一行代码加速Pytorch推理速度6倍
一行代码加速Pytorch推理速度6倍
Torch-TensorRT 是 PyTorch 的集成,它利用 NVIDIA GPU 上的 TensorRT 推理优化。 只需一行代码,它就提供了一个简单的 API,可在 NVIDIA GPU 上提供高达 6 倍的性能加速。
话不多说, 线上代码, 再解释原理!!
文章目录
- 一行代码加速Pytorch推理速度6倍
学习目标
本笔记本演示了在预训练的 ResNet-50 网络上使用 Torch-TensorRT 编译 TorchScript 模块并运行它以测试获得的加速的步骤。
内容
- 安装
- ResNet-50 概述
- 在没有优化的情况下运行模型
- 使用 Torch-TensorRT 加速
- 结论
1. 安装
NVIDIA 的 NGC 提供 PyTorch Docker Container,其中包含 PyTorch 和 Torch-TensorRT。 我们可以使用 最新的 pytorch容器来运行这个notebook。
2. ResNet-50 概述
PyTorch 有一个名为 PyTorch Hub 的模型存储库,它是常见模型的高质量实现的来源。 我们可以从那里获得在 ImageNet 上预训练的 ResNet-50 模型。
模型说明
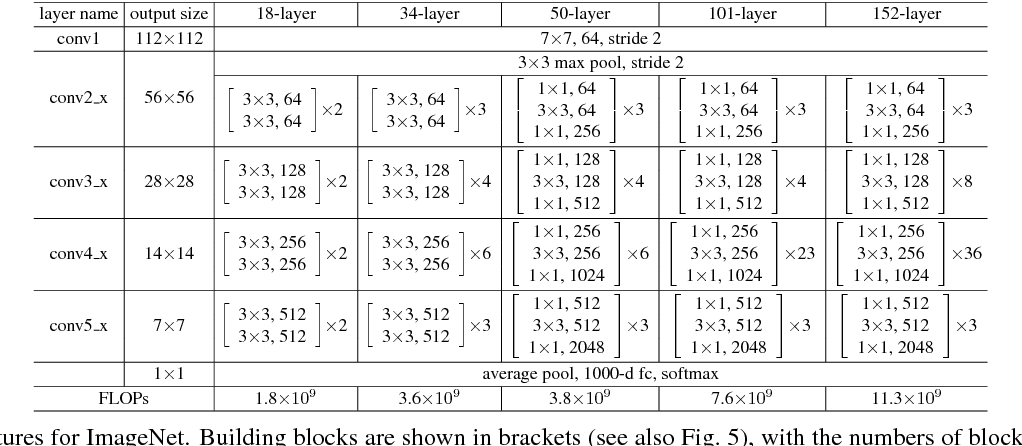
这个 ResNet-50 模型基于 Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition 论文,该论文将 ResNet 描述为“一种使用单一深度残差检测图像中对象的方法” 神经网络”。输入大小固定为 32x32。
3. 在没有优化的情况下运行模型
import torchimport torchvisiontorch.hub._validate_not_a_forked_repo=lambda a,b,c: Trueresnet50_model = torch.hub.load('pytorch/vision:v0.10.0', 'resnet50', pretrained=True)resnet50_model.eval()加载我们的模型后,让我们继续下载一些图像!
!mkdir -p ./data!wget -O ./data/img0.JPG "https://d17fnq9dkz9hgj.cloudfront.net/breed-uploads/2018/08/siberian-husky-detail.jpg?bust=1535566590&width=630"!wget -O ./data/img1.JPG "https://www.hakaimagazine.com/wp-content/uploads/header-gulf-birds.jpg"!wget -O ./data/img2.JPG "https://www.artis.nl/media/filer_public_thumbnails/filer_public/00/f1/00f1b6db-fbed-4fef-9ab0-84e944ff11f8/chimpansee_amber_r_1920x1080.jpg__1920x1080_q85_subject_location-923%2C365_subsampling-2.jpg"!wget -O ./data/img3.JPG "https://inaturalist-open-data.s3.amazonaws.com/photos/98797/large.jpg"!wget -O ./data/imagenet_class_index.json "https://s3.amazonaws.com/deep-learning-models/image-models/imagenet_class_index.json"所有预训练模型都期望输入图像以相同的方式归一化,
即形状为(3 x H x W)的 3 通道 RGB 图像,其中H和W预计至少为224。
图像必须加载到“[0, 1]”范围内,然后使用mean = [0.485, 0.456, 0.406]和std = [0.229, 0.224, 0.225]进行归一化
。
这是一个示例。
from PIL import Imagefrom torchvision import transformsimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltimport json fig, axes = plt.subplots(nrows=2, ncols=2)for i in range(4): img_path = './data/img%d.JPG'%i img = Image.open(img_path) preprocess = transforms.Compose([ transforms.Resize(256), transforms.CenterCrop(224), transforms.ToTensor(), transforms.Normalize(mean=[0.485, 0.456, 0.406], std=[0.229, 0.224, 0.225]), ]) input_tensor = preprocess(img) plt.subplot(2,2,i+1) plt.imshow(img) plt.axis('off')# loading labels with open("./data/imagenet_class_index.json") as json_file: d = json.load(json_file)在本教程中,我们将使用一些实用函数; rn50_preprocess 用于预处理输入图像,predict 用于使用模型进行预测,benchmark 用于对推理进行基准测试。 您无需了解这些函数, 通过这些实用函数即可使用 Torch TensorRT.
import numpy as npimport timeimport torch.backends.cudnn as cudnncudnn.benchmark = Truedef rn50_preprocess(): preprocess = transforms.Compose([ transforms.Resize(256), transforms.CenterCrop(224), transforms.ToTensor(), transforms.Normalize(mean=[0.485, 0.456, 0.406], std=[0.229, 0.224, 0.225]), ]) return preprocess# decode the results into ([predicted class, description], probability)def predict(img_path, model): img = Image.open(img_path) preprocess = rn50_preprocess() input_tensor = preprocess(img) input_batch = input_tensor.unsqueeze(0) # create a mini-batch as expected by the model # move the input and model to GPU for speed if available if torch.cuda.is_available(): input_batch = input_batch.to('cuda') model.to('cuda') with torch.no_grad(): output = model(input_batch) # Tensor of shape 1000, with confidence scores over Imagenet's 1000 classes sm_output = torch.nn.functional.softmax(output[0], dim=0) ind = torch.argmax(sm_output) return d[str(ind.item())], sm_output[ind] #([predicted class, description], probability)def benchmark(model, input_shape=(1024, 1, 224, 224), dtype='fp32', nwarmup=50, nruns=10000): input_data = torch.randn(input_shape) input_data = input_data.to("cuda") if dtype=='fp16': input_data = input_data.half() print("Warm up ...") with torch.no_grad(): for _ in range(nwarmup): features = model(input_data) torch.cuda.synchronize() print("Start timing ...") timings = [] with torch.no_grad(): for i in range(1, nruns+1): start_time = time.time() features = model(input_data) torch.cuda.synchronize() end_time = time.time() timings.append(end_time - start_time) if i%10==0: print('Iteration %d/%d, ave batch time %.2f ms'%(i, nruns, np.mean(timings)*1000)) print("Input shape:", input_data.size()) print("Output features size:", features.size()) print('Average batch time: %.2f ms'%(np.mean(timings)*1000))下载模型并编写 util 函数后,让我们快速查看一些预测,并在当前未优化状态下对模型进行基准测试。
for i in range(4): img_path = './data/img%d.JPG'%i img = Image.open(img_path) pred, prob = predict(img_path, resnet50_model) print('{} - Predicted: {}, Probablility: {}'.format(img_path, pred, prob)) plt.subplot(2,2,i+1) plt.imshow(img); plt.axis('off'); plt.title(pred[1])[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-Xtm8OXSF-1673840883587)(1.png)]
# Model benchmark without Torch-TensorRTmodel = resnet50_model.eval().to("cuda")benchmark(model, input_shape=(128, 3, 224, 224), nruns=100)Warm up ...Start timing ...Iteration 10/100, ave batch time 102.00 msIteration 20/100, ave batch time 102.01 msIteration 30/100, ave batch time 102.01 msIteration 40/100, ave batch time 102.02 msIteration 50/100, ave batch time 102.01 msIteration 60/100, ave batch time 102.00 msIteration 70/100, ave batch time 102.00 msIteration 80/100, ave batch time 101.99 msIteration 90/100, ave batch time 102.00 msIteration 100/100, ave batch time 101.99 msInput shape: torch.Size([128, 3, 224, 224])Output features size: torch.Size([128, 1000])Average batch time: 101.99 ms4. 利用Torch-TensorRT进行加速
继续下一步,使用 Torch TensorRT 加速。 在这些示例中,我们展示了 FP32(单精度)和 FP16(半精度)的结果。 我们不演示具体的调整,只是展示使用的简单性。 如果您想了解有关可能的自定义的更多信息,请访问我们的文档。
FP32 (single precision)
import torch_tensorrt# The compiled module will have precision as specified by "op_precision".# Here, it will have FP32 precision.trt_model_fp32 = torch_tensorrt.compile(model, inputs = [torch_tensorrt.Input((128, 3, 224, 224), dtype=torch.float32)], enabled_precisions = torch.float32, # Run with FP32 workspace_size = 1 << 22)继续运行benchmark
# Obtain the average time taken by a batch of inputbenchmark(trt_model_fp32, input_shape=(128, 3, 224, 224), nruns=100)Warm up ...Start timing ...Iteration 10/100, ave batch time 70.88 msIteration 20/100, ave batch time 71.09 msIteration 30/100, ave batch time 71.18 msIteration 40/100, ave batch time 71.27 msIteration 50/100, ave batch time 71.27 msIteration 60/100, ave batch time 71.26 msIteration 70/100, ave batch time 71.25 msIteration 80/100, ave batch time 71.32 msIteration 90/100, ave batch time 71.35 msIteration 100/100, ave batch time 71.36 msInput shape: torch.Size([128, 3, 224, 224])Output features size: torch.Size([128, 1000])Average batch time: 71.36 msFP16 (half precision)
import torch_tensorrt# The compiled module will have precision as specified by "op_precision".# Here, it will have FP16 precision.trt_model_fp16 = torch_tensorrt.compile(model, inputs = [torch_tensorrt.Input((128, 3, 224, 224), dtype=torch.half)], enabled_precisions = {torch.half}, # Run with FP16 workspace_size = 1 << 22)继续运行benchmark
# Obtain the average time taken by a batch of inputbenchmark(trt_model_fp16, input_shape=(128, 3, 224, 224), dtype='fp16', nruns=100)Warm up ...Start timing ...Iteration 10/100, ave batch time 17.40 msIteration 20/100, ave batch time 17.40 msIteration 30/100, ave batch time 17.60 msIteration 40/100, ave batch time 17.61 msIteration 50/100, ave batch time 17.57 msIteration 60/100, ave batch time 17.53 msIteration 70/100, ave batch time 17.61 msIteration 80/100, ave batch time 17.67 msIteration 90/100, ave batch time 17.72 msIteration 100/100, ave batch time 17.74 msInput shape: torch.Size([128, 3, 224, 224])Output features size: torch.Size([128, 1000])Average batch time: 17.74 ms可以看到此处的平均时间是没有利用TensorRT优化的5.7倍左右
5. 总结
在本教程中,我们介绍了使用 Torch-TensorRT 为 ResNet-50 模型编译 TorchScript 模型的完整过程,并测试了优化对性能的影响。 使用 Torch-TensorRT,我们在 NVIDIA V100 GPU 上观察到 FP32 的加速为 1.42x,FP16 的加速为 5.4x。 这些加速数字会因 GPU 的不同而不同(以及基于所使用的操作的不同实施),我们鼓励您尝试最新一代的数据中心计算卡以获得最大加速。
现在是时候在您自己的模型上试用 Torch-TensorRT 了。 如果遇到任何问题,可以在 https://github.com/pytorch/TensorRT 上填写。 您的参与将有助于 Torch-TensorRT 的未来发展。
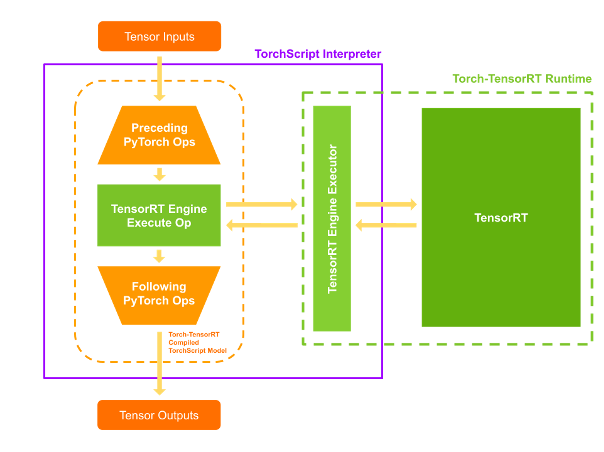
Torch-TensorRT 如何工作
Torch-TensorRT 作为 TorchScript 的扩展。 它优化并执行兼容的子图,让 PyTorch 执行剩余的图。 PyTorch 全面而灵活的功能集与 Torch-TensorRT 一起使用,解析模型并将优化应用于图的 TensorRT 兼容部分。
编译后,使用优化图就像运行一个 TorchScript 模块,用户可以获得更好的 TensorRT 性能。 Torch-TensorRT 编译器的架构由兼容子图的三个阶段组成:
- 简化 TorchScript 模块
- 转换
- 执行
简化 TorchScript 模块
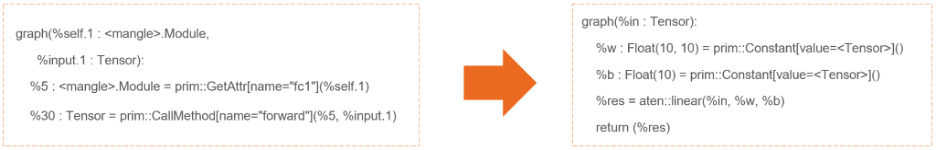
在第一阶段,Torch-TensorRT 简化了 TorchScript 模块,将常见操作的实现简化为更直接映射到 TensorRT 的表示。 需要注意的是,这种简化通道不会影响图形本身的功能。
转换
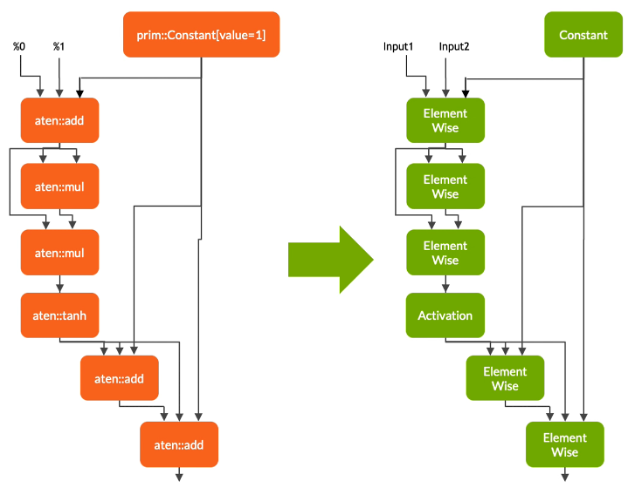
在转换阶段,Torch-TensorRT 会自动识别与 TensorRT 兼容的子图,并将其转换为 TensorRT 操作:
- 具有静态值的节点被评估并映射到常量。
- 描述张量计算的节点被转换为一个或多个 TensorRT 层。
- 其余节点保留在 TorchScripting 中,形成一个混合图,作为标准 TorchScript 模块返回。
修改后的模块会通过嵌入的 TensorRT 引擎返回给您,这意味着整个模型(PyTorch 代码、模型权重和 TensorRT 引擎)可以在单个包中进行移植。
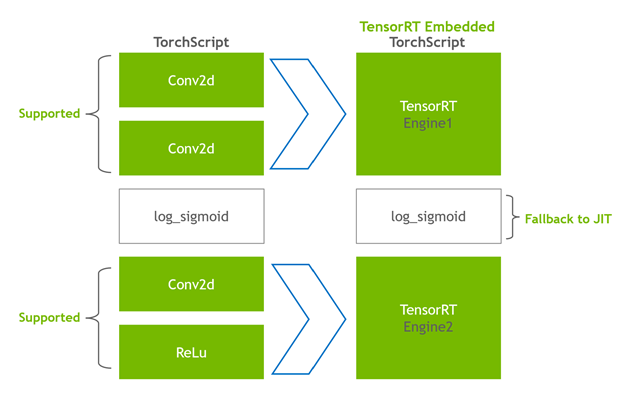
执行
当您执行已编译的模块时,Torch-TensorRT 会实时设置引擎并准备好执行。 当您执行这个修改后的 TorchScript 模块时,TorchScript 解释器会调用 TensorRT 引擎并传递所有输入。 引擎运行并将结果推送回解释器,就好像它是一个普通的 TorchScript 模块一样。