OpenGLRender开发记录(二): 阴影(shadowMap,PCF,PCSS)
目录
- 已实现功能
- 阴影
-
- shadowMap
- PCF
- PCSS
- 实现
-
- shadowMap
- PCF
- PCSS
- 阴影
GitHub主页:https://github.com/sdpyy1
OpenGLRender:https://github.com/sdpyy1/CppLearn/tree/main/OpenGL
已实现功能
除了上次实现IBL之外,项目目前新增了imGUI的渲染,更方便地进行调试

可以随意切换IBL贴图、模型控制、灯光控制灯。 并且添加了一个PBR材质的地板。下一步就是实现阴影
阴影
shadowMap
这个东西很简单,直接实现了,不讲原理
PCF
取周围一圈的像素求平均,让阴影更软
PCSS
① Blocker Search 阶段(寻找遮挡者)
目的:估算遮挡物与被遮挡物之间的距离 → 用于计算 penumbra(阴影模糊程度)
步骤:
从当前 fragment 的 light space 坐标,投影到 shadow map 中:projCoords.xy
以该位置为中心,在 shadow map 中进行 小范围采样(通常 3x3 或 5x5):
收集所有 比当前 fragment 深度更小的样本(说明它们挡住了光)
累加这些“遮挡者”的深度值
记录 blocker 数量
若存在 blocker:
计算平均 blocker 深度 avgBlockerDepth
② Penumbra Size 计算阶段(决定模糊程度)
目的:用当前 fragment 深度 与 avgBlockerDepth 的距离估算光源发散导致的阴影模糊程度
③ Filtering 阶段(模糊阴影边缘)
目的:根据 penumbra 大小,用可变范围 PCF 模糊阴影边缘
所以PCSS可以叫自适应PCF
实现
shadowMap
初始化一个FBO用于shadowMap的渲染,创建一张纹理存储深度结果
void ShadowPass::init() { glGenFramebuffers(1, &shadowFBO); // 创建深度纹理 glGenTextures(1, &shadowMap); glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, shadowMap); glTexImage2D(GL_TEXTURE_2D, 0, GL_DEPTH_COMPONENT, scene.width, scene.height, 0, GL_DEPTH_COMPONENT, GL_FLOAT, NULL); glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MIN_FILTER, GL_NEAREST); glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MAG_FILTER, GL_NEAREST); glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_WRAP_S, GL_REPEAT); glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_WRAP_T, GL_REPEAT); // attach 深度纹理到FBO glBindFramebuffer(GL_FRAMEBUFFER, shadowFBO); glFramebufferTexture2D(GL_FRAMEBUFFER, GL_DEPTH_ATTACHMENT, GL_TEXTURE_2D, shadowMap, 0); glDrawBuffer(GL_NONE); glReadBuffer(GL_NONE); glBindFramebuffer(GL_FRAMEBUFFER, 0); isInit = true;}下一步就是在光源视角下渲染,首先得找到摄像机的位置,其实就是MVP矩阵的VP用光源而不是用摄像机,下面是对于平行光的shadowMap渲染
void ShadowPass::render() { if (!isInit){ std::cout << \"shadowPass init\" << std::endl; return; } glViewport(0, 0, scene.width, scene.height); glBindFramebuffer(GL_FRAMEBUFFER, shadowFBO); glClear(GL_DEPTH_BUFFER_BIT);// glCullFace(GL_FRONT); // 可选,防止 Peter-panning shadowShader.bind(); glm::mat4 lightProjection, lightView; float orthoSize = 10.0f; float near_plane = 0.1f; float far_plane = 100.0f; // 你可以再根据场景大小动态调整 // 平行光使用正交投影 lightProjection = glm::ortho(-orthoSize, orthoSize, -orthoSize, orthoSize, near_plane, far_plane); // TODO:只实现了平行光,他的position存储的是方向,而不是位置,所以要取反 lightView = glm::lookAt(-scene.lights[0]->position * 10.0f, glm::vec3(0.0f), glm::vec3(0.0, 1.0, 0.0)); lightSpaceMatrix = lightProjection * lightView; shadowShader.setMat4(\"lightSpaceMatrix\", lightSpaceMatrix); // 渲染所有模型(只写深度) for (auto& model : scene.models) { glm::mat4 modelMatrix = model.getModelMatrix(); shadowShader.setMat4(\"model\", modelMatrix); model.draw(shadowShader); } shadowShader.unBind();// glCullFace(GL_BACK); glBindFramebuffer(GL_FRAMEBUFFER, 0); glViewport(0, 0, scene.width, scene.height);}顶点着色器,物体要乘以lightSpaceMatrix来转到光源视角下
#version 330 corelayout (location = 0) in vec3 aPos;uniform mat4 model;uniform mat4 lightSpaceMatrix;void main() { gl_Position = lightSpaceMatrix * model * vec4(aPos, 1.0);}片段着色器不需要执行操作
#version 330 corevoid main() { // 空着就行,只写深度}下一步将生成的shadowMap传递到lightPass来参与光照计算,另外需要把lightMatrix也传递过去,用于把模型距离值转移到视角下来进行比较
float ShadowCalculation(vec3 fragPosWorld, vec3 normal) { vec4 fragPosLightSpace = lightSpaceMatrix * vec4(fragPosWorld, 1.0); vec3 projCoords = fragPosLightSpace.xyz / fragPosLightSpace.w; projCoords = projCoords * 0.5 + 0.5; // [-1,1] → [0,1] // 从深度贴图采样 float closestDepth = texture(shadowMap, projCoords.xy).r; float currentDepth = projCoords.z; // 简单 bias 防止 shadow acne// float bias = max(0.005 * (1.0 - dot(normal, normalize(lightPos))), 0.001); // 超出边界不产生阴影 if (projCoords.z > 1.0) return 0.0; // 进行一次比较 return (currentDepth) > closestDepth ? 1.0 : 0.0;}有了计算阴影的函数后,只需要在计算光照的最后*(1-shadow)
vec3 Lo = (kD * albedo / PI + specular) * radiance * NdotL * (1-ShadowCalculation(WorldPos, N));结果如下,经典的自阴影现象,主要原因就是shadowMap的分辨率不足,一些不在同一高度的位置被记录了相同高度,在主摄像机渲染时,某个位置在shadowMap存储的高度比自己本来还要高,就会被认为是阴影(但是这种情况下很好分辨光源摄像机的覆盖范围,方便调试🙂)

当我把shadowMap的分辨率提高后,自然就消失了,但这肯定不是最优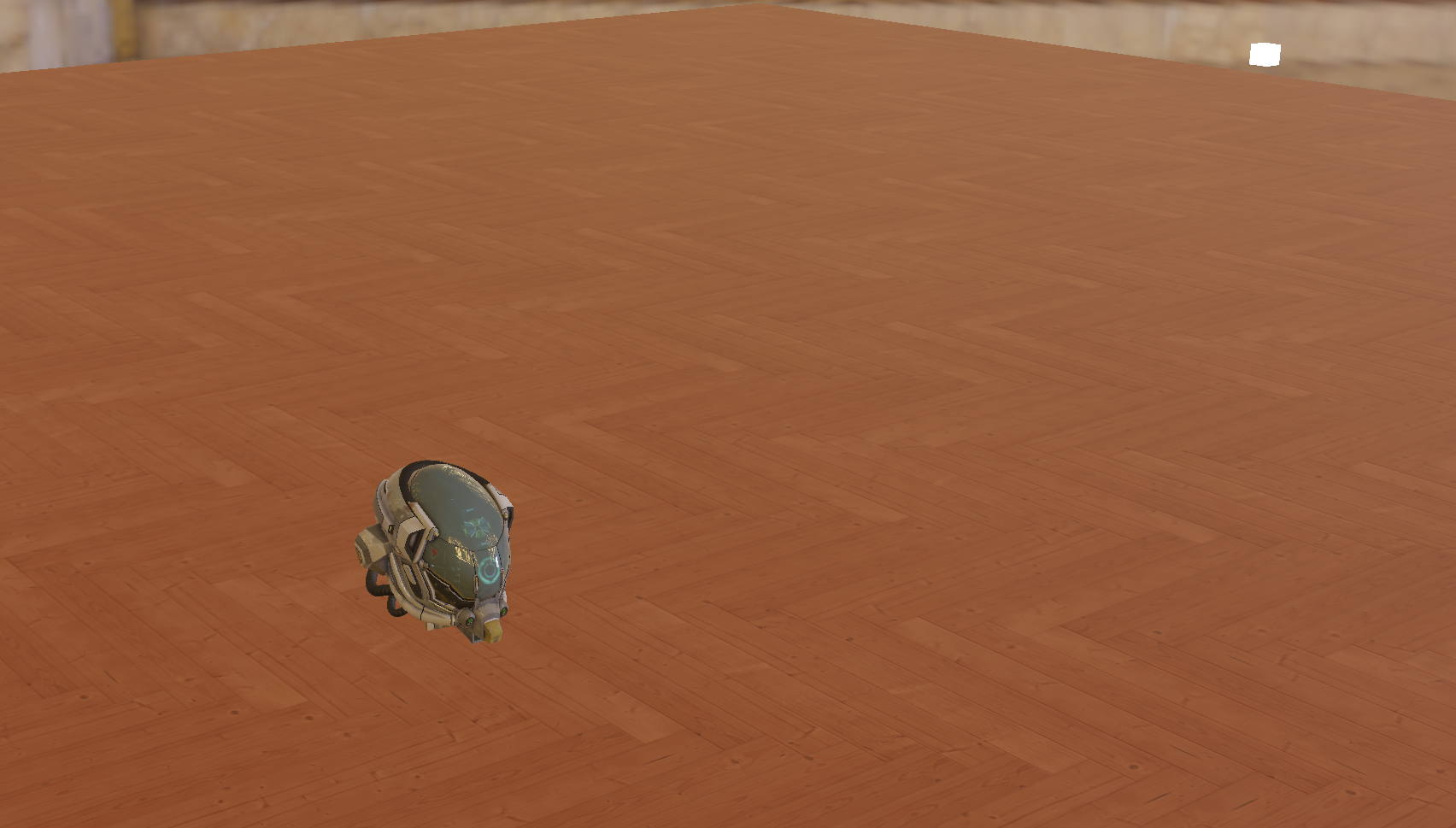
通常的做法是加一个自偏移,也就是说shadowMap存的高度和我用来比较的高度差异不超过bias,就认为没有阴影
float ShadowCalculation(vec3 fragPosWorld, vec3 normal) { vec4 fragPosLightSpace = lightSpaceMatrix * vec4(fragPosWorld, 1.0); vec3 projCoords = fragPosLightSpace.xyz / fragPosLightSpace.w; projCoords = projCoords * 0.5 + 0.5; // [-1,1] → [0,1] // 从深度贴图采样 float closestDepth = texture(shadowMap, projCoords.xy).r; float currentDepth = projCoords.z; // 简单 bias 防止 shadow acne float bias = max(0.005 * (1.0 - dot(normal, normalize(lightPos))), 0.001); // 超出边界不产生阴影 if (projCoords.z > 1.0) return 0.0; // 进行一次比较 return (currentDepth - bias) > closestDepth ? 1.0 : 0.0;}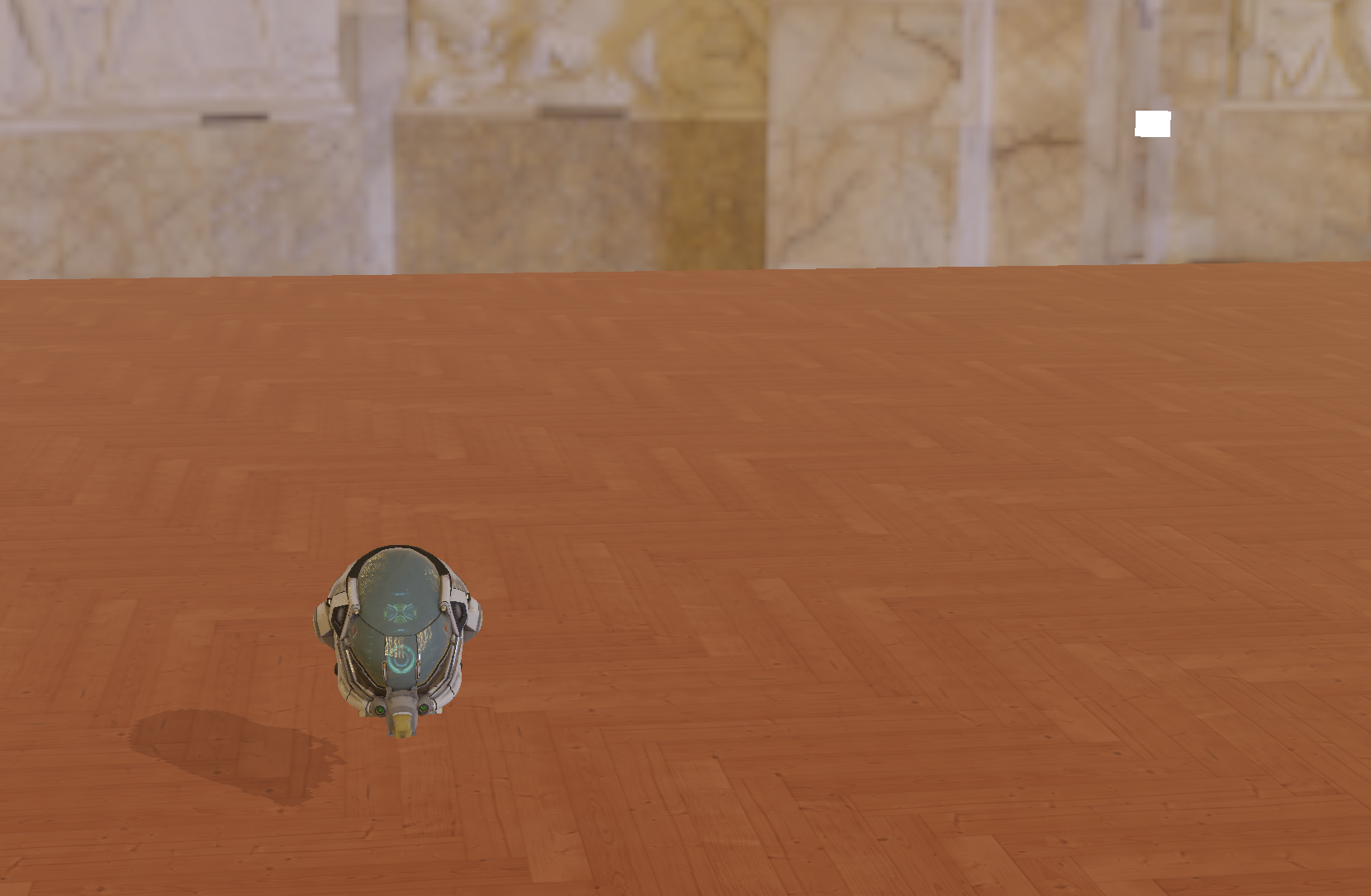
PCF
阴影问题解决了,下面就是提升效果,当前的阴影是硬阴影,锯齿很严重
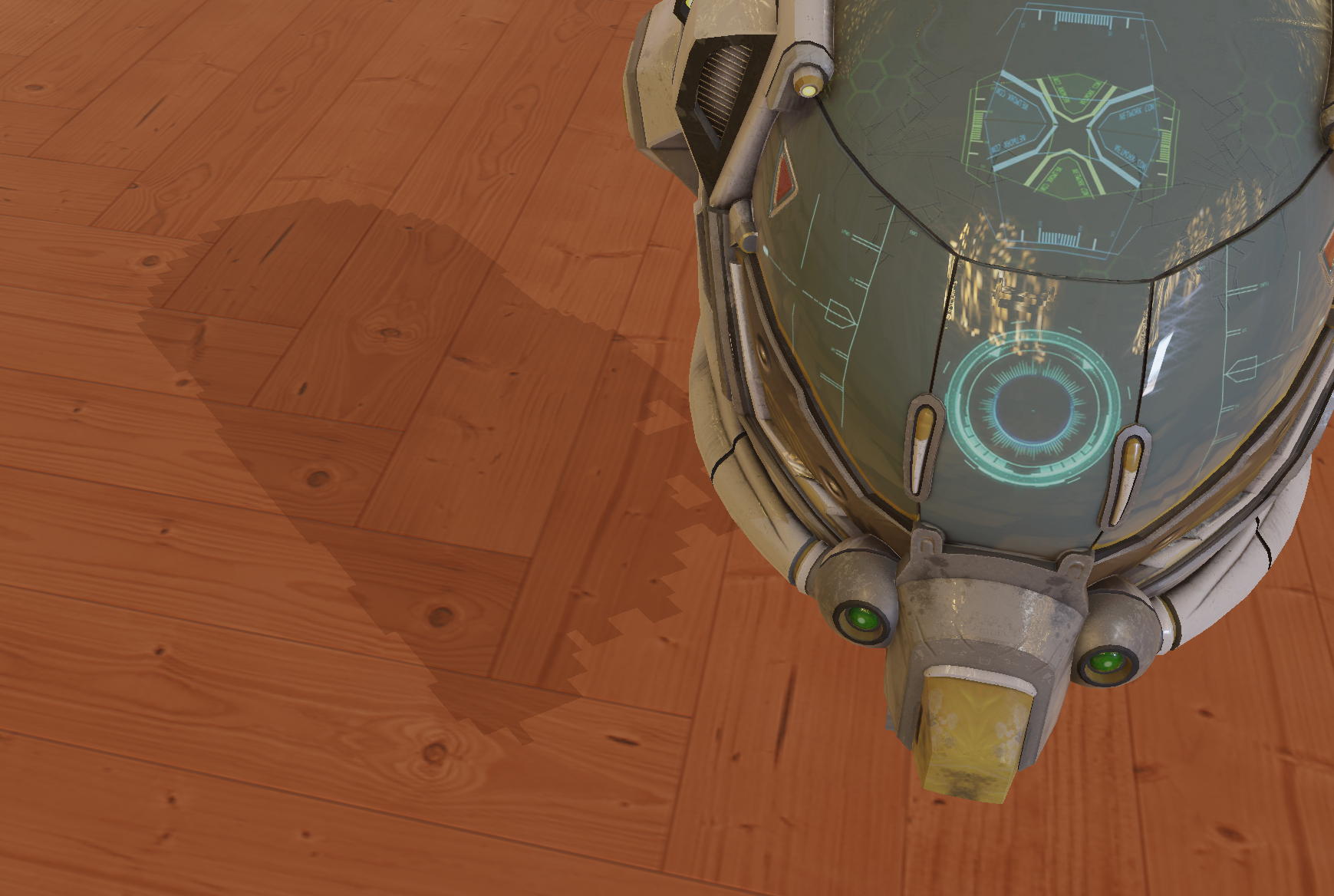


PCF思路就是取周围像素的shadow来取平均,柔化阴影边界
// --- PCF --- float shadow = 0.0; ivec2 texSize = textureSize(shadowMap, 0); vec2 texelSize = 1.0 /vec2(texSize); int range = 10; // 5x5 int samples = 0; for (int x = -range; x <= range; ++x) { for (int y = -range; y <= range; ++y) { float pcfDepth = texture(shadowMap, projCoords.xy + vec2(x, y) * texelSize).r; shadow += (currentDepth - bias > pcfDepth) ? 1.0 : 0.0; samples++; } } shadow /= float(samples); return shadow;
PCSS
三步走,一些参数我已经提取出去当uniform,可以控制第一步的搜索半径、第二步的半影大小、以及控制一下最大的滤波核大小
float avgBlockerDepth = 0.0; int blockers = 0; ivec2 texSize = textureSize(shadowMap, 0); vec2 texelSize = 1.0 / vec2(texSize); int searchRadius = int(PCSSBlockerSearchRadius); for (int x = -searchRadius; x <= searchRadius; ++x) { for (int y = -searchRadius; y <= searchRadius; ++y) { float sampleDepth = texture(shadowMap, projCoords.xy + vec2(x, y) * texelSize).r; if (sampleDepth < currentDepth - bias) { avgBlockerDepth += sampleDepth; blockers++; } } } if (blockers == 0) return 0.0; avgBlockerDepth /= blockers; float penumbra = (currentDepth - avgBlockerDepth) * PCSSScale; int kernel = int(clamp(penumbra * float(texSize.x), 1.0, PCSSKernelMax)); float shadow = 0.0; for (int x = -kernel; x <= kernel; ++x) { for (int y = -kernel; y <= kernel; ++y) { float sampleDepth = texture(shadowMap, projCoords.xy + vec2(x, y) * texelSize).r; shadow += (currentDepth - bias > sampleDepth) ? 1.0 : 0.0; } } shadow /= float((2 * kernel + 1) * (2 * kernel + 1)); return shadow;阴影
三种阴影可以写在一起
float ShadowCalculation(vec3 fragPosWorld, vec3 normal) { vec4 fragPosLightSpace = lightSpaceMatrix * vec4(fragPosWorld, 1.0); vec3 projCoords = fragPosLightSpace.xyz / fragPosLightSpace.w; projCoords = projCoords * 0.5 + 0.5; if (projCoords.z > 1.0) return 0.0; float closestDepth = texture(shadowMap, projCoords.xy).r; float currentDepth = projCoords.z; float bias = max(0.005 * (1.0 - dot(normal, normalize(lightPos))), 0.001); // shadow type switching if (shadowType == 0) { return 0.0; // no shadow } else if (shadowType == 1) { return (currentDepth - bias > closestDepth) ? 1.0 : 0.0; // hard shadow } else if (shadowType == 2) { // --- PCF --- float shadow = 0.0; ivec2 texSize = textureSize(shadowMap, 0); vec2 texelSize = 1.0 /vec2(texSize); int range = pcfScope; int samples = 0; for (int x = -range; x <= range; ++x) { for (int y = -range; y <= range; ++y) { float pcfDepth = texture(shadowMap, projCoords.xy + vec2(x, y) * texelSize).r; shadow += (currentDepth - bias > pcfDepth) ? 1.0 : 0.0; samples++; } } shadow /= float(samples); return shadow; } else if (shadowType == 3) { float avgBlockerDepth = 0.0; int blockers = 0; ivec2 texSize = textureSize(shadowMap, 0); vec2 texelSize = 1.0 / vec2(texSize); int searchRadius = int(PCSSBlockerSearchRadius); for (int x = -searchRadius; x <= searchRadius; ++x) { for (int y = -searchRadius; y <= searchRadius; ++y) { float sampleDepth = texture(shadowMap, projCoords.xy + vec2(x, y) * texelSize).r; if (sampleDepth < currentDepth - bias) { avgBlockerDepth += sampleDepth; blockers++; } } } if (blockers == 0) return 0.0; avgBlockerDepth /= blockers; float penumbra = (currentDepth - avgBlockerDepth) * PCSSScale; int kernel = int(clamp(penumbra * float(texSize.x), 1.0, PCSSKernelMax)); float shadow = 0.0; for (int x = -kernel; x <= kernel; ++x) { for (int y = -kernel; y <= kernel; ++y) { float sampleDepth = texture(shadowMap, projCoords.xy + vec2(x, y) * texelSize).r; shadow += (currentDepth - bias > sampleDepth) ? 1.0 : 0.0; } } shadow /= float((2 * kernel + 1) * (2 * kernel + 1)); return shadow; } return 0.0;}


