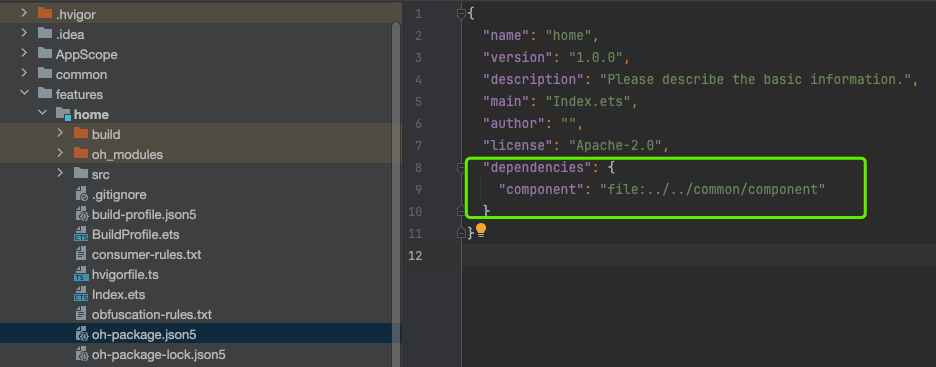
三、公用组件封装
基础组件封装
场景描述
在应用开发过程中,不同的业务场景可能需要使用相同功能或样式的ArkUI组件。例如,登录页面登录按钮和购物页面结算按钮可能样式相同。该场景常用方法是抽取相同样式的逻辑部分,并将其封装成一个自定义组件到公共组件库中。在业务场景开发时,统一从公共组件库获取封装好的公用组件。
ArkTS为每个系统组件提供了attributeModifier属性方法。该方法将组件属性设置分离到系统提供的AttributeModifier接口实现类实例中,通过自定义Class类实现AttributeModifier接口对系统组件属性进行扩展.
使用wrapBuilder方法有以下限制:
wrapBuilder方法只支持传入全局@Builder方法。
wrapBuilder方法返回的WrappedBuilder对象的builder属性方法只能在struct内部使用。
/** * @FileName : BaseButtonAttributeModifier * @Author : kirk.wang * @Time : 2025/5/16 10:23 * @Description : 基础组件Button封装 *///创建AttributeModifier接口的实现类export class BaseButtonAttributeModifier implements AttributeModifier { // 私有定义Button组件特有属性 private _buttonType: ButtonType = ButtonType.Normal; private _enabled: boolean = false; // 实现组件的普通状态下的样式方法,系统还提供了hover状态和其他状态下的样式方法 applyNormalAttribute(instance: ButtonAttribute): void { instance.type(this._buttonType) .stateEffect(true) .fontSize(16) .height(48) .enabled(this._enabled) } // 链式配置方法 type(buttonType: ButtonType): BaseButtonAttributeModifier { this._buttonType = buttonType; return this; } enabled(enabled: boolean): BaseButtonAttributeModifier { this._enabled = enabled; return this; }}使用方创建提供方的AttributeModifier实现类实例,并作为系统组件attributeModifier属性方法的参数传入。
/** * @FileName : GQButton * @Author : kirk.wang * @Time : 2025/5/16 15:35 * @Description : 自定义Button组件 */// src/main/ets/pages/CommonComponent.etsimport { BaseButtonAttributeModifier } from \"./BaseButtonAttributeModifier\";//提供方自定义组件并导出@Componentexport struct GQButton { @Prop text: string = \'\'; // 接受外部传入的AttributeModifier类实例 @Prop modifier: BaseButtonAttributeModifier; build() { Button(this.text)// 将入参的AttributeModifier类实例与系统组件绑定 .attributeModifier(this.modifier) .fontSize(20) .width(200) .height(50) }}通过以上方案,使组件封装更灵活,也保持了与系统组件一致的使用方式。
组合组件封装
在实际应用开发中,会有需要抽取复用的组件为多个系统组件的组合是情况,比如新闻APP,新闻列表的item就需要经常被使用,就需要封装一个。
封装自定义组件MediaCard并导出:
/** * @FileName : MediaCard * @Author : kirk.wang * @Time : 2025/5/16 15:05 * @Description : 复合组件封装-图片文本组件 */@Componentexport struct MediaCard { @Prop imageSrc: PixelMap | ResourceStr | DrawableDescriptor; @Prop title: string; @Prop content: string; @Prop imageModifier: AttributeModifier; @Prop titleModifier: AttributeModifier; @Prop contentModifier: AttributeModifier; build() { Column({ space: 8 }) { Image(this.imageSrc) .attributeModifier(this.imageModifier) Text(this.title) .attributeModifier(this.titleModifier) Text(this.content) .attributeModifier(this.contentModifier) } .padding(12) .backgroundColor(Color.White) .borderRadius(8) }}export class ImageModifier implements AttributeModifier { // 实现 AttributeModifier 接口 private imageWidth: Length = 0; private imageHeight: Length = 0; constructor(width: Length, height: Length) { this.imageWidth = width; this.imageHeight = height; } width(width: Length) { this.imageWidth = width; return this; } height(height: Length) { this.imageHeight = height; return this; } applyNormalAttribute(instance: ImageAttribute): void { instance.width(this.imageWidth); instance.height(this.imageHeight); instance.borderRadius($r(\'app.float.padding_borderRadius\')) }}export class TextModifier { private _fontSize: number | string | Resource| null = 14; constructor(fontSize?: number | string | Resource) { if(fontSize!==null){ this._fontSize = fontSize!; } } fontSize(fontSize: number | string | Resource): TextModifier { this._fontSize= fontSize; return this; } applyNormalAttribute(instance: TextAttribute): void { instance.fontSize(this._fontSize); }}导出自定义组件:
export { MediaCard,TextModifier,ImageModifier } from \'./src/main/ets/components/MediaCard\';使用:
import { BaseButtonAttributeModifier, GQButton, MediaCard, ImageModifier, TextModifier,DialogUtils, factoryMap} from \"component\";@Componentexport struct HomePage { build() { NavDestination() { MediaCard({ imageModifier: this.imagesAttribute, titleModifier: this.titleAttribute, contentModifier: this.contentAttribute, imageSrc: $r(\'app.media.icon_header\'), title: \'title\', content: \'content\' })}```ets### 自定义弹窗封装1. 使用方通过全局 @Builder 封装弹窗结构,定义弹窗的内容和样式。2. 提供方通过 UIContext 获取 PromptAction 对象,封装弹窗工具类。3. 提供方创建打开和关闭弹窗的接口,使用方通过调用这些接口实现弹窗的显示和隐藏。以下是弹窗工具类实现代码:```ets// 提供方封装的弹窗工具类/** * @FileName : DialogUtils * @Author : kirk.wang * @Time : 2025/5/16 16:25 * @Description : 封装弹窗的工具类 */import { ComponentContent, promptAction } from \'@kit.ArkUI\';export class DialogUtils{ private static dialog:DialogUtils; private data:PopViewModel[] = new Array; static getInstance(): DialogUtils { if (!DialogUtils.dialog) { DialogUtils.dialog = new DialogUtils(); } return DialogUtils.dialog; } //通过openCustomDialog创建打开弹窗的showDialog函数。 static showDialog(type: PopViewShowType, contentView: WrappedBuilder, args: T, options?: promptAction.BaseDialogOptions):void { let uiContext = AppStorage.get(\'uiContext\'); if (uiContext) { // The promptAction object was obtained. let prompt = uiContext.getPromptAction(); let componentContent = new ComponentContent(uiContext, contentView, args); let customOptions: promptAction.BaseDialogOptions = { alignment: options?.alignment || DialogAlignment.Bottom }; // Open pop-ups using openCustomDialog prompt.openCustomDialog(componentContent, customOptions); let data = DialogUtils.getInstance().data; let info: PopViewModel = { com: componentContent, popType: type }; data[0] = info; } }//通过closeCustomDialog创建关闭弹窗的closeDialog函数 static closeDialog(popType:PopViewShowType):void{ let context = AppStorage.get(\'uiContext\'); if(context){ let prompt = context.getPromptAction(); let sameTypeList = DialogUtils.getInstance().data.filter((model) => { return model.popType === popType; }) let info = sameTypeList[sameTypeList.length - 1]; if (info.com) { DialogUtils.getInstance().data = DialogUtils.getInstance().data.filter((model) => { return model.com !== info.com; }) prompt.closeCustomDialog(info.com); } } } static showPopView(contentView: WrappedBuilder, args: T, options?: promptAction.BaseDialogOptions):void { DialogUtils.showDialog(PopViewShowType.OPEN, contentView, args, options); } static closePopView():void { DialogUtils.closeDialog(PopViewShowType.OPEN); }}interface PopViewModel { com: ComponentContent; popType: PopViewShowType;}export enum PopViewShowType { OPEN}//使用 DialogUtils.showPopView(wrapBuilder(buildDialogView), new Object(), { alignment: DialogAlignment.Center });//构建buildDialogView@Builderexport function buildDialogView(_obj: Object) { Column({ space: 16 }) { Text($r(\'app.string.tips\')) .fontSize(16) .fontWeight(FontWeight.Bold) Text($r(\'app.string.content\')) .fontSize(16) Row() { Button($r(\'app.string.cancel\')) .fontColor(Color.Blue) .backgroundColor(Color.White) .margin({ right: 10 }) .width(\'42%\') .onClick(() => { DialogUtils.closePopView(); }) Button($r(\'app.string.confirm\')) .width(\'42%\') .onClick(() => { DialogUtils.closePopView(); }) } .justifyContent(FlexAlign.Center) .width(328) } .padding(18) .justifyContent(FlexAlign.Center) .alignItems(HorizontalAlign.Center) .backgroundColor(Color.White) .borderRadius($r(\'app.float.border_radius\'))}弹窗组件的封装更加简洁高效,使用方可以快速实现自定义弹窗。
三、组件工厂类封装
当需要为不同的业务需求提供多种组件时,组件工厂类封装是一种有效的解决方案。
实现流程优化
-
在组件工厂实现方,通过全局 @Builder 方法封装需要工厂化的组件。
-
将封装好的 @Builder 方法使用 wrapBuilder 函数包裹,并存入 Map 结构中,其中 key 为组件名,value 为 WrappedBuilder 对象。
-
在使用方,通过组件工厂的 key 值获取对应的 WrappedBuilder 对象,并在 build 方法中调用其 builder 属性方法获取组件。
以选择月份的组件为例,项目种有多个地方需要选择月份,那么以下是组件工程封装的实现代码:
// 组件工厂实现方/** * @FileName : FactoryMap * @Author : kirk.wang * @Time : 2025/5/18 00:50 * @Description :月份选择组件 */let mothList = [\"1\",\"2\",\"3\",\"4\",\"5\",\"6\",\"7\",\"8\",\"9\",\"10\",\"11\",\"12\"];@Builderfunction monthRadio() { Text($r(\'app.string.month\')) .width(\'100%\') .fontColor($r(\'sys.color.mask_secondary\')) List(){ ForEach(mothList, (item: string, index: number) => { ListItem(){ Row() { Radio({ value: `${index}`, group: \'radioGroup\' }) Text(`${item}月`) } .width(\'100%\') } }); }}// 创建组件工厂的集合let factoryMap: Map = new Map();//把需要的工厂存储在组件工厂中的组件。factoryMap.set(\'monthRadio\', wrapBuilder(monthRadio));// Export assembly factoryexport { factoryMap };//使用 HomePage.etsimport { factoryMap} from \"component\";@Componentexport struct HomePage { monthRadio: WrappedBuilder = factoryMap.get(\'monthRadio\') as WrappedBuilder; build() { NavDestination() { this.monthRadio.builder(); }}四、总结与展望
在鸿蒙应用分层架构下进行 ArkUI 组件封装,可以提高开发效率和代码复用率。通过合理利用 ArkTS 提供的 attributeModifier 属性方法、PromptAction 对象以及组件工厂模式,可以实现灵活、高效的组件封装。未来,随着鸿蒙应用生态的发展,组件封装技术将不断完善。开发者们可以探索更多创新的封装方式,为鸿蒙应用开发提供更强大的支持。
四、Demo代码仓
https://gitcode.com/kirkWang/componentMaster


